Neuroanatomy Exam 2 chapter5
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Spinal Cord housed in ?
housed in boney vertebral column
Spinal cord 5 sections (inferior to superior) or (superior to inferior)
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal sections (superior to inferior) head to feet
How many cervical spinal nerves?
thoracic spinal nerves
lumbar spinal
sacral spinal
coccygeal spinal
superior to inferior or inferior to superior
8
12
5
5
1
breakfast at 8, lunch at 12, dinner at 5 twice, and then a midnight snack at 1
superior to inferior
what is PNS and what is CNS
spinal nerves, spinal cord
spinal nerves - PMS
Spinal cord- CNS
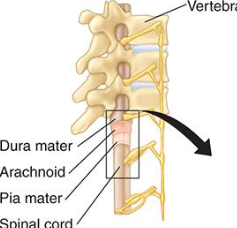
higher the spinal cord injury the ____ and more ______
higher the spinal cord injury the worse and more deadly
SAME
Sensory afferent, motor efferent
-body to brain- S
-brain to body - M
Spinal cord moves information that is motor or efferent as well as sensory info
yup
Four fiber types spinal cord External Organization
to skeletal muscles (somatic)-control
to smooth muscle, heart, glands (visceral- gut can’t really control)
from skin to brain - control
from lungs and digestive tract- can;t
GSE fibers: (———)
GVE fibers: (———-)
GSA fibers:
GVA fibers:
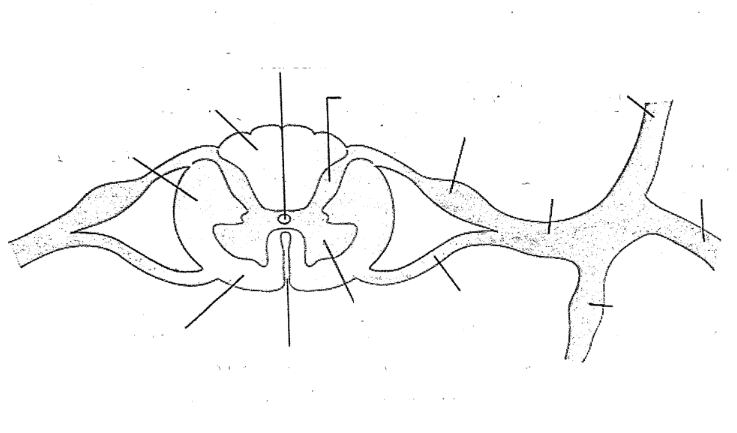
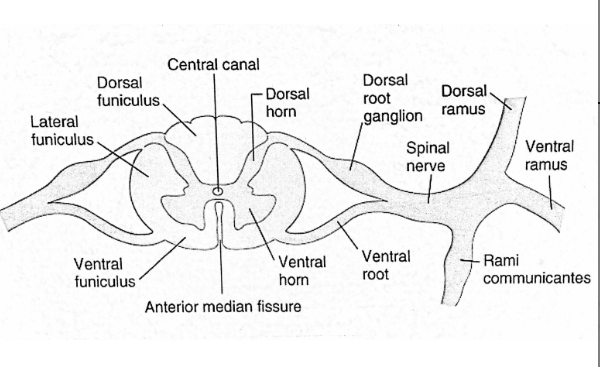
Dorsal ramus
ventral ramus
spinal nerve
dorsal root
ventral root
dorsal horn
ventral horn
anterior median fissure
central canal
rammi communicantis
lateral funiculus
ventral funiculus
dorsal furniculus
Dorsal ramus (toward back
ventral ramus (toward front near nose anterior
RAMUS means branch
spinal nerve
dorsal root
ventral root
dorsal horn
ventral horn
anterior median fissure
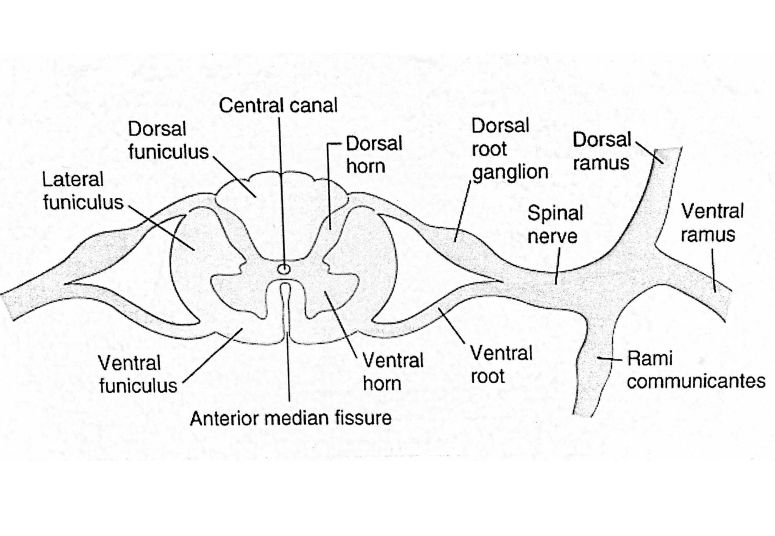
spinal cord: internal organization Major landmarks
Dorsal funiculus (bundle of fibers)
lateral funiculus
ventral funiculus
funiculus (white matter)
left vs right ?
