DSA01 - Pathology of Pituitary and Overview of Endocrine Pathology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
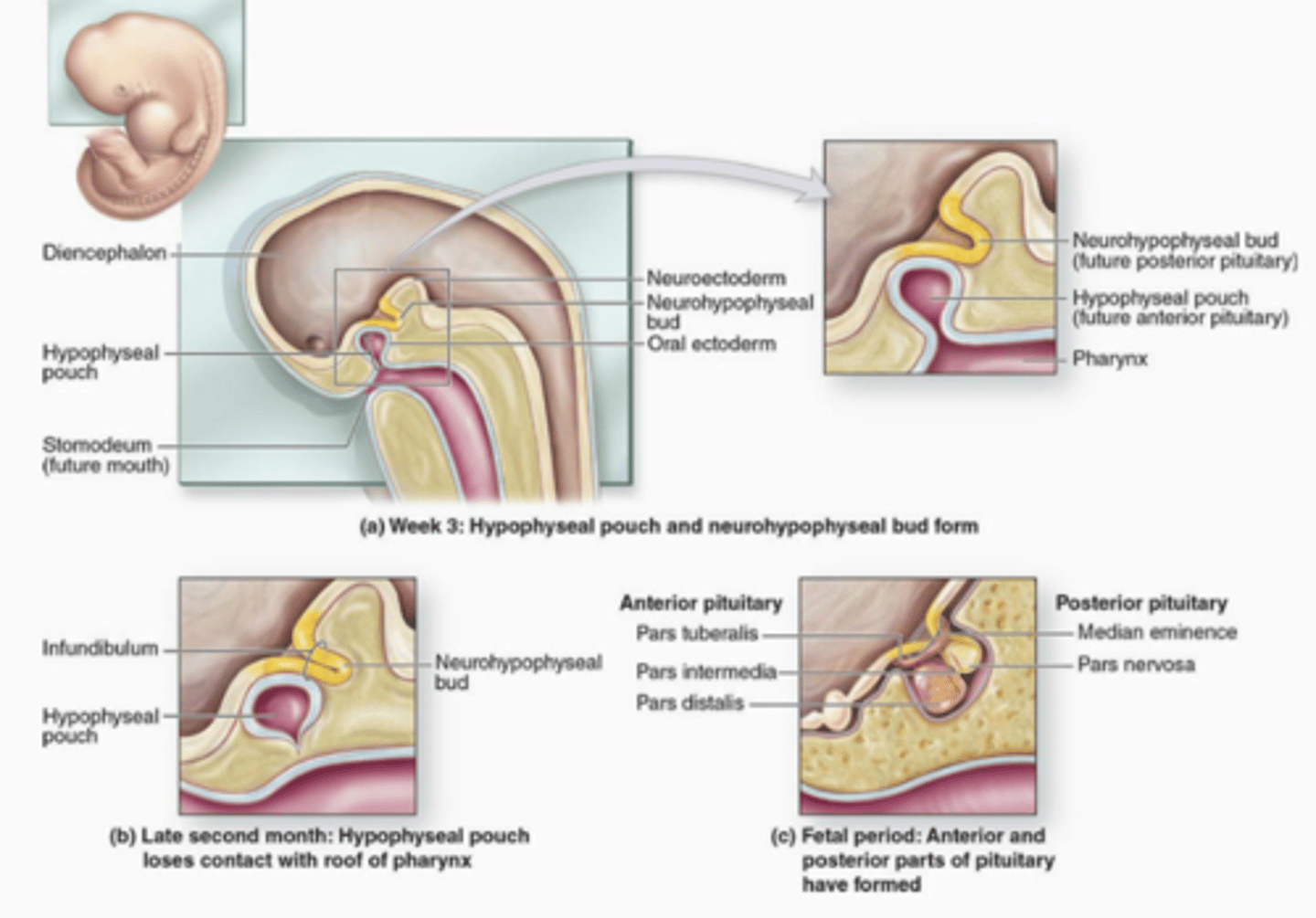
Rathke's pouch (outgrowth of foregut, oral ectoderm)
Where does the Anterior Pituitary/ADENOhypophysis come from?
-FSH
-LH
-ACTH
-TSH
-PRL
-b-Endorphin
-GH
What hormones are produced and secreted by the Anterior Pituitary?
Hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system
What is the main blood supply of the anterior pituitary that delivers releasing/inhibiting hormones from they hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary?
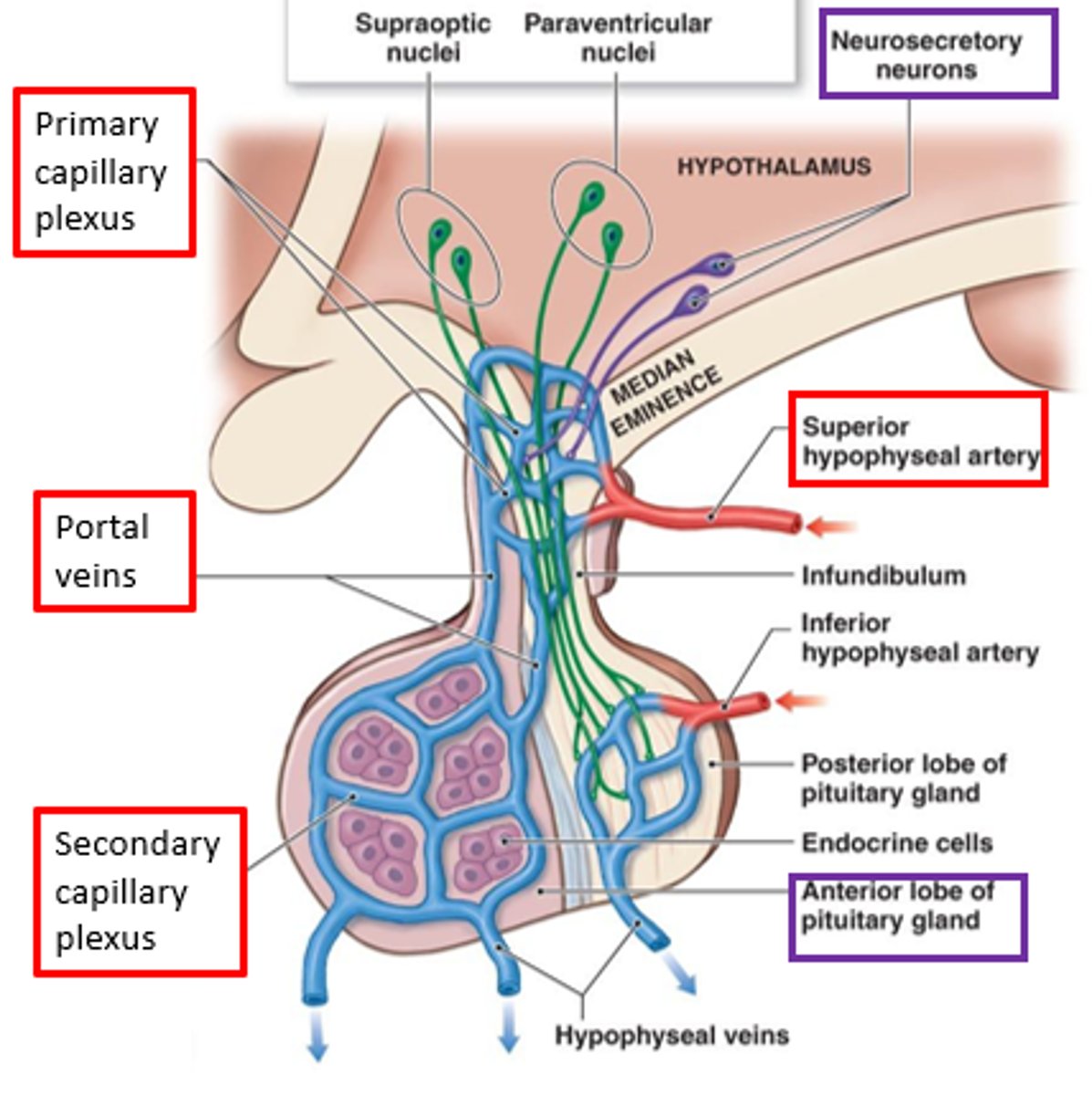
GnRH
What is the releasing hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary to INCREASE FSH/LH?
