Metabolism, Thermoregulation, and Exercise Physiology
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
When is body weight stable?
when there is equal energy intake and output around a homeostatic set point
What is body weight determined by?
a combination of environmental and hereditary factors
30-50% of variation between individuals is due to heredity
the rest is due to eating and exercise habits
What is a calorie?
the amount of heat required to raise temperature of 1g of water 1 degree Celsius
How many kcal/g do fats contain?
9 kcal/g
How many kcal/g do carbohydrates contain?
4kcal/g
How many kcal/g do proteins contain?
4kcal/g
What are considered “empty” calories?
sugar and alcohol
few nutrients but can still produce energy
can lead to malnutrition over time
displaces foods that contain essential nutrients
Definition of nutrients
ingested chemical used for growth, repair, or maintenance
Macronutrients
consumed in large amounts
ex: proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
Micronutrients
needed in small amounts
ex: vitamins/minerals
Recommended daily allowances (RDA)
safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs
essential nutrients cannot be synthesized
minerals, vitamins, 9 amino acids, and 2- fatty acids must be consumed in the diet (based on a 2000 calorie diet)
Functions of Minerals: calcium and phosphorus
bones and teeth
Functions of Minerals: Phosphorus
phospholipids, ATP, CP, buffers, nucleic acids
Functions of Minerals: calcium, magnesium, copper, and manganese
cofactors for enzymes
Functions of Minerals: Iron
essential for hemoglobin and myoglobin
Functions of Minerals: Chlorine
component of stomach acid (HCl)
Functions of Minerals: Mineral Salts
electrolytes
govern function of nerve and muscle cells
regulate distribution of body water
What are the dietary sources of minerals?
found naturally in soil, water, and food
vegetables, legumes, milk, eggs, fish, and shellfish
animal tissues contain large amounts of salt
carnivores rarely lack salt in their diets
What is the daily recommended sodium intake vs. typical American daily intake?
Recommended = 1.1g/day
American diet = 4.5g/day
Definition of vitamins
organic micronutrients that the body needs in small amounts to regulate metabolism
Which vitamins does the body synthesize from precursors?
niacin, vitamin A, vitamin D
vitamin K, pantothenic acid, biotin, folic acid
produced by intestinal bacteria
Which vitamins are water-soluble?
Vitamins C and B
absorbed with water in the small intestine
Which vitamins are fat-soluble?
Vitamins A, D, E, and K
absorbed with dietary lipids; stored
Which 3 places in the body are carbohydrates found?
Muscle
Liver glycogen
Blood glucose
What do most carbohydrates serve as?
fuel
neurons and RBCs depend on glucose
What do sugars serve as?
structural components
examples:
nucleic acids
glycoproteins
glycolipids
ATP
What is blood glucose carefully regulated by?
insulin and glucagon
Which nutrient has the greatest RDA scoring?
carbohydrates (175g/day)
rapidly oxidized
What are dietary sources of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
glucose, galactose, and fructose
liver converts galactose and fructose to glucose
Disaccharides
table sugar (sucrose), maltose, and lactose
Polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, and cellulose
Outside of the hepatic portal system, what is the only form of glucose?
blood sugar
What is the normal range for blood sugar concentration?
70-110mg/DL
Where do nearly all dietary carbohydrates come from?
plants
What is dietary fiber?
fibrous material that resists digestion
important to the diet
includes pectin and cellulose
What is the RDA for fiber?
30g/day
What does excessive fiber intake result in?
Interference with mineral absorption-such as iron
What is pectin?
water-soluble fiber
dissolves in water to form a viscous, gel-like substance—slows down rate
decreases blood cholesterol and LDL levels by absorbing it in the intestines
What is cellulose?
water-insoluble fiber
absorbs water in intestines
softens stool
gives stool bulk
speeds transit time of stool
What % of fat is the average adult male and female?
Male: 15%
Female: 25%
What is considered the body’s stored energy?
lipids
contains 2X energy/g
compact storage
What vitamins are fat-soluble?
A, D, E, K
absorbed with dietary fat
What amount of fat-soluble vitamin ingestion would result in risk of deficiency?
less than 20g/day
What are the functions of lipids?
