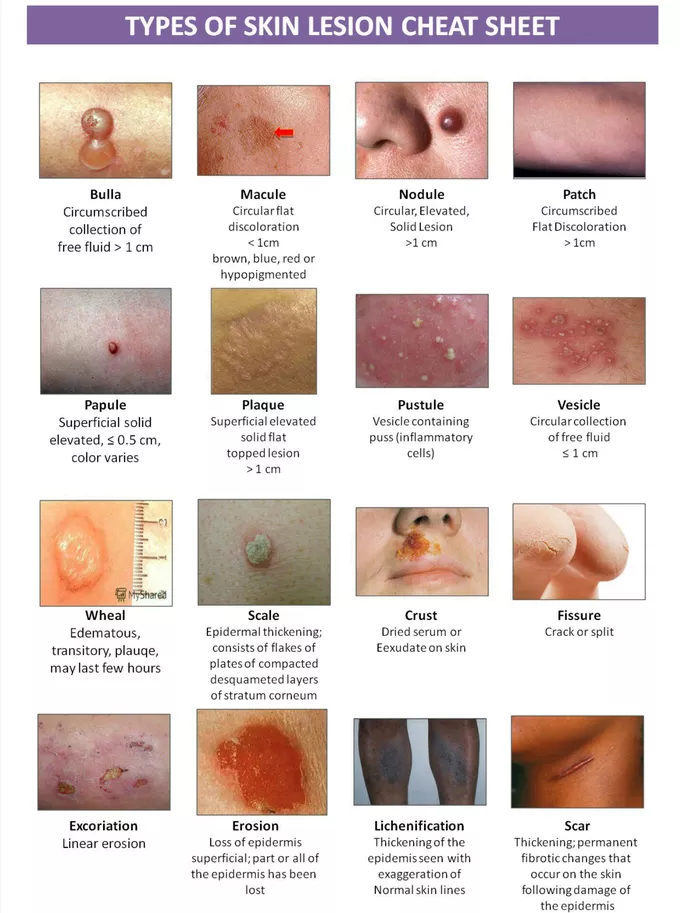
NURS 125 Hair, skin and nails
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
epidermis
outermost layer of the skin where vitamin D synthesis happens
acts as the body’s first line of defense
it has 5 layers( stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale→ Come lets get sun burnt)
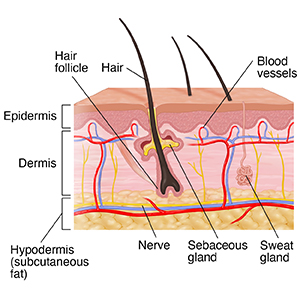
dermis
supports the epidermis and is made mostly of connective tissue and collagen
highly vascular
components include:
blood vessels
nerves
lymphatic vessels
hair follicles
sweat glands
hair
made of keratin produced by follicles in the dermis except palms and soles of the feet
2 types:
Vellus→ fine, short, light coloured hair you are born with usually(peach fuss)
Terminal→ dark, coarser, found on scalp, brows and postpubertal areas
sweat glands
two types:
aprocine→ found in specific areas like armpits and groin, they secrete a thicker fluid and are activated by stress and hormones