Gonads
What are FSH/LH's Target Tissues?
CRH
What is the releasing hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary to INCREASE POMC Protein --> b-Endorphin --> ACTH --> MSH (aka "Go Pro with a BAM")?
Adrenal Cortex (2/3 layers)
What is ACTH's Target Tissue?
TRH
What is the releasing hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary to INCREASE TSH & Prolactin?
Mammary Glands
What is Prolactin's Target Tissue?
It inhibits the release of GnRH from the Hypothalamus
What else does Prolactin affect and how?
Thyroid
What is TSH's Target Tissue?
PIF (Dopamine)
What is the releasing and/or inhibitory hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary for DECREASED Prolactin & Increased/Decreased GH?
GHRH
What is the releasing hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary to INCREASE GH?
Liver + Other Tissues
What is GH's Target Tissue?
GHIH (Somatostatin)
What is the releasing hormone from the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary to DECREASE GH & TSH?
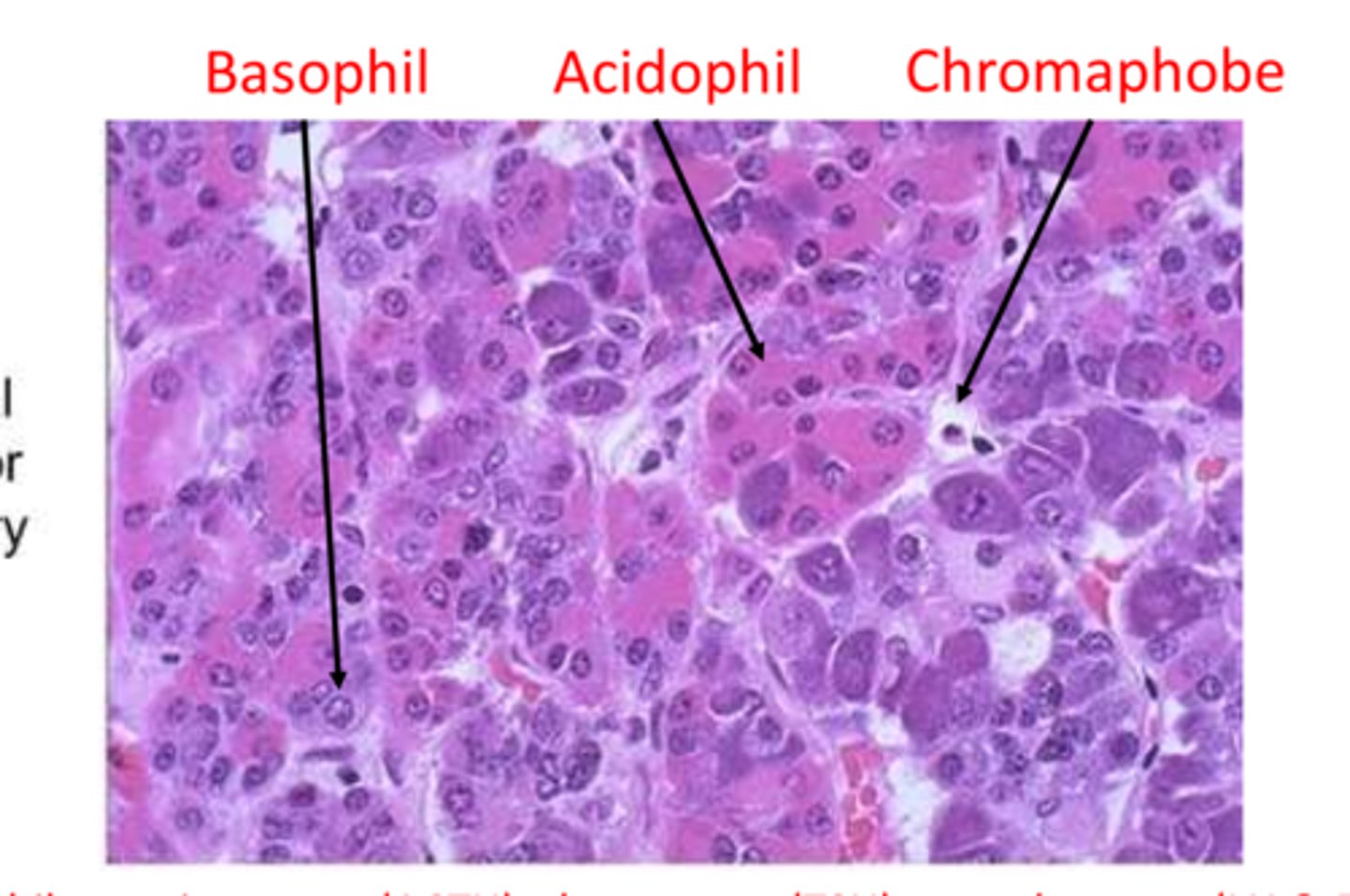
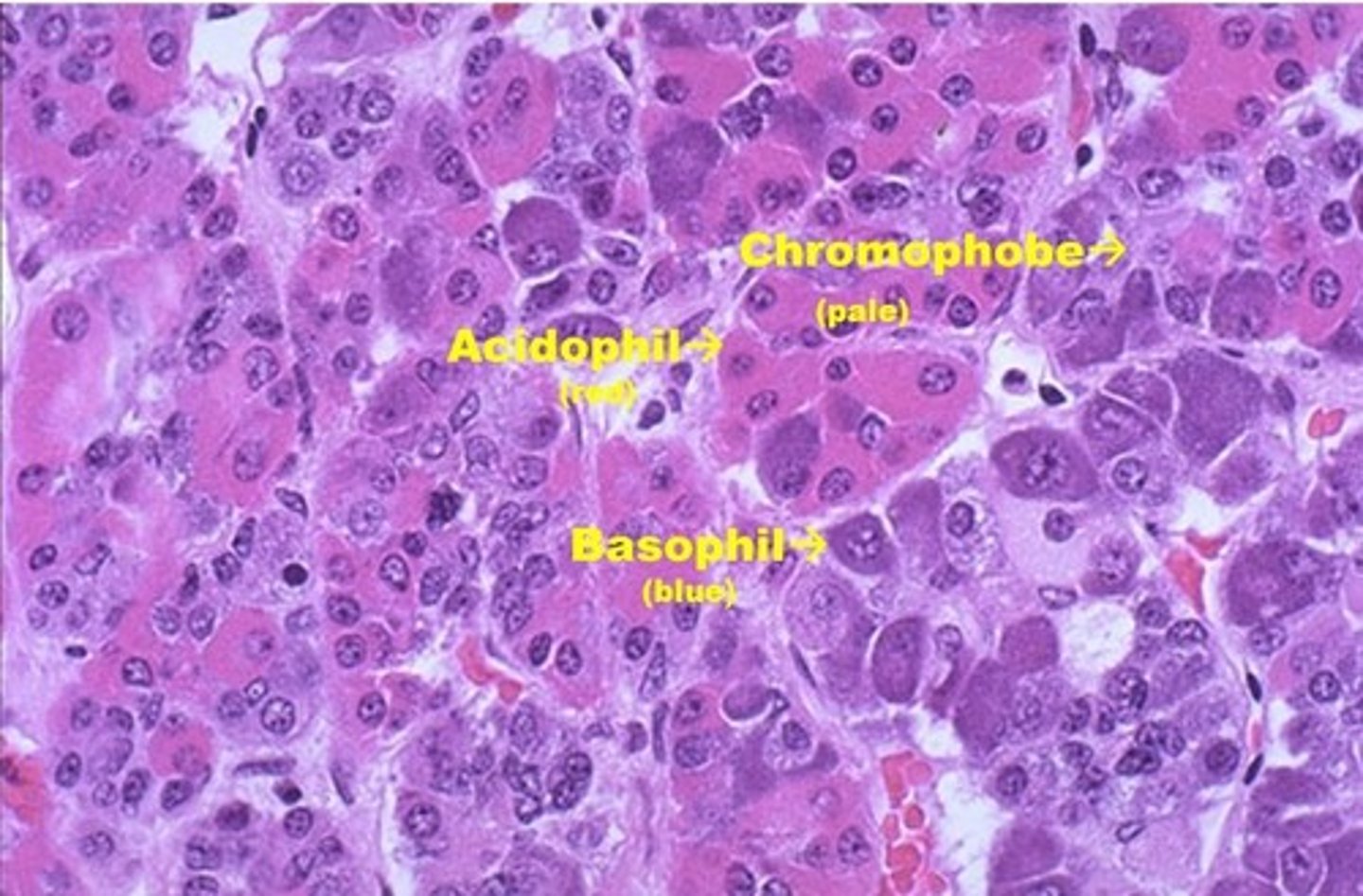
- Chromophils (Larger, granular, secretes hormones)
- Chromophobes (Smaller, clear/no cytoplasm, no secretion)
What are the two types of cells in the Anterior Pituitary/ADENOhypophysis?
-Prolactin/Lactotrophs (PRL)
-Growth Hormone/Somatotrophs (GH)
What do Acidophils (type of Chromophil) secrete?
(think "Acid PiG")
-FSH/LH (Gonadotrophs)
-ACTH (Corticotrophs)
-TSH (Thyrotrophs)
What do Basophils (type of Chromophil) secrete?
(think "B-FLAT")
Neuroectoderm from diencephalon
Where does the Posterior Pituitary/NEUROhypophysis come from?
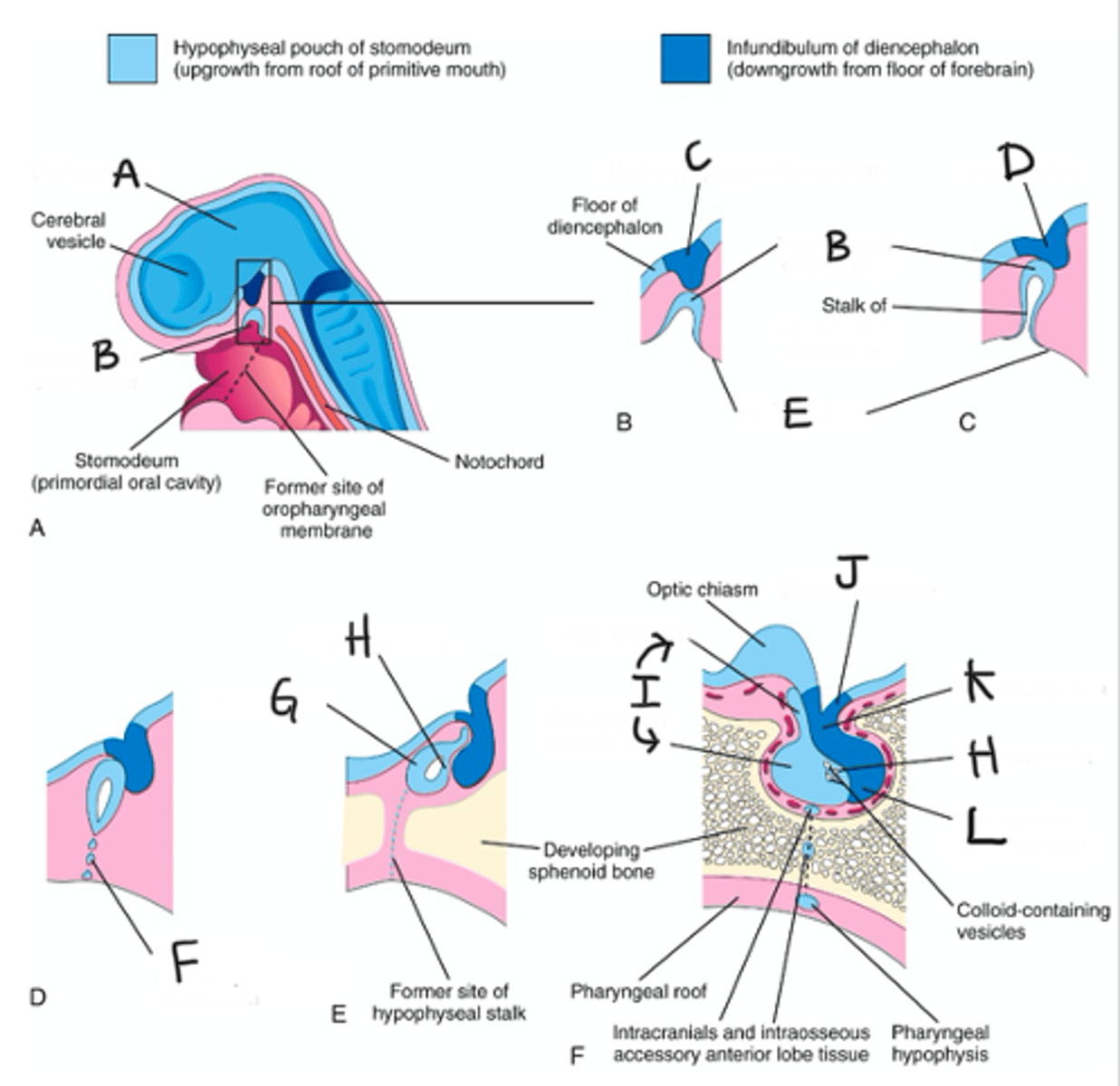
ADH/Vasopressin & Oxytocin; Made by Hypothalamus
What hormones are ONLY Stored & Secreted by the Posterior Pituitary/NEUROhypophysis? What PRODUCES them?
Consists of NEURAL Tissue (UNMYELINATED Axons)
How does the Posterior Pituitary/NEUROhypophysis appear histologically?
