Rotorcraft Theory
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Last updated 3:38 PM on 1/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Which vehicles can be categorized as rotorcrafts?
Helicopter, Autogiros, Tiltrotor (they must be heavier than air)
2
New cards
What are the two main issues driving the multi-rotor configurations widely used in the early
rotorcraft development?
rotorcraft development?
Balancing the torque of each rotor system and balancing the rolling moment in forward flight
3
New cards
How does the single-rotor helicopter deal with the torque balance?
By using a tail rotor
4
New cards
How does the single-rotor helicopter deal with the rolling moment in forward flight?
Use a flapping hinge to balance the rolling moment a provide balance
5
New cards
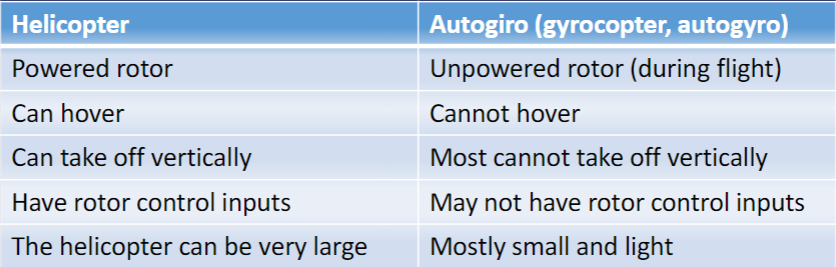
What are the differences between helicopters and autogiros?
6
New cards
Why does not the autogiro need a tail rotor?
The rotor of the autogiro does not connect with the engine, and it cannot transmit torque to the
vehicle
vehicle
7
New cards
What is the fundamental difference between the helicopter and the autogiros?
The rotor powered by the engine in the cruise flight
8
New cards
How do single-rotor rotorcrafts provide control forces and
control moments?
control moments?
• Vertical force: Main rotor thrust
• Longitudinal force: Main rotor tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotor tilt fore/aft
• Roll attitude: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Yaw attitude: Tail rotor thrust/engine torque
• Longitudinal force: Main rotor tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotor tilt fore/aft
• Roll attitude: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Yaw attitude: Tail rotor thrust/engine torque
9
New cards
How do tandem rotorcrafts provide control forces and control moments?
• Vertical force: Collective main rotor thrusts
• Longitudinal force: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotors tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotor tilt fore/aft and/or differential main rotor thrust
• Roll attitude: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Yaw: Differential main rotor tilt in lateral directions
• Longitudinal force: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotors tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotor tilt fore/aft and/or differential main rotor thrust
• Roll attitude: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Yaw: Differential main rotor tilt in lateral directions
10
New cards
How do side-by-side (transverse) rotorcrafts provide control forces and control moments?
• Vertical force: Collective main rotor thrusts
• Longitudinal force: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotors tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Roll attitude: Main rotors tilt lateral and/or differential main rotor thrusts
• Yaw: Differential main rotor tilt fore/aft
• Longitudinal force: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotors tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Roll attitude: Main rotors tilt lateral and/or differential main rotor thrusts
• Yaw: Differential main rotor tilt fore/aft
11
New cards
How do coaxial rotorcrafts provide control forces and control moments?
• Vertical force: Collective main rotor thrusts
• Longitudinal force: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotors tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Roll attitude: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Yaw: Differential main rotor torques
• Longitudinal force: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Lateral force: Main rotors tilt lateral
• Pitch attitude: Main rotors tilt fore/aft
• Roll attitude: Main rotor tilt lateral
• Yaw: Differential main rotor torques
12
New cards
What is the function of a swashplate?
Adjust the blade control angle at different azimuth angles
13
New cards
What is the difference between thrust and lift?
* Thrust is in the rotor axial direction
* Lift is normal to the inflow direction
* Lift is normal to the inflow direction
14
New cards
What are the assumptions of the momentum theory?
