A&P of the Ear
1/28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
external ear
Composed of Auricle and External Auditory Meatus; the visible part of the ear that collects and directs sound waves towards the middle ear.
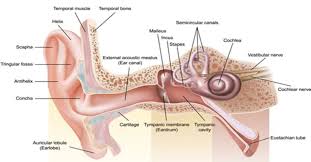
auricle
the visible outer part of the ear primarily made of cartilage and covered ins kin, including the earlobe.
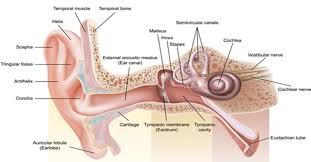
external auditory meatus
a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear
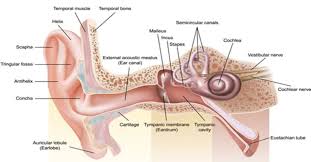
middle ear
composed of auditory tube and tympanic membrane; air-filled cavity located between the eardrum and the inner ear, has ossicles that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
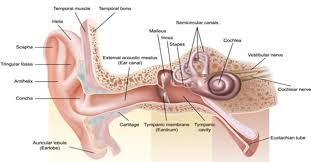
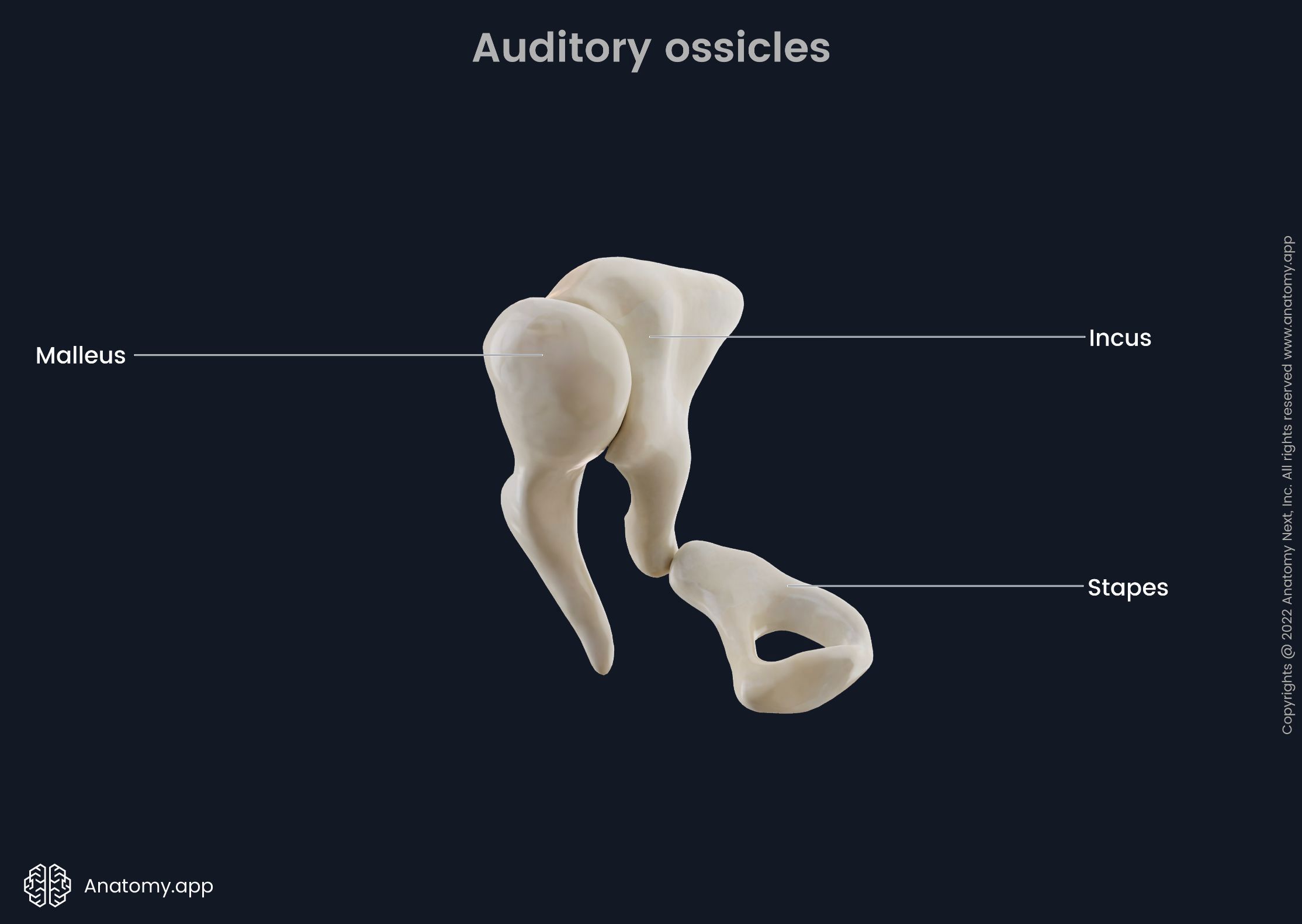
ossicles
composed of Malleus, incus and stapes; three irregular bones in the middle ear that move sound vibrations from eardrum to cochlea
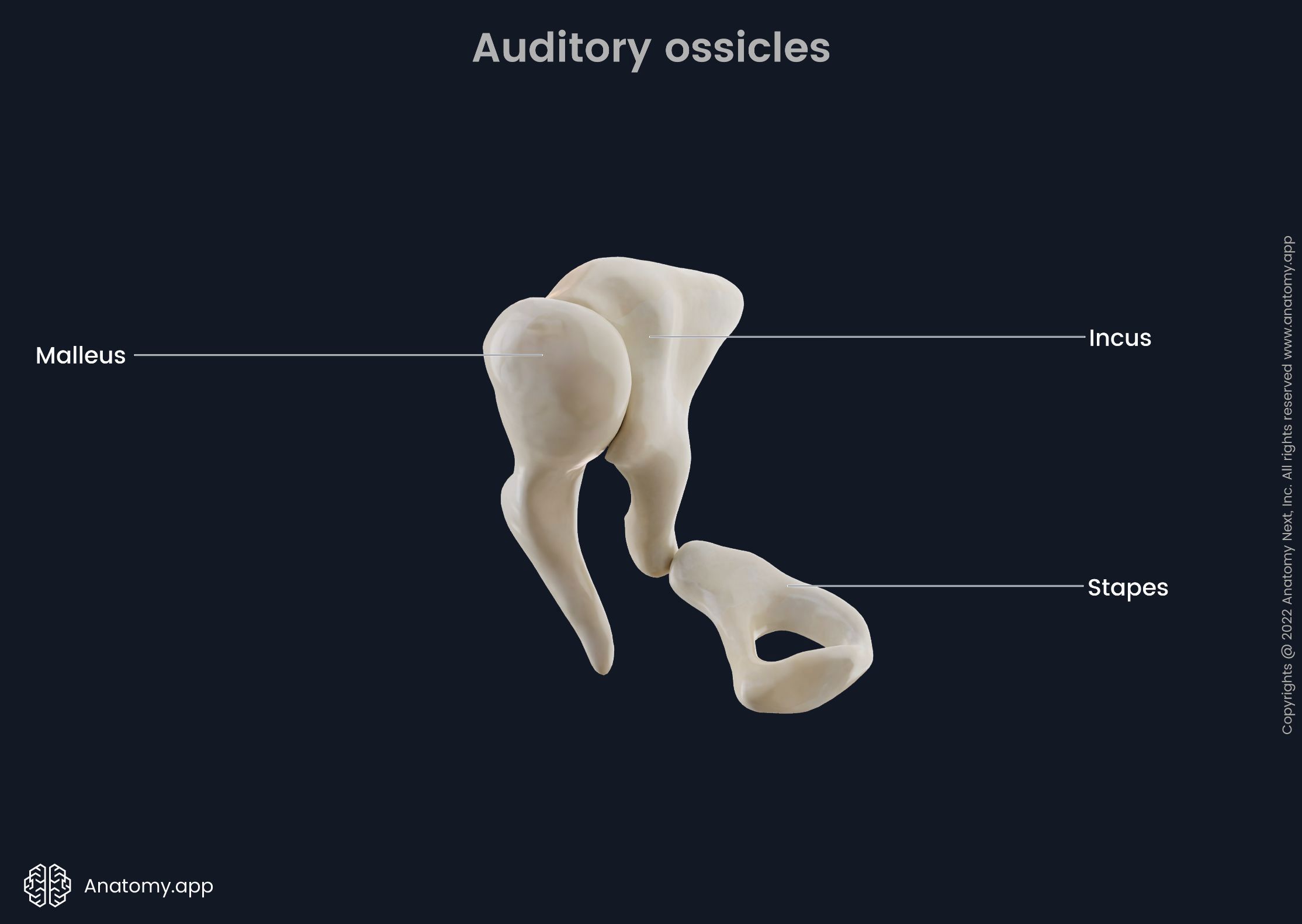
stapes
a small stirrup-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations from the incus to the inner ear; third in the order of the ossicles (M.I.S)
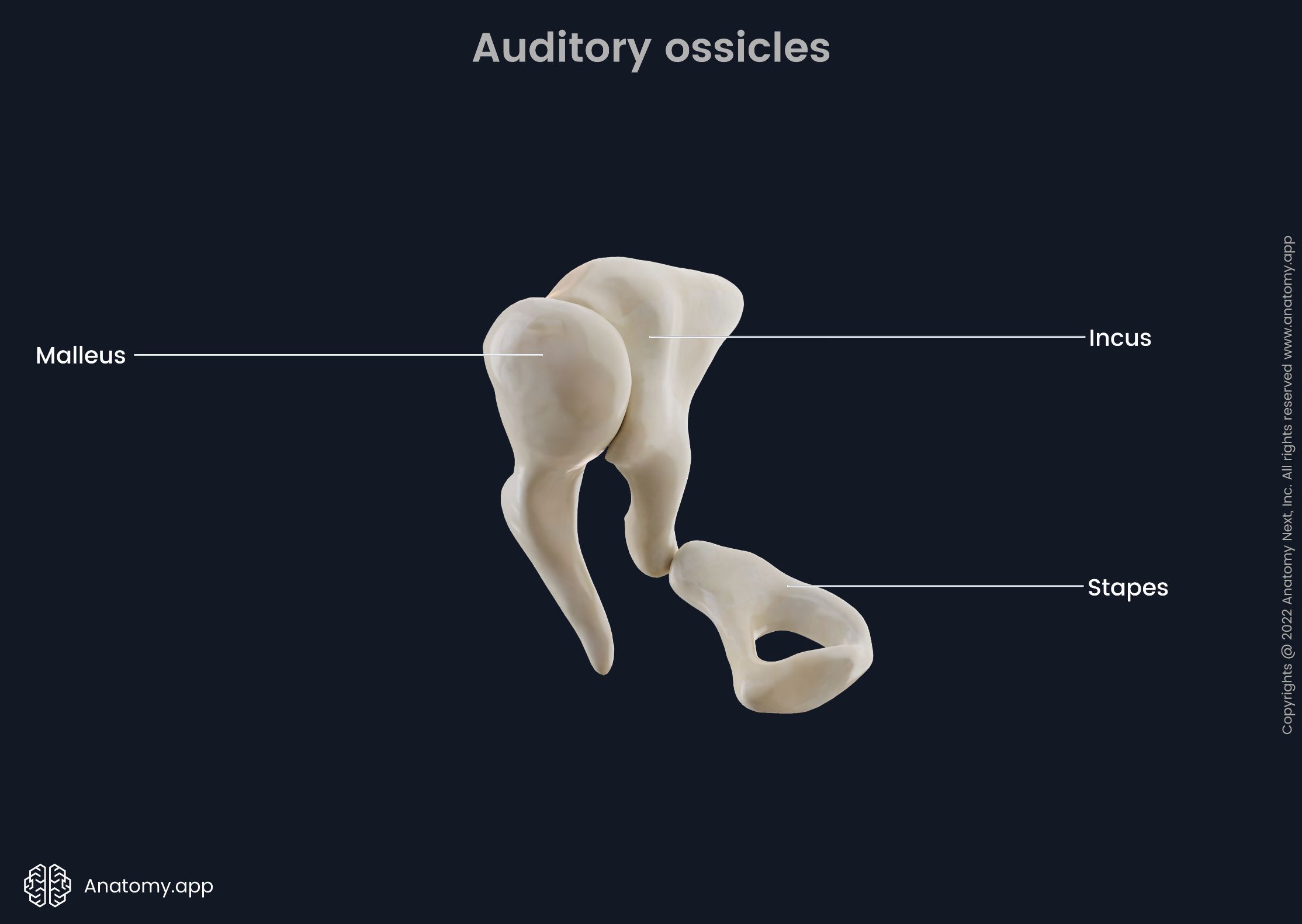
incus
anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear that transmits sound vibrations to the inner ear; second in the order of the ossicles (M.I.S.)