Structural
phospholipids and cholesterol are components of plasma membranes and myelin
Chemical Precursors
cholesterol
fatty acids
What is cholesterol a precursor of?
steroids, bile salts, and vitamin D
What are fatty acids precursors of?
prostaglandins and other eicosanoids
What is the recommended fat intake vs. the typical American’s fat intake?
Recommended = 30% of daily calorie intake
American diet = 40-50% of daily calorie intake
What are most fatty acids synthesized by?
the body
essential fatty acids must be consumed
ex) omega 3,6
What are saturated fats?
fats originating from animals
ex: meat, egg yolks, and dairy products
result in arteriole sclerosis if consumed in excess
What are unsaturated fats?
fats found in nuts, seeds, and most vegetable oils
help clean out your system
What foods include cholesterol?
egg yolks, cream, shellfish, organ meats, and other meats
What are serum lipoproteins?
Lipids transported in the blood as lipoproteins
protein and phospholipid coat around a hydrophobic cholesterol and triglyceride core
soluble in plasma; bind to cells for absorption
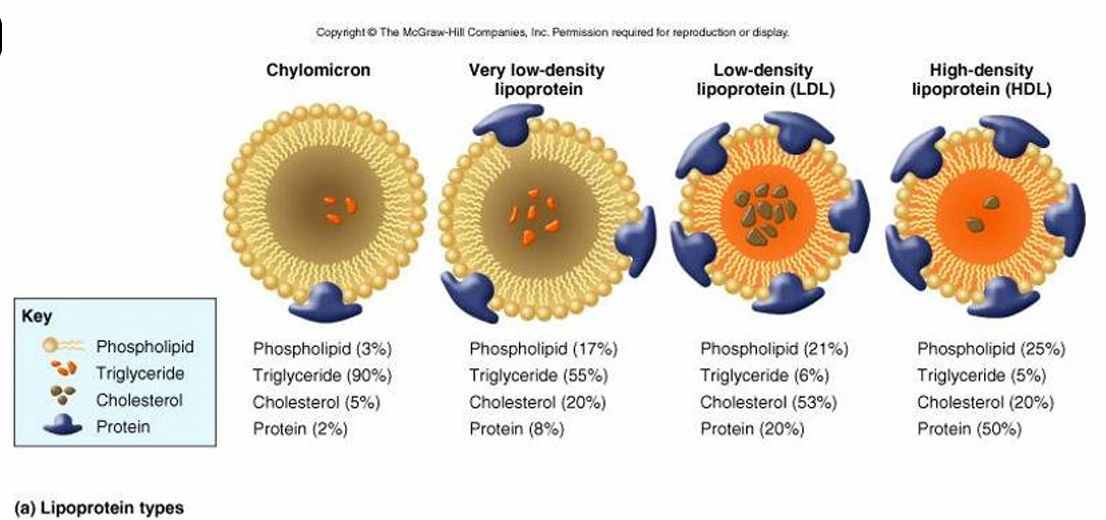
Serum lipoproteins: categorized into 4 groups by density
more protein=higher density
Chylomicrons
Very low-density (VLDLs)
Low-density (LDLs)
High-density (HDLs)
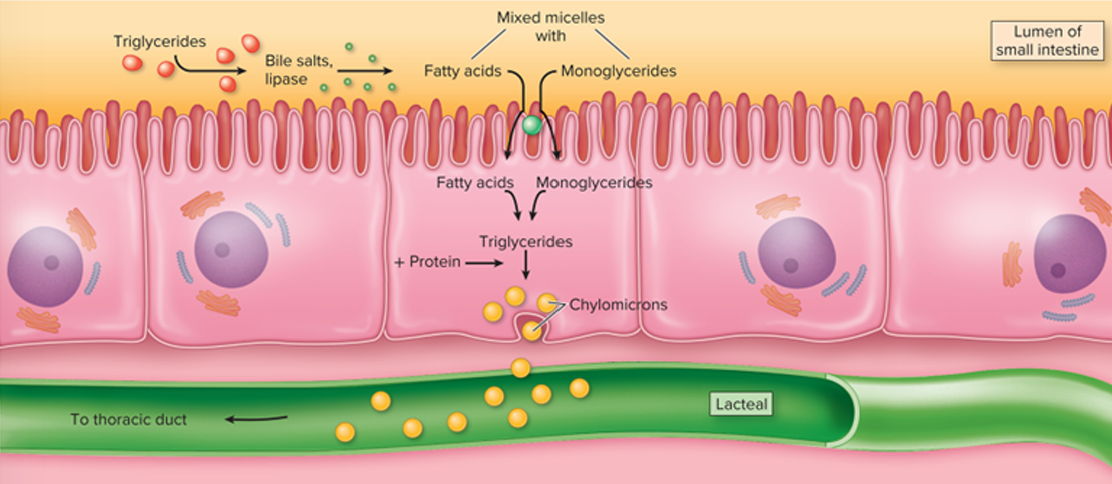
Describe how chylomicrons form
capillary endothelium has lipoprotein lipase to hydrolyze monoglycerides
resulting free fatty acids and glycerol enter fat cells to be resynthesized into triglycerides for storage
chylomicrons form in absorptive cells of the small intestine
enter the lymphatic system, then the blood
remnants of chylomicrons are degraded by the liver
What is VLDL?
