3. Properties & pharmacology of blood vessels
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
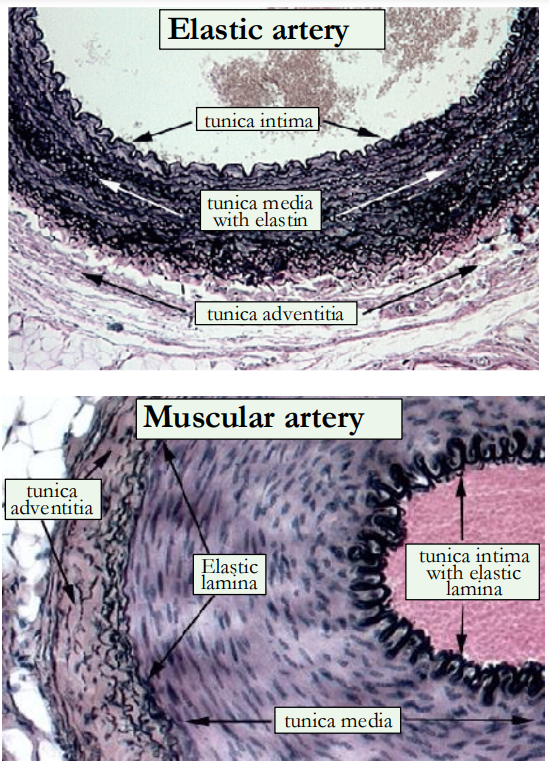
Outline the structure of elastic & muscular arteries.
tunica intima: an inner lining of endothelial cells
tunica media: larger elastic arteries have a high proportion of elastic tissue, smaller muscular arteries have more smooth muscle
tunica adventitia: collagen fibres, elastic tissue, nerves and lymphatic vessels
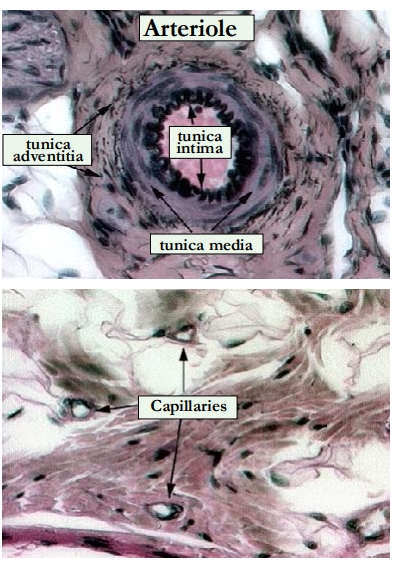
What do the elastic arteries branch into?
They branch into smaller muscular arteries then into arterioles beforve reaching capillaries which bridge the arterial & venous systems.
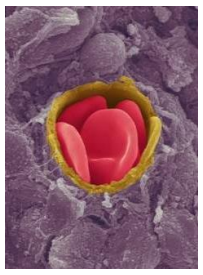
What is a continuous capillary?
simple tube of endothelial cells 8μm in diameter (red blood cell is 7.7μm).
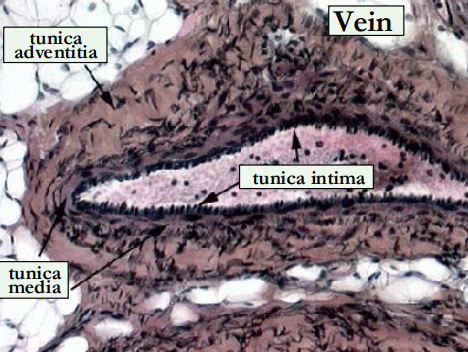
Outline the structure of the veins.
venous walls are thinner, distensible & compressible
semilunar bicuspid valves keep blood moving in right direction
What is the thoracoabdominal pump?
physiological mechanism by which respiratory movements facilitate venous return to the heart.
Inspiration - pressure in the thoracic cavity is reduced, pulling blood into the vena cava.
Exhalation - blood is forced into the right atrium
Outline what occurs when the aorta stiffens & what causes it.
Age related
Exacerbated by hypertension
Due to loss of elastin. Elastin replaced by collagen
Consequence: Increase in cardiac workload
define atherosclerosis.
Buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls
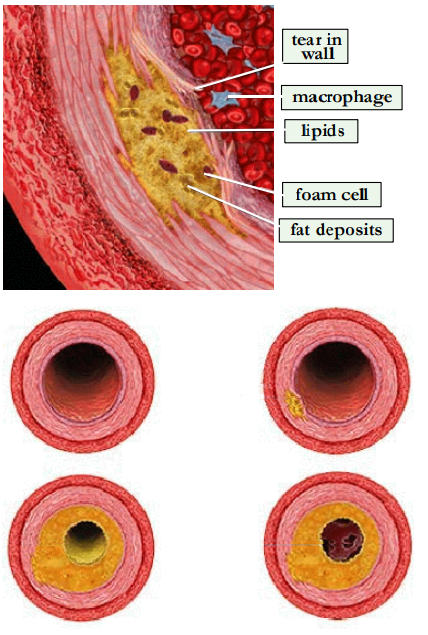
Outline how atherosclerosis occurs.
Plaque formation is initiated by endothelial damage
Platelets, macrophages and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) adhere to the endothelium
Macrophages release free radicals causing peroxidation of LDL, which is then ingested by the macrophages (foam cells)
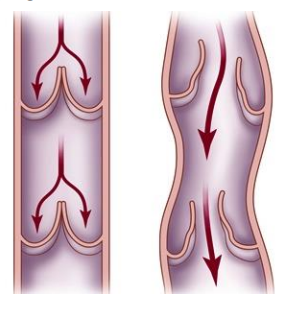
Explain varicose veins.
With age, the walls of the veins become distended (swollen) on the heart side of each valve.
This cause blood to pool instead of flow efficiently back to the heart.
Often seen in veins of the arms or legs, where blood flow opposes gravity
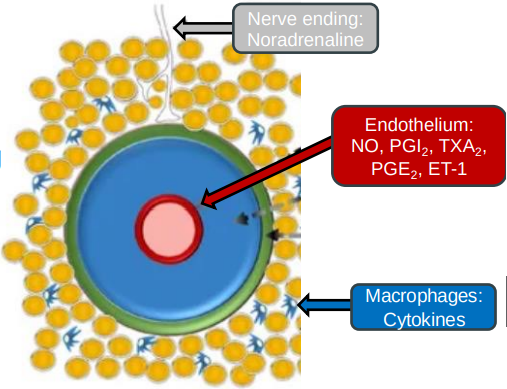
Outline how vascular tone (muscle contraction) is regulated.
Sympathetic nerves release noradrenaline, causing blood vessels to constrict and ↑ BP.
Vascular endothelium lining releases nitric oxide (NO) for vessel relaxation (dilation) & endothelin for vessel contraction.
Adrenaline (from adrenal medulla) can cause dilation or constriction, depending on the receptors it activates in blood vessels.
Renin–angiotensinaldosterone system (RAAS) releases hormones like angiotensin II which cause vessel constriction and ↑ BP.
Explain how vascular smooth muscle tone is controlled.
vascular smooth muscle contracts when the intracellular calcium concentration [Ca2+]i rises
Vasoconstrictors & vasodilators act by ↑ing or ↓ing [Ca2+]i &/or by altering the sensitivity of the contractile machinery to [Ca2+]i.
![<ul><li><p>vascular smooth muscle contracts when the intracellular calcium concentration [Ca2+]i rises</p></li><li><p>Vasoconstrictors & vasodilators act by <span>↑</span>ing or <strong>↓</strong>ing [Ca2+]i &/or by altering the sensitivity of the contractile machinery to [Ca2+]i.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e4483b45-9b27-46aa-87e7-58bc7393dc49.png)
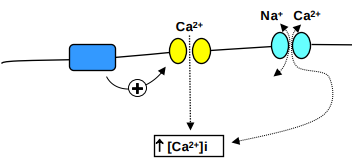
What does the regulation of [Ca2+]i depend on?