* Exiting a steamtube (axially symmetric surface passing through the rotor disc perimeter which isolates the flow through the rotor)
* Incompressible flow
* Velocity imparted to the fluid is constant across the disk
* Far away from the disk, the air is at rest
* Incompressible flow
* Velocity imparted to the fluid is constant across the disk
* Far away from the disk, the air is at rest
15
New cards
What is the definition of the induced velocity?
Velocity increment due to the rotor
16
New cards
What is the condition of the momentum theory applicable to the vertical descent flight?
|𝑈𝐴|>2𝑣𝑖, ℎ𝑜𝑣
17
New cards
Right or wrong:
A figure of merit is used to evaluate the rotor performance in the vertical flight.
A figure of merit is used to evaluate the rotor performance in the vertical flight.
Wrong: It is used to evaluate rotor performance in hover.
18
New cards
Right or wrong:
Rotor power calculated from the momentum theory and blade element torque is the same.
Rotor power calculated from the momentum theory and blade element torque is the same.
Wrong: the power from the moment theory is the induced power (induced + parasite power in forward flight), and the power from the blade element theory is the all rotor power consumption
19
New cards
What issues do tandem rotorcrafts experience that results in imbalance?
The differential main rotor thrust unbalances the \n aircraft in yaw.
There is no good alternative to differential \n thrust to change aircraft pitch attitude.
The pilot or the control system must cope with the coupling the results.
There is no good alternative to differential \n thrust to change aircraft pitch attitude.
The pilot or the control system must cope with the coupling the results.
20
New cards
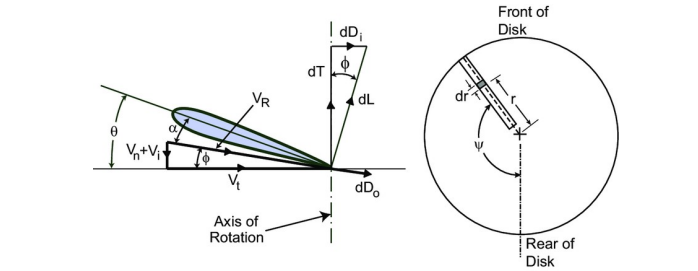
Use the following figure to indicate why the rotor cannot provide any thrust in the vortex-ring state
The vortex ring state sucks the downstream flow back, increasing the normal velocity Vn significantly, which makes most of the blade in the stall condition
21
New cards
What is the most reasonable pilot control strategy to get rid of the vortex ring state?
Push longitudinal cyclic pitch to increase forward speed
22
New cards
From the view of the blade element theory and considering the attack angle and the inflow condition, why does the rotor need the pre-twist angle?
The pre-twist angle allows most of the blade element (especially the blade tip section) to be in the optimal attack angle (maximise the ratio between lift and drag)
23
New cards
Demonstrate the function and mechanism of the pre-rotator
* Function: Reduce the take-off distance of the auto-rotator and even allow the autogiro to have vertical take-off capability
* Mechanism: Let the engine link with the rotor on the ground to make the rotor rotate, which will disconnect with the rotor after take-off
* Mechanism: Let the engine link with the rotor on the ground to make the rotor rotate, which will disconnect with the rotor after take-off
24
New cards
From the view of the blade element theory, how does the rotor maintain the rotational speed?
P75 but im not sure which bit
25
New cards
Demonstrate the control strategy of the collective pitch during the autorotational landing
Reduce the collective pitch to maintain the rotational speed, and when the vehicle is close to the ground, increase the collective pitch to add additional vertical acceleration to reduce the vertical speed
26
New cards
Right or wrong:
In the autorotation process, the helicopter is similar to the autogiro’s rotor, providing no torque to the vehicle
In the autorotation process, the helicopter is similar to the autogiro’s rotor, providing no torque to the vehicle
Right
27
New cards

Based on this figure, get the rotor rotational direction and the thrust direction of the tail rotor in normal forward flight
Anti-clockwise: the tail rotor direction is to the right if you are seated in the pilot position
28
New cards
Which azimuth angle will be the highest point if we only consider the dynamic pressure difference in forward flight?