Very low density lipoproteins
produced by the liver to transport lipids to adipose tissue for storage
when triglycerides are removed by lipoprotein lipase, VLDL become LDLs (mostly cholesterol)
What is LDL?
low density lipoproteins
absorbed by cells in need of cholesterol for membrane repair or steroid synthesis
What is HDL + its production and function?
High density lipoprotein
liver produces an empty protein shell
travels through the blood and picks up plaque (cholesterol)
delivers cholesterol to the liver for elimination in the bile
What is the desirable total cholesterol concentration?
< 200 mg/dL
*measurement derived from HDL levels with everything else extrapolated
What are some ways to lower blood cholesterol levels?
most cholesterol is endogenous
dietary restrictions can lower blood cholesterol levels
restriction of dietary cholesterol: lowers levels by 5%
restriction of certain saturated fats: lowers levels by 15-20%
Vigorous exercise lowers blood cholesterol
What are the desirable lipoprotein levels?
HDL: high levels
indicates cholesterol is being removed from the arteries
LDL: low levels
high LDL correlates with cholesterol deposition in arteries
Recommendations:
Ratio 2 LDL : 1 HDL
Norms 2-5: 1
exercise regularly
avoid smoking, saturated fats, coffee, and stress
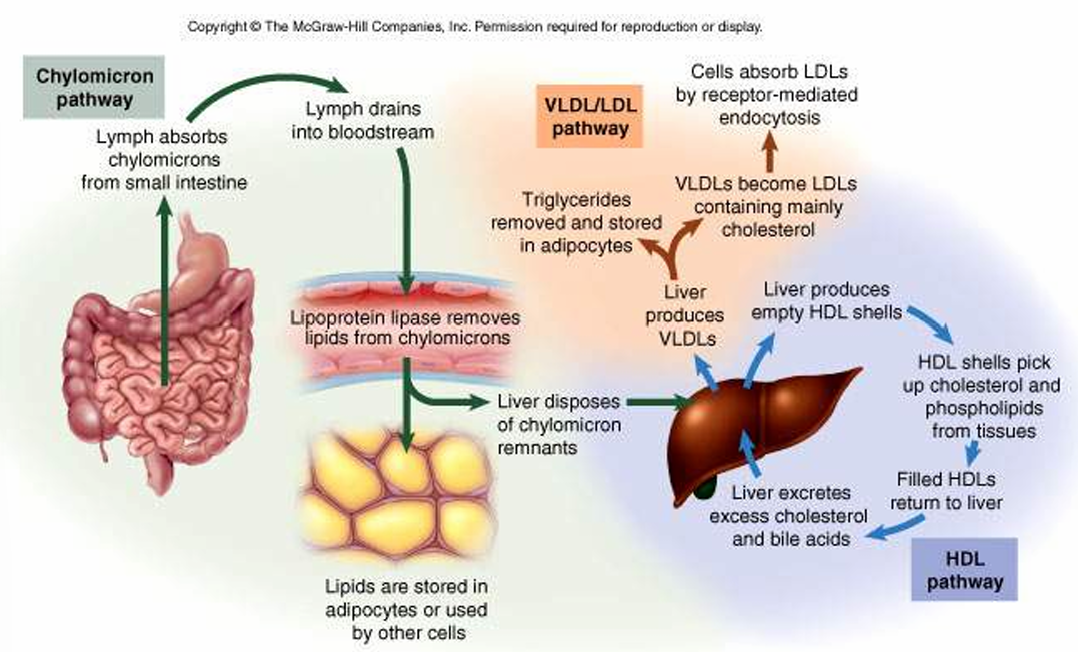
Describe the 3 pathways for lipoprotein processing
Chylomicron pathway
Lymph absorbs chylomicrons from small intestine
lymph drains into the bloodstream
lipoprotein lipase removes lipids from chylomicrons
lipids are stored in adipocytes or used by other cells OR liver disposes of chylomicron remnants
VLDL/LDL pathway
liver produces VLDLs
2. triglycerides are removed and stored in adipocytes
OR
2. VLDLs become LDLs containing mainly cholesterol
3. cells absorb LDLs by receptor-mediated endocytosis
HDL pathway
Liver produces empty HDL shells
HDL shells pick up cholesterol and phospholipids from tissues
Filled HDLs return to the liver
Liver excretes excess cholesterol and bile acids
What percentage of body mass do proteins account for?
12-15%