Excess hormone secretion
What are the effects of Hyperpituitarism (usually from anterior pituitary adenoma/Pituitary Neuroendocrine tumor aka PitNET)?
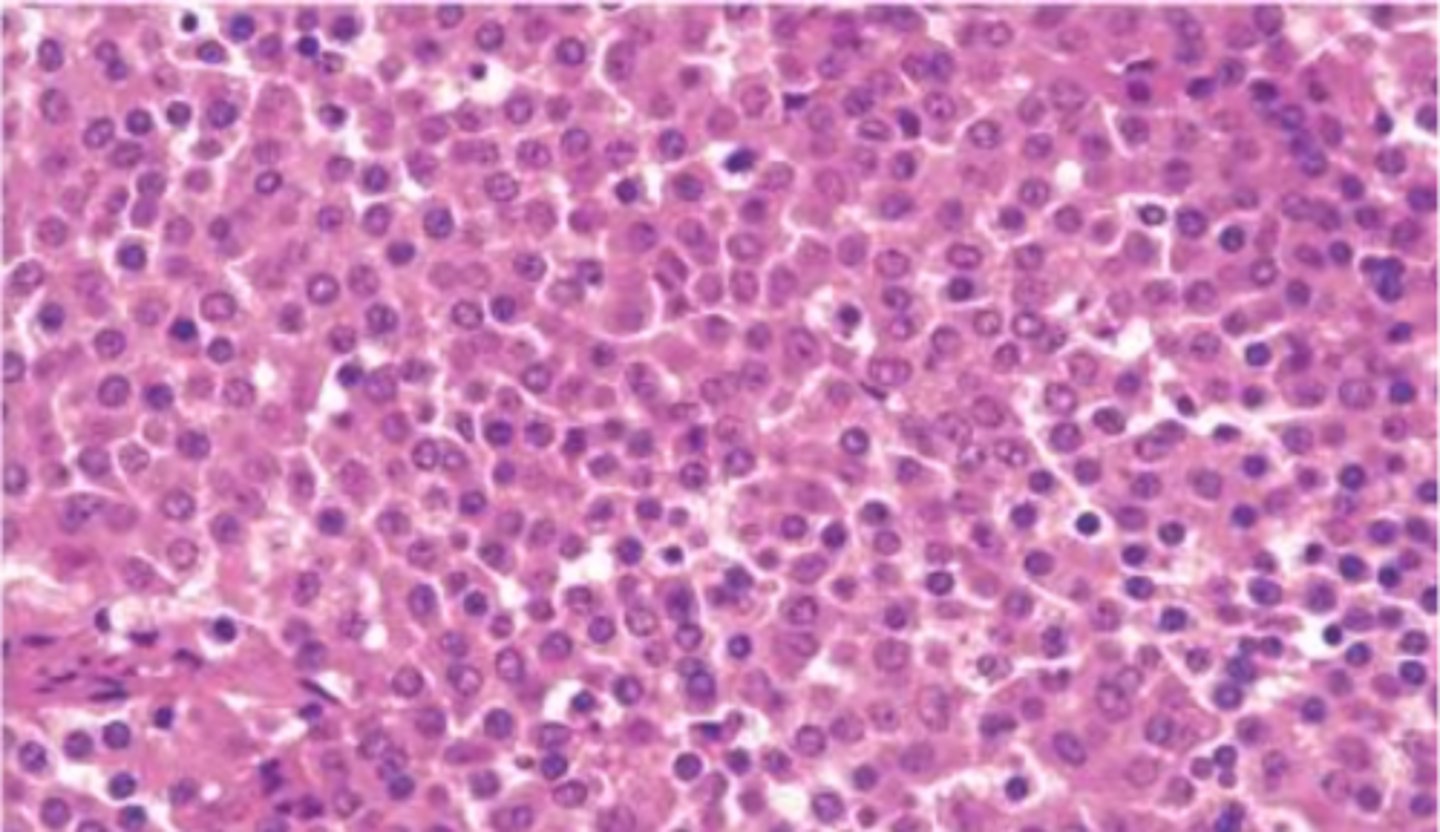
Uniform, polygonal cells arranged in sheets, cords, or papillae with little to no connective tissue or reticulin
How do Anterior PitNETs appear histologically?
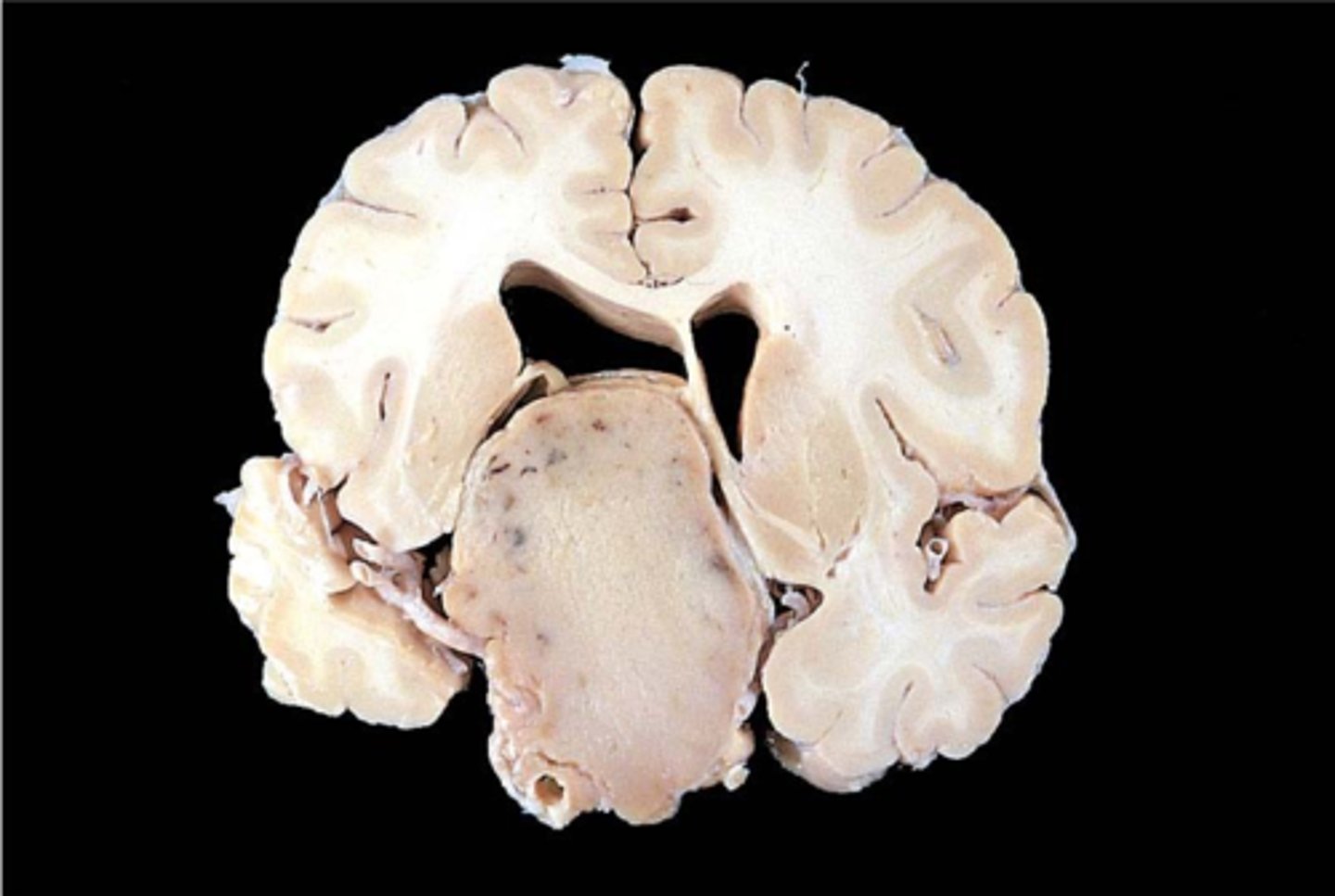
Macroadenoma
What is a PitNET considered if it's > 1 cm in diameter?
