2018 Rat Gross Path - flashcards | Quizlet
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Wistar: original outbred albino lab rat; common in Europe; relatively small; long lived
Sprague‐Dawley (SD): derived from Wistar; early sexual maturity; large F344: commonly used by NIH; small; long lived
Two common rat strains and their general phenotypes?
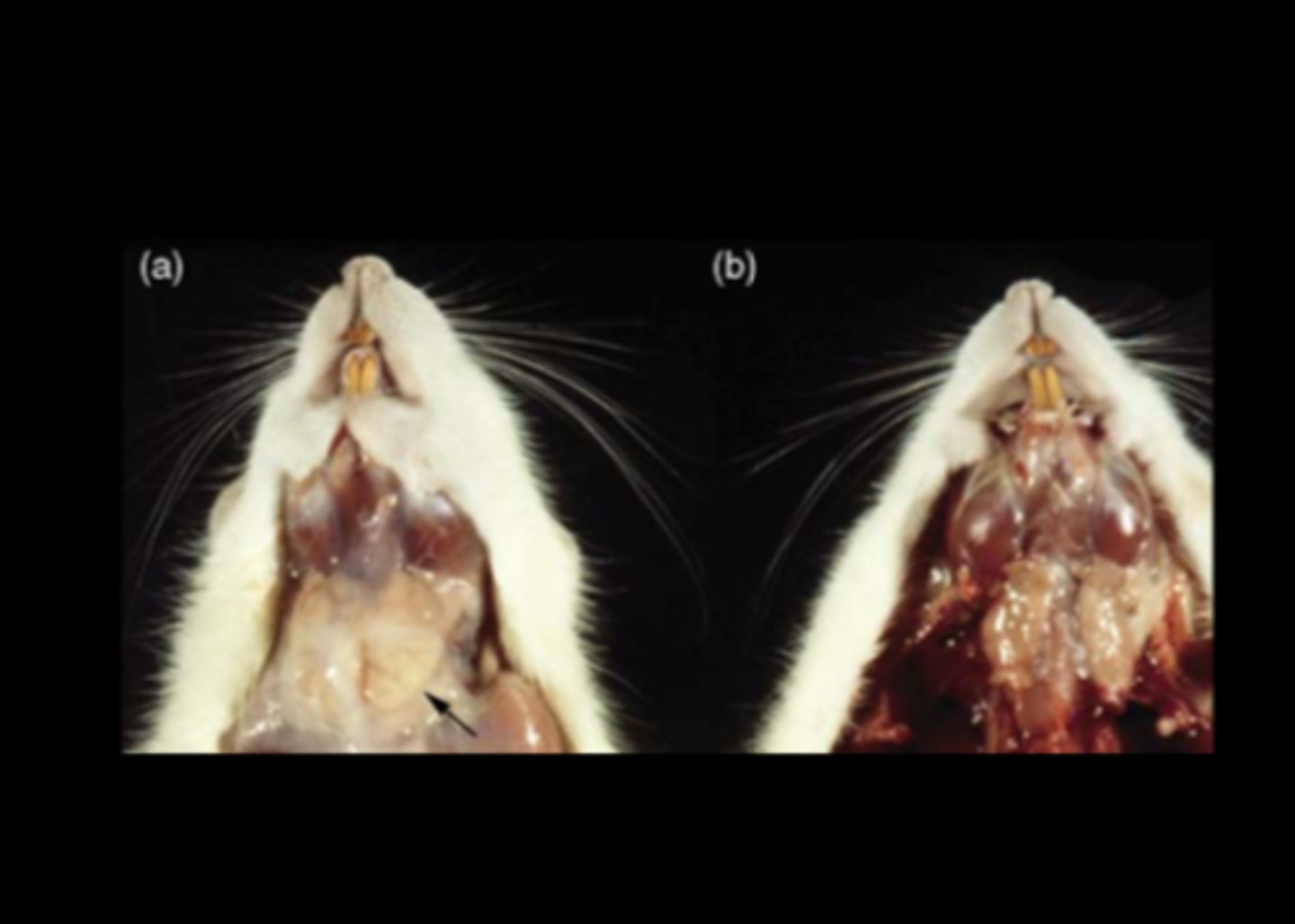
Salivary gland
Diffuse necrotizing sialoadenitis with edema
(normal in a)
Sialodacryoadenitis virus (SDAV)
(Rat coronavirus)
Highly contagious. Transmitted by aerosol, contact, fomites. High morbidity, low mortality.
Gross: chromodacryorrhea; swollen salivary glands with edema and necrosis; enlarged cervical lymph node; rhinitis; interstitial pneumonia; eye lesions due to Harderian gland damage (keratoconjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, megaloglobus, exophthalmos, hypopyon, hyphema)
Histo
- Sialoadenitis (parotid and submaxillary salivary glands) and dacryoadenitis (Harderian and other lacrimal glands) with ductal edema, necrosis and/or squamous metaplasia