Which type of muscles are proteins primarily found in?
skeletal
What are the functions of proteins?
muscle contraction
movement of the body, cells, and cell structures
cell membranes (receptors, cell identity, pumps)
fibrous proteins (collagen, keratin)
structural
globular proteins
functional
plasma proteins: blood osmolarity and viscosity
What are some examples of globular proteins?
antibodies, myoglobin, enzymes
What is the RDA requirement for protein?
44-60g/day
differs for activity levels, breastfeeding, pregnancy
What does the nutritional value of proteins depend on?
proportions of amino acids
9 essential amino acids cannot be synthesized
complete proteins (dietary) require a supply of all amino acids in the right amount in order to synthesize protein
What are the 9 essential amino acids?
isoleucine
leucine
lysine
methionine
phenylalanine
threonine
tryptophan
valine
histidine
Do cells store surplus protein?
no, they break them down
protein → amino acids -→ deamination → ammonia (NH3) → urea → excreted in urine
What are the dietary sources of protein?
Animal proteins (meat, eggs, and dairy) are complete proteins
closely match human proteins in amino acid composition
Plant sources must be combined in the right proportions
beans and rice are a complementary choice
What is the nitrogen balance?
rate of nitrogen ingestion = rate of excretion
proteins are chief dietary source of nitrogen
excretion chiefly as nitrogenous wastes
What is a positive nitrogen balance?
when you ingest more than you excrete
found in children
goal with athletes
promoted by growth and sex hormones
What is a negative nitrogen balance?
body proteins are broken down for fuel (muscle atrophy)
glucocorticoids promote protein catabolism in states of stress
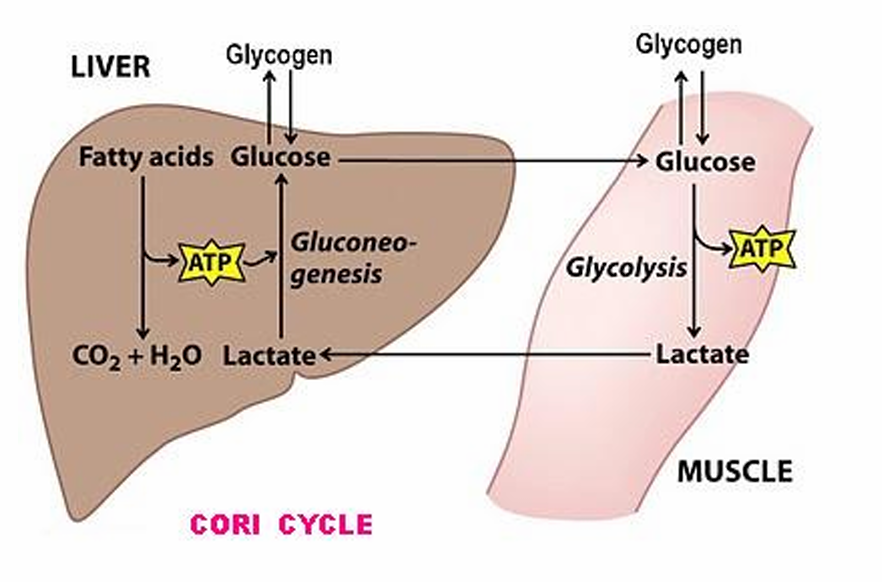
Describe the process of glucose storage and use
The Cori Cycle:
Liver:
Fatty acids → CO2 + H2O + ATP
Lactate + ATP → Glucose (through gluconeogenesis)
Glucose can be produced by/ produce glycogen outside of liver
Muscle
glucose → lactate + APT (through glycolysis)
lactate will be brought to the liver
Where are triglycerides stored?