180°
29
New cards
Which azimuth angle will be the highest point if we only consider the coning angle in forward flight?
270°
30
New cards
Which azimuth angle will be the highest point if we only consider the longitudinal cyclic pitch (use it to increase forward speed)?
0°
31
New cards
If we want to provide additional right force along from the rotor in an anti-clockwise rotor, which direction should the swash plate change?
Tilt backwards
32
New cards
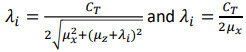
Right or wrong:
The below equations can be both used in estimating the induced velocity in high-speed forward flight?
The below equations can be both used in estimating the induced velocity in high-speed forward flight?
Right
33
New cards
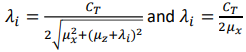
Right or wrong:
The below equations can be both used in estimating the induced velocity in low-speed forward flight?
The below equations can be both used in estimating the induced velocity in low-speed forward flight?
Wrong, the second equation cannot be used to calculate the induced velocity in low-speed forward flight
34
New cards
By optimising the pre-twist angle, which component of the power consumption will be reduced?
Profile power
35
New cards
By optimising the geometry of the fuselage, which component of the power consumption will be reduced?
Parasite power
36
New cards
Which component of power will increase due to the tip blade compressibility effect?
Profile power
37
New cards
Why is the induced power reduced with forward speed increases?
The local dynamic pressure is higher
38
New cards
Which components provide the mass, damping, and stiffness terms of the rotor flapping dynamics equation?
Inertia force, aerodynamic force, and centrifugal force, respectively
39
New cards
What is the flapping offset influence on the flapping frequency and flapping phase delay angle?
Increase the flapping frequency angle and reduce the flapping phase delay angle
40
New cards
Why the flapping phase angle is close to 90°?
* The natural frequency of the flapping motion is close to the rotational speed, and the excitation frequency is equal to the rotational speed
* Thus, the system is in the resonance condition, in which the phase delay is 90°
* Thus, the system is in the resonance condition, in which the phase delay is 90°
41
New cards
What causes the lead-lag motion and why the rotor must have the lead-lag hinge?
* The lag (lead-lag) motion is due to the Coriolis forces provided by the flap
* The lead-lag hinge is used to reduce this harmonic load damage on the rotor hub
* The lead-lag hinge is used to reduce this harmonic load damage on the rotor hub
42
New cards
With forward speed increase, how will the reverse flow area change and how will it influence the rotor aerodynamics?
The reverse flow area will increase with forward speed, and it would reduce the rotor thrust and increase the rotor drag
43
New cards
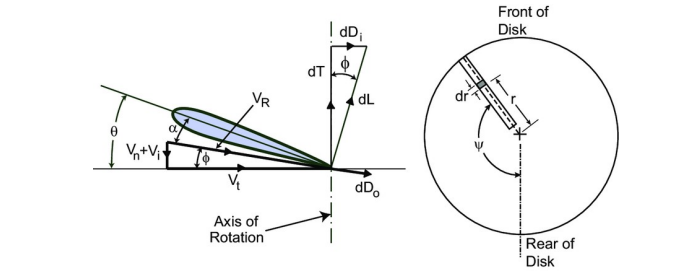
Using the blade element theory shown in this figure, which parameter will be changed considering the flapping motion?
Vn
44
New cards
Write the comprehensive expression of the blade control angle and indicate which is the longitudinal and lateral cyclic pitch.
\
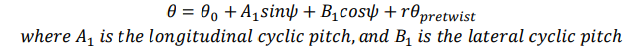
45
New cards
How will the flapping offset provide additional control moments and how will it influence the pitching and rolling damping?
* The flapping offset gives a moment to let the rotor thrust contribute to the control moment, which is called the hub moment
* The flapping offset can make the rotor provide additional pitching and rolling damping
* The flapping offset can make the rotor provide additional pitching and rolling damping
46
New cards
i have not done chapter 7 yet
47
New cards

Here is the single-rotor helicopter with the centre of gravity after the rotor hub.