Microadenoma
What is a PitNET considered if it's < 1 cm in diameter?
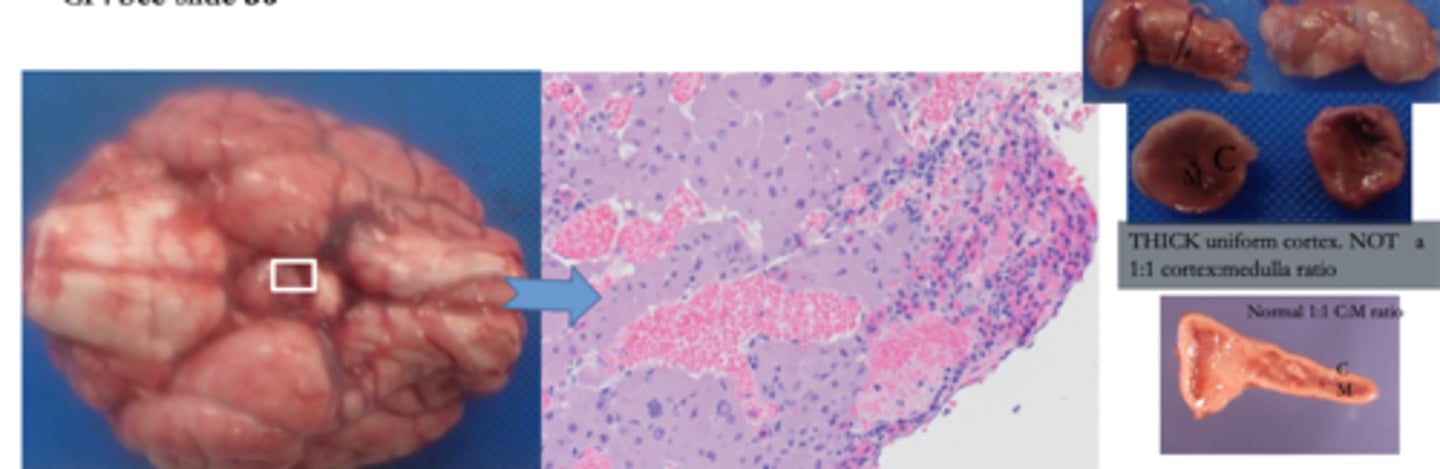
Lactotroph Adenoma (AKA Prolactinoma)
Define Adenoma:
FIRST MC type of FUNCTIONAL PitNET (30-50%)
-Path: Secrete Excess PRL --> Hyperprolactinemia
==> Stimulates LACTATION in breast tissue
==> Inhibits GnRH Synthesis/Release ==> Inhibits OVULATION in Females/SPERMATOGENESIS in Males
-Sx/PE:
> Galactorrhea (More PRL)
> Amenorrhea (Less GnRH --> Less FSH/LH --> Less gonadal fxn)
> Lower Libido (Less GnRH --> Less FSH/LH --> Less gonadal fxn)
-Dx: (Histo)
> Sparsely Granulated
> Uniform medium-sized cells w/ pale eosinophilic cytoplasm of central nuclei
> Perinuclear, Golgi-like Immunoreactivity
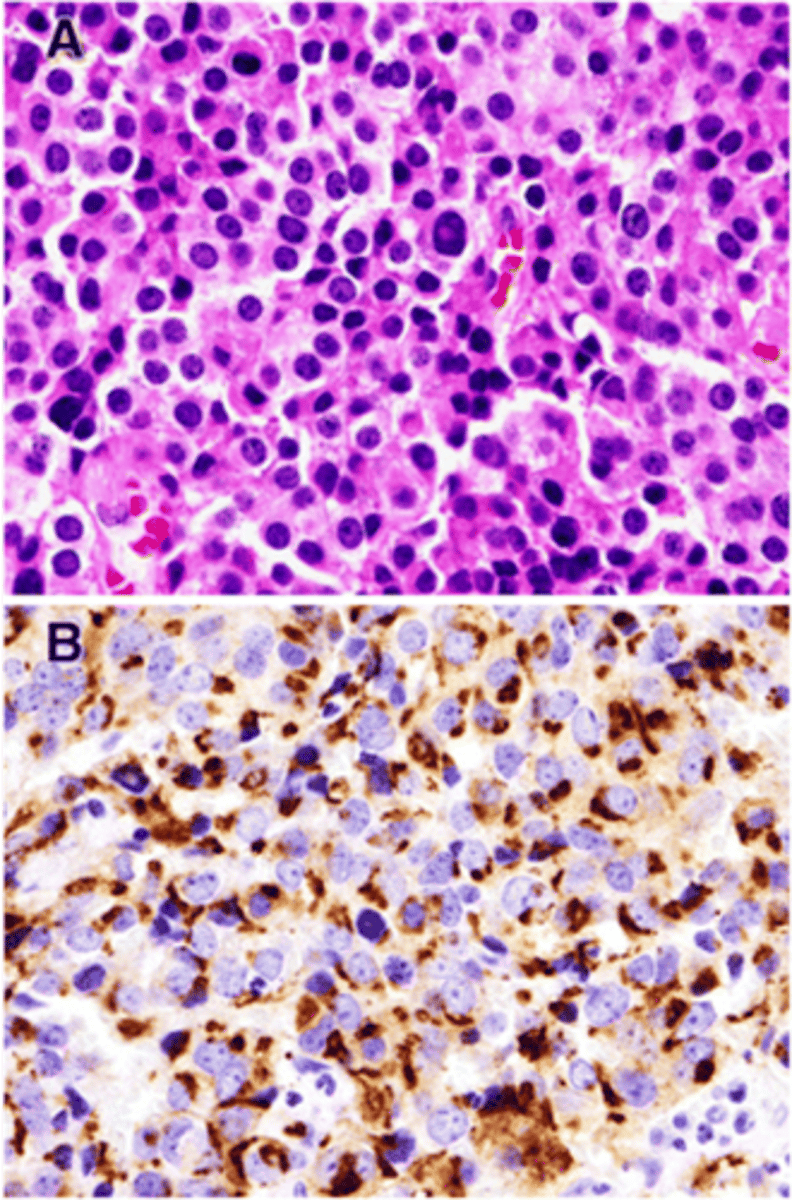
Somatotroph Adenoma
Define Adenoma:
SECOND MC type of FUNCTIONAL PitNET (10%)
-Path: Secrete Excess GH --> Liver produce IGF-1 ==> TISSUE GROWTH & INSULIN RESISTANCE
**~40% have activating mutation in Gs-alpha protein subunit**
-Sx/PE:
> GIGANTISM in Children (More Linear Bone Growth from UNFUSED Epiphyseal Plates)
> ACROMEGALY in Adults (Disproportionate growth after epiphyseal plates fuse) --> Enlarged hands, feet, jaw + Growth of Visceral Organs (Heart Failure) + Enlarged Tongue