in adipocytes
constant turnover of molecules every 3 weeks
released into the blood, transported and either oxidized or redeposited in other fat cells
What is lipogenesis?
synthesizing fat from other sources
amino acids and sugars are used to make fatty acids and glycerol
What is lipolysis?
breaking down fat for fuel
glycerol is converted to PGAL — enters glycolysis
fatty acids are broken down to 2 carbons at a time to produce acetyl-CoA (beta oxidation)
Describe the lipogenesis and lipolysis pathways
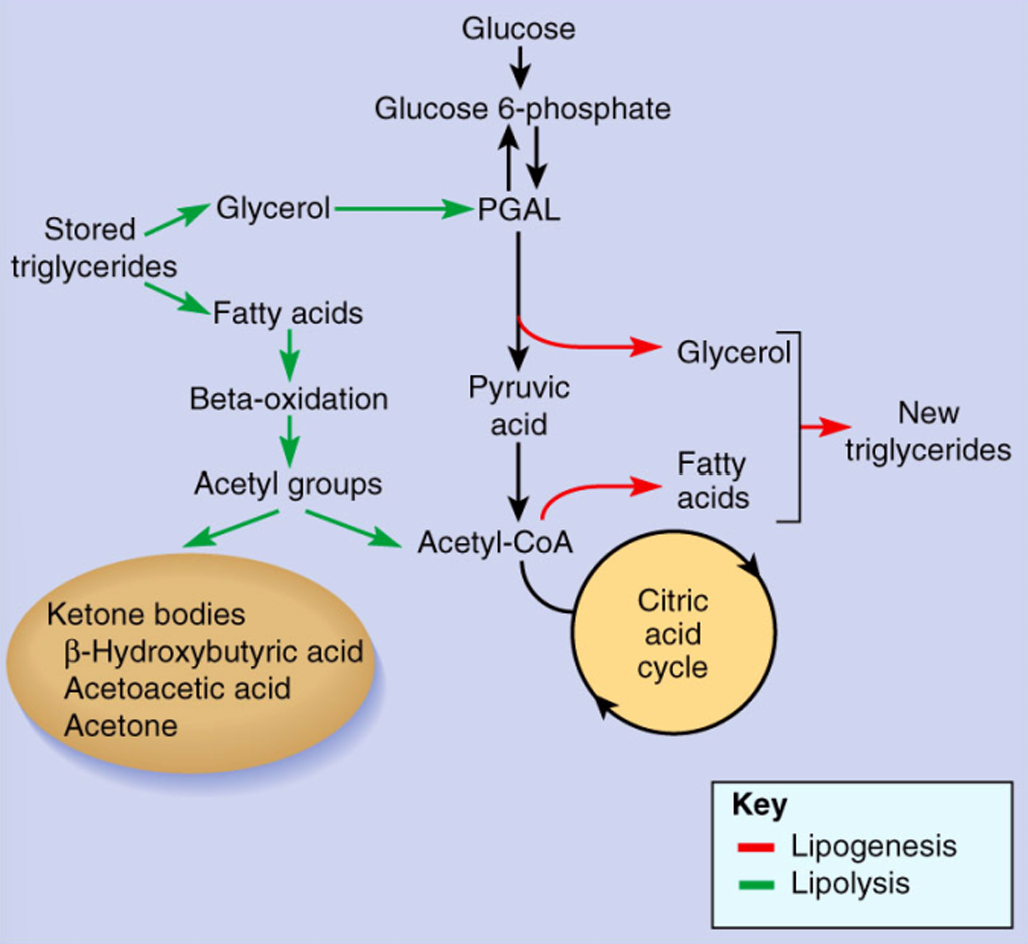
What is ketogenesis
When fatty acids are catabolized into acetyl groups (by beta-oxidation in mitochondrial matrix)
may enter citric acid cycle as acetyl-CoA and undergo ketogenesis
metabolized by liver to produce ketone bodies
What are examples of ketone bodies?