Eccrine→ found everywhere and regulate body temperature through sweat production
sebaceous glands
found everywhere except the palms and soles
secrete sebum to retain moisture and reduce friction
integumentary system
includes the hair, skin, nails, sebaceous and sweat glands that protect the body and help regulate temperature
skin=body’s largest organ important function is to assist the body in adapting to environmental influences
skin is one of the main sites of sensory messaging
constitutive colour
the general colour of a person’s skin
the areas unaffected by lesions, rashes, skin alterations are “considered their normal”
can be affected by sun damage, ethnicity, and assessors colour blindness
it is important to understand this about a patient
Fitzpatrick skin type
way to describe and classify skin types in order to determine potential treatments, risk factors, etc
more risk factors related to the extremes
darker skin: higher risk of not absorbing vitamin D
lightest eye, hair & skin: higher risk for sun damage
albinism, lesions, hyperpigmentation add another risk factor
risk factor
anything that increases the chance of skin, hair or nail problems
e.g. excessive sun exposure, poor hygiene, harsh chemicals, smoking
protective factor
anything that helps maintain healthy skin, hair, and nails
e.g. sunscreen use, proper hydration, gentle skincare, balanced diet
modifiable factor
a factor you can change to improve skin, hair, and nail health
e.g. medication sthat have effect in the sun, modify usage by not taking it while exposed to the sun
non-modifiable factor
a factor that cannot be changed
e.g. genetics, age, skin type-Fitzpatrick, hereditary condition
history of present illness(look at textbook for possible questions)
Location
Associated signs or symptoms
Timing
Exposure
Reliving factors
Severity
Nature/quality
Aggravating factors
Patient perspective
Significance to the patient
pallor
paleness