- Interstitial pneumonia with necrotizing bronchitis and bronchiolitis; hyperplastic BALT
- Necrotizing laryngitis, tracheitis, and rhinitis +/- epithelial hyperplasia
- Ocular changes secondary to lacrimal gland damage (keratitis sicca, impaired drainage, hyphema, megaloglobus)
DDx: cytomegalovirus, papovaviral sialoadenitis (athymic nude rats), hypovitaminosis A (squamous metaplasia of salivary gland ducts)
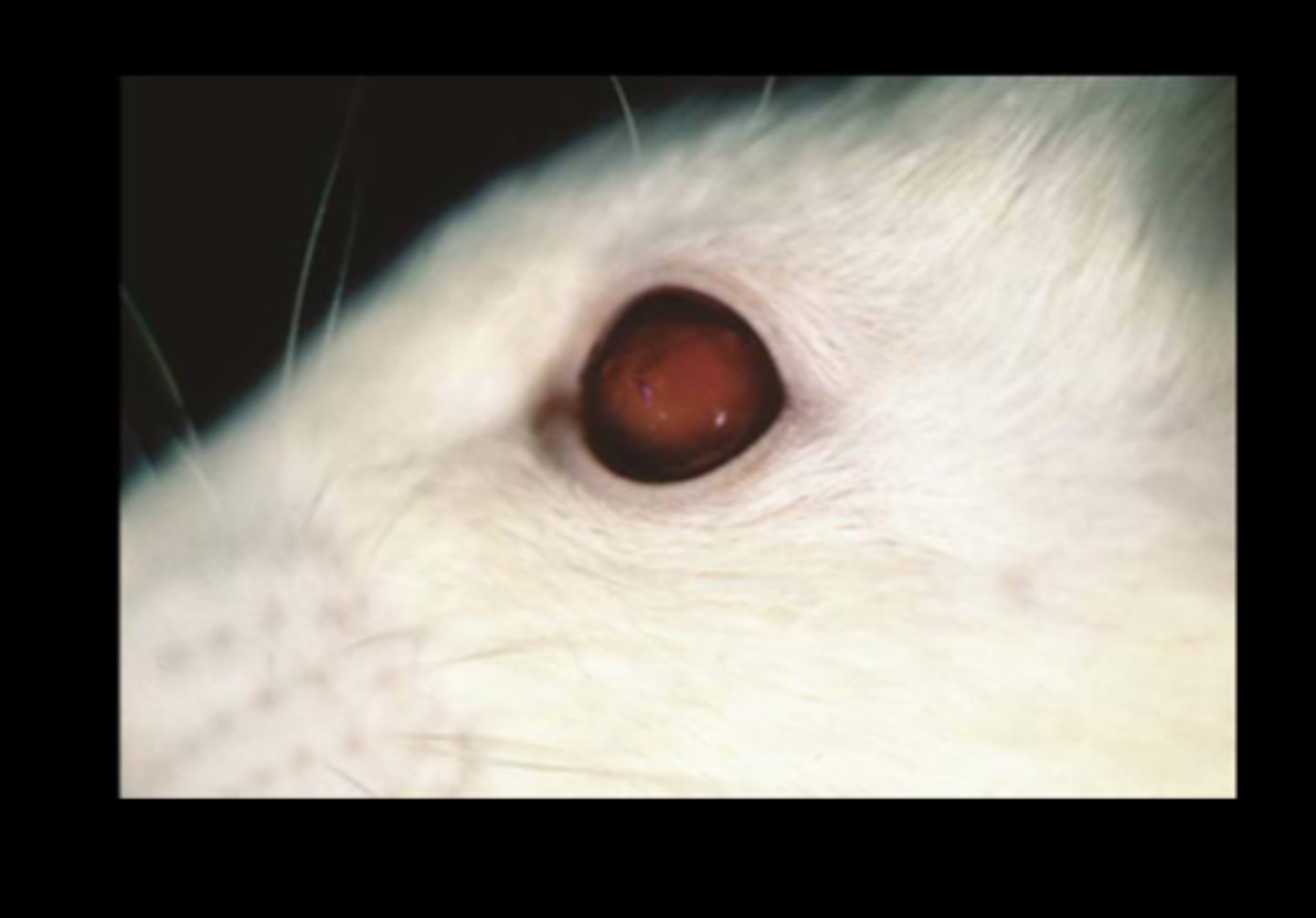
Eye
Megaloglobus with hyphema
Sialodacryoadenitis virus (SDAV)
(Rat coronavirus)
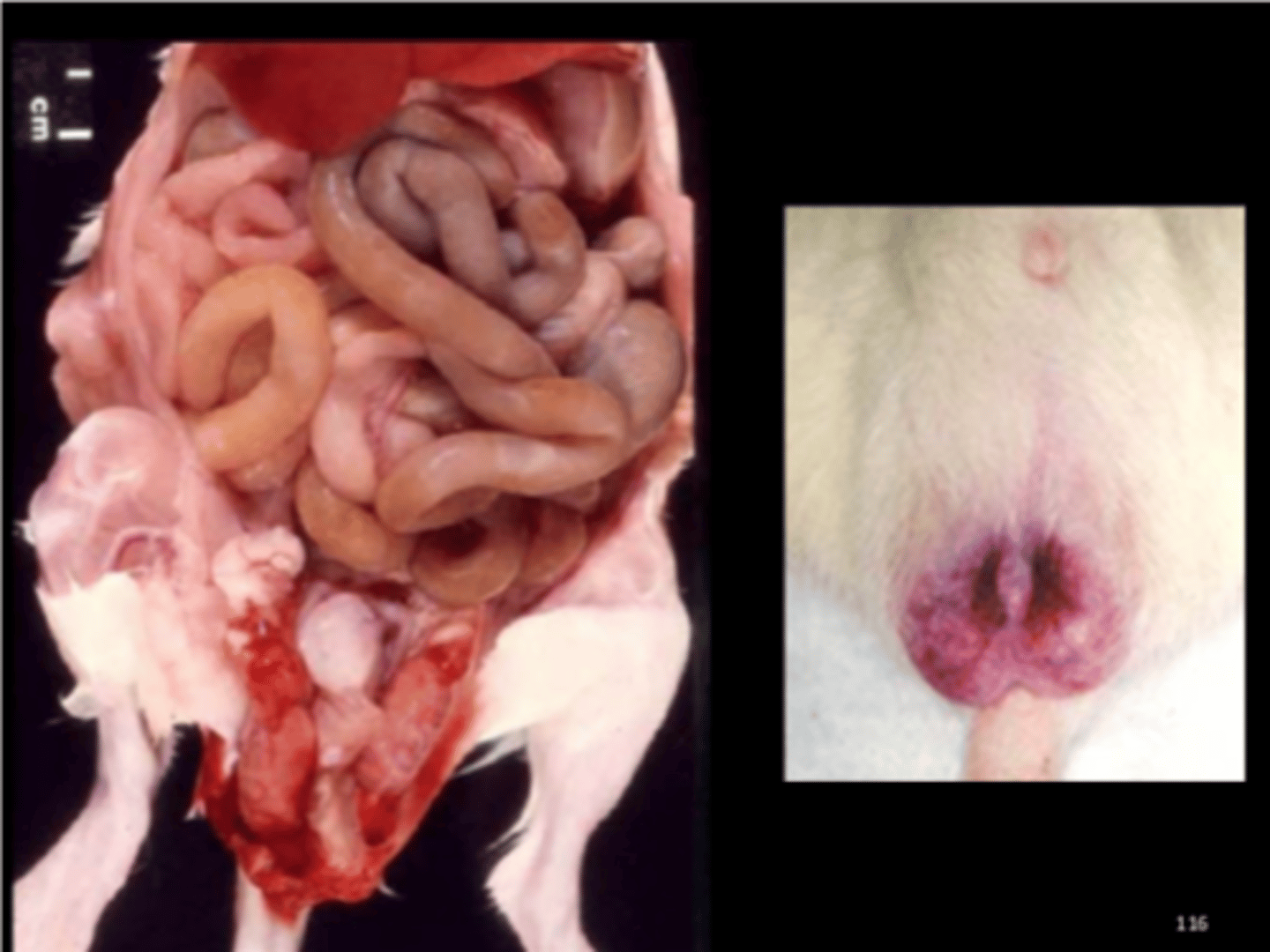
Scrotum
Multifocal scrotal hemorrhage
Kilham's rat virus or Rat virus
One of several rat parvoviruses. Common in lab, wild, and pet rats. Common contaminant in biological products.
Transmission: oronasal, transplacental, milk, feces, urine, fomites Pathogenesis
- Infects rapidly growing cells: vascular endothelium, lymphoreticular and hematopoietic tissues, developing cerebellum and liver
- Endotheliotropic: causes thrombosis and infarction
Gross
