Unemployment
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the effects of unemployment on firms?
reduced demand
easier to recruit workers
decreased productivity
What are the effects of unemployment on the government?
higher taxpayer costs
decreased VAT
higher benefit costs
What are the effects of unemployment on individuals and communities?
higher crime and violence
decreased standard of living
increased leisure time
What are the effects of unemployment on the economy as a whole?
lower GDP
negative output gap
negative multiplier effect
What counts as long term unemployed?
Those who are out of work but actively seeking it for over a year.
What us hysteresis?
A lagging effect
What is labour market hysteresis?
When the long term unemployed may give up searching for a job and completely withdraw from the labour force.
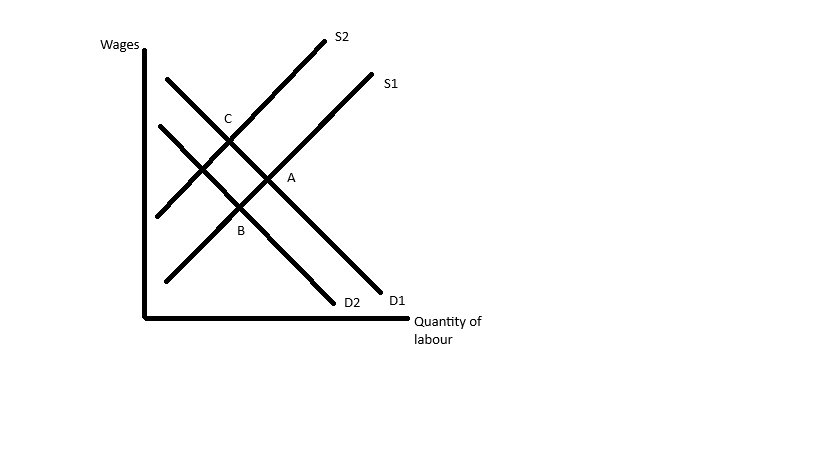
Diagram for labour market hysteresis
Point A- the economy is in equilibrium at full employment
Point B- a recession has caused demand to fall
Point C- fall in demand may lead to a permanent fall in supply
What us frictional unemployment?
Individuals moving between jobs
What is regional unemployment?
When certain areas are heavily reliant upon particular firms and industries and that firm closes this can create a particular regional problem.
What is voluntary unemployment?
Some people register as unemployed and do not want to work at the current wage rate.
What is technological unemployment?
When improvements in technology reduce the demand for labour.
What is real wage/cyclical unemployment?
Created by imposing a minimum wage which creates an excess supply of labour.
What is seasonal unemployment?
Some jobs are dependent upon the weather and the seasons.
What is demand deficient/cyclical unemployment?
When the actual level of GDP is below the full unemployment level of GDP, usually during a recession.
What is structural unemployment?
Results from a change in the industrial structure of the economy, the decline of one and the eventual rise of another due to changes in demand etc.
What policies can be used to reduce frictional unemployment?
Supply-side policies are used:
reduce benefits, creating an incentive to work faster
improve spending on job search services
What policies can be used to reduce seasonal unemployment?
Improve training and education for people in those specific industries
What policies can be used to reduce structural unemployment?
Retraining, subsidised training schemes, government provision of training schemes.
What policies can be used to reduce regional unemployment?
Subsidies for firms to encourage relocation to depressed areas
subsidise training schemes for unemployed workers in depressed areas
housing grants, low cost loans to help workers relocate
What policies can be used to reduce technological unemployment?
Improve education provision to increase skills
training schemes for those who have lost jobs to tech
Why might technological unemployment be a myth?
Jobs which require more compassion, creativity or social intelligence more likely to continue being run by humans
better education/training means lower chances of being unemployed
‘compensation effect’ often tech creates jobs
What policies can be used to reduce voluntary unemployment?
Carrots:
higher minimum wages
in work benefits/tax credits
Sticks:
reduce welfare benefits
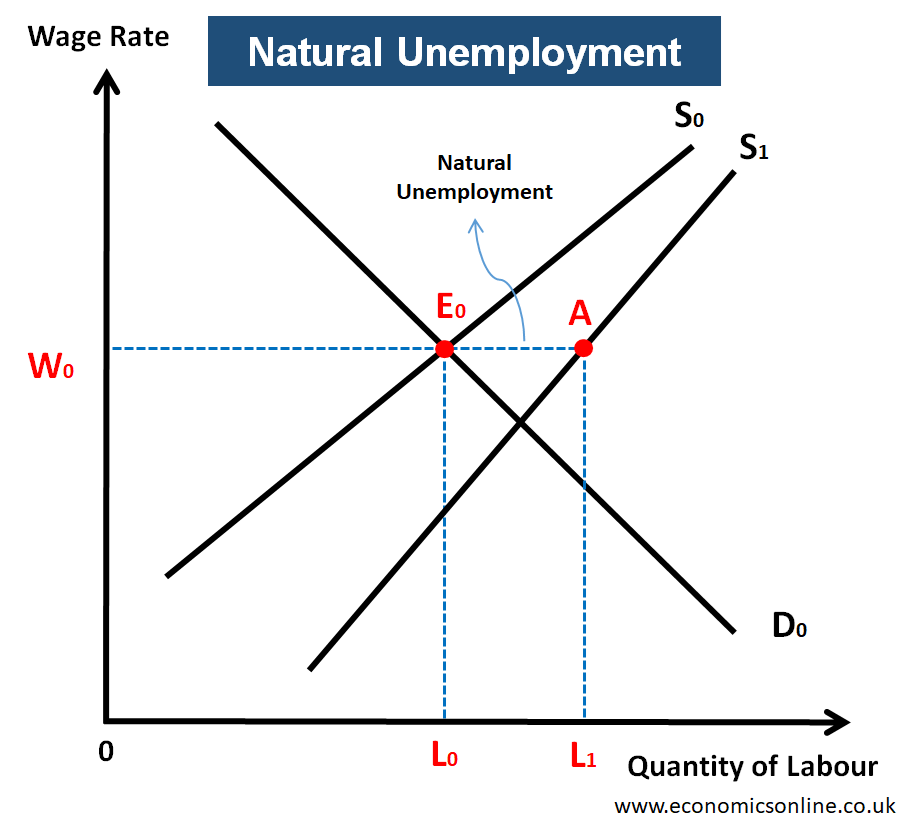
Diagram for the natural rate of unemployment
There is a difference between the registered labour force (A) and the actual supply of labour (E).
What policies can be used
What policies can be used to reduce demand deficient unemployment?
higher gov spending and lower taxes
reduction in interest rates
Why might uncertainty be a limitation to policy solutions?
knowledge of the multiplier is based on past data
the level of AD at full employment is just an estimate
What is crowding out?
Gov increases AD using expansionary fiscal policy
may experience a budget deficit
will then borrow money so interest rates will rise to convince the private sector to take on debt
will reduce C and I.
Why might crowding out be a limitation to policy solution?
Government spending will now be a larger proportion of AS which is not as efficient as private sector spending due to lack of a profit incentive.
Why might debt be a limitation to policy solutions?
In the future the gov will have higher interest payments so therefore there is an opportunity cost.