acetoacetic acid
B-hydroxybutyric acid
acetone
What could a rapid/incomplete oxidation of fats result in?
raises blood ketone levels (ketosis)
may lead to pH imbalance (ketoacidosis)
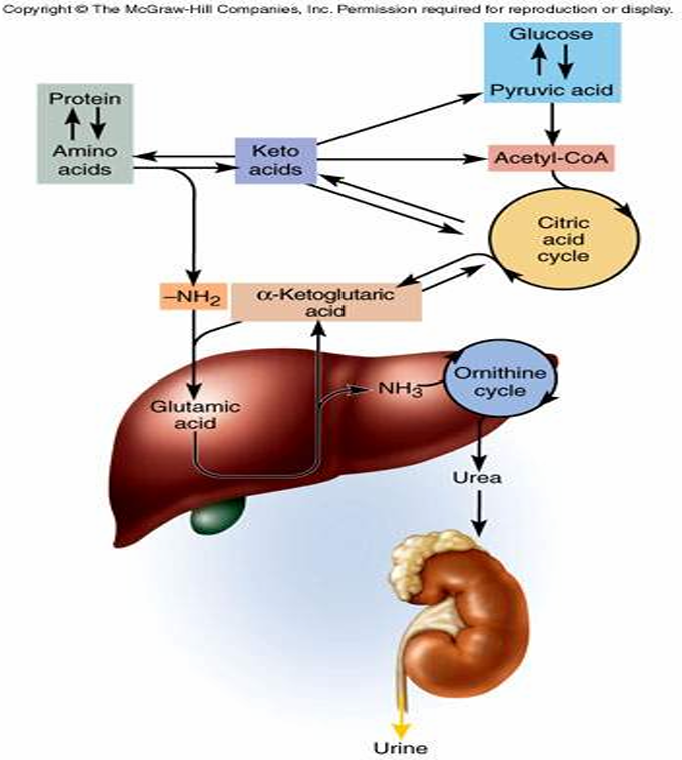
What is the amino acid pool?
dietary amino acids + 100g of tissue protein broken down each day into free amino acids
may be used to synthesize new proteins
as fuel: must be deaminated (through removal of NH2)
remains are converted to pyruvic acid, acetyl-coA, or part of the CAC
What happens during a shortage of amino acids?
NH2 becomes ammonia (NH3), which is toxic
the liver will convert the ammonia to urea, which is excreted in the urine
Pathway of amino acid metabolism
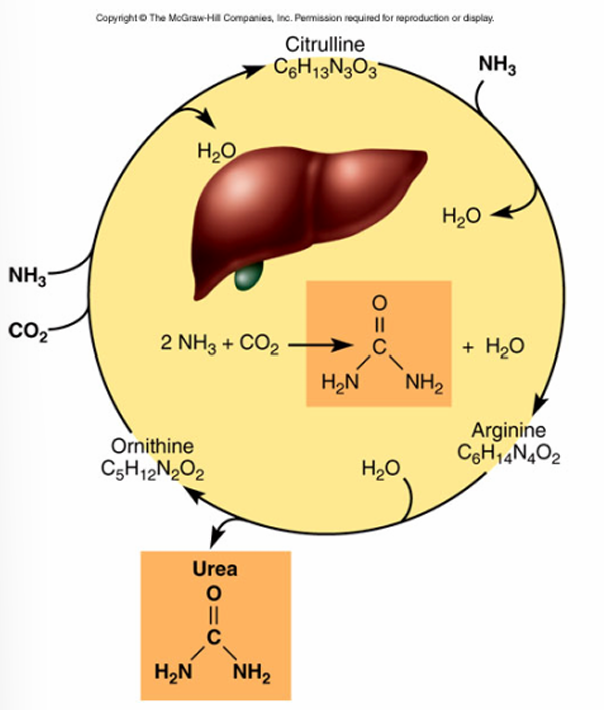
What happens in urea synthesis?