- Congestion and hemorrhage (scrotal and testicular site is classic) - Hemorrhagic encephalopathy with malacia
- Cerebellar hypoplasia (neonates if in utero infection)
- Decreased fertility, fetal resorption, small litters, runts possible
Histo
- Endothelial cell and megakaryocyte damage -> hemorrhage, thrombosis, necrosis
- IN inclusions
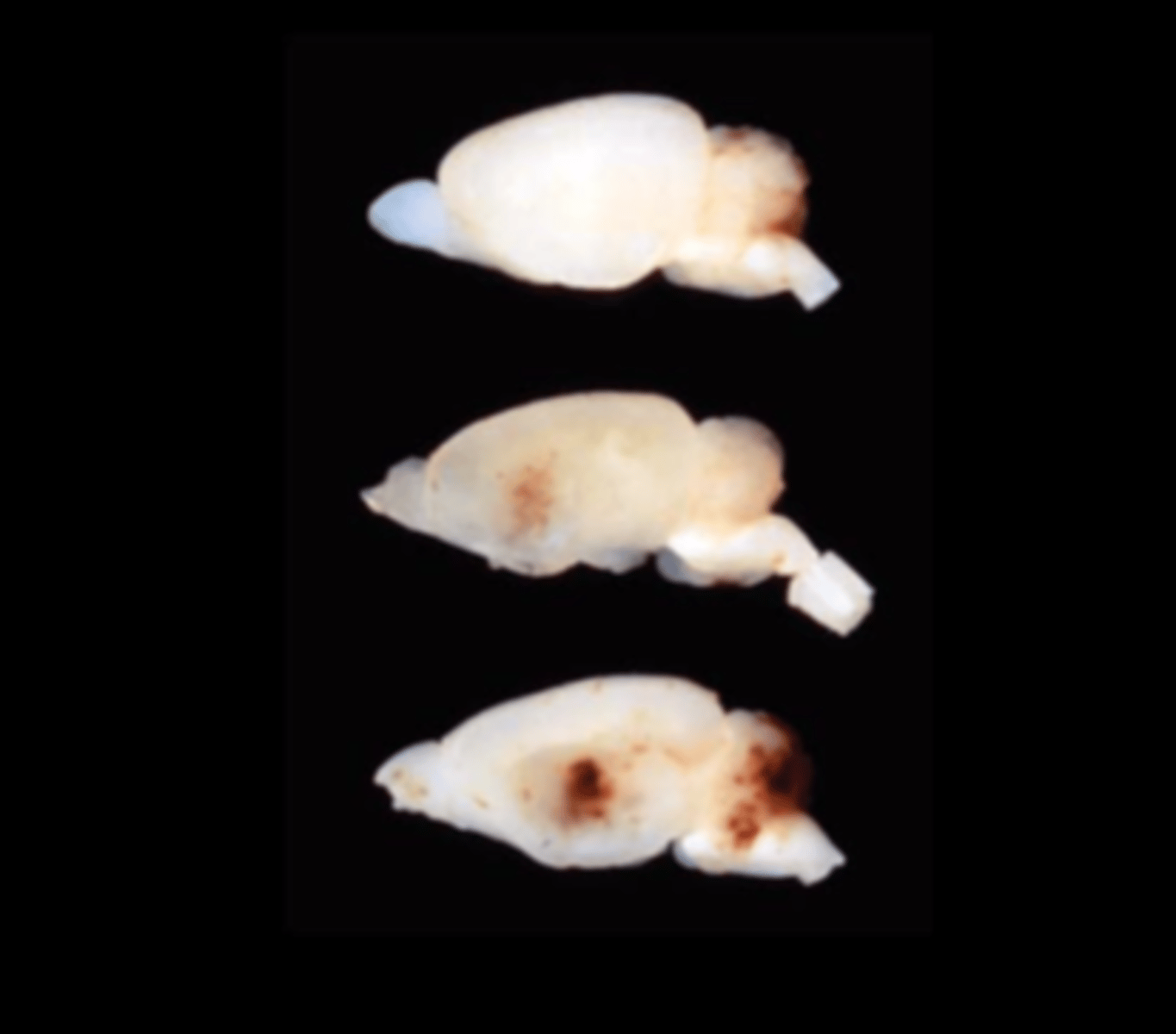
Brain (fixed)
Multifocal cerebral and cerebellar hemorrhage and malacia
Kilham's rat virus or Rat virus
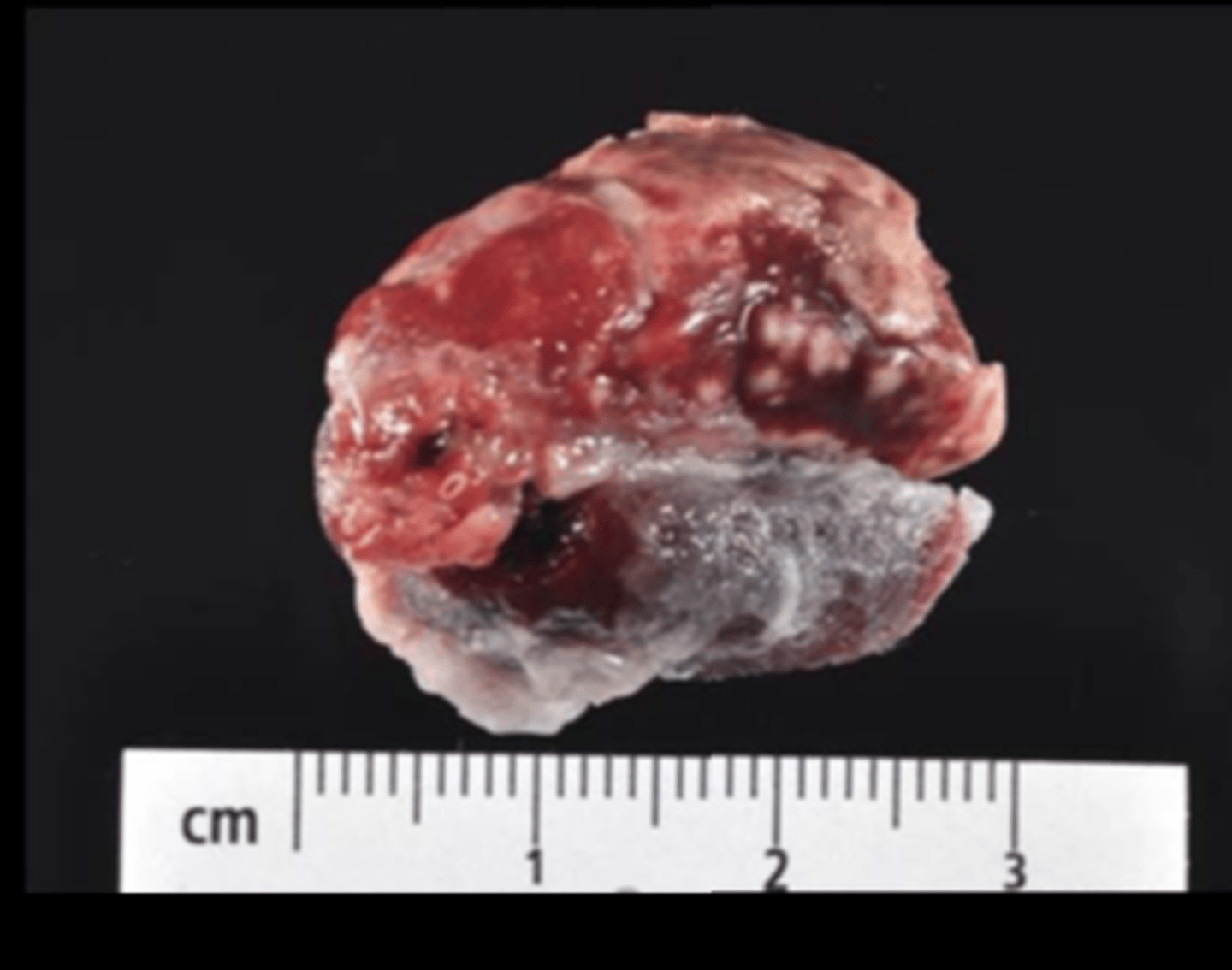
Lung
Multifocal to coalescing necrosuppurative pneumonia +/- pleuritis
Pseudotuberculosis
Corynebacterium kutscheri
Transmission: direct contact, oronasal. Persistent asymptomatic carriers common (latent infections may advance with age and immunosuppressive conditions - stress, other infections, irradiation, experimental manipulation). Low morbidity, high mortality in affected. Lesions in any tissue, but in rat, lung is major site. Septic emboli trapped in organs or tissues with large capillary network (lung, liver, kidney) and/or responsible for filtering blood (synovia, glomeruli).
