Diagram of Metallic bonding: Elements compounds and mixtures: Chemistry: (9:1) | Quizlet
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
TERM
Delocalised electrons
DEFINITION
an electron that is able to move freely throughout a structure
TERM
Positive metal ions
DEFINITION
Metal atoms that have lost their outer electrons
Lattice
Regular arrangement of particles.
Giant structure
A huge 3D network of atoms or ions
Electrostatic forces of attraction
Strong forces of attraction between oppositely charged particles
Metallic bonding
A lattice of positive metal ions surrounded by delocalised outer electrons, held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction
Melting and boiling points of metallic substances
high
Reason for metals high melting and boiling points
Strong electrostatic forces between positive metal ions and negative delocalised electrons
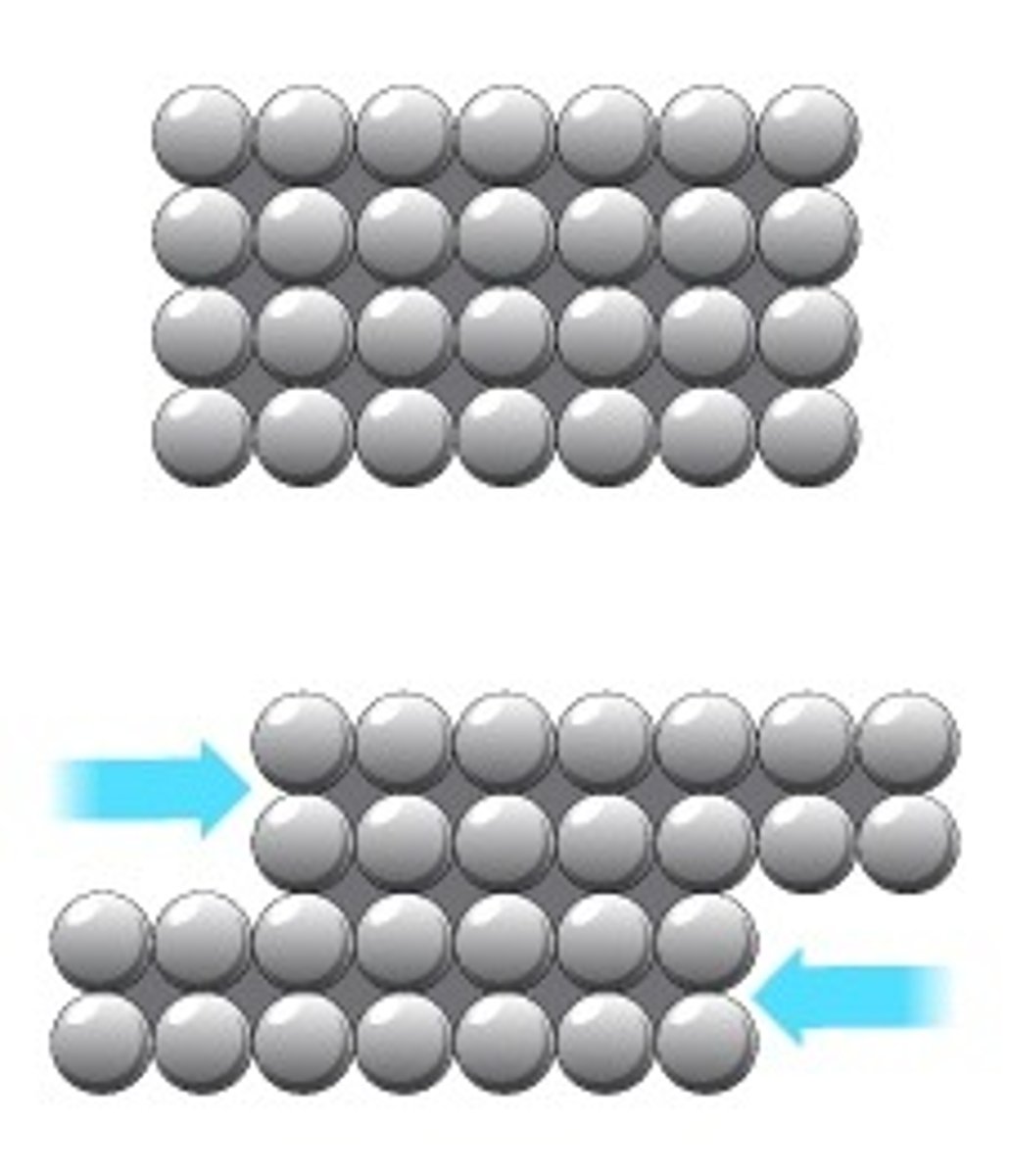
Reason for metals being malleable
Layers of metal ions can slide over each other
Reason alloys are harder than pure metals
Different sized atoms disrupt the layers of ions, preventing layers from sliding
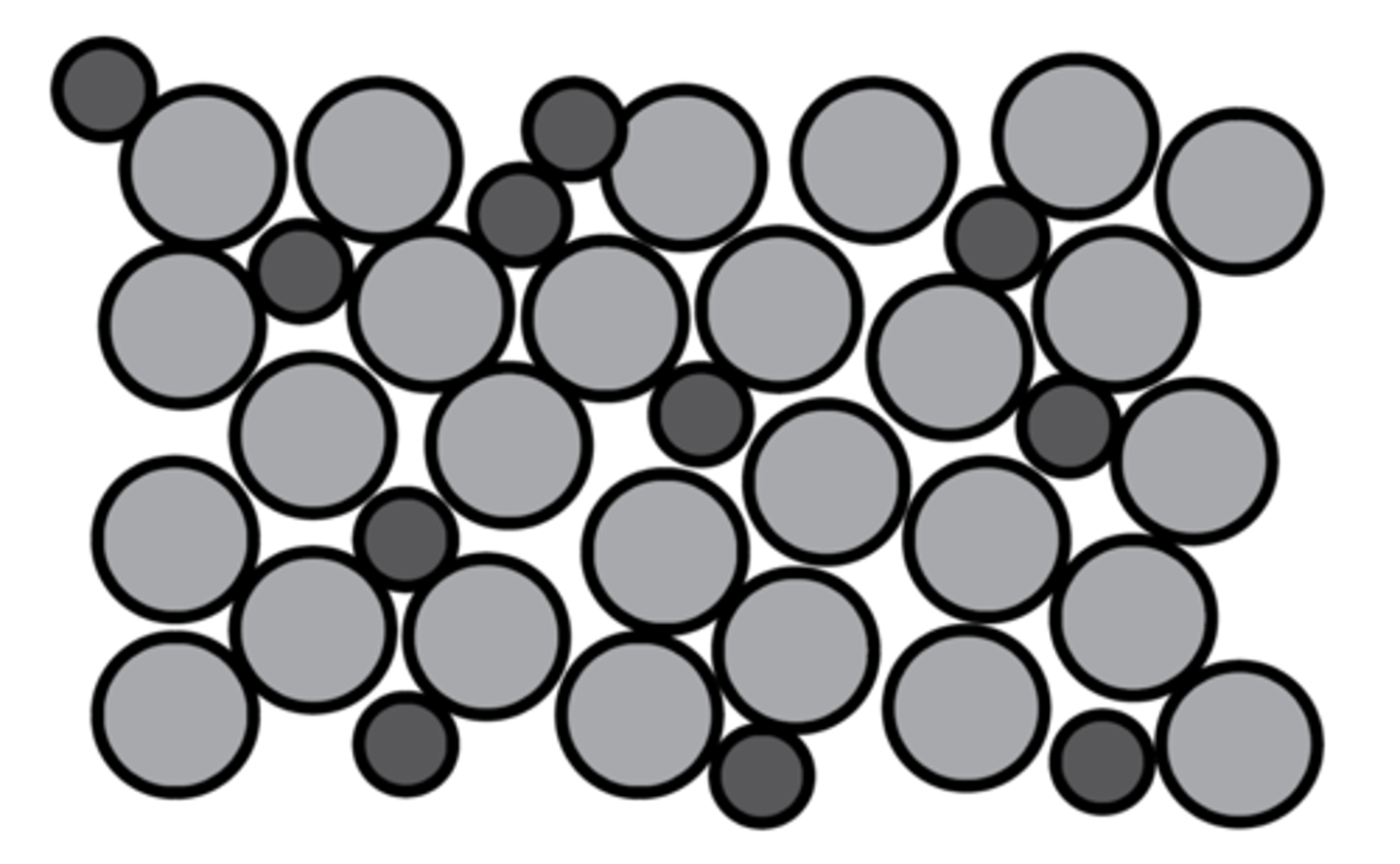
Usefulness of pure metals
Too soft for most uses.
Reason metals conduct heat well
Delocalised electrons can transfer heat energy quickly.
Reason metals conduct electricity well
Delocalised electrons can carry electrical charge through the structure.