Spinal Cord Function
relaying efferent and afferent information between body and brain
Mediating reflexes through the reflex arc
Major motor tracts DON”T NEED TO KNOW TRACTS
Lateral corticospinal contralateral body movement
anterior (or ventral) corticospinal: trunk muscles
Rubrospinal: flexor tone
Vestibulospinal: extensor tone
Major sensory tracts of internal organization of spinal cord
Dorsal columns: fine touch, pressure, proprioception
Spinothalamic: regulates pain, temperature, crude touch
Spinocerebellar: helps with proprioception (sensation of knowing body in space)
Spinal Cord Disorders
Spinal cord Injury, Spina Bifida, Myelitis, Peripheral Neuropathy
Spinal cord injury About and implications
About- Paresis (incomplete) or plegia (complete)
loss of sensation or movement
Implications- Loss of movement may
impact speech production
Vehicular accidents account for 40% of cases
Spina Bifida ( spinal cord or Brainstem?)
about and implication
Spinal cord
About- Neural tube defect occurring early in
development, causing lower limb paresis,
bowel and bladder issues
Implications- No direct speech or
language implications
possible paraparesis and bowel and bladder issues
Myelitis (spinal cord or Brainstem?)
about and implication
inflammation of the spinal cord can be caused by virus, bacteria, fungi, parasites, and toxic agents (lead poisoning)
Different types (Poliomyelitis - affects gray matter MOTOR LOSS
Leukomyelitis- affects white matter SENSORY LOSS
Transverse myelitis- affects both gray and white matter MOTOR AND SENSORY LOSS
No direct speech or
language implications
Peripheral Neuropathy (spinal cord or Brainstem?)
about and implication
Implications-
Inflammation of PNS, resulting in
degeneration of the spinal nerves. Caused
by toxic poisoning, infections, metabolic
disorders, and nutritional issues. Causes
loss of sensation. Leads to paresthesia or anesthesia
Implications-
No direct speech or
language implications.
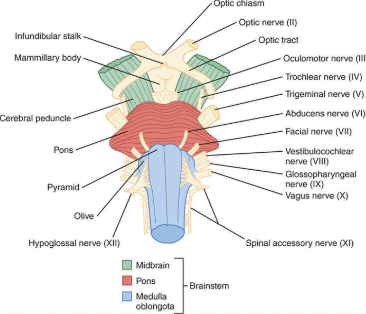
The Brainstem: anterior external organization
what 3 parts does it consist of ?