Which components significantly contribute to forward speed damping, vertical speed damping, and pitching damping?
Which components significantly contribute to forward speed damping, vertical speed damping, and pitching damping?
* Forward speed damping: Rotor Fuselage
* Vertical speed damping: Rotor
* Pitching: Horizontal tail
* Vertical speed damping: Rotor
* Pitching: Horizontal tail
48
New cards

Here is the single-rotor helicopter with the centre of gravity after the rotor hub.
Which components contribute to the velocity stability derivative and incidence stability derivatives?
Please also the direction (+/-) of these stability derivative
Which components contribute to the velocity stability derivative and incidence stability derivatives?
Please also the direction (+/-) of these stability derivative
Velocity stability (positive means stable)
* Rotor-> positive velocity stability derivative
* Horizontal tail->If the horizontal tail pre-setting angle is positive, negative velocity stability derivative. Otherwise, the positive velocity stability derivative
Incidence stability (negative means stable)
* Rotor-> positive incidence stability derivative
* Horizontal tail->Negative incidence stability
* Rotor-> positive velocity stability derivative
* Horizontal tail->If the horizontal tail pre-setting angle is positive, negative velocity stability derivative. Otherwise, the positive velocity stability derivative
Incidence stability (negative means stable)
* Rotor-> positive incidence stability derivative
* Horizontal tail->Negative incidence stability
49
New cards

Here is the single-rotor helicopter with the centre of gravity after the rotor hub.
What is the influence of the centre of gravity on the velocity stability derivatives and incidence stability derivative?
What is the influence of the centre of gravity on the velocity stability derivatives and incidence stability derivative?
* Changing the centre of gravity backwards will increase the amplitude of the velocity stability and incidence stability derivatives
* As the rotor provides unstable incidence stability, it would lead the vehicle more unstable
* As the rotor provides unstable incidence stability, it would lead the vehicle more unstable
50
New cards
What are the two most significant coupled control moments provided by the tail rotor?
* Sideward force
* Rolling moment
* Rolling moment
51
New cards
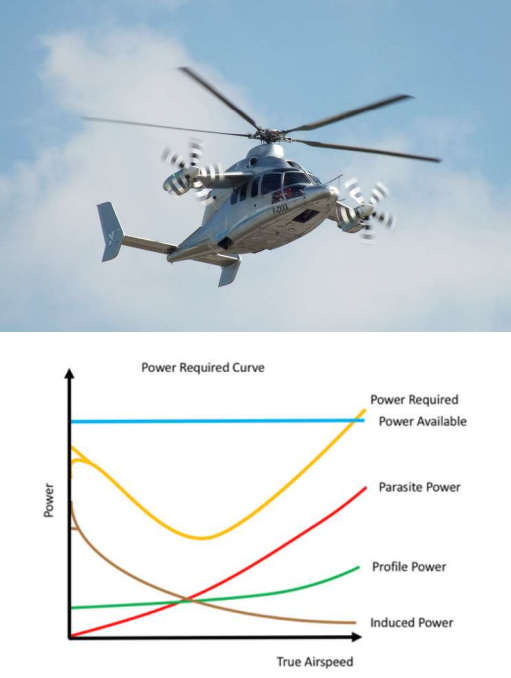
Here is the x3 rotorcraft and its power consumption figure. This helicopter can fly at a higher forward speed compared to the traditional helicopter.
Find the speed point corresponding to the maximum flight duration and maximum flight range and indicate to it on the figure.