usually related to lack of iron(anemia) or early lack of perfusion

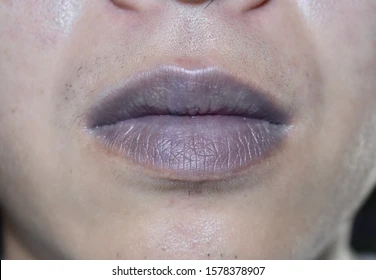
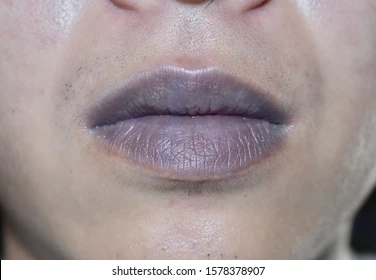
cyanosis
bluish discoloration
first indicated in the lips(blueish lips)
clubbing
lack of perfusion to extremities due to cardiovascular concern
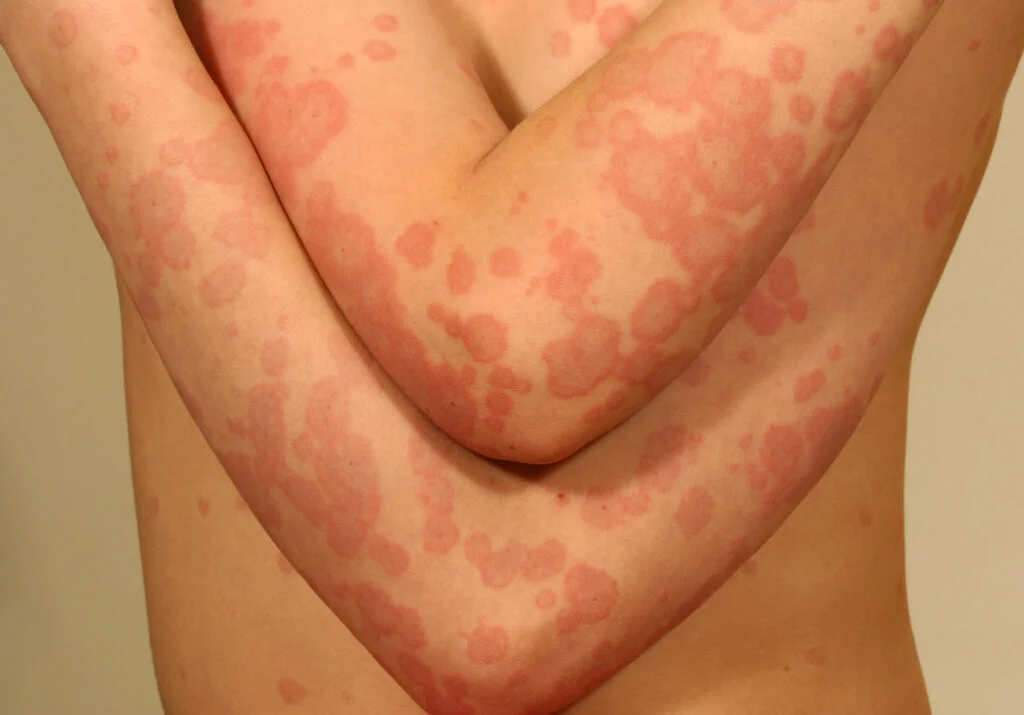
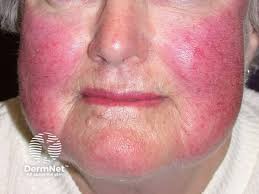
erythema
redness
body’s response to irritation due to heat, abrasions, infections, etc
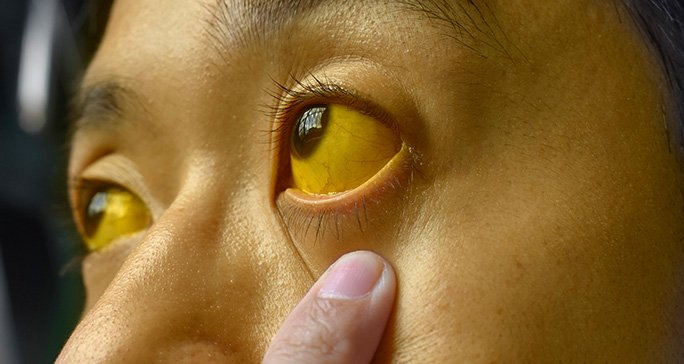
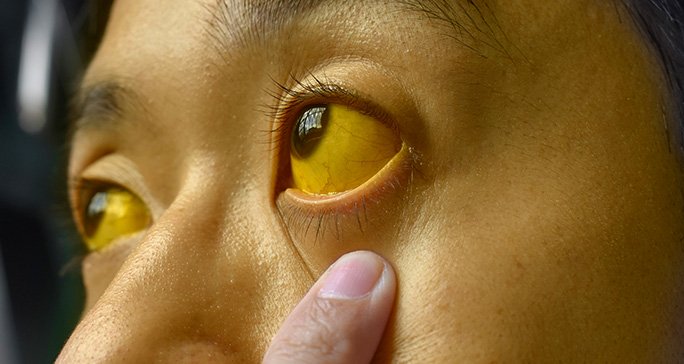
jaundice
yellowish discolouration of skin and sclera
skin does not blanch
physiologic jaundice happens 24 hrs and continues after 72 hrs of birth(for babies)
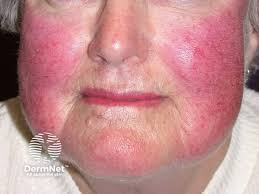
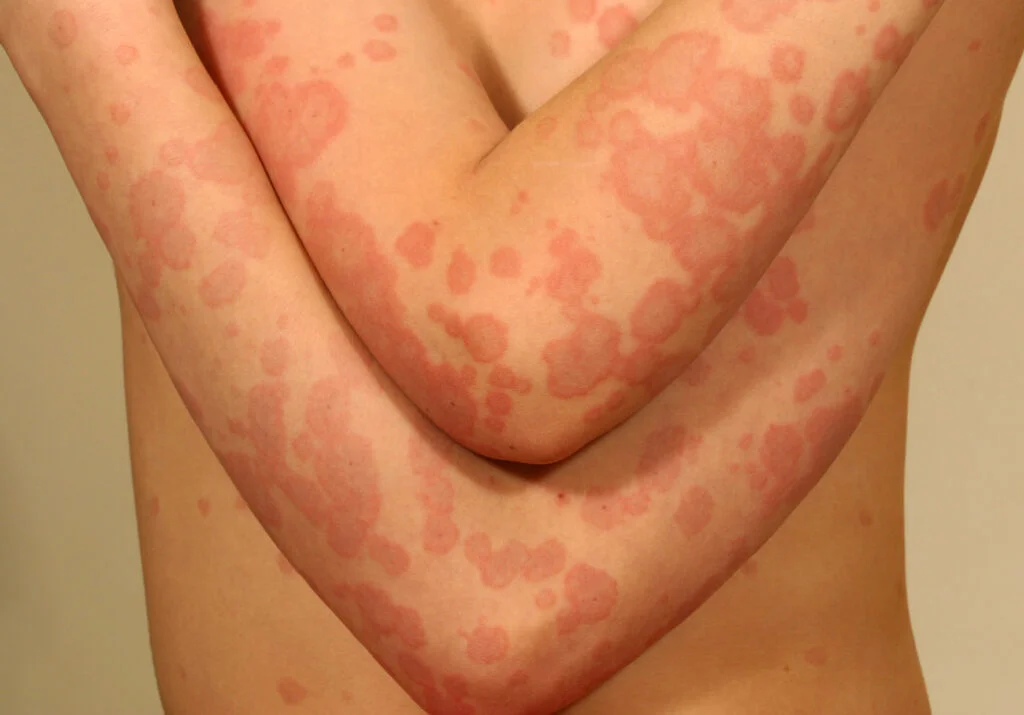
flushing
temporary redness of the skin
caused by increased blood flow and increased permeability of the peripheral capillaries
sometimes caused by excessive alcohol drinking

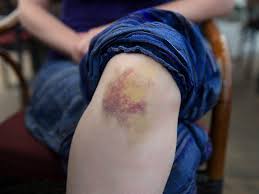