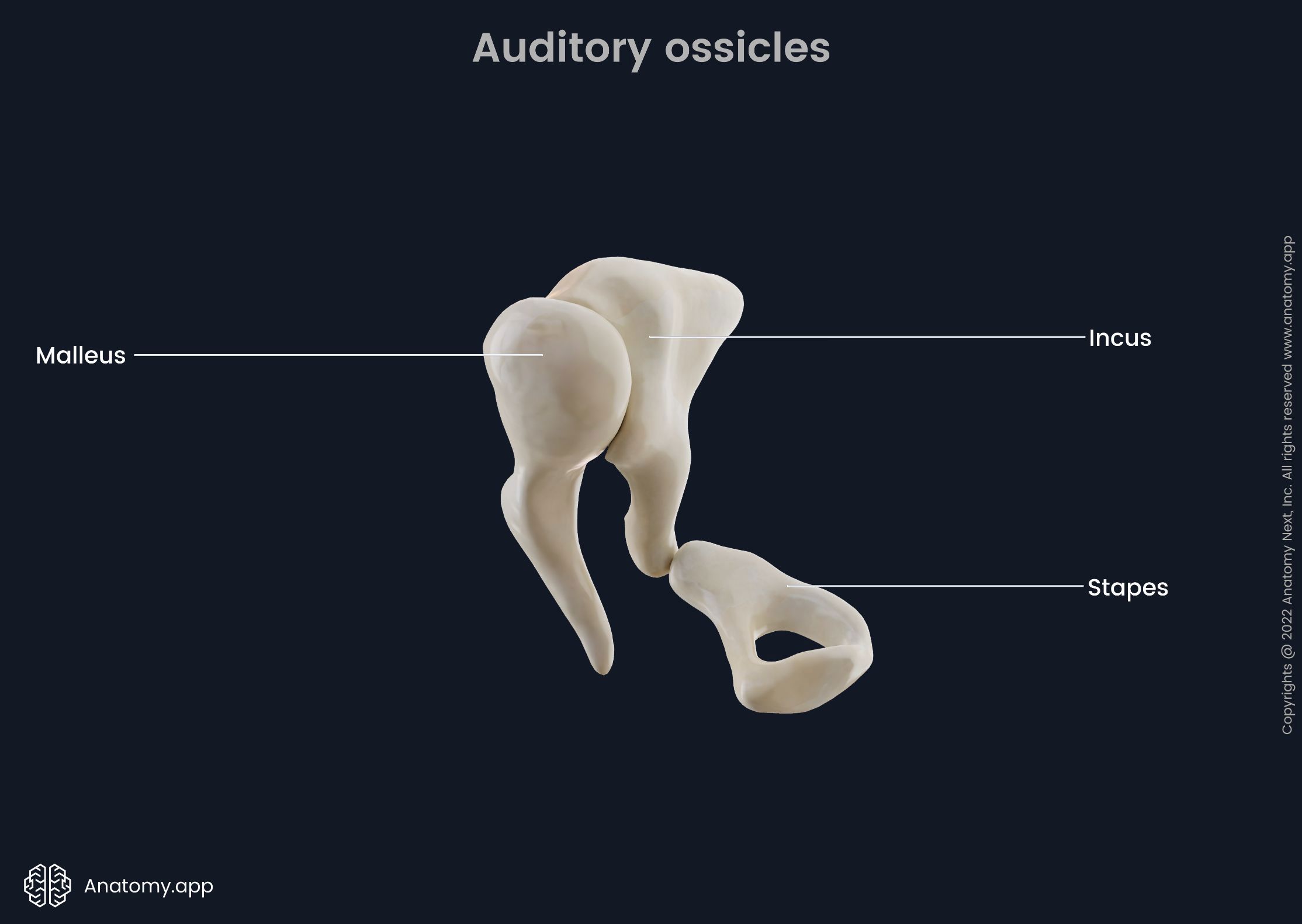
malleus
a small bone in the middle ear which transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus; hammer shaped; first in the order of the three ossicles (m.i.s)
inner ear
composed of oval and round windows; innermost part of the hearing system and home to the vestibular system as well as the cochlea.
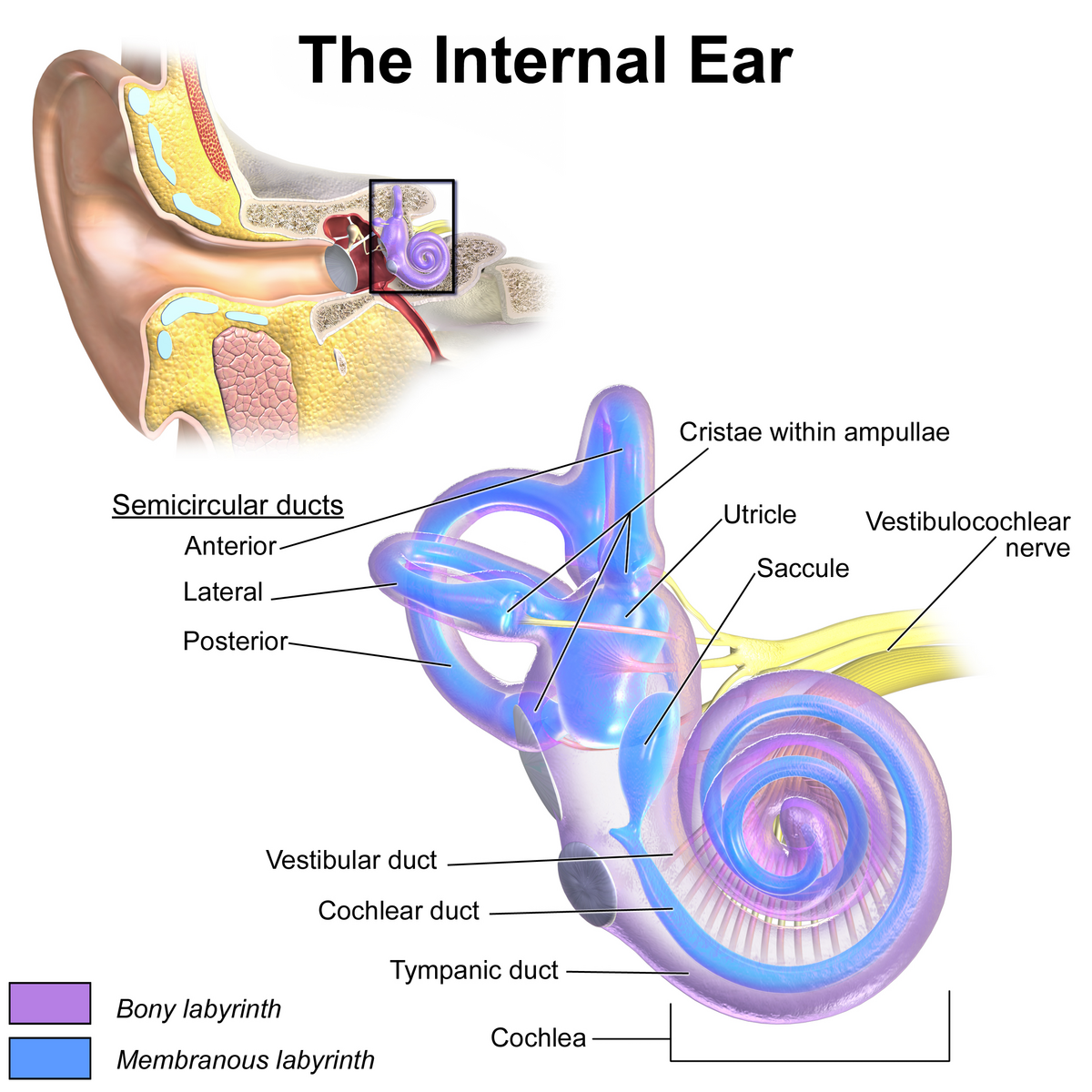
vestibule
the central egg-shaped cavity of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, located between the cochlea and semicircular canals; two fluid-filled sacs (utricle and saccule) which are crucial components dealing with equilibrium/balance.