Gross: systemic suppurative inflammation w/ necrosis
- Lung: abscesses +/- hemorrhage and pleuritis (fibrinous or fibrous)
- Abscesses in liver, kidney, preputial glands, skin
- Suppurative arthritis, otitis media, pododermatitis
- Hepatic necrosis, pyelonephritis, fistulous tracts in skin
Histo: bacteria prominent in lesions
- Lung: interstitial abscesses (hematogenous spread), caseous necrosis, suppurative exudate in airways
- Liver: caseous necrosis
- Kidney: embolic glomerulitis, abscesses, +/- pyelonephritis
DDx: opportunistic bacteria, Mycoplasma, fungal pneumonia
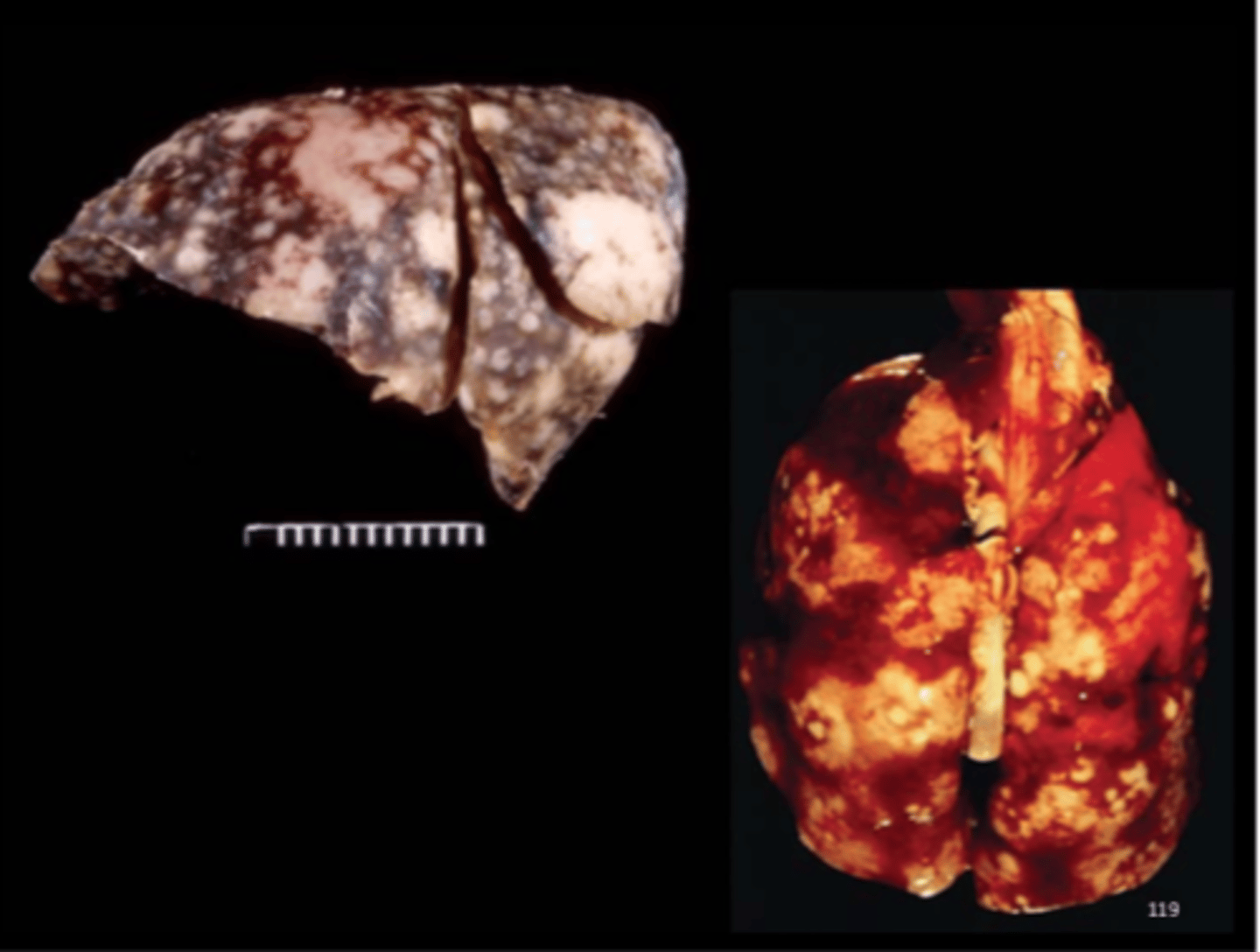
Lung (fixed)
Multifocal to coalescing necrosuppurative pneumonia +/- pleuritis
Pseudotuberculosis
Corynebacterium kutscheri
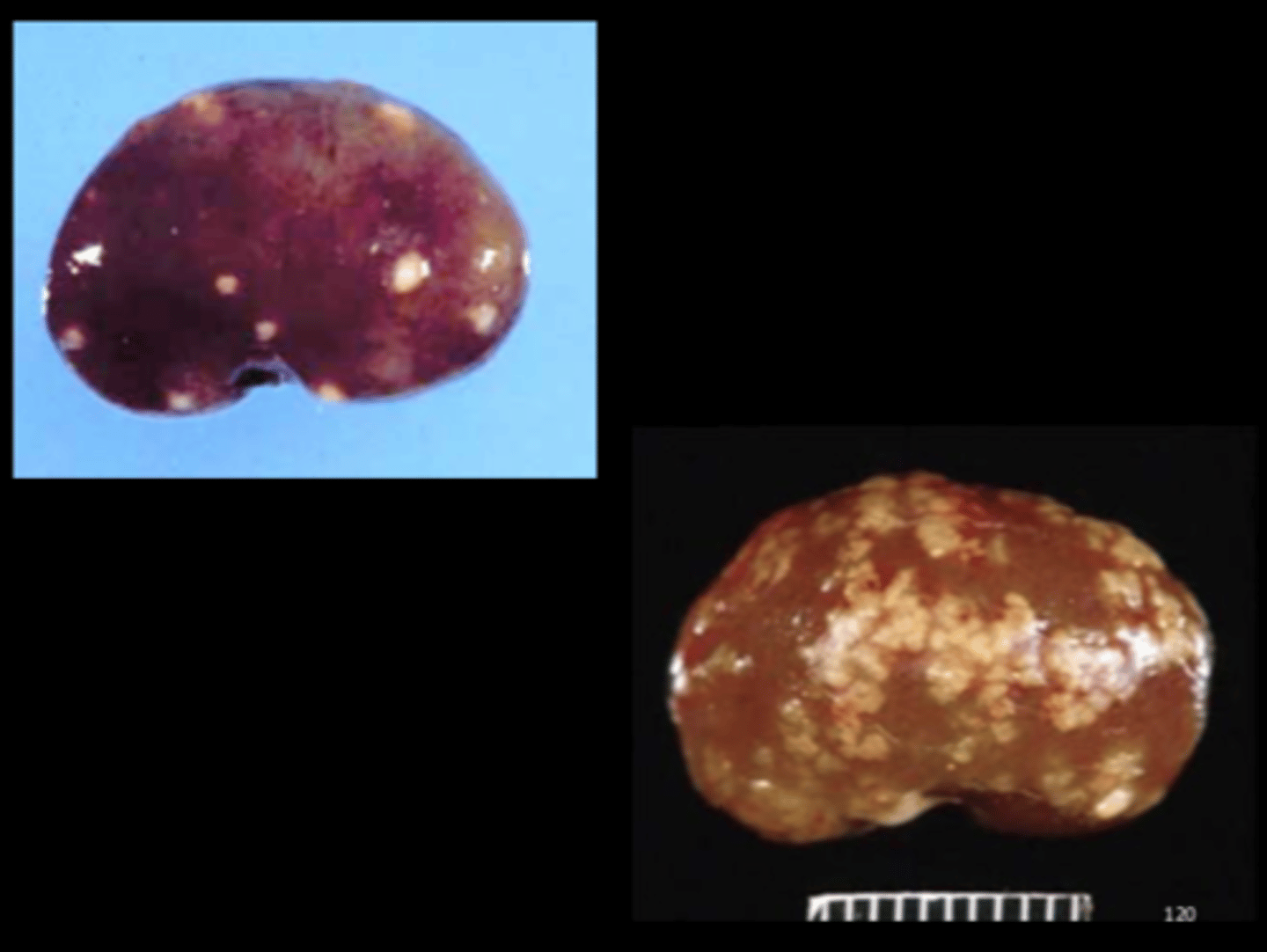
Kidney
Multifocal suppurative embolic nephritis
Pseudotuberculosis
Corynebacterium kutscheri
Heart, liver
Multifocal necrotizing myocarditis and hepatitis
Tyzzer's Disease
Clostridium piliforme
Transmission: ingestion of infective spores from feces/contaminated food or bedding/environment (up to 1 yr).