ecchymosis
bruising
usually trauma related
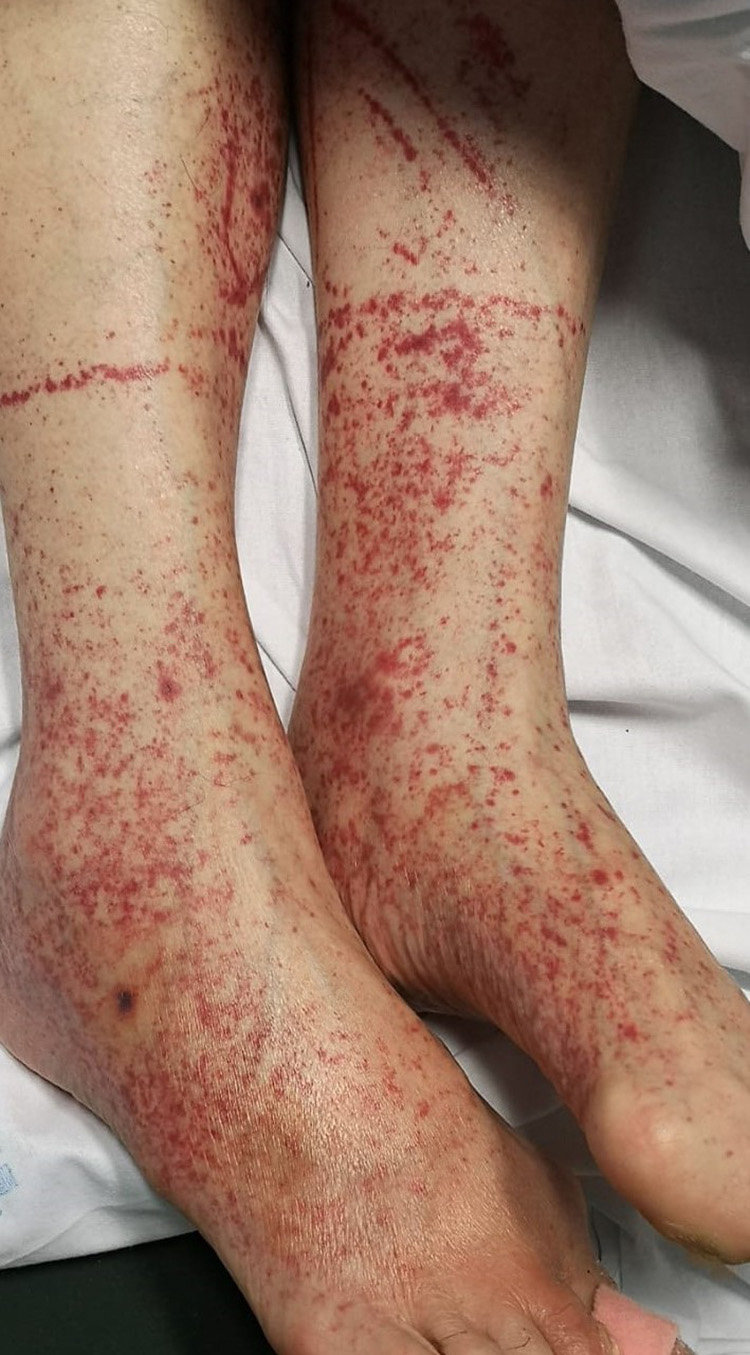
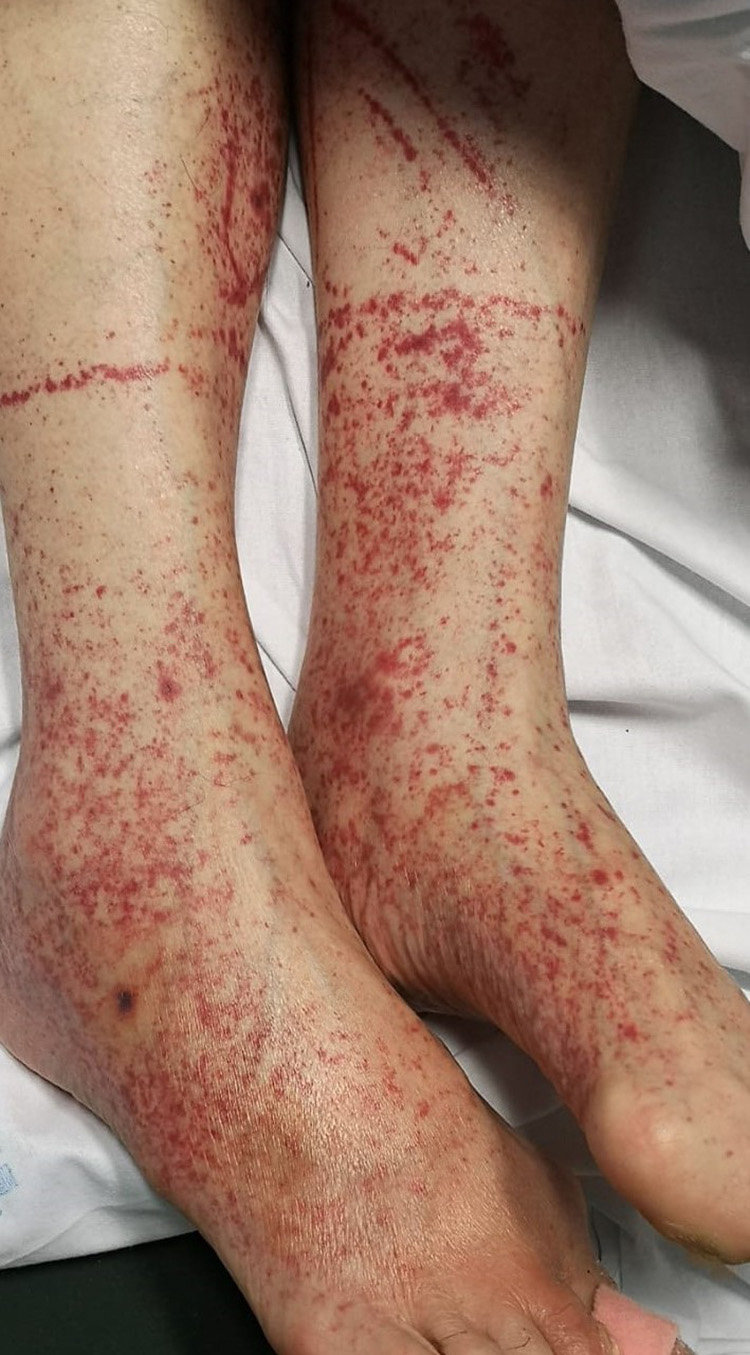
petechiae
small reddish to purple macules or papules
develop in response to hematological issues or regional trauma
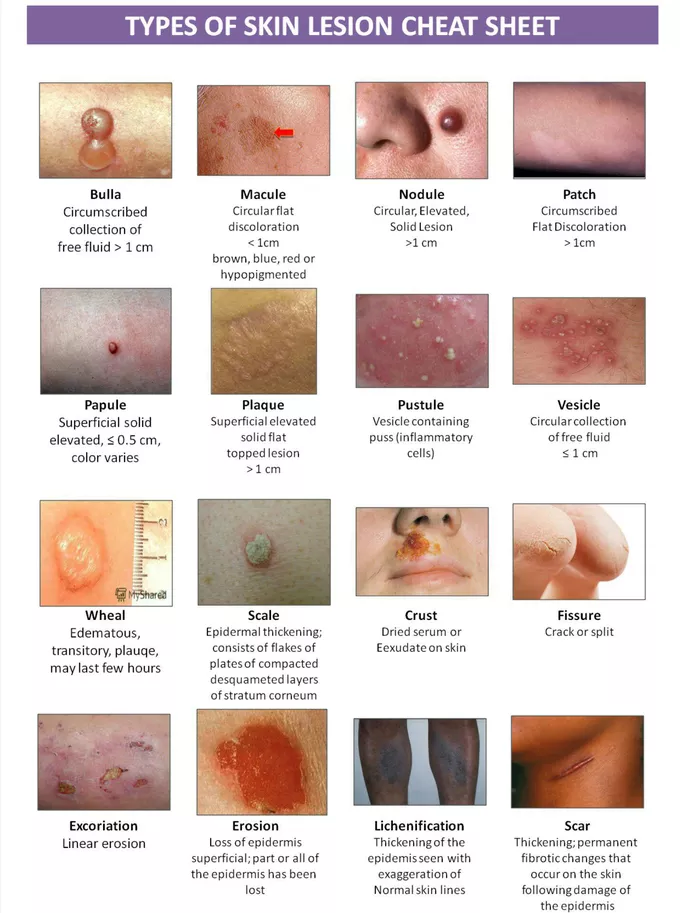
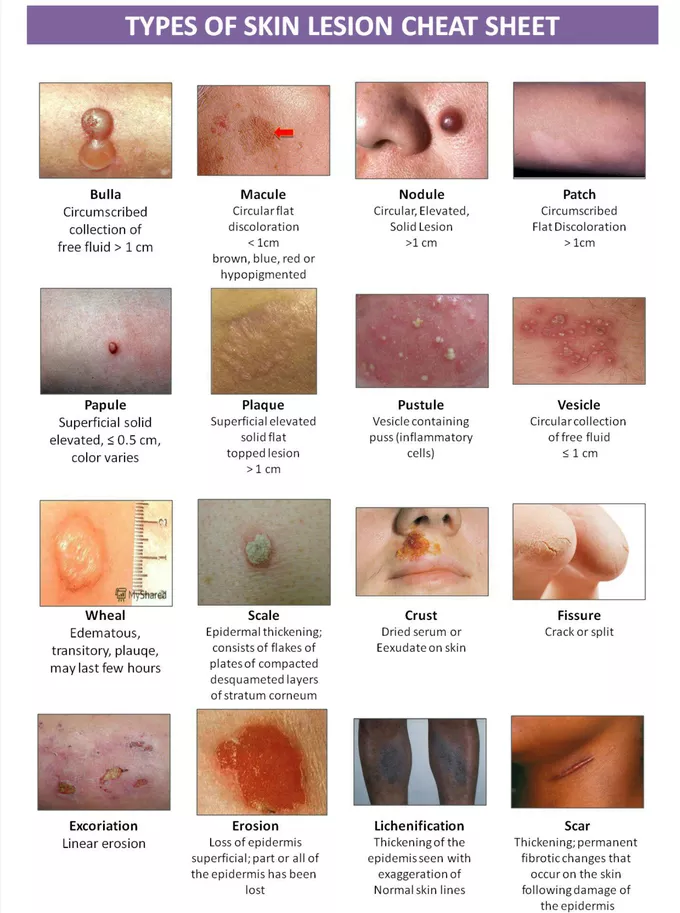
primary lesions
arise from previously intact skin
includes macules, papules, nodules, polyps, vesicles, cysts ,
secondary lesions
arise from primary lesions and include scales, crusts, ulcers, fissures, and scars
what to inspect and palpate for skin lesions/rashes?
size
colour
shape
texture
exudate→ fluid that leaks out of blood vessels into nearby tissues
tenderness
configuration
location and distribution
vascular=check for pulsations and blanching
configuration
the shape of single lesions and the arrangement of a group of regions
e.g. linear, annular, target(bull’s eye)
shingles configuration lies against the dermatomes
macules