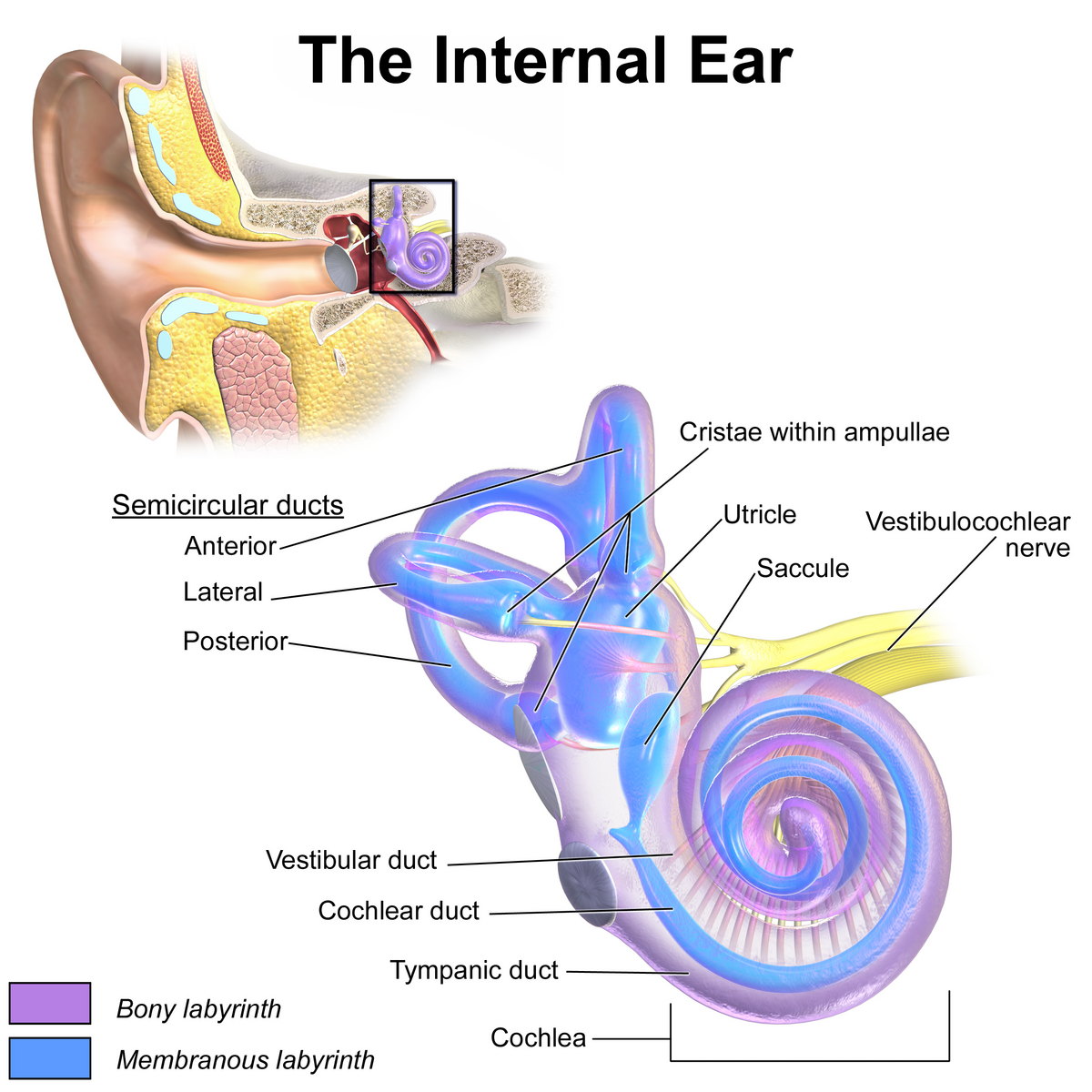
utricle
a small, oval-shaped sensory organ located in the inner ear, specifically in the vestibule; filled with fluid and contains a specialized sensory epithelium (macula — has hair cells that are sensitive to linear acceleration and head tilt); superior to saccule.