Gross: focus on intestine, liver, heart
- Multifocal necrosis in liver, heart
- Megaloileitis: greatly dilated, hyperemic ileum
- Terminal ileum, LI: hyperemia, edema, hemorrhage, and/or necrosis
- Mesenteric ln: enlarged, hyperemic and edematous
Histo
- Necrotizing hepatitis, enterotyphlocolitis and myocarditis +/- hemorrhage, dystrophic calcification, fibrosis
- GIT: can have edema, blunted and fused villi, crypt epithelial hyperplasia, ulceration
- Vegetative form of bacteria (pickup sticks) may be visible at edge of lesions with H&E or Warthin-Starry silver stain
DDx for necrotizing hepatitis: Clostridium piliforme, Salmonella spp., other gram negatives
DDx for megaloileitis: IP chloral hydrate anesthesia
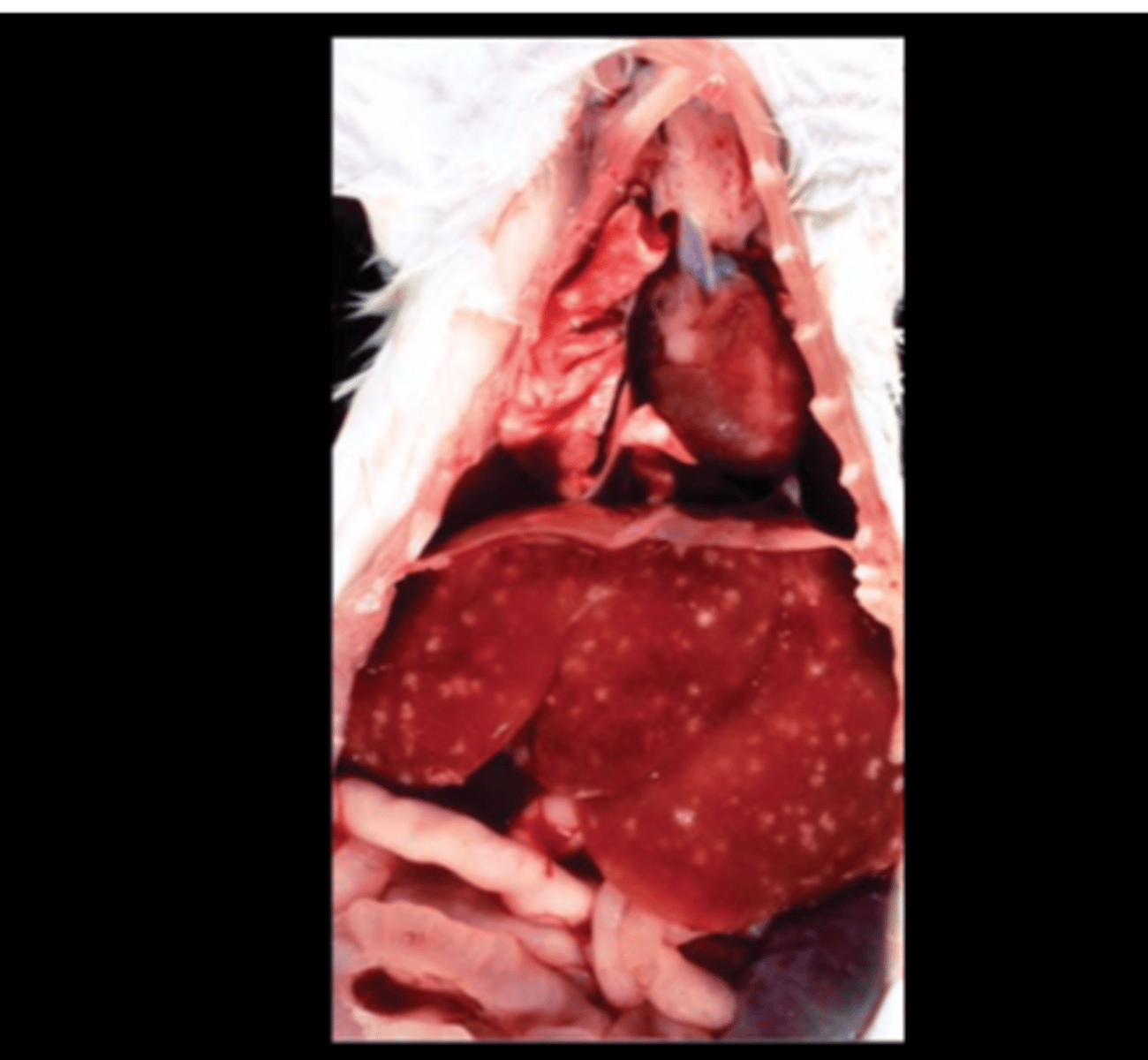
Intestine
Necrohemorrhagic ileitis with adynamic ileus (megaloileitis)
Tyzzers
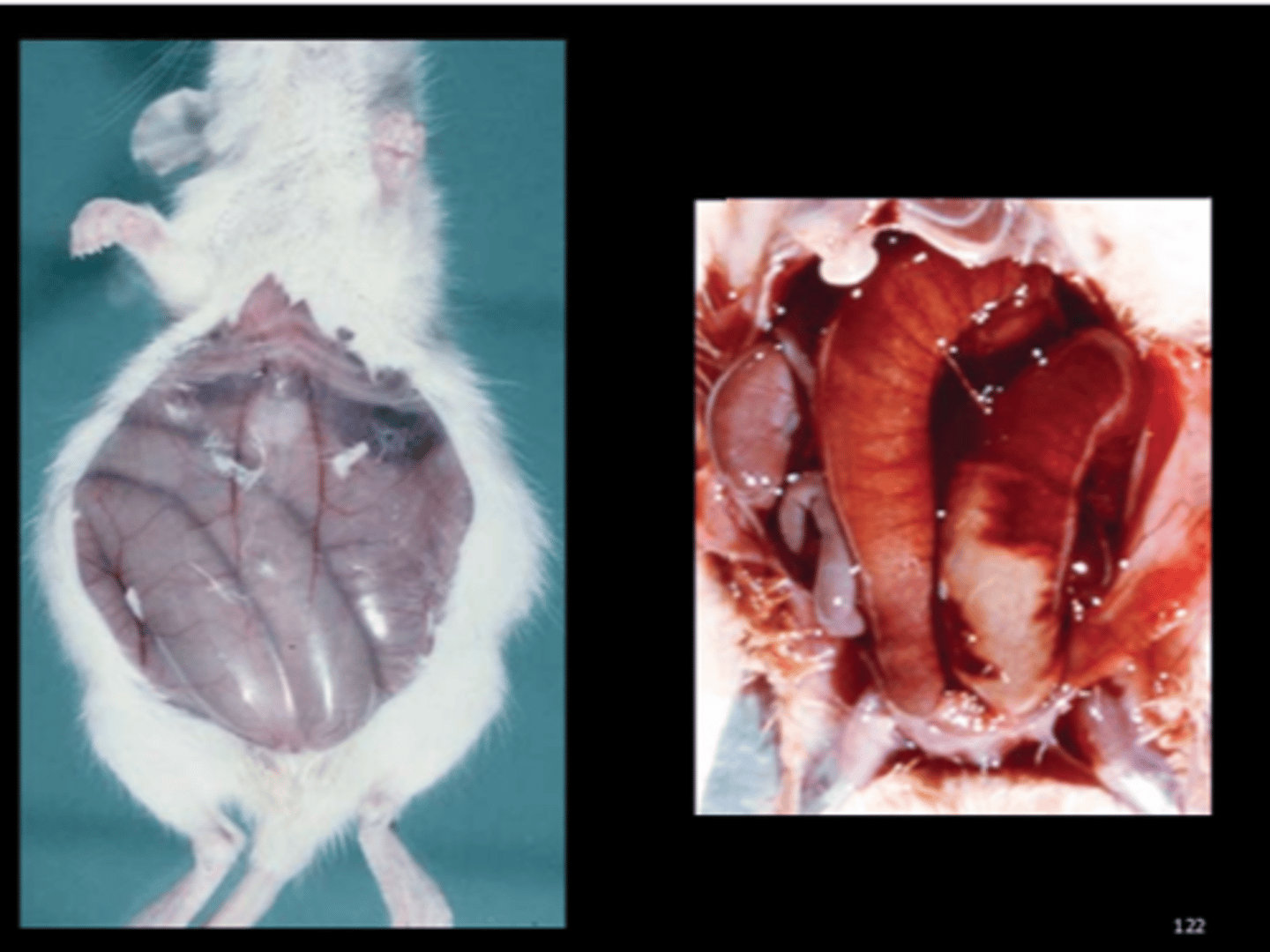
Lung
Multifocal to coalescing suppurative bronchopneumonia with bronchiectasis
Mycoplasma pulmonis
Endemic in wild, pet rodents. Infected animals NOT suitable for research. Disease outcome depends on strain, age, concurrent infections, nutritional status, environmental factors.