flat, discolored spots on the skin usually <1 cm
e.g. freckles(ephelides) , flat moles
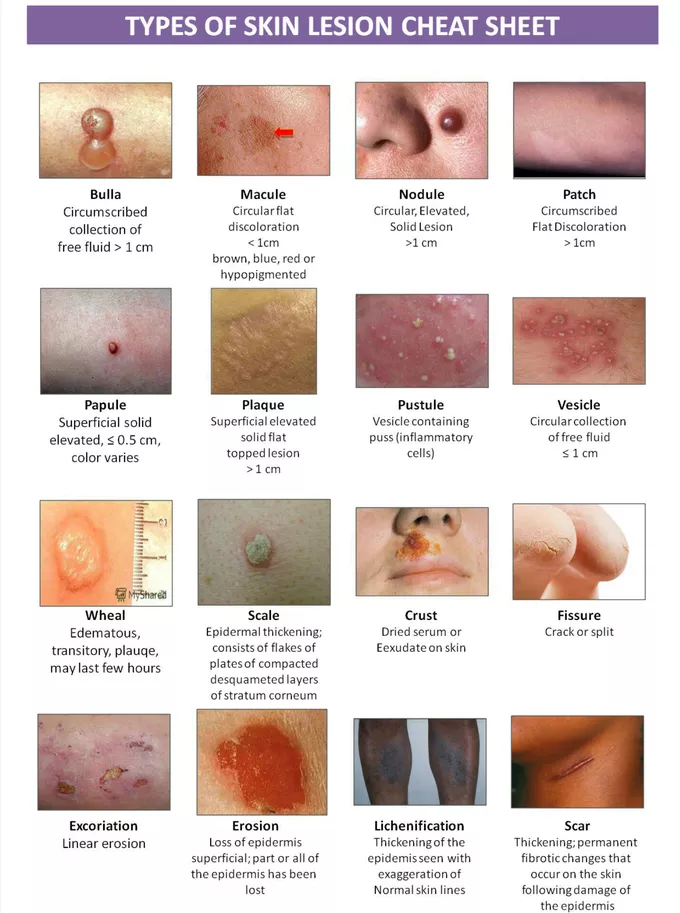
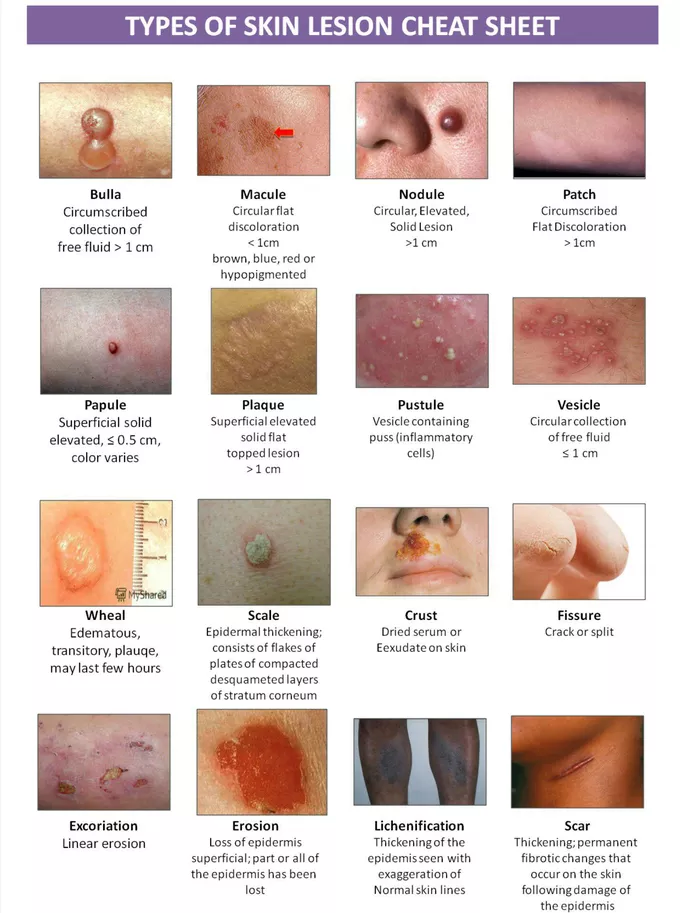
papules
lesion with layer of skin on top of it
small raised, solid bumps, usually <1 cm
e.g. warts, insect bites
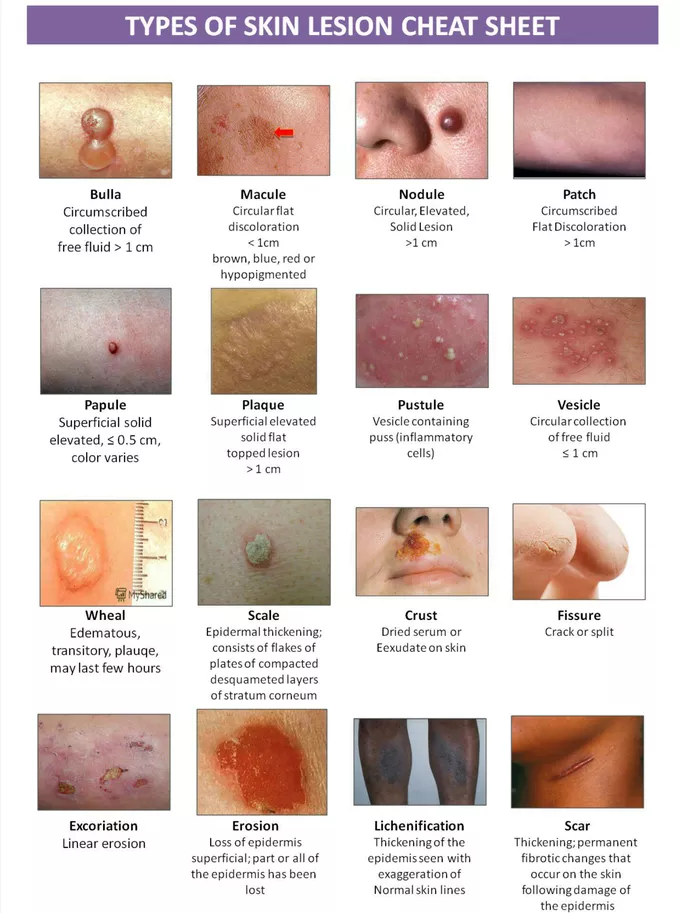
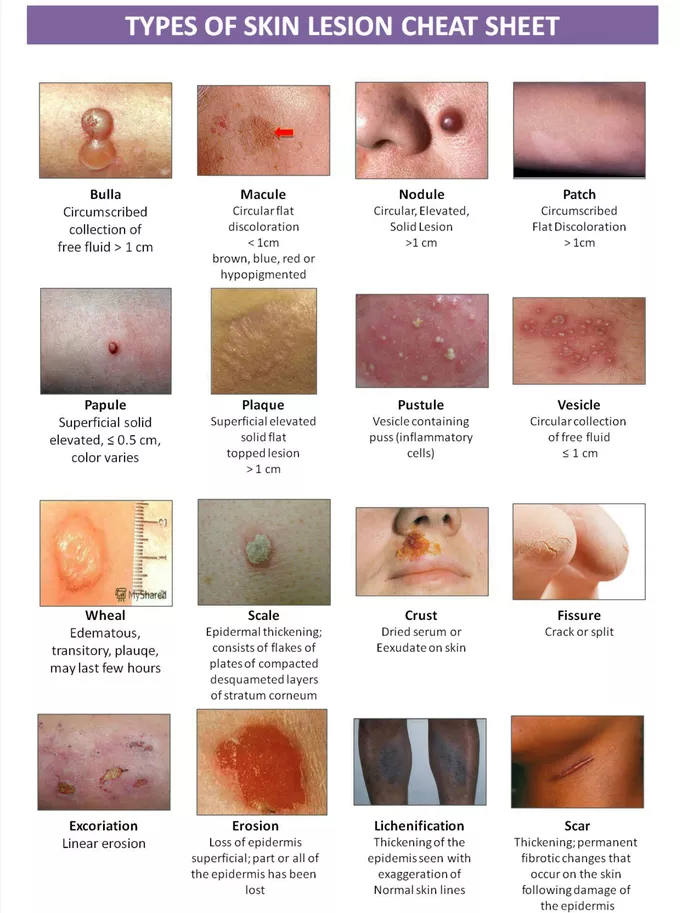
pustules
small, pus filled bumps usually <1 cm
show an elevation of the epidermis
leak bacteria but in thicker areas of the skin
e.g. acne, impetigo
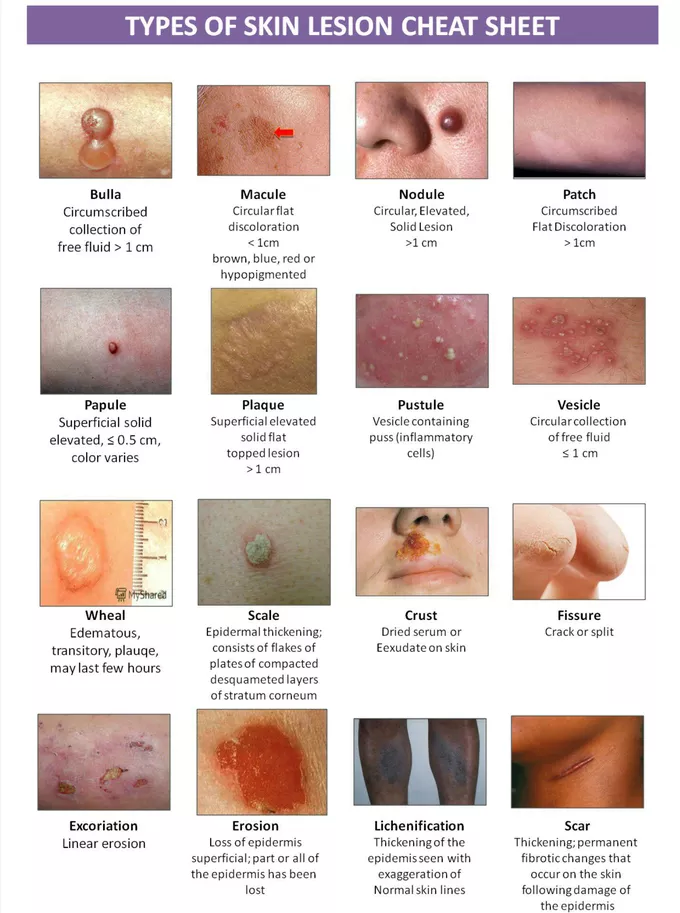
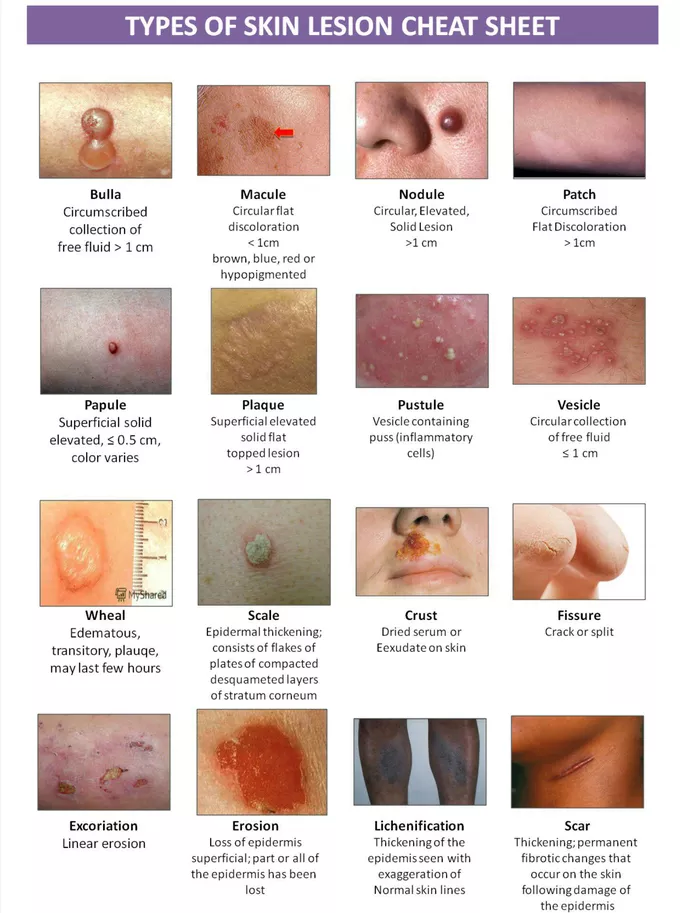
plaques
raised, flat-topped lesions >1 cm
e.g. psoriasis patches
scale
thin, flaky pieces of skin that shed from the outer layer of the skin, often seen in conditions like psoriasis or eczema.
purpura
purple or red spots on the skin due to bleeding underneath
blood is trapped in cells underneath the skin
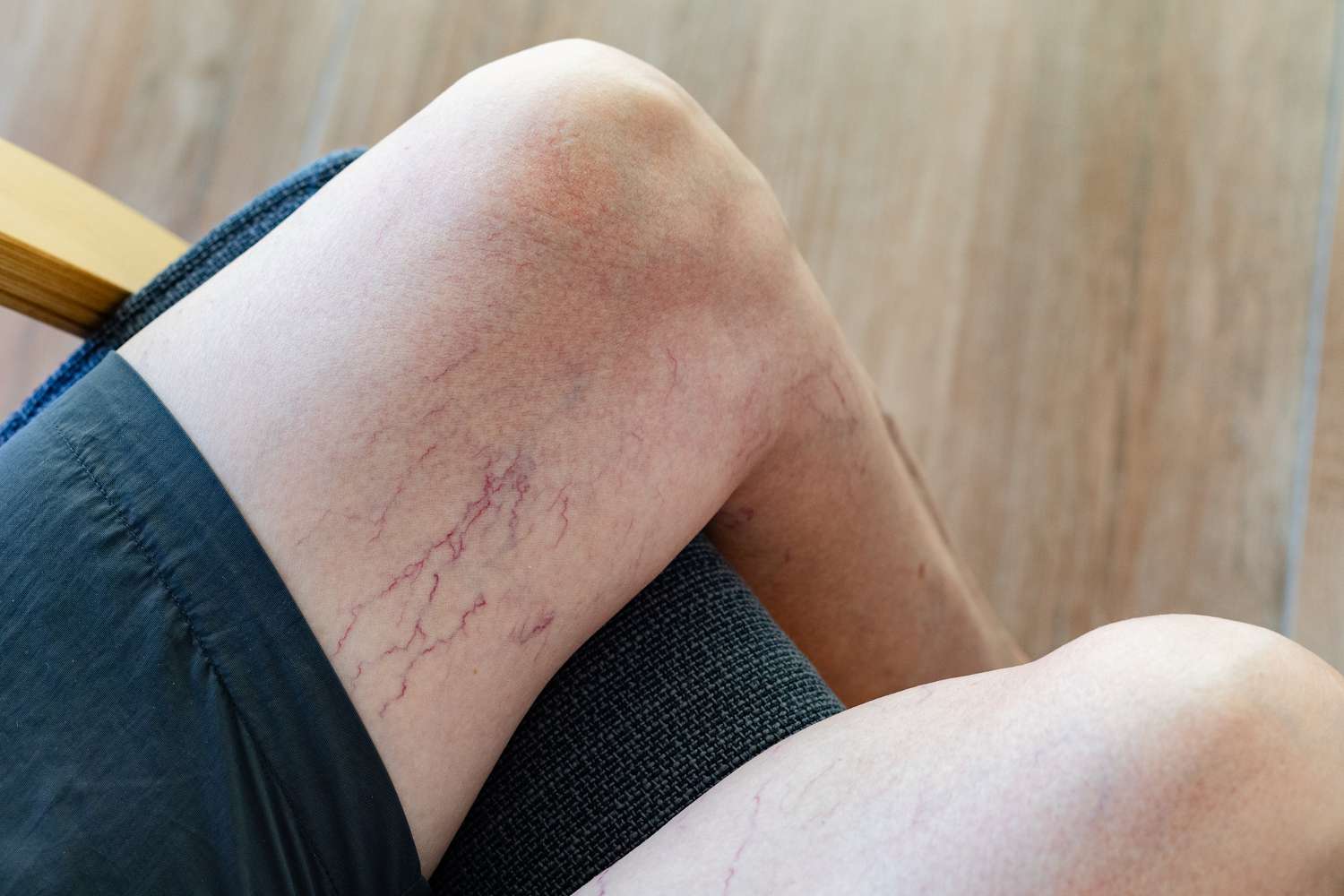
telangiectasia