Entry/exit of Ca2+ across the plasma membrane - voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open when the cell is depolarised
second messengers produced by G-protein coupled receptors
Ca2+ exit is mediated by Na+/Ca2+-ATPase and Na+ /Ca2+ exchange
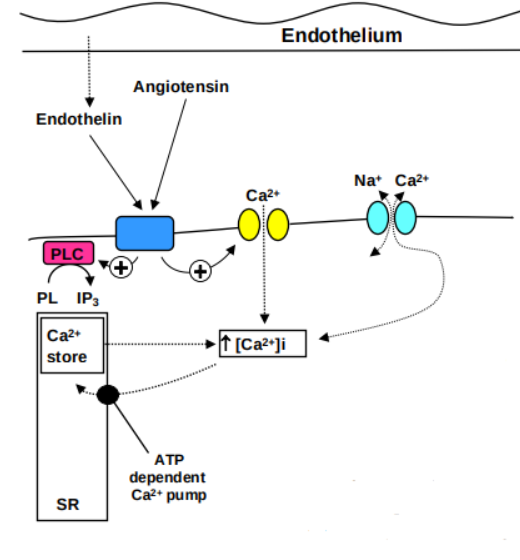
Outline how [Ca2+]i is regulated.
Intracellular Ca2+ in vascular smooth muscle is contained in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, the main storage site of releasable Ca2+
vasoconstrictors activate membrane-bound phospholipase C, which ↑ levels of IP3 .
This acts on receptors on the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release Ca2+ into the cytoplasm
Ca²⁺ is recaptured by ATP-driven active transport system
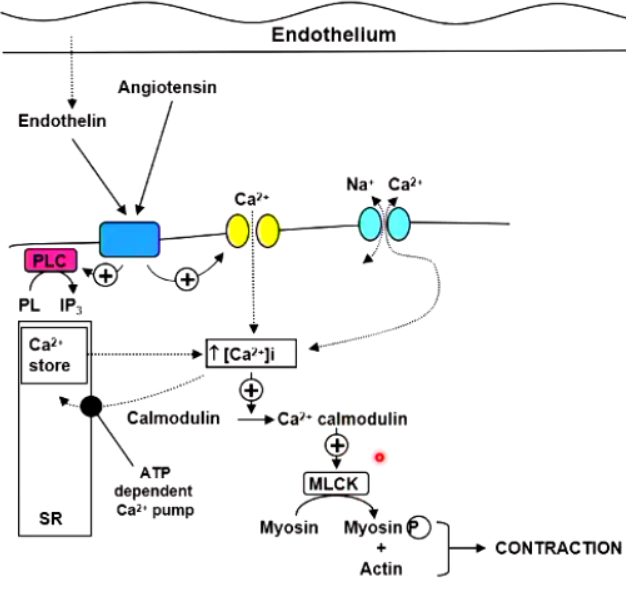
How does [Ca2+]i link smooth muscle contraction?
Ca2+-calmodulin activates myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK)
MLCK phosphorylates myosin light-chains, enabling myosin & actin to interact, initiating contraction
↓ in Ca2+ leads to dephosphorylation of myosin light-chains by myosin phosphatase (MP) leads to relaxation
Outline the mechanisms through which vasoconstrictors cause smooth muscle contraction.
Intracellular Ca²⁺ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum as a result of receptor-mediated IP₃ production.
Membrane depolarisation allowing Ca2+ entry through Ca2+ channels.
Ca2+ entry through receptor operated channels
Outline the mechanisms through which vasocodilators cause smooth muscle relaxtion.
Inhibition of Ca2+ entry through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, either directly (Ca2+ channel blockers) or indirectly by hyperpolarising membrane (K+ channel activators)
↑ of intracellular cAMP or cGMP concentrations: cAMP causes inactivation of MLCK while cGMP opposes agonist-induced increases in [Ca2+]i.
Outline the 5 clinically important vasodilator drugs.
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (e.g. captopril, enalapril)
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB) (e.g. losartan, valsartan)
Ca2+ channel blockers especially dihydropyridines (e.g. nifedipine, amlodipine)
K+ channel activators (e.g. minoxidil) relax smooth muscle by increasing membrane permeability to K+.
Nitrates (e.g. GTN) spontaneously break down under physiological conditions to Nitric Oxide (NO) to mediate relaxtion.