Transmission: contact, aerosol, intrauterine
Target tissues: respiratory tract, middle ear, endometrium, synovium
Lesions
- "Cobblestone" lung (older adults) - suppurative bronchopneumonia +/- abscesses, atelectasis, bronchiolitis with bronchiolectasis, lymphoid hyperplasia, type II pneumocyte hyperplasia
- Female repro lesions (partially resorbed fetuses, suppurative salpingitis, oophoritis and/or endometritis)
- Chronic suppurative rhinitis, otitis media, laryngitis, tracheitis
- Chronic suppurative arthritis (rare component of disease in the rat) DDx (respiratory lesions): CAR bacillus, Corynebacterium kutscheri ***Vet Pathol 2009;46:952-959 - "Lymphomas" in rat (Europe)
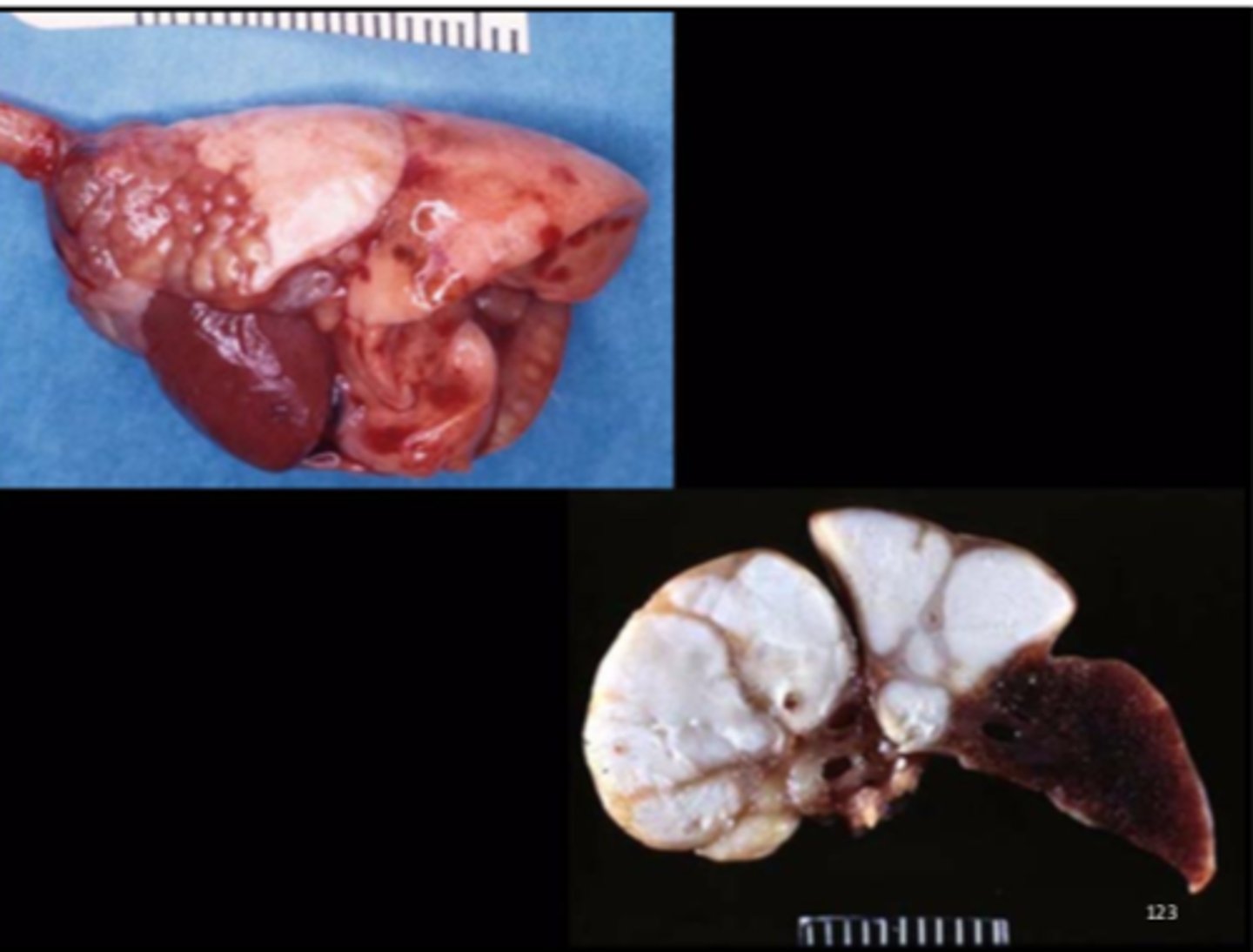
Ear (fixed)
Bilateral suppurative otitis media
Mycoplasma pulmonis
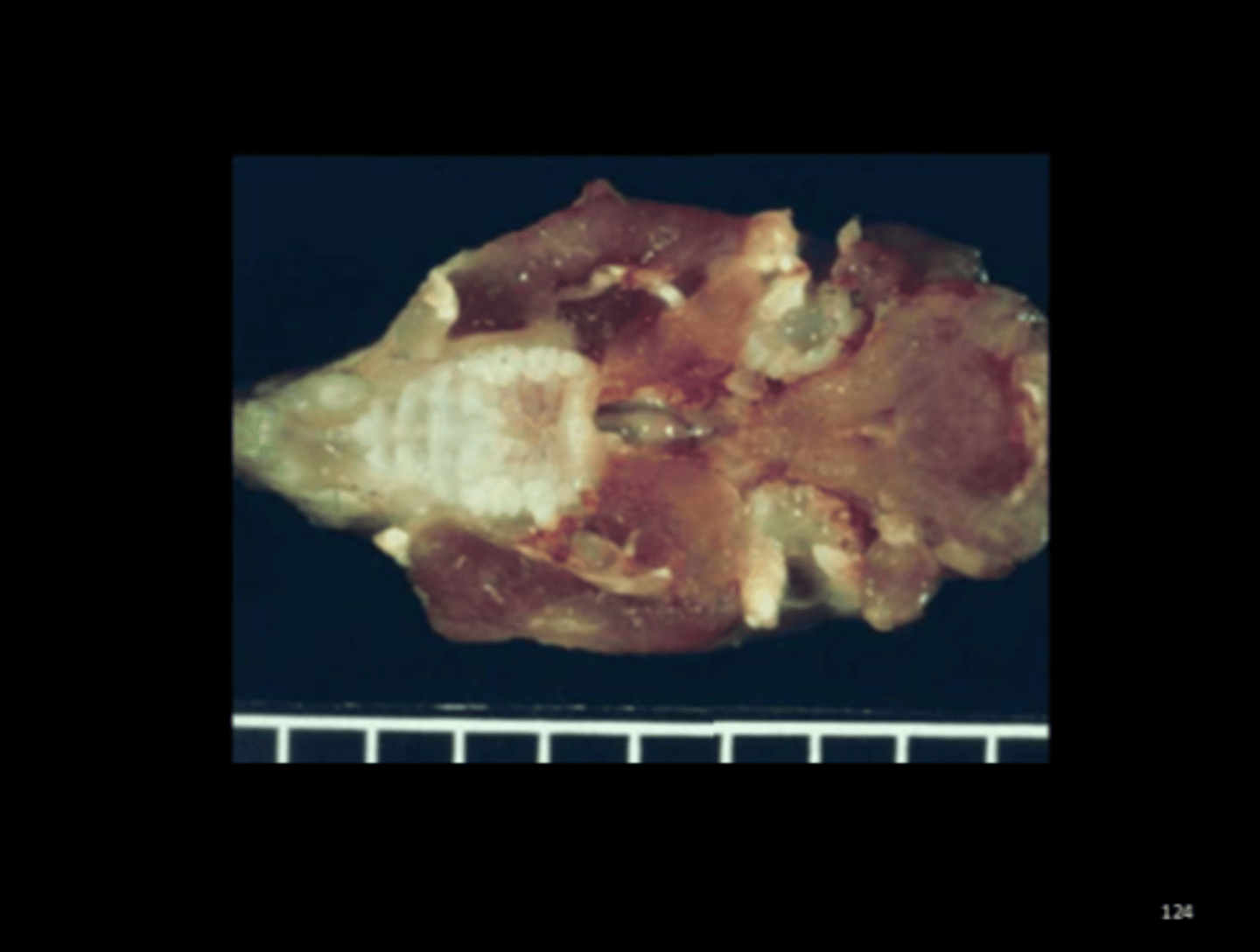
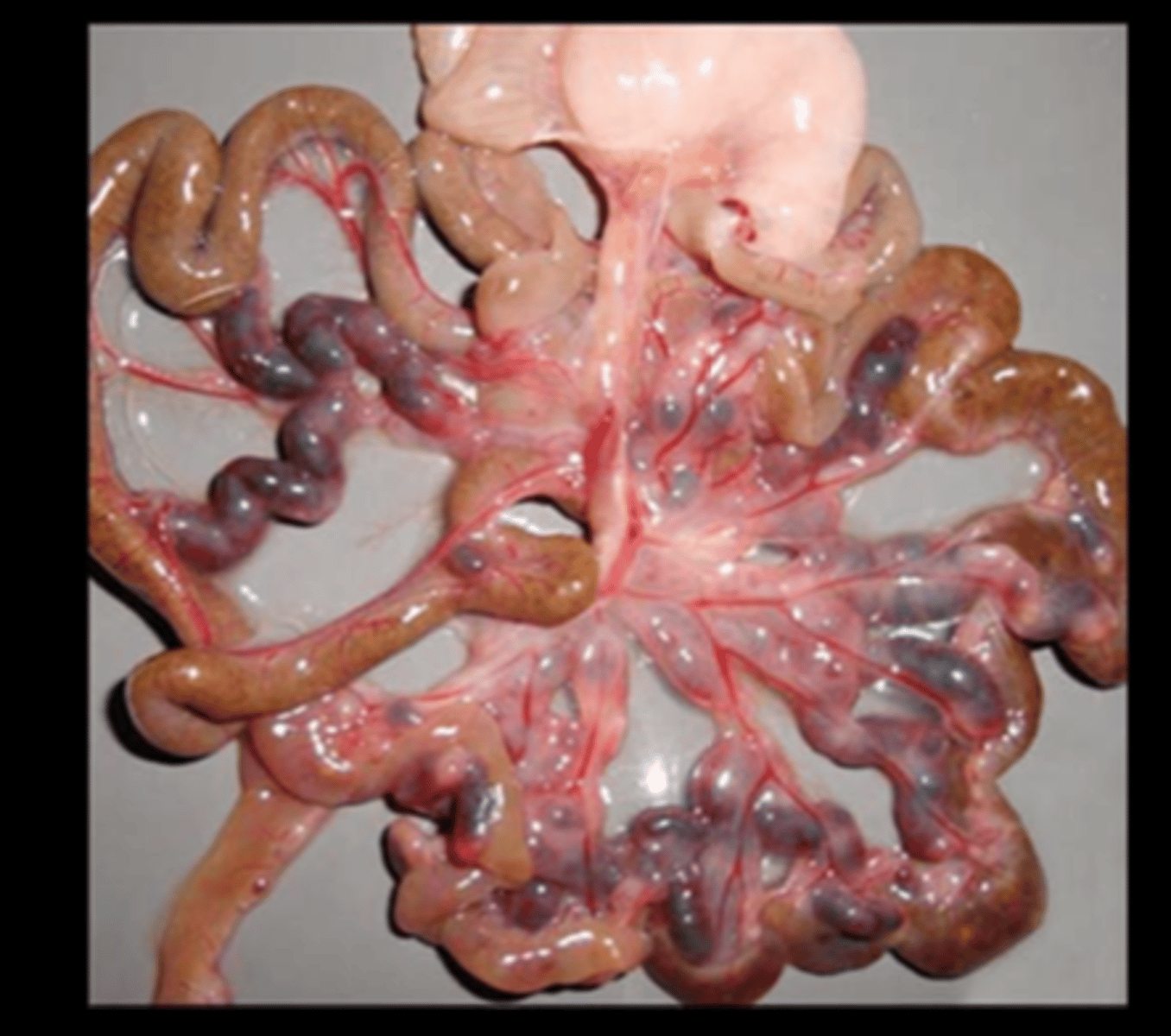
Mesenteric arteries
Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing and proliferative mesenteric arteritis with aneurysmal dilatation
Polyarteritis nodosa
Incidence high in SD and Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHR), esp in aged males and those with late-stage chronic nephropathy.