> Diabetes Mellitus (Insulin Resistance)
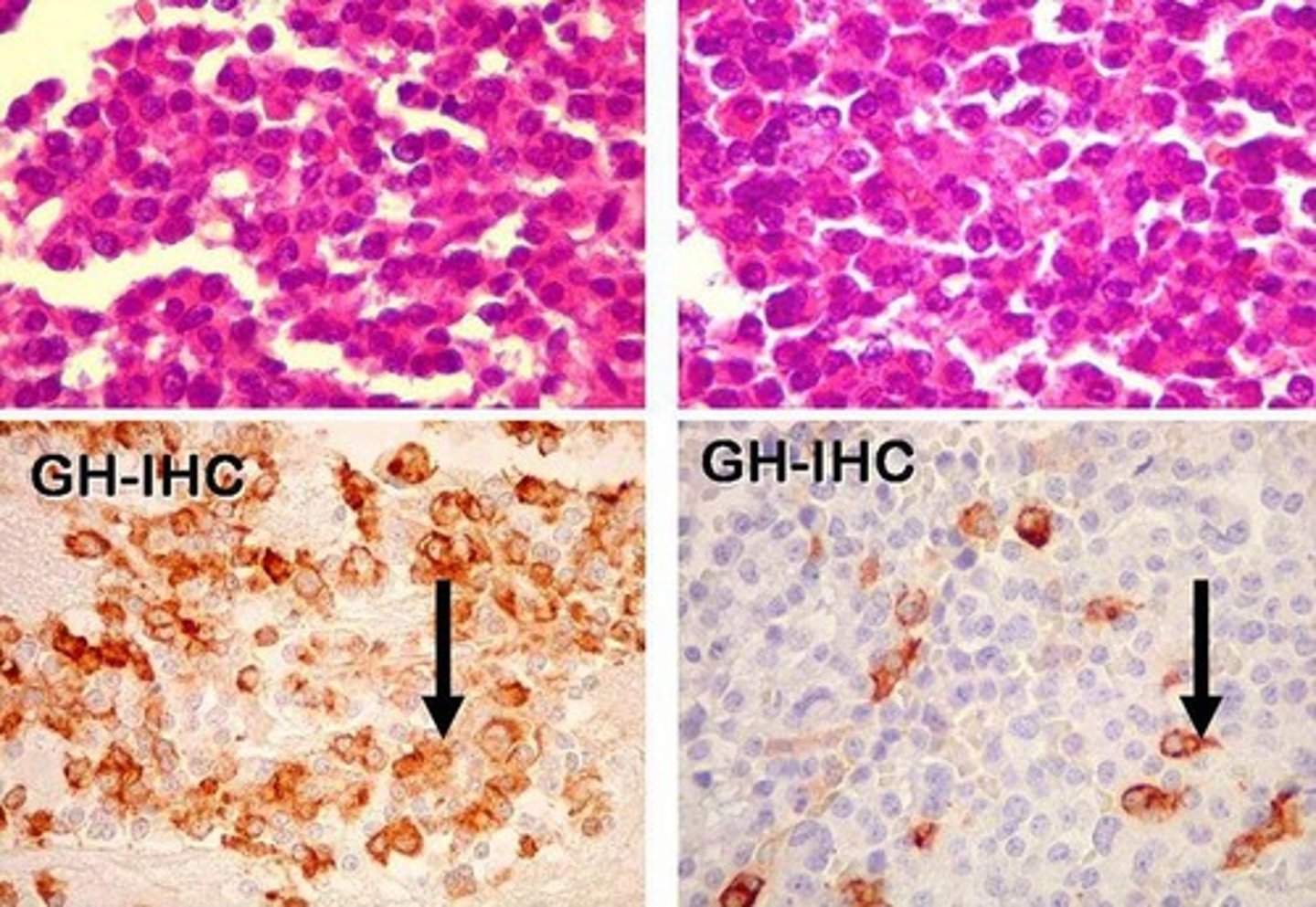
Corticotroph Adenoma
Define Adenoma:
5% of PitNETs
-Path: Secrete Excess ACTH --> Bilat Adrenal Hyperplasia --> HYPER-SECRETION of Cortisol from Adrenal Cortex
-Sx/PE:
> Cushing Disease (From HYPER-SECRETION of CORTISOL)
> Hyperpigmentation (More POMC --> ACTH, More MSH --> More Melanin)
-Dx: (Histo)
> Sheets of Basophilic Pituitary Cells w/ scant reticulin
Excess secretion of FSH/LH
What do Gonadotroph adenomas cause?
Excess secretion of TSH
What do Thyrotroph adenomas cause?
Hormonal deficiency
What are the effects of Hypopituitarism (usually from destructive processes that damage the pituitary)?
> Tumors/Mass Lesions (Pituitary Adenoma, Craniopharnygioma)
> Sheehan Syndrome (Ischemic Necrosis)
> Ablation of Pituitary (surgery, radiation - aka Iatrogenic)
What are can be causes of Hypopituitarism?
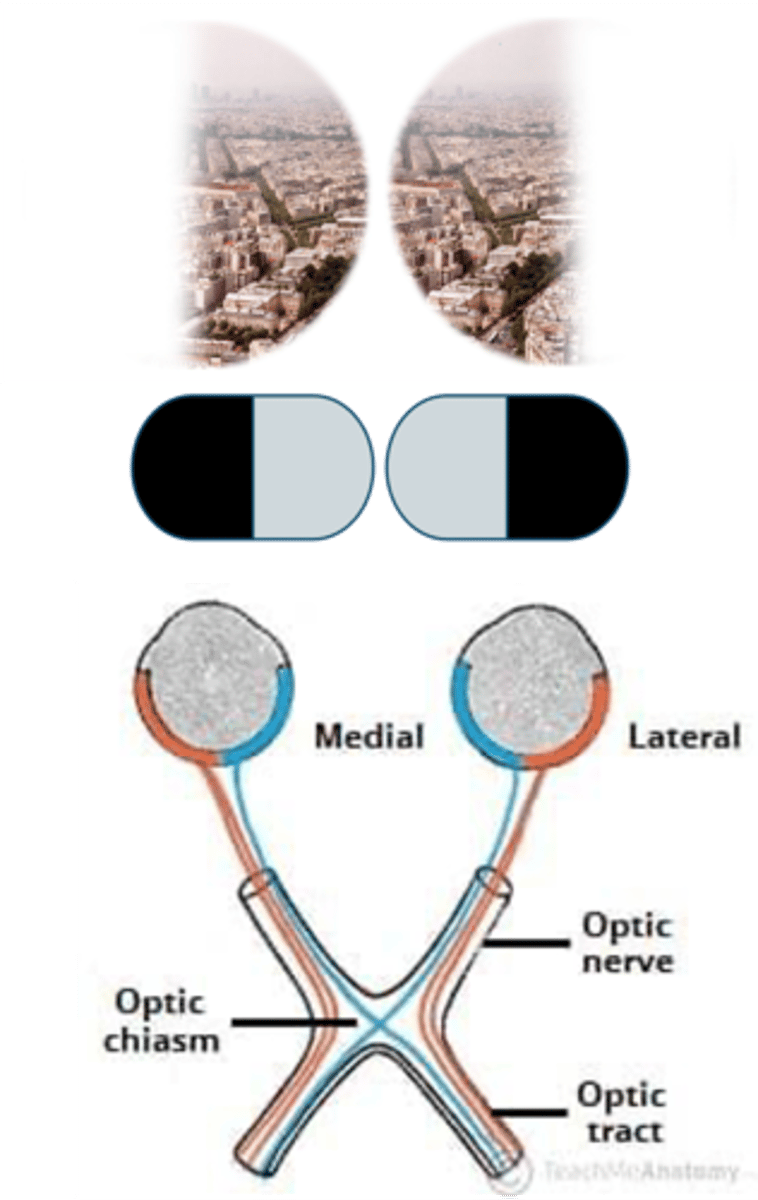
Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas may compress the optic chiasm (also causes increased ICP --> HA, N/V) - aka cause MASS EFFECTS
How do expanding pituitary lesions cause Bilateral Hemianopsia?
