Ohm's Law & Electric Power
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
3 components of electricity
voltage, current, and resistance
voltage (V)
-potential difference between the strength of the electron supply and the electron shortage
-measure of the amount of potential energy per electric charge or Coulomb
volts (V)
units for voltage
1 Volt = Energy / Electric Charge = Joule / Coulomb = J / C
coulomb
unit of electric charge
energy
J = V * C
measure of work
joules
units for energy
voltage is _____ when two batteries are in series (stacked)
doubled
-putting batteries in parallel (next to each other) allows longer battery life
2 ways of combining resistors
series and parallel
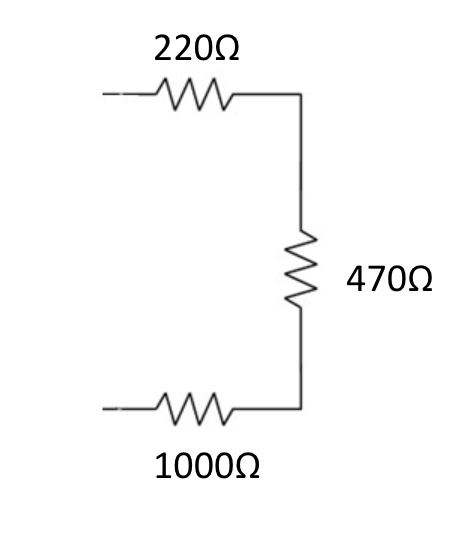
series
electrons flow in one path in sequence through resistors
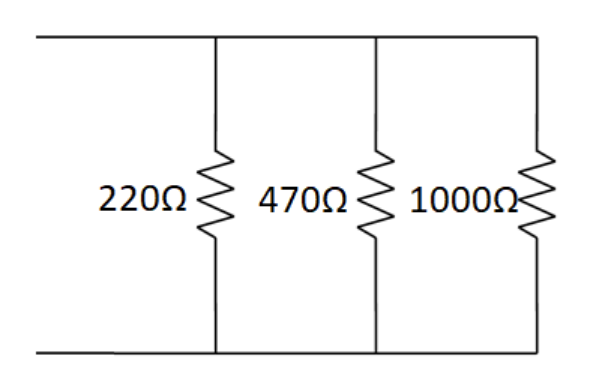
parallel
electrons divide to pass through each other
current (I)
-net flow of electrons through a material
-amount of charge passing a point per unit time
amperes (A)
-units for electric current
1 Amp = (6.24 × 10^18 electrons passing a point / second) = 1 Coulomb / second = C / s
1 C = 6.24 × 10^18 electrons
resistance (R)
-measure of a material’s opposition to the passage of electric current
-measure of the frictional force encountered by electrons as they attempt to pass through a material
R = V / I
ohms (Ω)
units for resistance
circuits
-used to induce current flow by giving it a path or closed circuit
-creating closed circuits causes the voltage to push the electrons to move
-resistors included along the path (ex: bulb)
circuit diagram
-graphical representation of electric circuit
-physical components: power source, resistive element, conductive material (wire)
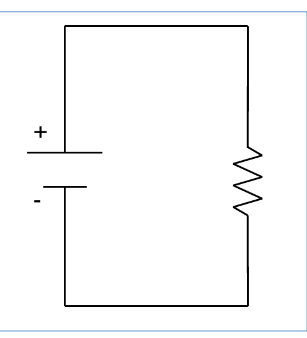
power source
-orientation matters
-ex: battery
resistor
-orientation does not matter
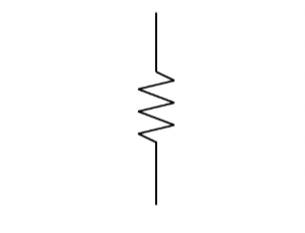
conductor
-wire
-assumed resistance is zero

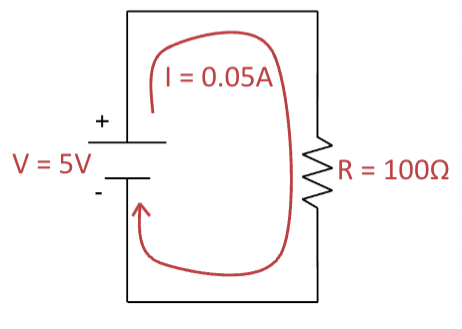
ohm’s law
V = I * R
-relates voltage, current, and resistance to each other
power
Joule’s Law: P = I * V
-work performed per unit time
The third stripe of a color code on a resistor represents the number of _____ to add after the first two digits.