Causes: spontaneous, immune-mediated, drug-induced
Site: medium-sized arteries/arterioles in any tissue except lung (common in mesentery, heart base, testes, epididymides, spermatic cord and connective tissue of spleen, pancreas). VEINS ARE SPARED.
Gross: thickened tortuous arteries/nodular arterial thickening (hemoabdomen if rupture)
Histo: transmural lymphohistiocytic periarteritis, proliferation, fibrinoid degeneration/necrosis of intima and media. Chronically there is intimal hyperplasia, medial and periarterial fibrosis, mineral, +/- thrombosis. Other species affected
- Mice (necrotizing polyarteritis) - typically present with head tilt/ vestibular syndrome
- NHPs (polyarteritis nodosa)
- Dogs (Beagle pain syndrome) - typically present with neck pain
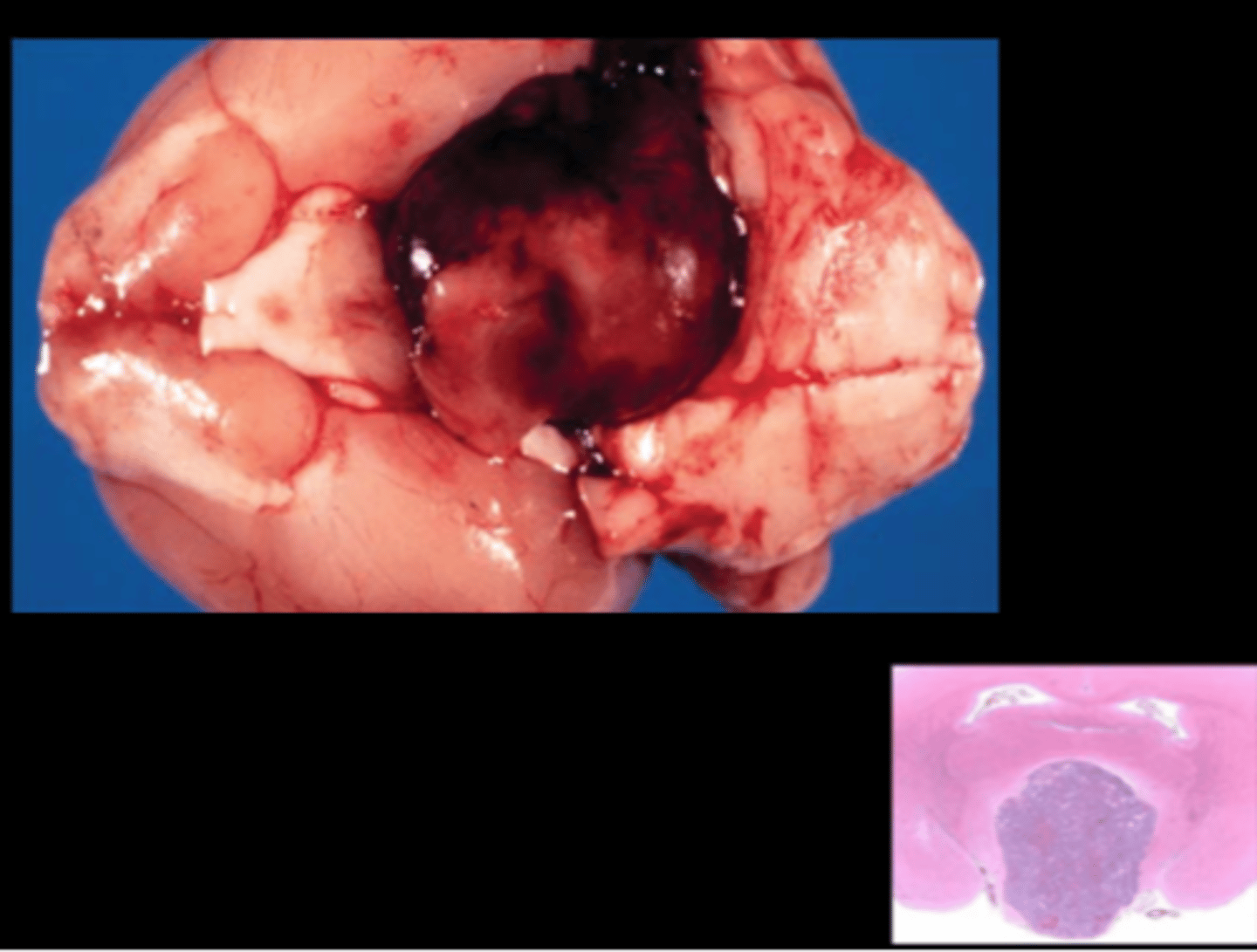
Pituitary gland
Pituitary adenoma +/- compression of overlying brain
Common in SD (~80% females, 60% males); slightly less in Wistar. Predisposing factors: age, genetics, diet, breeding history.
Most arise from pars distalis, but pars intermedia tumors possible also. Most often chromophobe adenomas and prolactin producing.