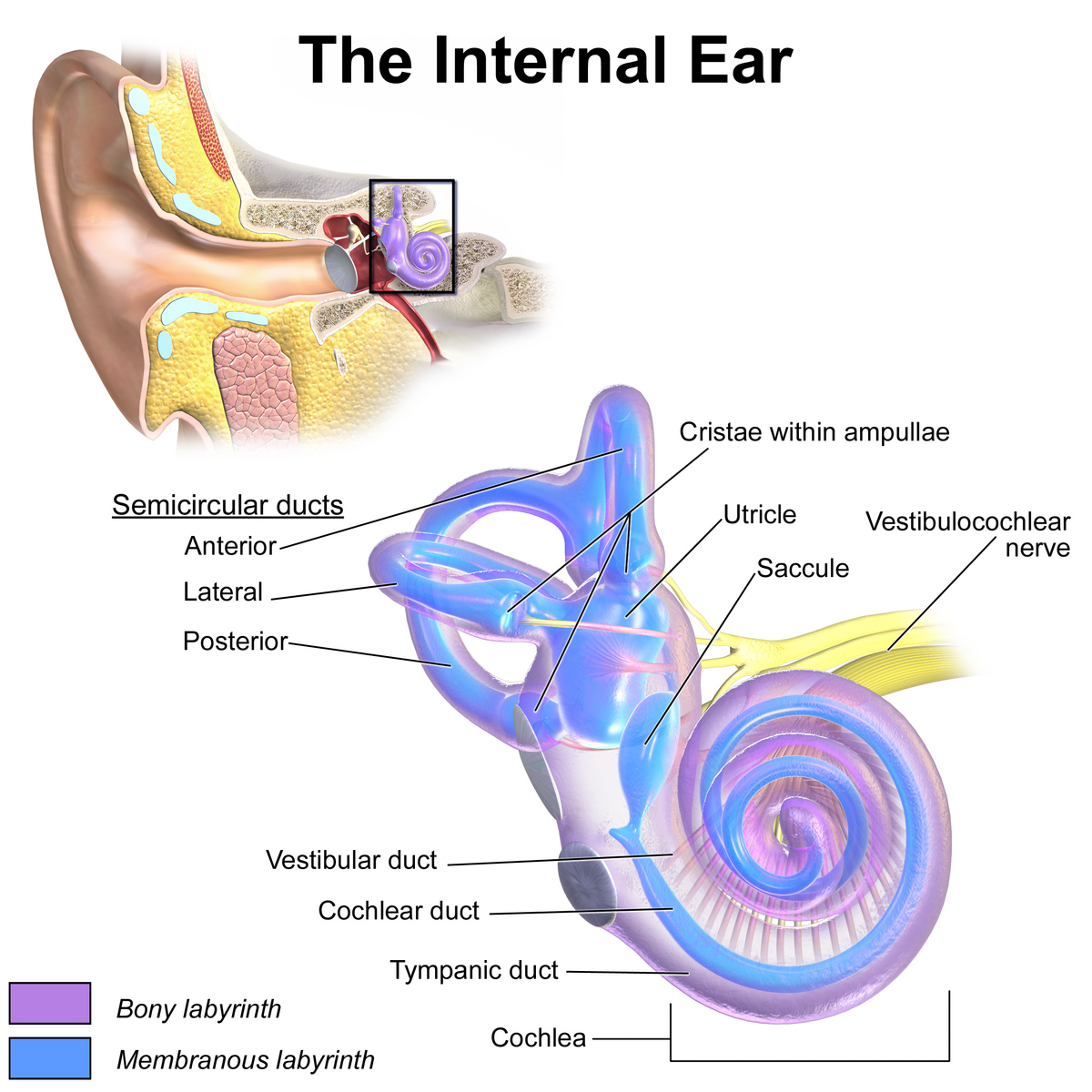
saccule
a small membranous sac, paired with utricle, within the vestibule of the inner ear; part of the membranous labyrinth and plays an important role in vertical tilt; inferior to semicircular canals and utricle.
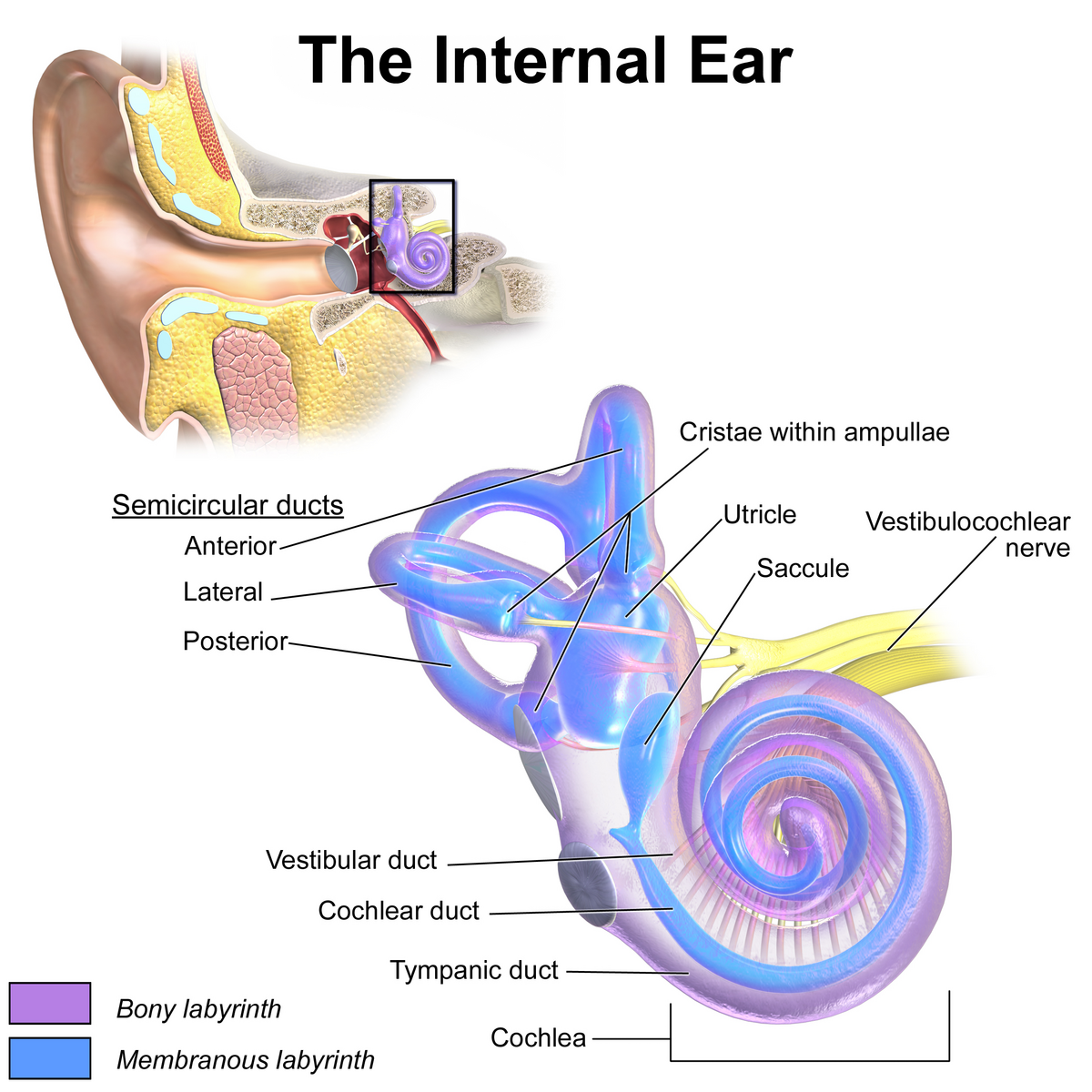
semicircular canals
three fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that, along with the saccule and utricle, form part of the vestibular system; detect rotational movements of the head (nodding/shaking)
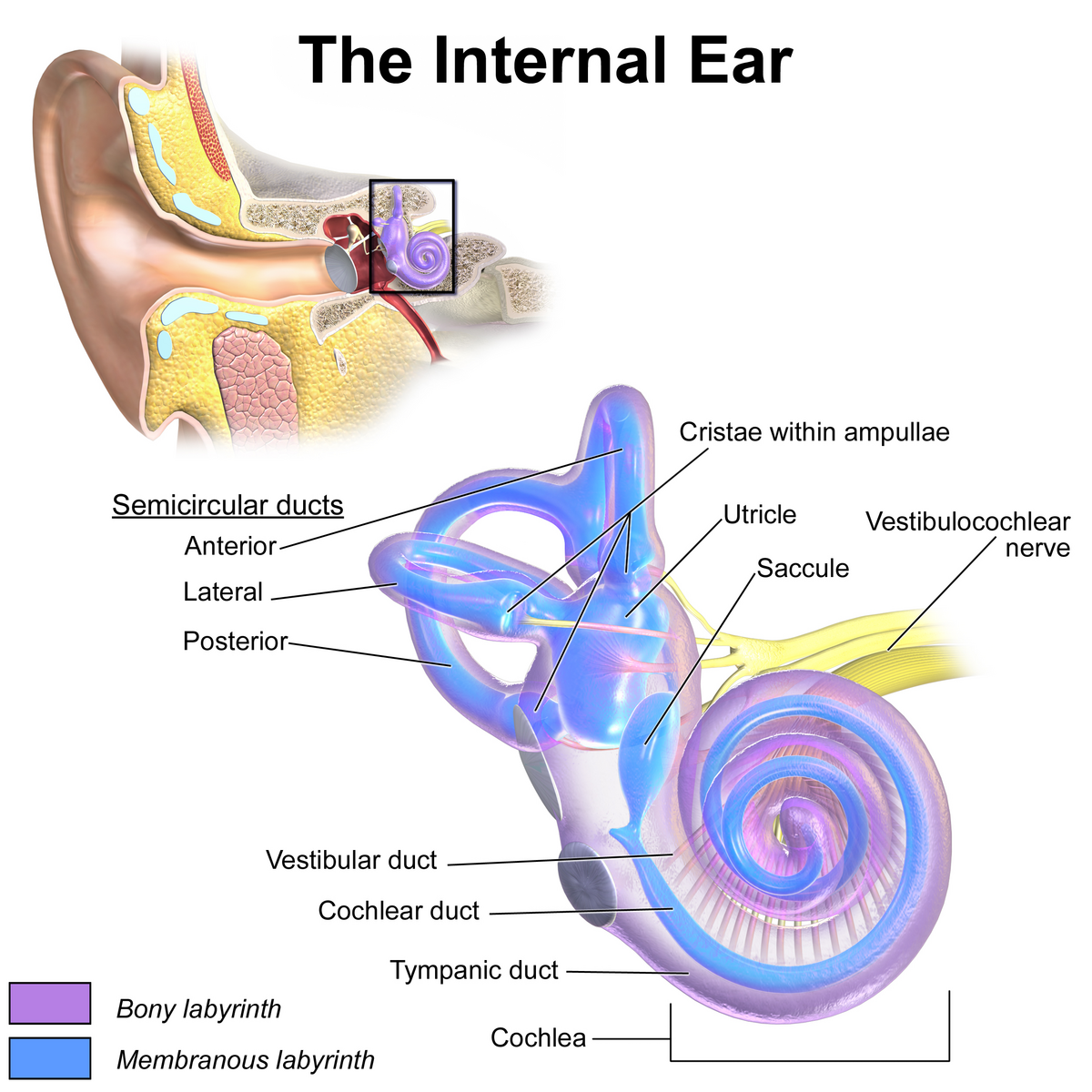
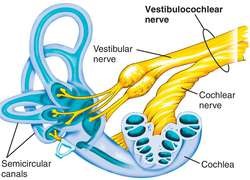
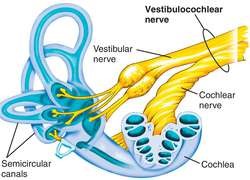
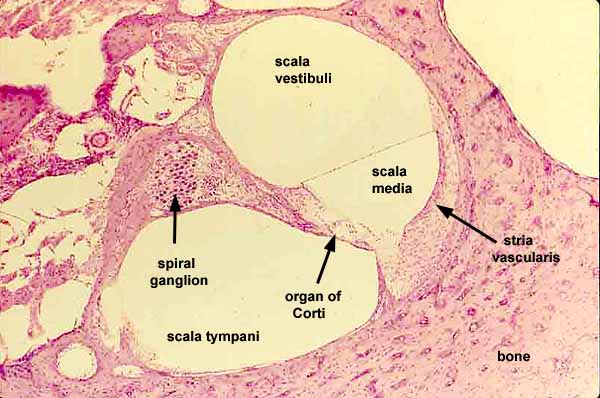
cochlea
spiral cavity of the inner ear containing the organ of corti, involved in hearing
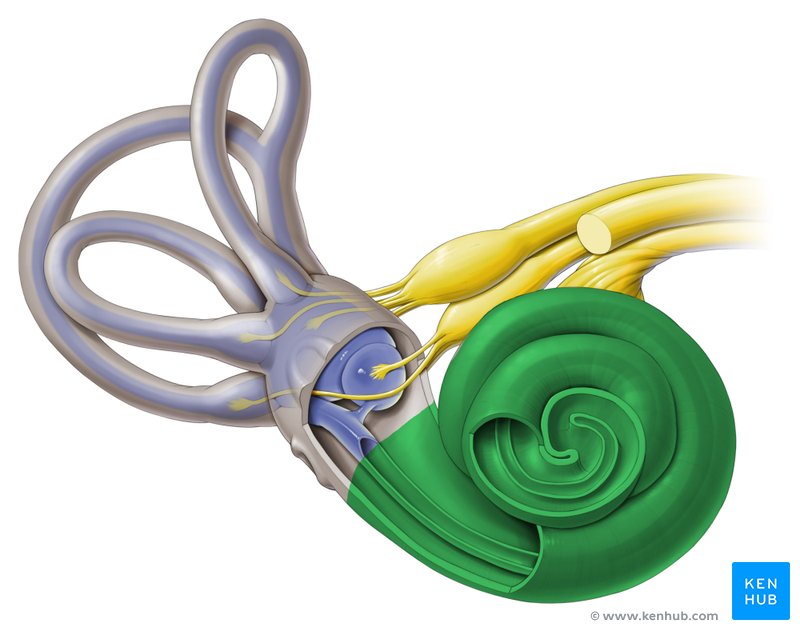
