Art History- High Roman Empire
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Overview—Peak of Roman Power
Rome reaches its greatest territorial extent, economic stability, and military strength.
Era of the 5 good emperors (Nerva → Trajan → Hadrian → Antonius Pius → Marcus Aurelius)
Height of imperial building projects, monumental art, and engineering.
Portraiture shifted towards intellectualism (Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius) and eventually instability.

Bust of Trajan—Rome, marble
Trajan was the first emperor of High Empire
Gains legitimacy through the military; senate give him the title of Optimus Princeps
Funded massive construction through money from Dacian wars
Seen as a model emperor of justice, discipline and military greatness
Portraits of him are clean-shaven and idealized but still realistic.
Who were the members of the Antonine Dynasty? What were their accomplishments?
Antoninus Pius: Known for peace
Marcus Aurelius: known for stability
Lucius Verus: Legal reforms
Commodus: Cultural flourishing
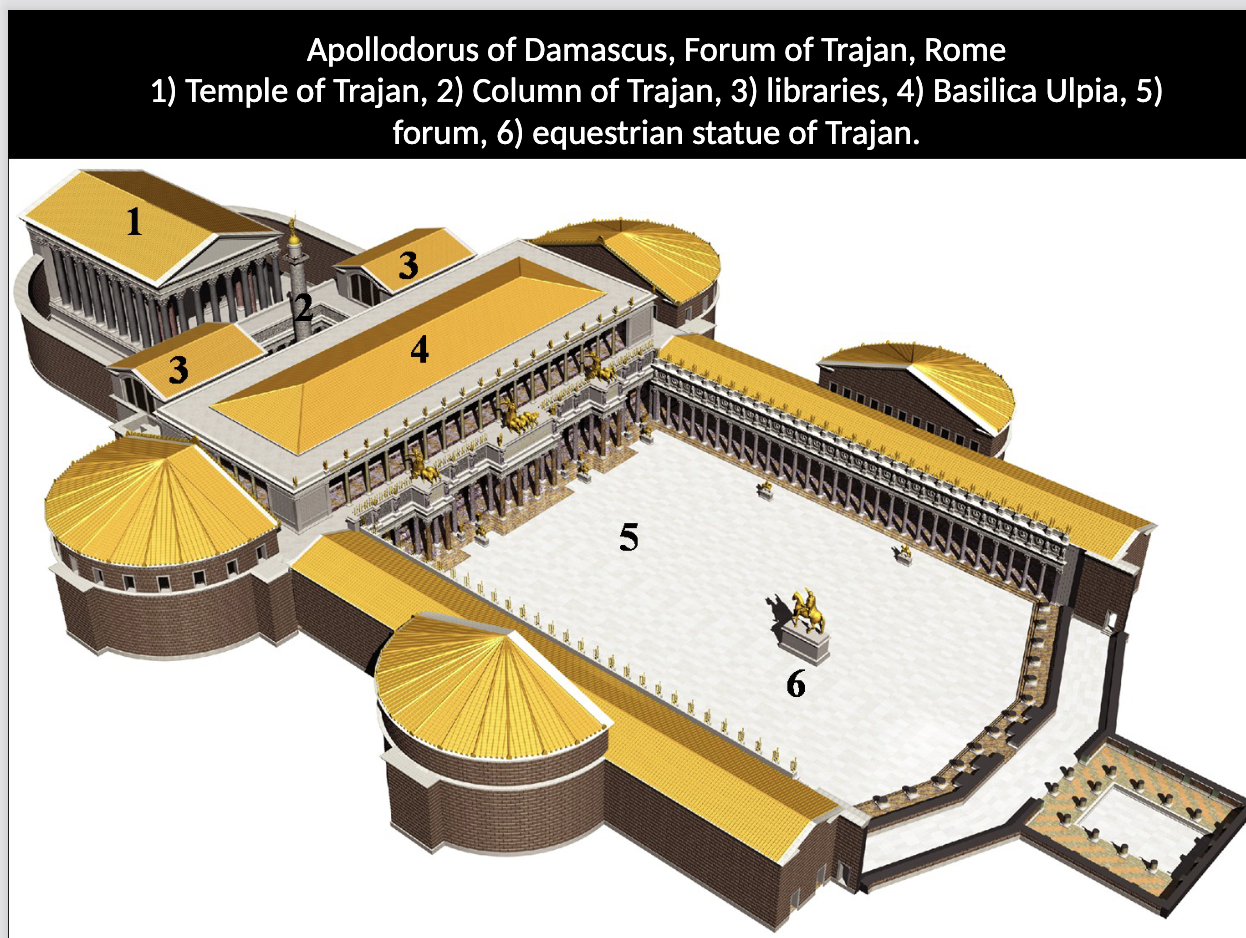
Forum of Trajan, Apollodorus of Damascus (architect)
Describe the Forum of Trajan. What buildings and monuments were included in the forum? What money was used to pay for its construction? Who was the forum’s architect?
Largest imperial forum ever built
Included: Basilica Ulpia, massive piazza, libraries, Trajan’s Column, and markets
Paid for by Dacian war money
Designed to be a political, judicial, and commercial center—imperial propaganda and civic use
Architect: Apollodorus of Damascus

Column of Trajan
Describe the Column of Trajan. What was the function of the Column of Trajan? What is depicted in its sculptural decoration?
Burial place of Trajan’s ashes
The spiral frieze depicts Dacian campaigns in great detail
shows roman energinerring, road building, diplomacy and battle
Function and imagery
Monumental propaganda
continuous narrative relief

Portrait of Hadrian
Adopted son of Trajan—through politically disputed
Has a beard, creating a new fashion look, imitates greek philiosphers
Known for travel—visited more provinces than other emperors
Promotes Greek culture

Pantheon, Rome
Built under Hadrian, NOT AGRIPPA
The interior dome symbolizes the heavens- the oculus is the eye of Jupiter
Perfect circle inside a cylinder- largest dome in history (unreinforced)
Used of coffering to reduce weight
Why was the Pantheon thought to be depicted by Agrippa? Where was the inscription?
Agrippa inscription on the front was copied earlier Pantheon.
Large bronze letters recorded Agrippa's original building
What information was included in the Severus/Caracalla inscription?
Recorded their restorations
located on the architrave
shows continuity of imperial mainteance maintenance
What types of inscription did Augustus place of buildings? Did he name himself?
often modest inscriptions
Augustus avoided overclaiming credit
Why did Hadrian place Agrippa’s name rather than his own?
Hadrian respected earlier buildings.
Reflected antiquarian, modest building ideology

Pantheon, Rome
Why was the Pantheon long thought to have been depicted by Marcus Agrippa? Where was the Agrippa inscription on the Pantheon? How large was it, and what information did it include? What was Agrippa’s association with the Pantheon?
The Agrippa inscription was reused on the front of the Pantheon.
Hadrian kept Agrippa’s name to show modesty
Severus and Caracalla inscription documents repairs
Augustus often used modest inscriptions, and Hadrian follows this tradition
Hadrian places Agrippa’s name as an ideological statement linking his rule to Rome’s past.
What was

Marcus Aurelius on Horseback- 164-166
How is Marcus Aurelius in the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius? What is the significance of his gesture? Why did this statue, standing alone out of numerous equestrian statues of roman emperors, survive?
Made of gilded bronze
gesture: saying a speech, orator pose or addressing troops
This survived because medieval people thought he was Constantine, who was the first Christian emperor. - MISIDENTIFIED
Marked by the crisis or german wars and the Antonine Plague.
Calm authority