OBGYN : Abortion, Ectopic Pregnancy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
*Q* what is a spontaneous abortion?
the unexpected, unplanned loss of pregnancy before end of 20th week
*Q* what is a threatened abortion?
any uterne bleeding in 1st 20 weeks of pregnancy
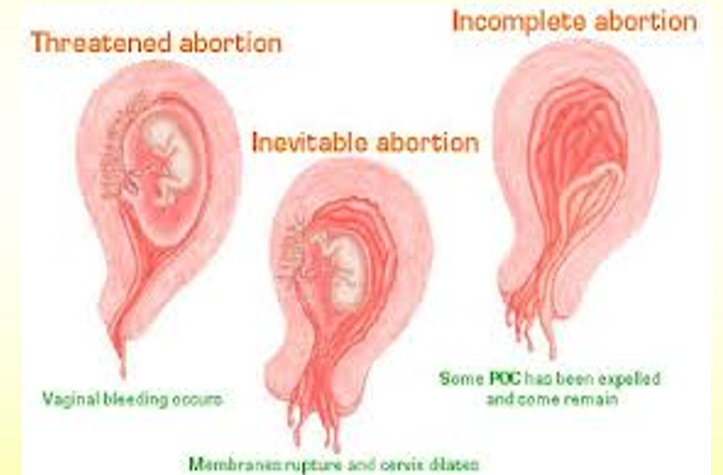
*Q* what is inevitable abortion?
bleeding in 1st 20 weeks accompanied by rupture of membranes or dilatation of cervix
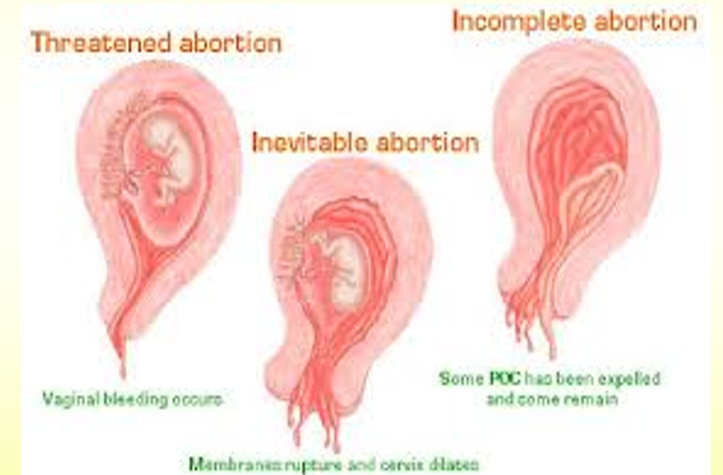
*Q* what is an incomplete abortion?
some products of conception have been expelled
some remain in uterus
risk of blood loss
*Q* what is a missed abortion?
embryo or fetus already dead but retained in uterus
*Q* what is a septic abortion?
products of conception and upper genital tract infected
*Q* what is a recurrent abortion?
occurence of 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions
what is the incidence of spontaneous abortion?
50% of all pregnancies will end in SAB
when do most SABs occur?
>80% of SABs occur within first three months of pregnancy
what is the biochemical phase?
egg became fertilized and early implantation took place; no proof of pregnancy from US; only proof is from +UHCG/BHCG
at what amount of beta HCG would it be possible to see evidence of pregnancy on US?
>2000 mIU/ml
*Q* what are the genetic factors that may cause SAB?
type 1 : defective development of ovum or sperm with defects in embryo or placental, no chromosomal abnormality, accidental (ie blighted ovum)
type 2 : chromosomal defects (aneuploidies, translocations)
what are the causes of spontaenous ABs?
genetics factors
endocrine abnormalities
reproductive organ abnormalities
infectious diseases
environmental influences
maternal systemic diseases
what endocrine abnormalities can cause SABs?
luteal phase defects, thyroid or pituitary disorders
*Q* what reproductive organ abnormalities can cause SABs?
congenital defects of uterus
uterine fibroid tumors (myomas)
scarring inside uterus due to durgical trauma to basal layer of endometrium
cervical injuries from surgical dilatation or childbirth (incompetent cervix)
what environmental influences can cause SABs?
teratogens
smoking 1 pack per days (4x increase liklihood)
alcohol
exposure to high concentrations of toxic chemicals (living near toxic waste dump)
sperm could become defective from environmental exposures
what maternal systemic diseases can cause SABs?
nutritional deficiencies
liver and renal disease
diabetes
lupus
*Q* how is a threatened abortion managed?
US to determine viability
if viable
bed rest, pelvic rest, pprogesterone suppositories for luteal phase defect
if not viable
expectant management or surgical removal (D&C)
if excessive bleeding - AB inevitable
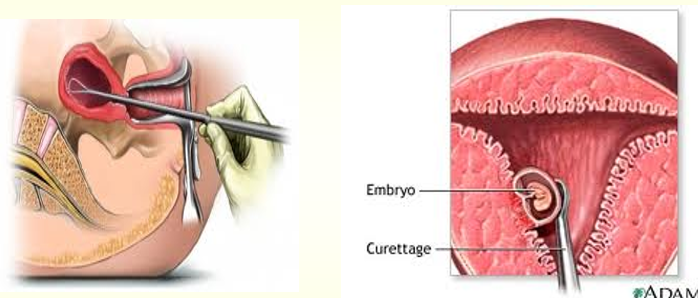
how is a missed abortion managed?
expectant : serial beta HCG levels to be sure of diagnosis
if women does not abort, D&C recommended to prevent infection and coagulation disorders
*Q* how is a septic abortion managed?
intensive care, IV fluids, antibiotics
followed by D&C and hysterectomy
*Q* how is a recurrent abortion managed?
infertility workup, genetic counseling, endocrine tests, tests for infections (STDs)
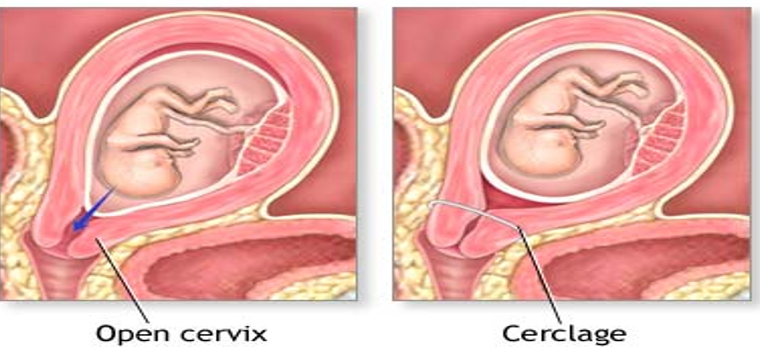
*Q* what is an incompetent cervix?
painless and unexpected cervical dilation in 2nd trimester, with loss of non viable fetus
how is incompetent cervix treated?
cerclage
purse string suture placed at level of internal os
performed in 2nd trimester
suture removed at 37 weeks to allow for normal labor
what is an induced abortion?
deliberate removal of fetal tissue from uterus in a menner than ensures fetus will not survive
what is ETOP? VTOP? VIP? TOP?
ETOP : elective termination of pregnancy
VTOP : voluntary termination of pregnancy
VIP : voluntary interruption of pregnancy
TOP : termination of pregnancy
what is the cut off for an abortion?
in 48 states cut off at 24 weeks of earlier