Craniopharyngioma
Define Cause of Hypopituitarism:
Rare, BENIGN tumor of CNS
-Hx: MC Childhood Supratentorial Tumor
BIMODAL AGE:
> 5-14
> 50-74
-Path: Derived from remnants of Rathke's Pouch
-Sx/PE:
> HA
> Bitemporal Hemianospia
> Hypopituitarism
-Tx: Surgical Resection
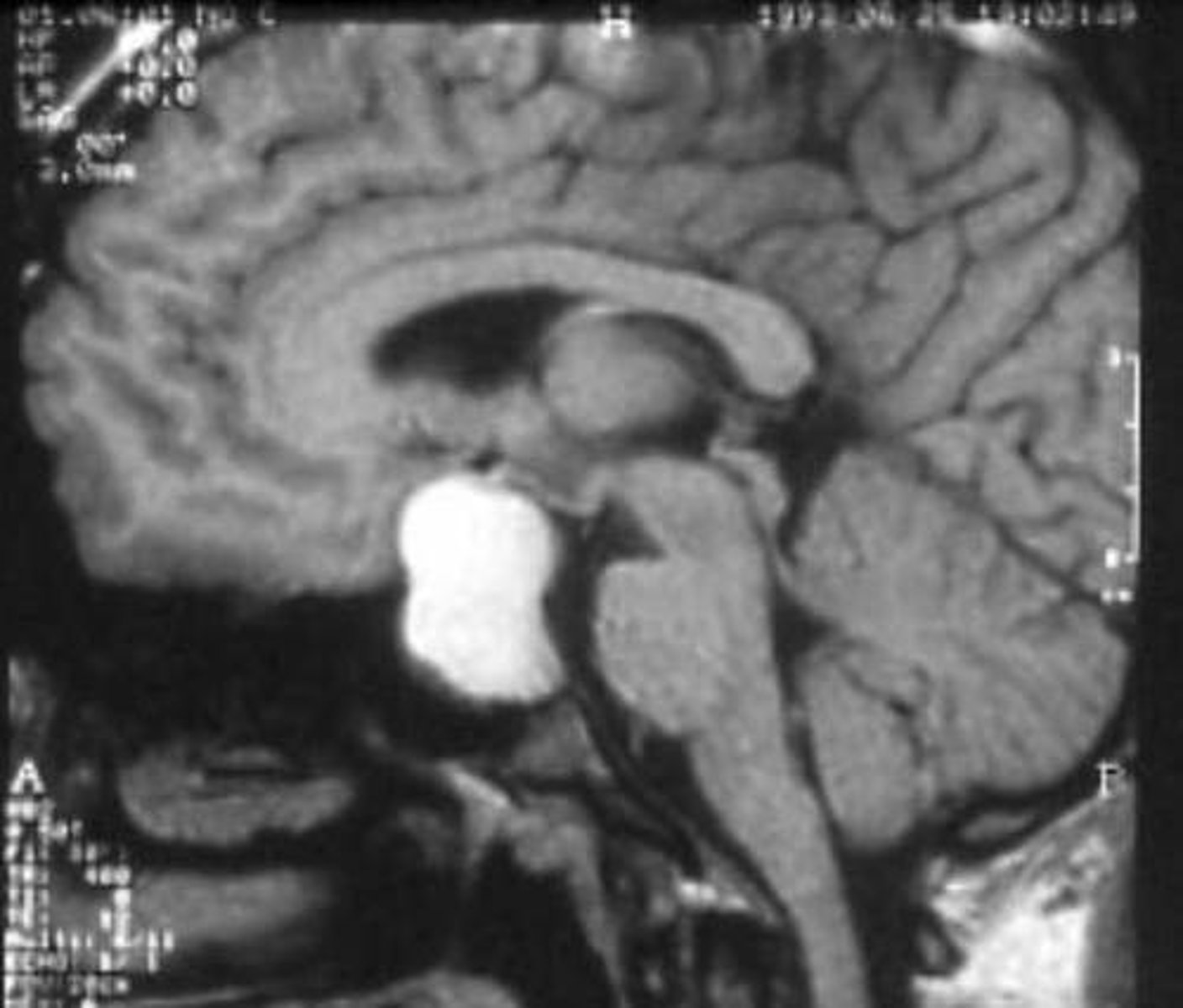
Sheehan Syndrome
Define Cause of Hypopituitarism:
Postpartum ischemic necrosis of Anterior Pituitary
-Path: During pregnancy, ↑size and ↑number of PRL secreting cells -> ant. pituitary enlargement, but blood supply doesn’t increase proportionately -> ant. pituitary is vulnerable to infarction due to hypovolemic shock
-Sx/PE
> Postpartum hemorrhage/blood loss
> Pituitary infarction -> hypopituitarism
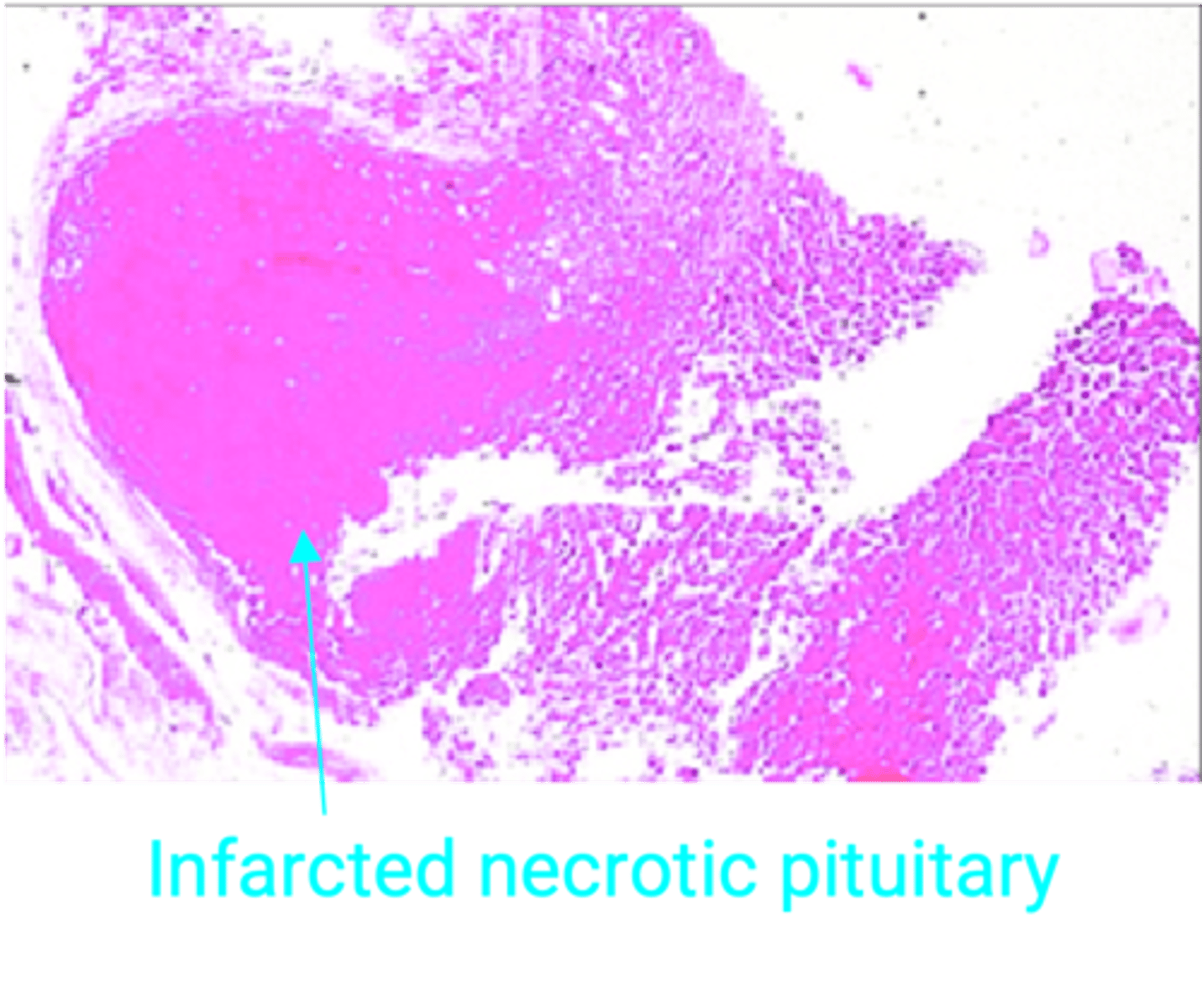
