Atomic Structure and Bonding Flashcards
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is group 1 of the elements of the periodic table, where are they and what are their properties
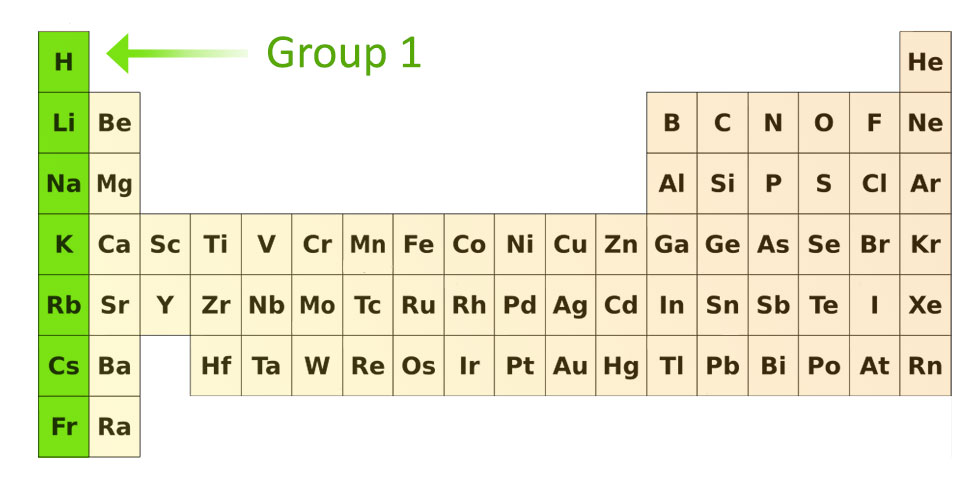
Group 1 is called the alkali metals and they are known for being highly reactive
What is group 3-12 of the elements of the periodic table, where are they and what are their properties
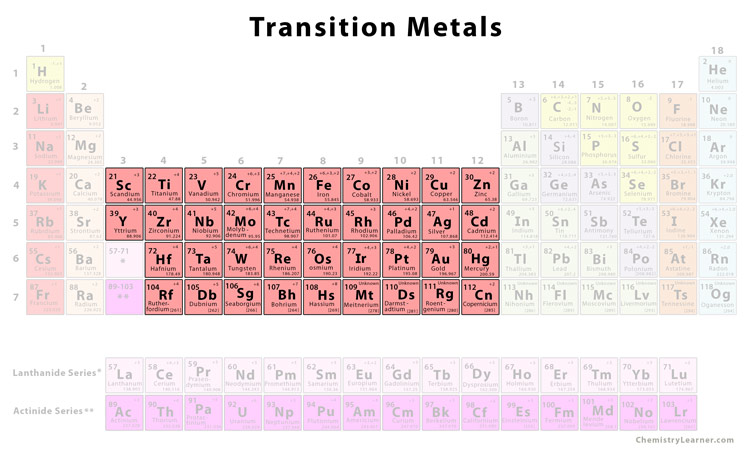
Group 3-12 are transition metals and are all metals
What is group 7 of the elements of the periodic table, where are they and what are their properties
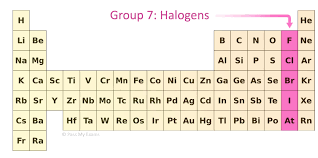
Group 7 is the halogens and they are known for being highly non-reactive and form salts a result
What is group 0 of the elements of the periodic table, where are they and what are their properties
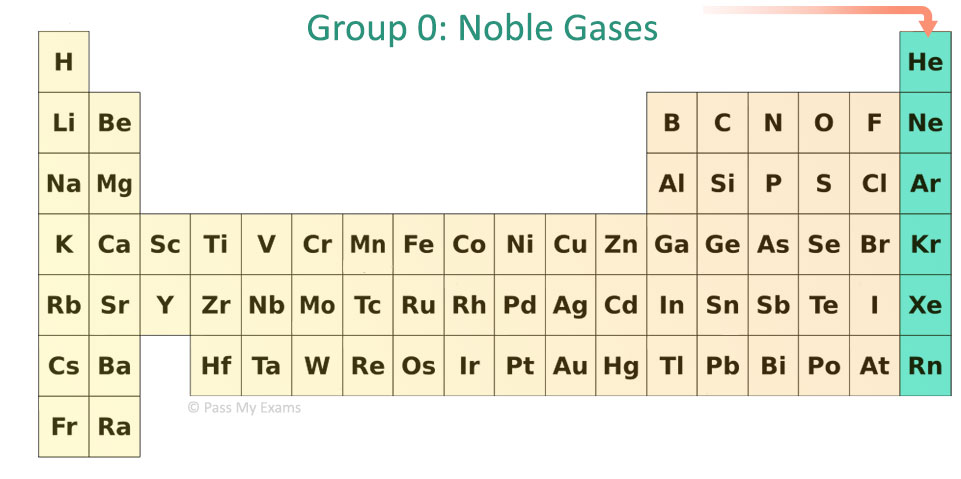
Group 0 is noble gases and they are known for being highly unreactive
What is the mass, charge and location of a proton
Mass - 1
Charge - +
Location - in the nucleus
What is the mass, charge and location of a electron
Mass - 0
Charge - -
Location - Orbiting the nucleus
What is the mass, charge and location of a neutron
Mass - 1
Charge - 0
Location - in the nucleus
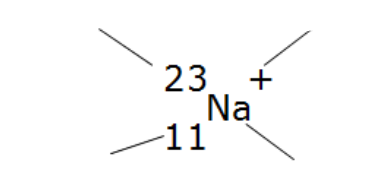
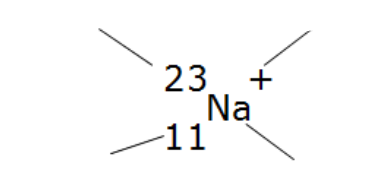
Label these parts of the nuclide notation
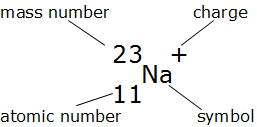
Mass number, charge, atomic number and symbol
What does mass number equal
Protons + neutrons
What do protons equal
The atomic number
What are isotopes
Atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers
What does RAM stand for
Relative Atomic Mass
What is RAM (not what it stands for)
The average mass of all an atoms isotopes
What are ions
Ions are formed when an atom gains or loses electrons
How do you find an elements similar chemical property
By finding an element in the same group as it
What kind of density and melting point do alkali metals have
Low
Why are alkali metals stored in mineral oil
To stop them from reacting with air/oxygen and water
What is the formula for calculating RAM
RAM = (Mass of isotope A x abundance) + (Mass of isotope A x abundance) / 100
Note - It doesn’t always have to be two abundances