zeroes
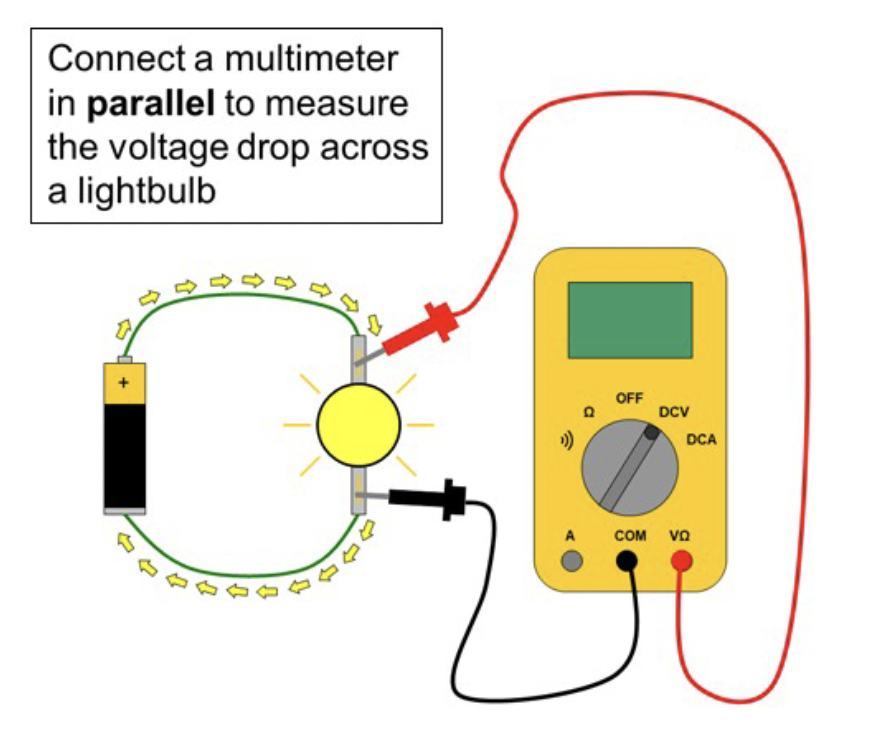
Using a multimeter, voltage must be measured in _____ to the circuit.
parallel
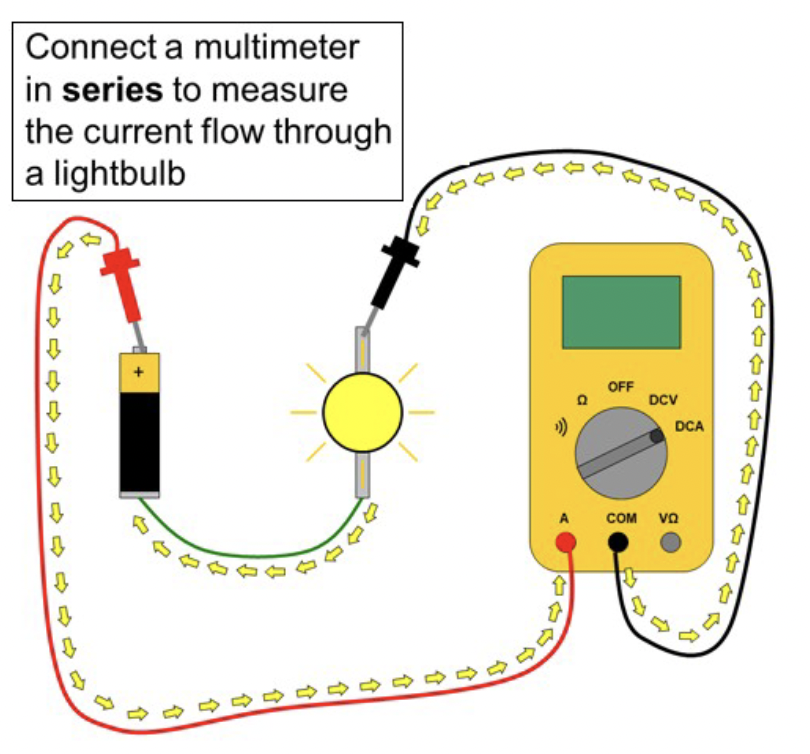
Using a multimeter, current must be measured in ______ with the circuit.
series
Using a multimeter, resistance must be measured in a ________ circuit.
disconnected
kirchoff’s voltage law
the algebraic sum of voltages around a closed loop in a circuit is 0
Voltage rises - voltage drops = 0
kirchoff’s current law
the current entering a junction point/node equals the sum of currents leaving a node