Liver converts ammonia (NH3) to urea, which is removed from the blood by the kidneys
What is the absorptive state and its effects on carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids?
The “fed” state
lasts about 4 hours during and after a meal
time of nutrient absorption and use for energy needs
Carbohydrates:
blood glucose is available to all cells for ATP synthesis
excess is converted by liver to glycogen or fat
Fats
taken up by fat cells from chylomicrons in the blood
primary energy substrate for liver, fat, and muscle cells
Amino acids
most pass through the liver and go onto other cells in liver cells
may be used for protein synthesis, fuel for ATP synthesis, or fatty acid synthesis
Absorptive state of carbohydrates
Main pathway: glycogenesis (glucose → glycogen)
Storage form/use: glycogen
Location: liver, muscle
Absorptive state of lipids
Main pathway: Lipogenesis (Fatty acids + glycerol → triglycerides)
Storage form/use: fat storage
Location: adipose tissue
Absorptive state of proteins
Main pathway: protein synthesis (amino acids → protein synthesis)
Storage form/use: new proteins
Location: all tissues
What regulates the absorptive state?
insulin
What is insulin secreted in response to?
elevated blood glucose
amino acid levels
hormones
gastrin
secretin
cholecystokinin
What does insulin cause?
increases the cellular uptake of glucose by 20-fold
stimulates glucose oxidation, glycogenesis, and lipogenesis
inhibits gluconeogenesis
stimulates active transport of amino acids into cells and promotes protein synthesis
high protein, low carbohydrate meals, stimulate release of insulin + glucagon, preventing hypoglycemia
What is the postabsorptive state and its affect on carbohydrates, fat, and protein metabolism?
The fasting state
Homeostasis of blood glucose is critical to brain
when stomach and small intestine are empty, the stored fuels are used
Carbohydrates
glucose is drawn from glycogen reserves for up to 4 hours and then synthesized from other compounds
Fat
adipocytes and liver cells convert glycerol to glucose
FFAs are oxidized by the liver to form ketone bodies
other cells use for energy, leaving glucose for the brain
Protein metabolism
used as fuel when glycogen and fat reserves depleted
wasting away occurs with cancer and other diseases from loss of appetite and altered metabolism
What regulates the postabsorptive state?
Sympathetic nervous system
as blood glucose drops 4-6 hours after meal OR during stress/exercise/anger
glucagon secreted
glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis raise glucose levels
lipolysis raises FFA levels
Adrenal Gland
enhance these effects through hormones
medulla: epinephrine and norepinephrine
cortex: cortisol
Anterior Pituitary
growth hormone: glucose sparer (save for brain)
increases lipolysis -→ releases fatty acids for energy
What is metabolic rate?
amount of energy used in the body in a given period of time (kcal/ hr or kcal/day)
measured directly in calorimeter (water bath)
measured indirectly by oxygen consumption
What is basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
the amount of energy used with relaxed, awake, fasting, room comfortable temperature
adult male BMR is 2000 kcal/day (slightly less for females)
strongly influenced by thyroid hormone
What are factors that affect total metabolic rate?
pregnancy, anxiety, fever, eating, thyroid hormones, and depression
What are the symptoms of metabolic syndrome?
3 or more of the following 5 conditions (or taking medication for that condition)
Large waistline (abdominal fat)
men > 40 inches (102cm)
women > 35 inches (88cm)
High Triglycerides
> 150 mg/dL
Low HDL Cholesterol
men < 40 mg/dL
women < 50 mg/dL
High Blood Pressure
> 130/85 mmHg
High Fasting Blood Glucose
> 100 mg/dL
What does homeostasis require?
heat loss to match heat gain
What is hypothermia?
excessively low body temperature
can slow metabolic activity and cause death
What is hyperthermia?
excessively high body temperature
can disrupt enzymatic activity and metabolic activity and cause death
What is thermoregulation?
the ability to balance heat production and heat loss