dilated small blood vessels near the surface of the skin, often appearing as red or purple lines
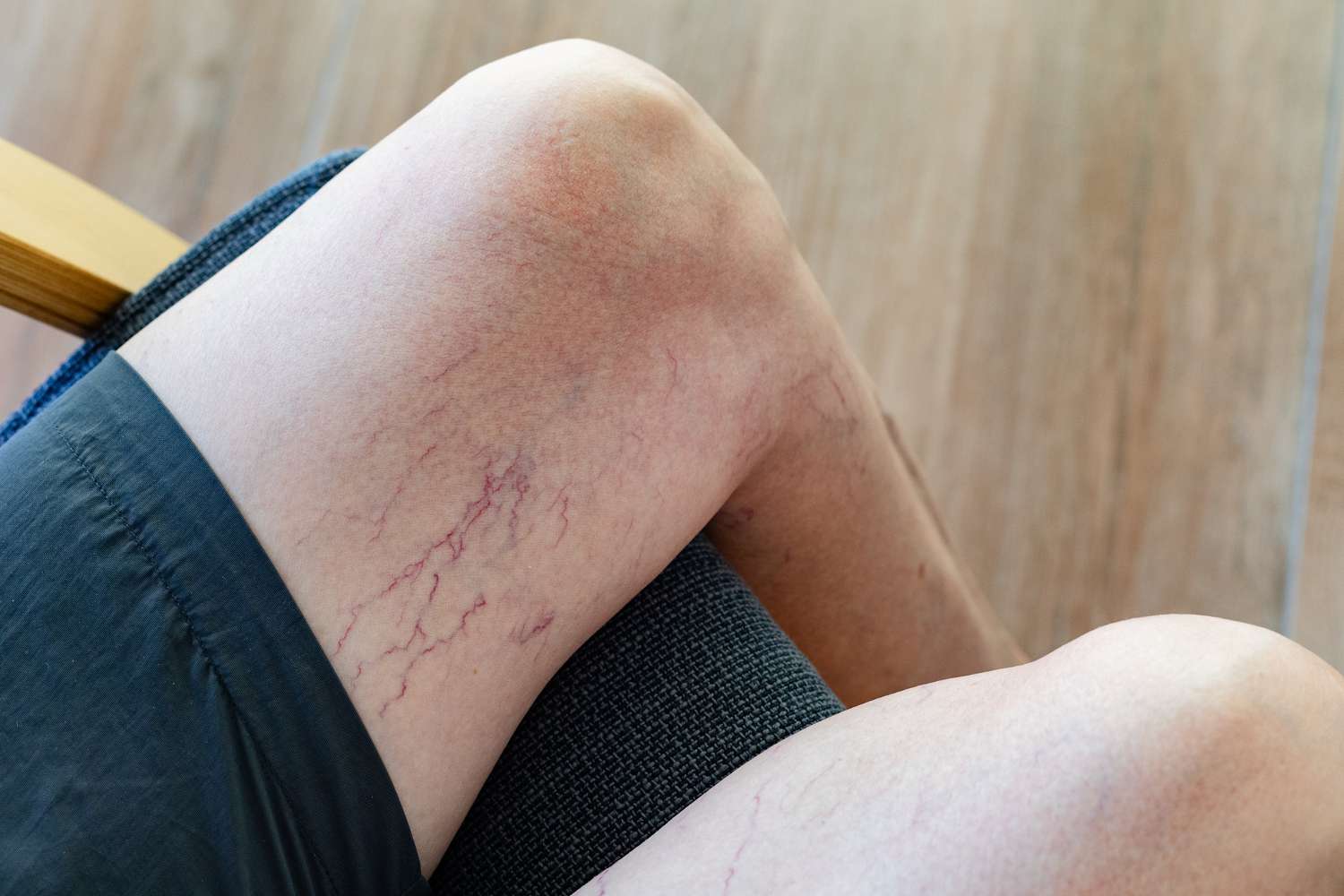
lesion colours
red
orange
yellow
violet(vascular lesions)
black→ melanocytic
shades of blue, silver, and gray
location and distribution of the lesions
can tell us the cause or source of the problem
describe number of lesions(single or multiple), are they in a pattern or random?
symmetric or asymmetric
what body part→ sun exposed or sun protected?
ABCDE’s of hyperpigmented lesions
A: Asymmetry→ does one half look life the other?
is it round symmetric lesion
if you draw a line through the middle the halves of the melanomas won’t match in size
B: Border→ is the border, ragged, notched uneven or crusty?
C: Colour→ does the mole have variety of shapes or different colours
healthy moles are uniform in colour
D: Diameter→ is the lesion larger than 6mm?(larger than a pencil eraser)
E: Evolving→ has the lesion changed in size, shape, or colour over time?
