LECTURE 20 STUDY GUIDE (AMNIOTES)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is amniote?
tetrapods that develop from an amniotic egg
which three groups of vertebrates are amniotes?
reptiles, birds, and mammals
amniotes fall within one of three lineages: diapsid, synapsid, or anapsid? how do these lineages differ?
the three groups are recognized based on openings in the skull near temples
synapsids include mammals
diapsids include all reptiles and birds
anapsids include turtles
why was the amniotic egg so significant in animal evolution?
decouples reproduction from water and enabled amniotes to stray far from water
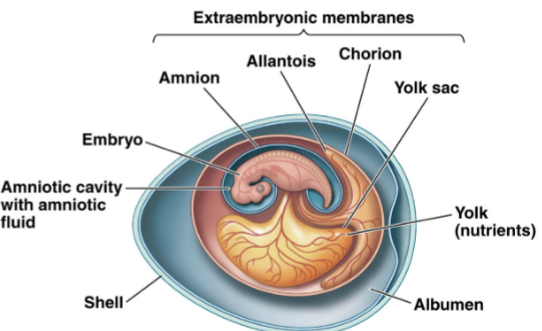
what are the four extra-embryonic membranes and what are their locations and functions?
amnion: surrounds the embryo and amniotic fluid that cushions and protects the embryo
yolk sac: surrounds an embryo’s primary food called yolk; proteins and lipids produced by moms liver
allantois: reservoir for metabolic wastes and may be used in gas exchange along with the chorion
chorion: envelops the embryonic mass isolating it from egg albumen in shelled eggs; exchanges gases
how do the eggs of oviparous amniotes differ from ovoviviparous amniotes?
oviparous amniotes secrete significant amounts of albumen (egg white) and a leathery or calcareous shell around their eggs to offer additional nutrients/protection respectively
ovoviviparous amniotes give live birth
what is incubation?
act or process of an amniote mother sitting on her eggs to keep them warm to allow them to hatch
why might oviparous amniotes incubate eggs?
to regulate the eggs temperature to prevent them from variable temperature
what important population-level variable is influenced by incubation temperature in some reptiles?
sex ratio
in most, what is the ribcage used for?
to ventilate the lungs
turtles do not ventilate their lungs through their ribcage, why?
turtles have their pectoral and pelvic girdles within their ribcage
their ribs flatten and fuse to form the basal layer of the dorsal carapace and a superficial layer of dermal scutes later forms the visible portion of the shell
when they inhale, they expand their body out of their shell
when they exhale, they contract viscera against lungs
describe the changes in amniote skin
skin became keratinized to reduce water loss
various epidermal modifications evolved: reptiles —> scales; birds —> feathers; mammals —> hair
how many heart chambers do amniotes possess?
reptiles possess three chambered heart
crocodilians, birds, and mammals have four
what is the general blood circulation for a non bird reptile?
systemic tissues —> systemic veins —> right atrium —>ventricle —> pulmonary arteries —> lungs —> pulmonary veins —> left atrium —> ventricle —> left systemic aorta —> systemic arteries —> systemic tissues
what is the gas exchange circuit called in amniotes?
pulmonary circuit
some reptiles that dive beneath water for extensive periods have a modified cardiovascular system. what is this modification?
may use a cardiac shunt when diving which means blood is shunted away from pulmonary circulation by diverting it into the right systemic aorta (purple vessel)
what is ectothermic?
must acquire extrinsic heat by basking in the sun and must shade to cool themselves (non-bird reptiles)
what is endothermic?
derive heat intrinsically from metabolism of food
meaning they usually eat more (birds and mammals)
what is poikilothermic?
have highly variable body temperature (non-bird reptiles)
what is homeothermic?
regulate body temp at a set point via homeostasis (birds and mammals)
which three forms of nitrogenous waste do amniotes excrete?
urea [(NH2)2CO2] —> usually in mammals
medium complexity
medium toxicity
medium amount of water
uric acid (C5H4N4O3) —> birds
most complex
least toxic
requires least amount of water
ammonia (NH3/NH4+) —> aquatic forms (fish)
less complex
toxic
requires a lot of water
the mojave desert has numerous non-bird reptiles. considering what you now know about amniotes, which adaptions do mojave non-bird reptiles possess that enable them to be so successful in such a forbidding habitat?
most of the non-bird reptiles excrete uric acid because it requires less water