Midbrain - most superior (closer to brain)
Pons - inferior to midbrain superior to medulla
Medulla - inferior to pons
Brainstem Functions
Regulating major life functions (e.g., heart beat, respiration)
Mediating head and neck reflexes (e.g., gag) via cranial nerves (see next slide)
Regulating alertness and wakefulness
Where do most cranial nerves originate and which do not originate in the brain stem
medulla area and 1 and 2 do not originate in brain stem
First Cranial nerve
function and pathologies
Olfactory
Origin = Olfactory bulb
Fiber type = SVA
Function(s) = Smell
Problem(s) = Anosmia (lack of smell)
afferent
Sensory
Cranial Nerve 2
Olfactory Nerve II
Origin = Thalamus
Fiber type = SSA
Function(s) = Vision
Problem(s) = Visual disturbances; loss of vision (blindness)
Sensory
Cranial nerve 3
III. Oculomotor Nerve
Origin = Midbrain
Fiber type= GSE, GVE
Function(s) = motor movement
GSE: Moves eyes left and right; controls eyelid
GVE: pupil constrictor
Problem(s) = Loss of pupillary light reflex; papilledema; ptosis
MOTOR
Cranial nerve 4
IV. Trochlear Nerve
Origin = Midbrain
Function(s) = Moves eyes up and down
Problem(s) =Diplopia; nystagmus; difficulty moving eyes up and down
Motor
Cranial nerve 5
V. Trigeminal Nerve DETAILS
Origin = Pons
Fiber type = SVE, GSA
Function(s) =
GSA: touch, pain, temp. and vibration for face, mouth, ant. 2/3 of tongue
GVE: Chewing muscles
SENSORY and MOTOR
Problem(s) = Loss of above sensations; difficulty chewing; abnormal jaw-jerk reflex
TRI - THREE MAJOR BRANCHES- ophthalmic, maxillary branch, mandibular branch
Cranial Nerve 6
VI. Abducens Nerve
6 pack- abs- abducens
Origin = Pons
Fiber type = GSE
Function(s) = Rotates eyes out
Problem(s) = eye rotates in (strabismus) and diplopia; nystagmus
Motor
Cranial Nerve 7
VII. Facial Nerve
Origin = Pons
Functional Category = SVE, GVE, GSA, SVA
Function(s) =
SVE: Muscles of face
GSA: Sensation near ears
SVA: Taste in ant. 2/3 of tongue
GVE: Salivary glands
Problem(s) = Facial paralysis/paresis; taste loss
smile, blink, squeeze face, puff cheeks, kiss
Motor and sensory
Cranial nerve 8
VIII. Vestibulocochlear Nerve*
Also known as auditory nerve
Origin = Pons/medulla junction
Fiber type = SSA
Function(s) = Hearing and balance
Problem(s) = Hearing loss; balance problems
Sensory
Cranial nerve 9
IX. Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Origin = Pons/medulla junction
Fiber type = SVE, GVE, GVA, SVA
Function(s) =
SVE: Pharyngeal movement
GVE: Parotid gland (salivation)
GVA: Middle ear, pharynx, post. 1/3 of tongue
SVA: Taste on post. 1/3 of tongue
Movement of pharynx, responsible for taste on back of tongue
GLOSSO- sensory
Pharyngeal- motor
Problem(s) = Absent gag and swallow reflex; loss of taste; loss of pharyngeal movement
MOTOR and Sensory
Cranial nerve 10
X. Vagus Nerve
Origin = Medulla
Fiber type = SVE, GVE, GSA, GVA, SVA
Function(s) =
SVE: Pharyngeal and laryngeal muscles
GVE: helps Heart, lungs; digestive tract
GSA: Tactile sensation to external ear canal
GVA: Pain from mucous membranes
SVA: Taste from epiglottis and pharynx
Problem(s) = Absent gag and swallow reflex; loss of velar movement; loss of voice
Sensory and motor
Cranial nerve 11
XI. Spinal Accessory Nerve
Origin = Medulla, spinal cord
Fiber type = SVE
Function(s) = Neck and shoulder muscles
Problem(s) = Droopy shoulder; movement of neck
Motor
Cranial nerve 12
XII. Hypoglossal Nerve
Origin = Medulla
Fiber type = GSE
Function(s) = Muscles of tongue
Problem(s) = Loss of tongue movement; tongue fasciculations, tongue atrophy
speech and swallowing
only for motor movement
Brainstem Disorders
Wallenberg Syndrome
location, about implication
-Medulla
-Usually caused by stroke affecting a vessel
leading to the brainstem.
-Ataxia, paralysis of
ipsilateral palate and vocal
fold, dysphagia. Violent
hiccups impacting
speaking, eating, and
sleeping.