vestibulocochlear nerve
CN VIII, conveys sensory impulses from the organs of hearing and balance in the inner ear to the brain; composed of two branches — vestibular and cochlear
internal cochlear structures
vestibular duct, cochlear duct, tympanic duct, organ of corti, basilar membrane, tectorial membrane, hair cells, cochlear nerve and spiral ganglion cells;
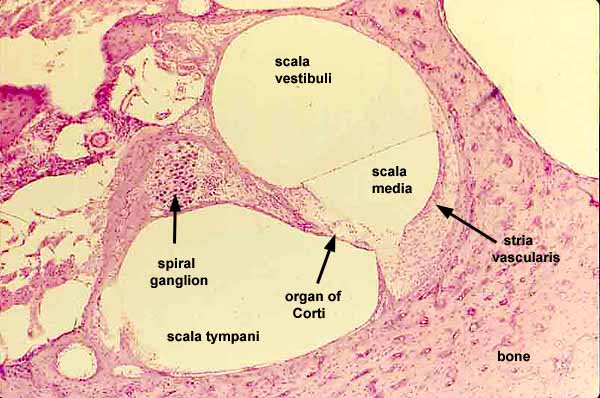
vestibular duct
part of the cochlea that conducts sound; filled with perilymph; referred to as the Scala vestibuli
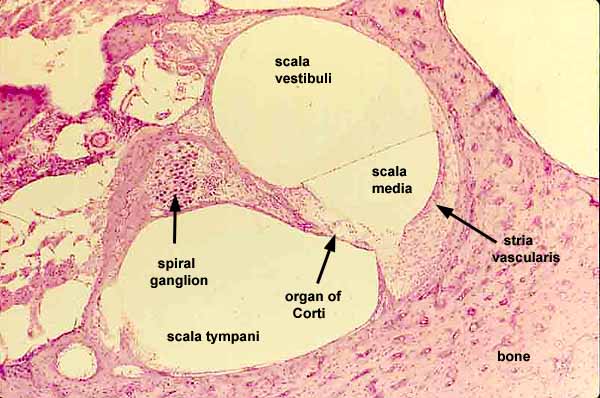
cochlear duct
contains the organ of corti and hearing sensory receptors; between the vestibular and tympanic ducts separated by Reissner’s membrane and basilar membrane; referred to as the Scala media and contains endolymph