Pituitary Apoplexy
Define Cause of Hypopituitarism:
Sudden hemorrhage OR infarction of pituitary gland
-Hx: Pituitary Adenoma
-Path: SHEEHAN SYNDROME (During or right after birth)
-Sx/PE:
> Severe HA
> Visual Impairment
> Hypopituitarism
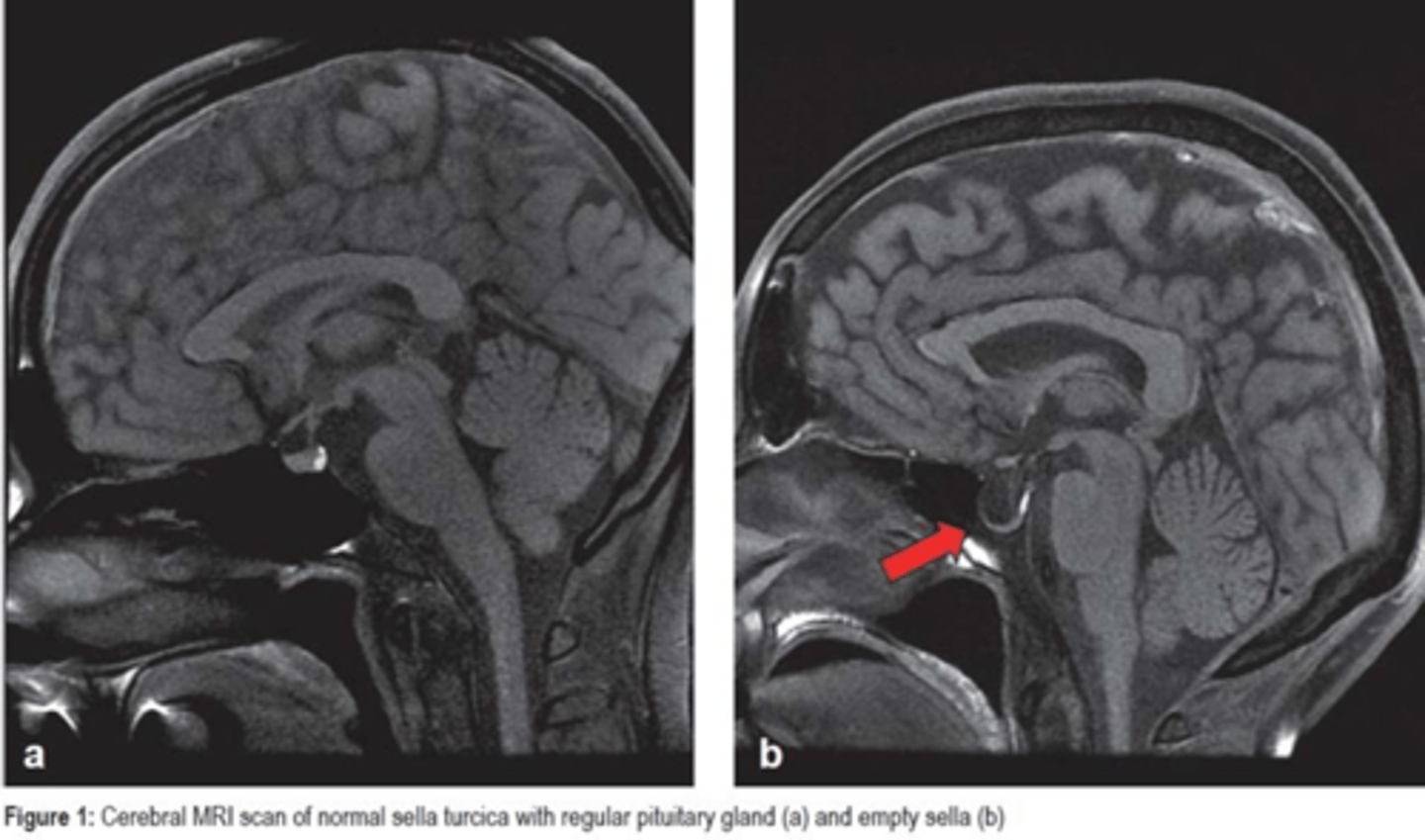
Empty Sella Syndrome
Define Cause of Hypopituitarism:
Herniation of Arachnoid and CSF into Sella Turcica
-Hx:
> Idiopathic (a/w Idiopathic Intracranial HTN)
> More in Females
-Path: Compresses and DESTROYS PITUITARY GLAND
-Dx: (Imaging)
> ABSENT Pituitary Gland (Empty Sella Turcica)
Adrenal Insufficiency
ACTH Deficiency causes what?
Hypothyroidism
TSH Deficiency causes what?
Hypogonadism
Gonadotrophin (FSH/LH) Deficiency causes what?
Poor Growth/Short Stature
GH Deficiency causes what?