Brainstem Disorders
locked in Syndrome
location, about implication
-pons
-Causes quadriplegia and cranial nerve
paralysis
-Inability to speak or
swallow
Brainstem Disorders
Webers syndrome
location, about implication
-Midbrain,
-Contralateral hemiplegia and ipsilateral
oculomotor paralysis with ptosis.
-Hemiparesis affects the
lower face muscles and
tongue
Brainstem Disorders
Benediktis syndrome
location, about implication
-midbrain
-Contralateral hemiparesis and ataxic
tremor
-Hemiparesis affects the
lower face muscles and
tongue
Brainstem Disorders
Cerebellar Hemispheral syndrome
location, about implication
-Cerebellum
-Caused by stroke, tumor, and multiple
sclerosis. Affects ipsilateral limbs causing
tremor, dysmetria, and
dysdiadochokinesia, Holmes’ rebound
affect.
-No direct speech or
language implications
Brainstem Disorders
Vermal syndrome
location, about implication
-Cerebellum
-Damage of the vermis resulting from
stroke, tumor, MS, and other degenerative
disorders. Affects trunk muscles with
symptoms such as unsteadiness , tremor,
postural issues, and gait ataxia
-No direct speech or
language implications
Brainstem Disorders
Friederichs Ataxia
location, about implication
-Cerebellum
-Inherited, progressive neurological disorder
of autosomal recessive pattern. Causes
progressive muscle weakness in limbs, loss
of coordination, curvature of the spine,
vision problems.
-Dysarthria, hearing issues
Brainstem Disorders
Cerebellar Agenesis
location, about implication
-Cerebellum
-No cerebellum
-No direct speech or
language implications
Cranial nerves
-1 gave wif - sensory nerve - olfactory is the way
-second nerve helps me see right - central peripheral sight central peripheral sight sensory nerve for eye Optic nerve is the way
-pupils constricting, third nerve eyes are moving, prevents eyelid drooping oculomotor nerve baby
-the trochlear nerve works the superior oblique this is the fourth nerve. Hard to look down if it’s weak
-trigeminal nerve works mastificaiton, deals with sensory and motor, deals with face sensation
-abducent is the sixth, does eye abduction, motor nerve for motion, helps prevent double vision
-facial is the 7th, does facial expression, it’s sensory and motor, 2/3 of taste sensation
-Vestibulocochlear is the 8th, body balancer, used for the ear, sound sensor
-Glossopharyngeal nerve, senses taste from the 1/3 back of the tongue, the 9th it helps us swallow hey
-tenth nerve is vagus, lets us speak and say stuff, it’s sensory and motor, baby
Accessory nerve - is the 11th, so shrug your shoulders, and test head resistance
-the hypoglossal nerve, is the twelfth nerve, deals with tongue movement,
major cerebellar pathways and functions
Vestibulocerebellar
Vermal spinocerebellar
Paravermal spinocerebellar
Pontocerebellar
Vestibulocerebellar- overall body posture and balance; coordination of eye movements
Vermal spinocerebellar -trunk and girdle muscle tone and posture
Paravermal spinocerebellar - distal muscle group tone and posture
Pontocerebellar- planning, initiating and timing of volitional motor activity
Functions of Cerebellum
Motor and Linguistic
Motor:
Helps in planning, monitoring, and correction of motor movement using sensory feedback
Coordinates fine motor activity
Monitors head and body position
Participates in learning of new motor skills
Linguistic:
Perception of speech/language, verbal working memory, verbal fluency, grammar processing, writing, and reading
Testing the cerebellum
-finger to nose test
-Diasochokinesia (pat-ta-ka)
-uncoordinated sloppy movement may indicate cerebellar damage
Damage to Cerebellar may lead to symptoms
ataxia
dysmetria
Dysdiadochokinesia
Nystagmus
Ataxic dysarthria
Hypotonia
ataxia - Discoordinated, clumsy movements
dysmetria- over-or undershooting touching a mark
Dysdiadochokinesia- inability to perform rapid, alternating movements or hands or mouth
Nystagmus - fast, involuntary eye movements either side to side or up and down
Ataxic dysarthria -slurred or scanning (broken into syllables speech)
Hypotonia- reduced muscle tone and reflexes, muscle tire