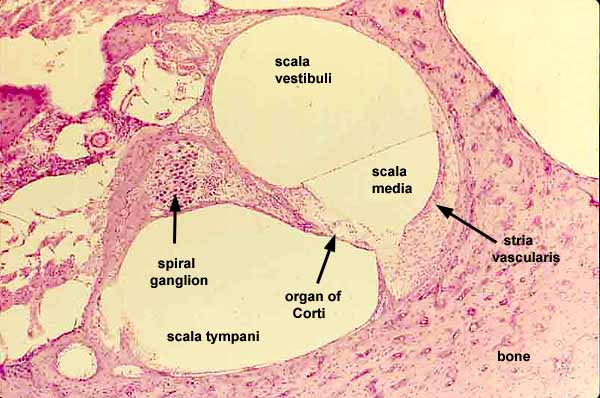
tympanic duct
located beneath the organ of corti and filled with perilymph; receives vibrations from the oval window and transmits them via the basilar membrane to the organ of corti where they are converted into neural signals that the brain interprets as sound; referred to as the Scala tympani
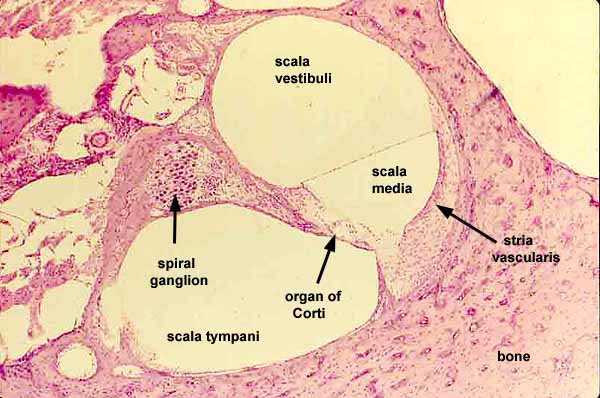
organ of corti
a structure in the cochlea of the inner ear which produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations; composed of hair cells, nerve fibers, and supporting structures
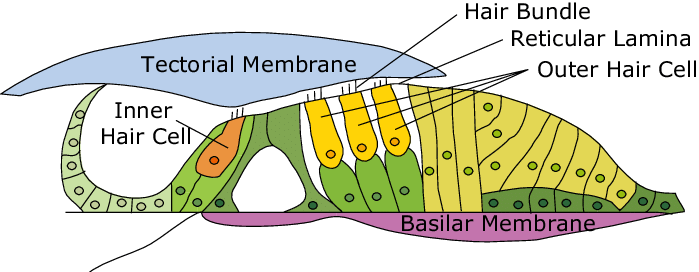
basilar membrane
a flexible membrane in the inner ear’s cochlea that vibrates in response to sound waves, acting as a frequency analyzer to separate different sound frequencies; supports organ of corti.