Find the speed point corresponding to the maximum flight duration and maximum flight range and indicate to it on the figure.
max flight duration - middle of power required line
max flight range - draw a line from 0 to end of power available, where that intersects with power required is the maximum flight range
max flight range - draw a line from 0 to end of power available, where that intersects with power required is the maximum flight range
52
New cards
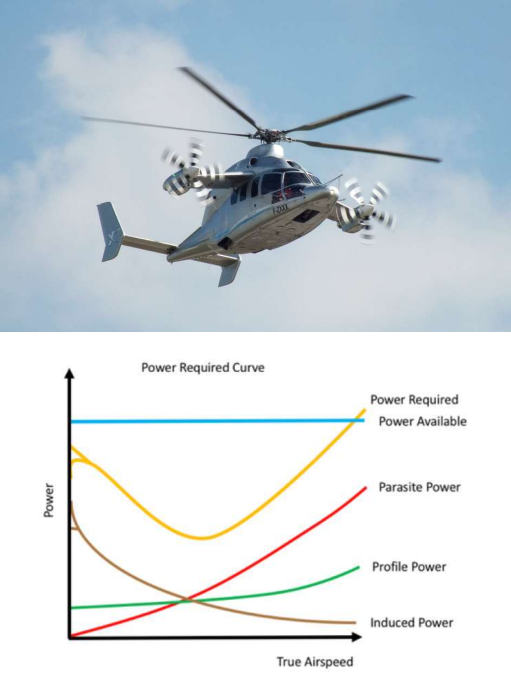
Here is the x3 rotorcraft and its power consumption figure. This helicopter can fly at a higher forward speed compared to the traditional helicopter.
Indicate the reason why this vehicle ground effect is lower than the single-rotor helicopter configuration.
Indicate the reason why this vehicle ground effect is lower than the single-rotor helicopter configuration.
* The rotor wake is affected by the wing system
* Therefore the airflow momentum that can hit the ground would be reduced
* Therefore the airflow momentum that can hit the ground would be reduced
53
New cards
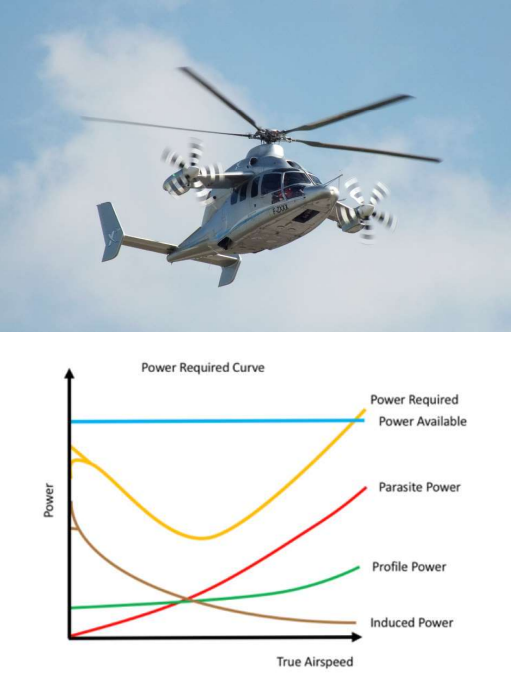
Here is the x3 rotorcraft and its power consumption figure. This helicopter can fly at a higher forward speed compared to the traditional helicopter.
What are the two main reasons related to the rotor that limits the helicopter's maximum flight speed?
What are the two main reasons related to the rotor that limits the helicopter's maximum flight speed?
* Advancing tip compressibility effect
* Stall condition in the retreating side
* Stall condition in the retreating side
54
New cards
Here is the x3 rotorcraft and its power consumption figure. This helicopter can fly at a higher forward speed compared to the traditional helicopter.
Why this helicopter can fly at a higher speed compared to the traditional single-rotor with tail rotor configuration?
Why this helicopter can fly at a higher speed compared to the traditional single-rotor with tail rotor configuration?
* The wing and propeller will offload the rotor in the high-speed flight
* Thus, the compressibility effect and the stall condition will be delayed to a higher speed range
* Thus, the compressibility effect and the stall condition will be delayed to a higher speed range
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
Foundations of govt, British history, DOI, Articles of Confederation
Updated 881d ago