Physics Year 10
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Scalar

¡Quantities where only the magnitude (size) is important. E.g. distance, speed, time

Quantities where both magnitude (size) and relevant direction is needed, ex displacement
distance
¡Is the cumulative length an object travels measured in meters (m)

displacement
¡Is the straight line distance between an objects initial and final position. Needs a direction and is measured in meters.

Velocity IN M/S
¡ is a measure of how quickly an object is moving in a particular direction. It is measured in km/h or m/s plus a direction where ¡= x/t
¡where x = displacement and t = total time taken

speed
¡Speed is a measure of how quickly an object is moving. It is measured in km/h or m/s
¡Speed = total distance travelled S=D/T
¡ total time taken

acceleration
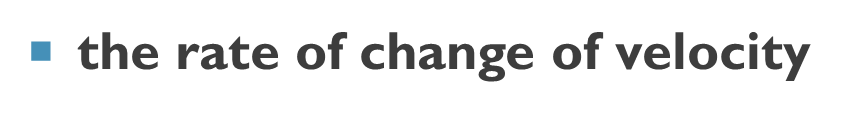
the rate of change of velocity
Acle= Final- Initial velocity/ time taken
forces
The action of one object (a push or a pull) on another object causing an object to accelerate deaccelerate change direction or changed shape Measured Newton (N) units for force

FR
Force of resistance
FA
Force applied
FG
Force of gravitational pull
Labelling Force Diagrams
should be labelled force OF___ ON ____
FT
Force of Tension
FN
Normal Force reaction
FB
Force of buoyancy
Net Force
The overall force acting on an object, calculated as the vector sum of all individual forces acting on it.
Gravity
the force that attracts a body towards the center of earth or towards any other physical body having mass
mass
the quantity of matter which a body has units of kilograms or grams. Same at places and is scalar
weight
The force exerted on the mass of a body by a gravitational force. Differs from gravitational force and is vector
weight formula
Weight= mass times gravity
Newtons 1st law
An object will remain in a constant state of motion unless acted upon an unbalanced force.
Force formula
F= M x G
Unbalanced Forces
forces acting on an object where the net force is not zero
Vertical plane use sin

Vertical plane use sin
Horizontal plane use cos
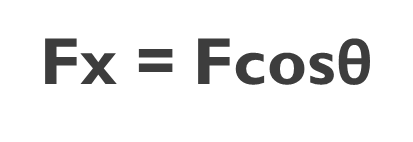
Horizontal plane use cos
Net Force
Net force is the sum of all forces acting on an object in an certain direction (newtons)
Final Velocity formula
v = u + at ( UNITS M/S)
Newtons 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force applied and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. F=MA
F=MA
2nd Law force= mass times acceleration
instantaneous values
values in motion and forces refer to the values of velocity, acceleration, and force at a specific point in time, rather than over a period.
Contact Forces
Forces that require one object to touch another one
Non Contact Forces
Forces that act without the need for objects touching
3 types of non contact forces
Gravitational Force
Magnetic Forces
Electrostatic Forces
Gravitational Force
the force of attraction between all masses in the universe
Magnetic Forces
is the force of a magnet pulling on some metallic objects.
Electrostatic Forces
is a force exerted between electrically charged objects
Weight Formula
W= mass times gravity
Component Forces
the individual parts of a single force vector, broken down into two or more directions, often the x and y axes, that together have the same effect as the original force.
Net force for X or Y
cos is used to find horizontal net force while sin is for vertical (NEWTONS unit)
Acceleration formula
A= (V Final - V Intial / Time
VELOCITY IS ALWAYS GIVEN WITH A DIRECTION
VELOCITY IS ALWAYS GIVEN WITH A DIRECTION