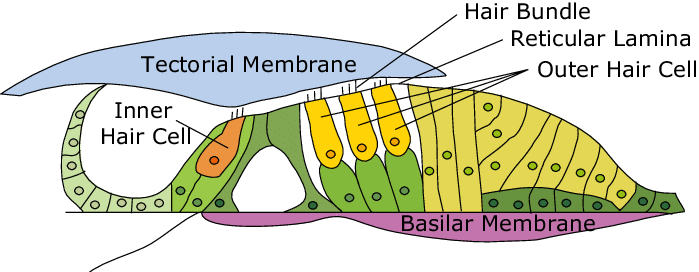
tectorial membrane
a gelatinous, protein-rich extra cellular matrix that sits over the organ of corti and is essential fro auditory processing and hearing
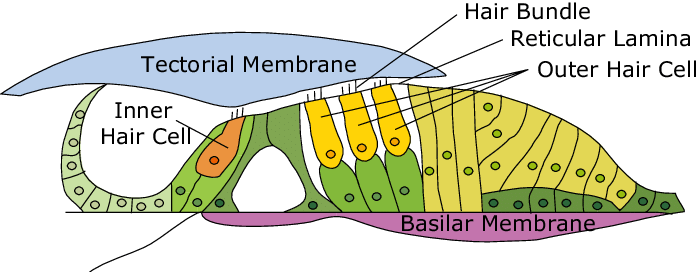
hair cells
sensory receptors for hearing, converting sound vibrations into electrochemical signals that the brain interprets as sound; have hairlike structures that bend due to sound waves; inner and outer components
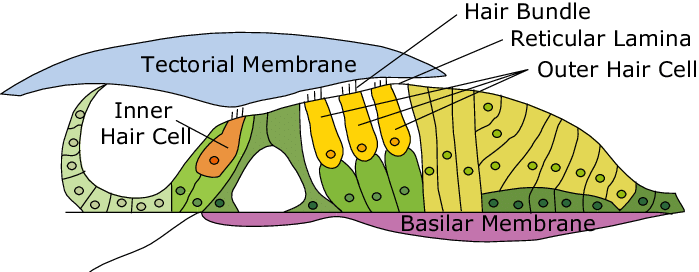
cochlear nerve
½ of CN VIII, a sensory nerve that plays a crucial role in hearing, connected to the cochlea, can be seen in the histology of the cochlea
spiral ganglion cells
specialized neurons in the cochlea of the inner ear that transmit auditory information from hair cells to the brain
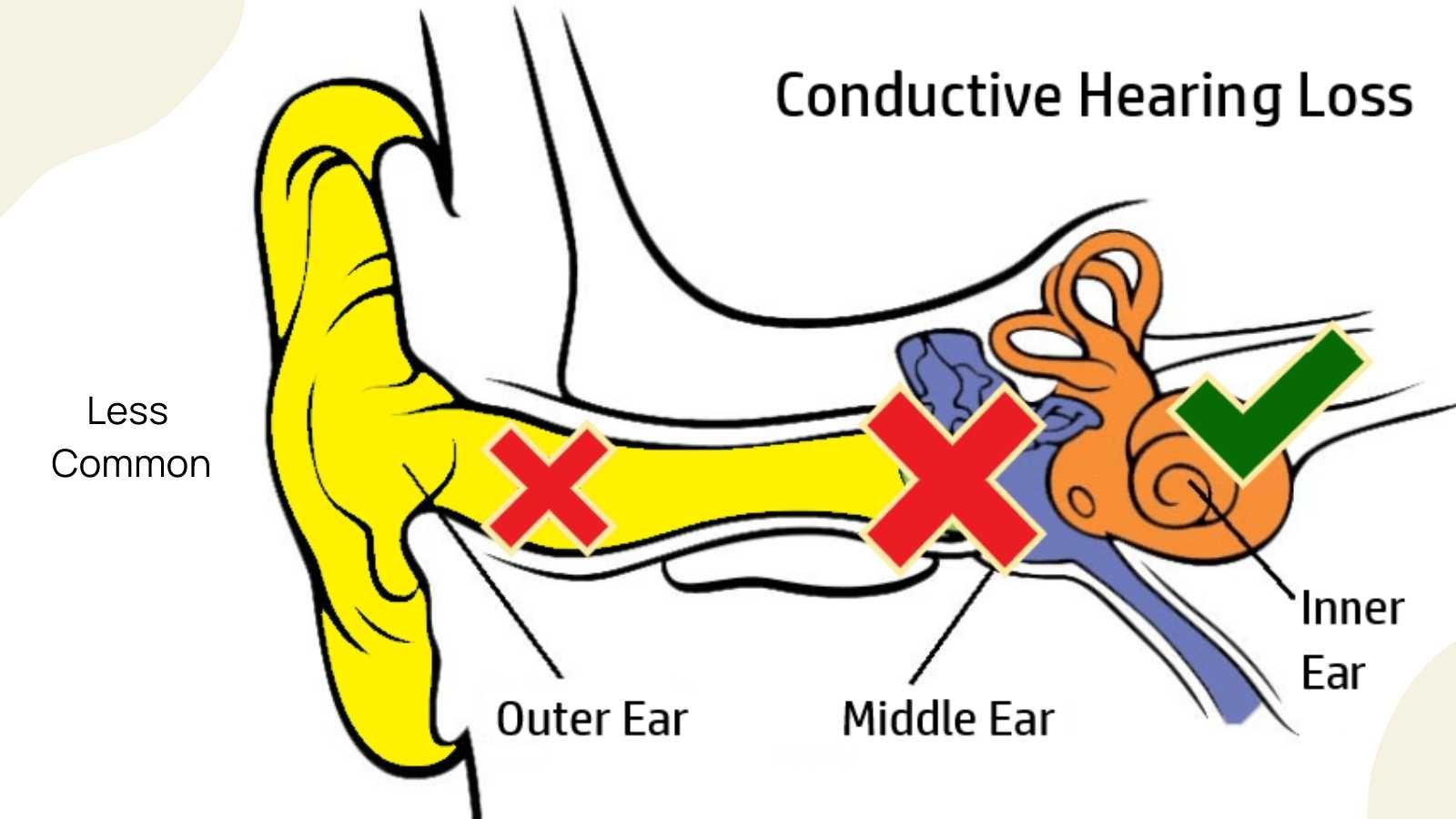
conductive deafness
a type of hearing loss caused by problems with the outer or middle ear that precent sound from reaching the inner ear
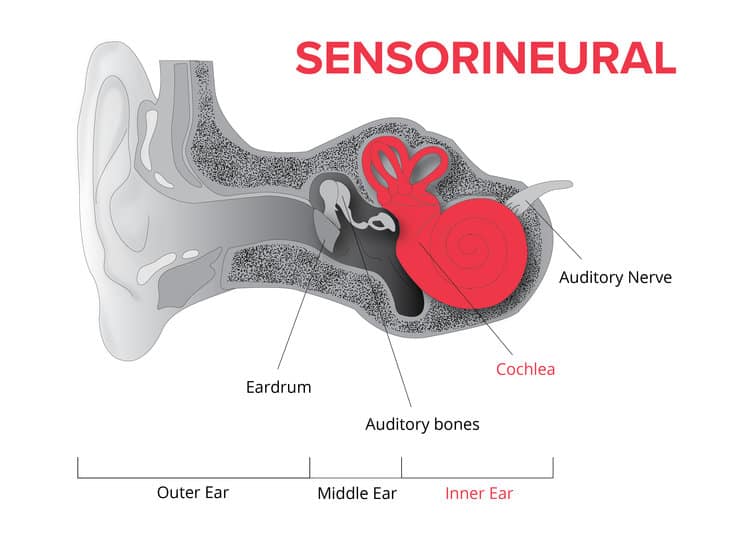
sensorineural deafness
a type of hearing loss that affects the inner ear and the nerve that carries sound signals to the brain
Rinne test
used to evaluate hearing loss in 1 ear; done by striking a tuning fork against a hard surface and placing the base of the tuning fork on the mastoid process of the ear being tested, better for testing for conductive deafness
Weber test
used to evaluate for sensorineural hearing loss; done by striking a tuning fork against a hard surface and placing it on top of the patients head and seeing where the patient best hears sound.