bleeding, scabs, tenderness point to danger also
pressure injuries
pressure of bony prominence against surface for long period of time
can be as short as 15 minutes
friction→ e.g. feet rubbing against wheelchair handle
shear→ e.g. thinned skin person ripping skin with fingernail
Braden scale for risk assessment
looks at the risk for developing pressure sores
acral lentiginous melanoma(ALM)
most common melanoma found in people of colour
skin turgor
measure of skin elasticity
how to assess: pinch the skin and lift off the body→ watch how long it takes to return to normal
less than or equal to 3 secs is normal
can be affected by hydration
decreases as a result of the thinning of the dermis and reduced elastin production
inspection of hair
colour, infestations, hygiene, quantity
distribution→ affected by age, gender, or genetics(puberty brings onset of pubic hair)
pattern of loss
colour→ some illness affect ahir colour
texture→ any change in texture dry, coarse, fine, silky
note areas of absent hair(alopecia) or lesions
hair shaft should be smooth, shiny, of even consistency, without evidence of breakage
palpation of hair
lightly palpate the texture, moisture, hygiene
scalp should be mobile and non-tender
hair should be smooth
not excessive hair loss and then assess for absence or presence of hair bulb
inspection of nails
assess for colour, shape, thickness, and consistency
have patient place the fingernails of both index fingers together to assess the nail angle(heart with finger)→ diamond shaped opening should be visible
palpation of nails
nails are smooth, non-tender
lateral and proximal folds are non-tender
assess capillary refill: apply pressure to the nail bed to cause blanching (change to white/lighter colour)
less than 3 secs
> 4 secs indicates severe dehydration or insufficient vascular supply
capillary refill
determines if there is good prefusion
to assess: apply pressure to the nail bed to cause blanching (change to white/lighter colour)
less than 3 secs
> 4 secs indicates severe dehydration or insufficient vascular supply
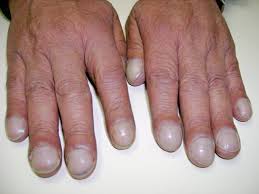
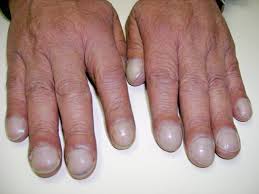
nail clubbing
indicates chronic hypoxia or peripheral vascular disease(extent of clubbing shows extent of illness)'
when the angle of the nail to the finger is more than 160 degrees
fingernails do not touch when put together(heart with fingers)
nails beds are spongy
Beaus lines
results from slowed or halted nail growth in response to illness, physical trauma, or poisoning
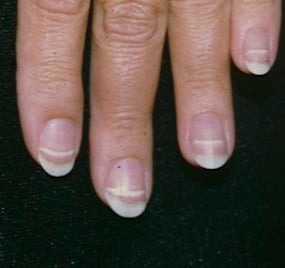
spooning nails
Nails that curve inward, like a spoon
can indicate health issues like iron deficiency anemia or trauma, and may increase the risk of infection
red flags
pressure injury→ we use Braden Scale for risk assessment
acute dehydration
cyanosis
melanoma
acute trauma and burns
inspection
colour: use natural or halogen lamp(not fluorescent) and assess uniformity
sun exposed areas vs not exposed
assess mucous membranes and conjunctiva
hygiene→ odour, infection
Lesions/ rashes/swelling/erythema/discharge→ just because it is in one spot does not mean it is not anywhere else
palpation of skin
temperature, moisture, thickness, texture, turgor
temperature→ using dorsal surface of hands
moisture→ using palmar surface of fingers and hands, a to assess moisture and texture
thickness
turgor→ skin turgor test
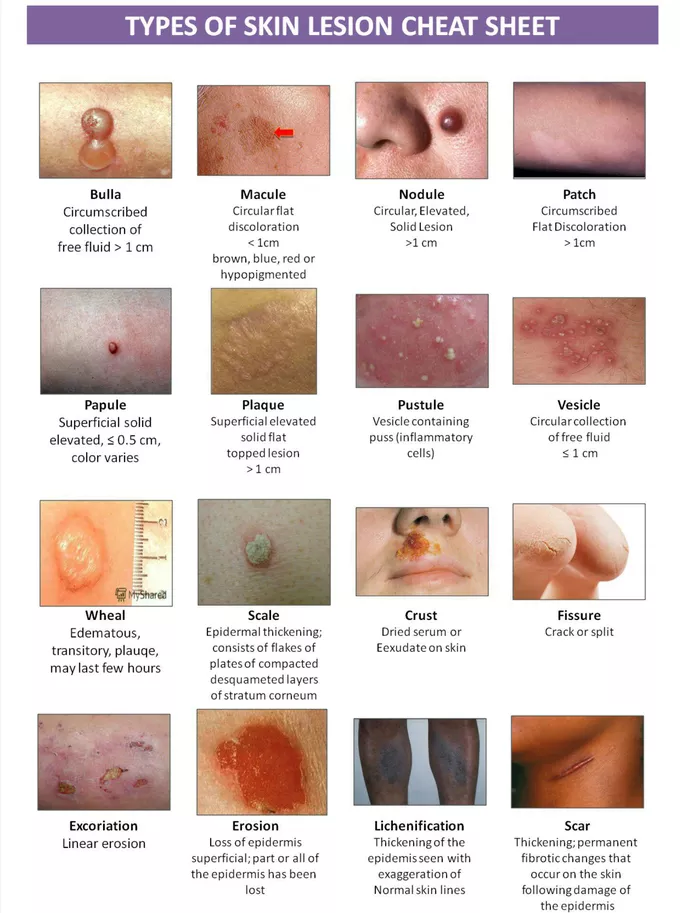
nodules
solid, raised skin lesions, usually > 1 cm and deeper than papules
e.g. lipomas, cysts
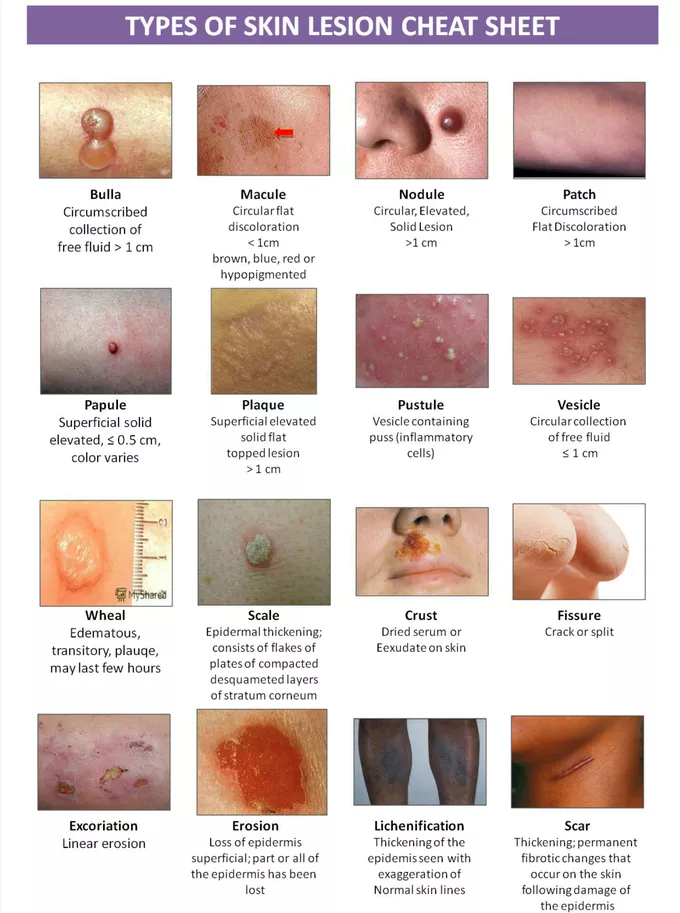
vesicles
small, clear skin coloured lesion with water but no erythema- fluid filled blisters
usually <1 cm
e.g. chickenpox, herpes
urticara(hives)
raised, red, itchy, welts of varying sizes
usual appear in clusters
usually an allergic reactioj
bullae
large fluid-filled blisters usually
> 1 cm in diameter
can be caused by burns, contact dermatitis, or infections