Gross: hemorrhagic, expansile, may compress ventral brain
Histo: usually sharp demarcation from brain, cells are larger than normal with abundant pale cytoplasm, few mitoses
IHC: usually prolactin +
DDx pituitary hyperplasia: very common in aged rats
DDx carcinoma: more infiltrative, but rarely metastasize
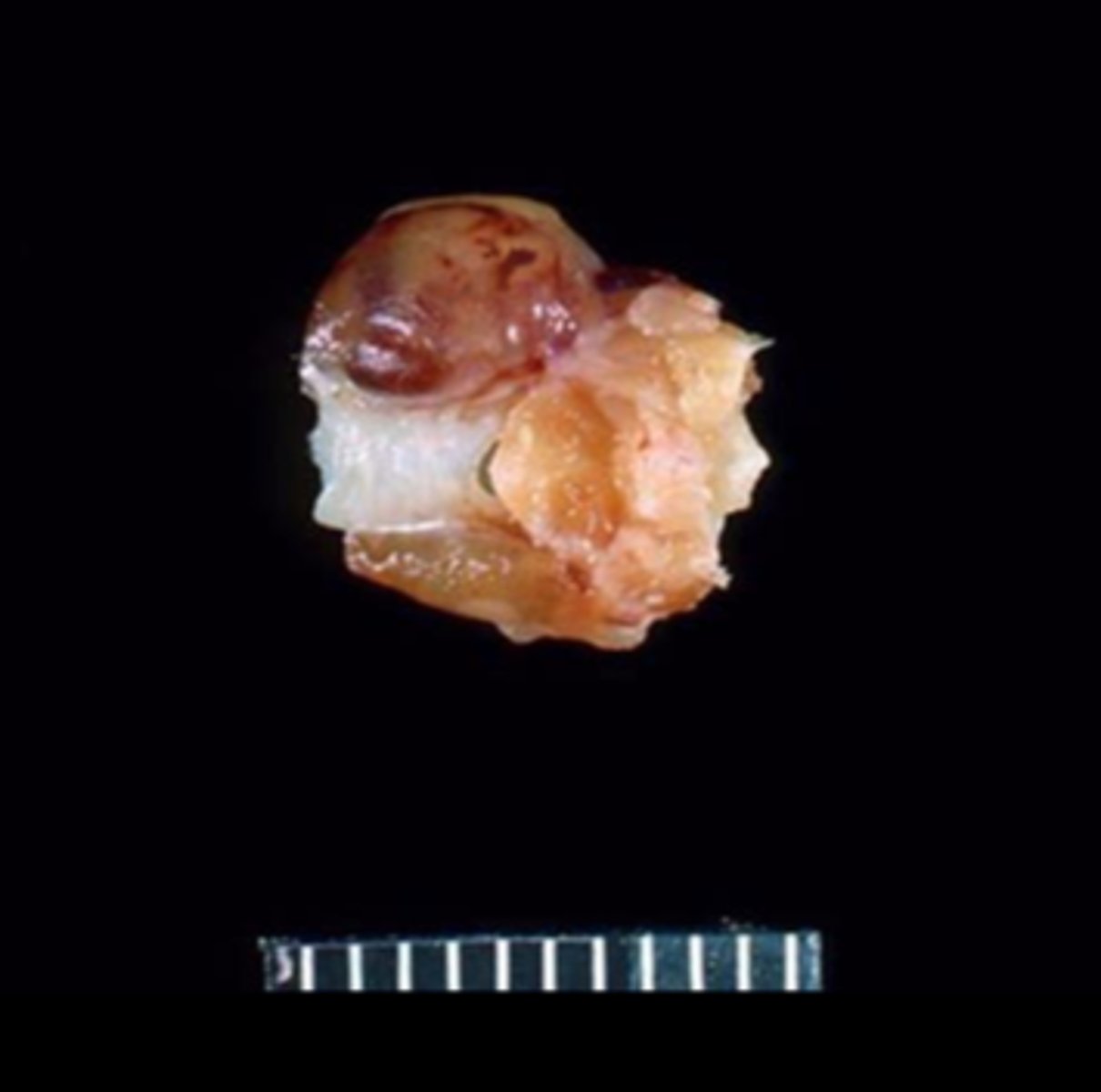
Thyroid gland
Unilateral thyroid adenoma
Spontaneous or induced
The most common thyroid tumors are C-cell neoplasms, followed by follicular cell tumors. No sex predilection. Can be induced with simvastatin.
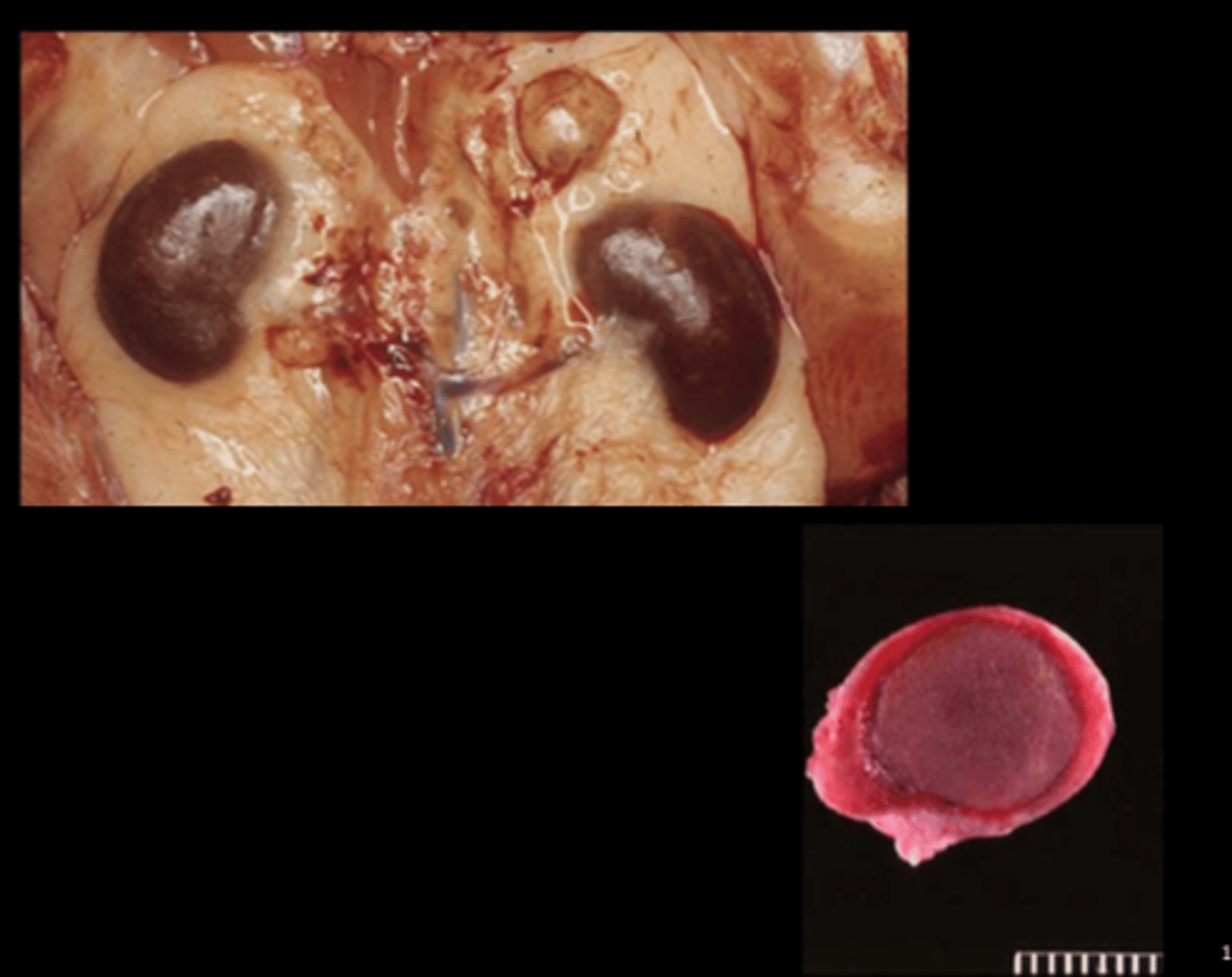
Adrenal gland
Pheochromocytoma
Common neoplasm in certain strains (male F344).
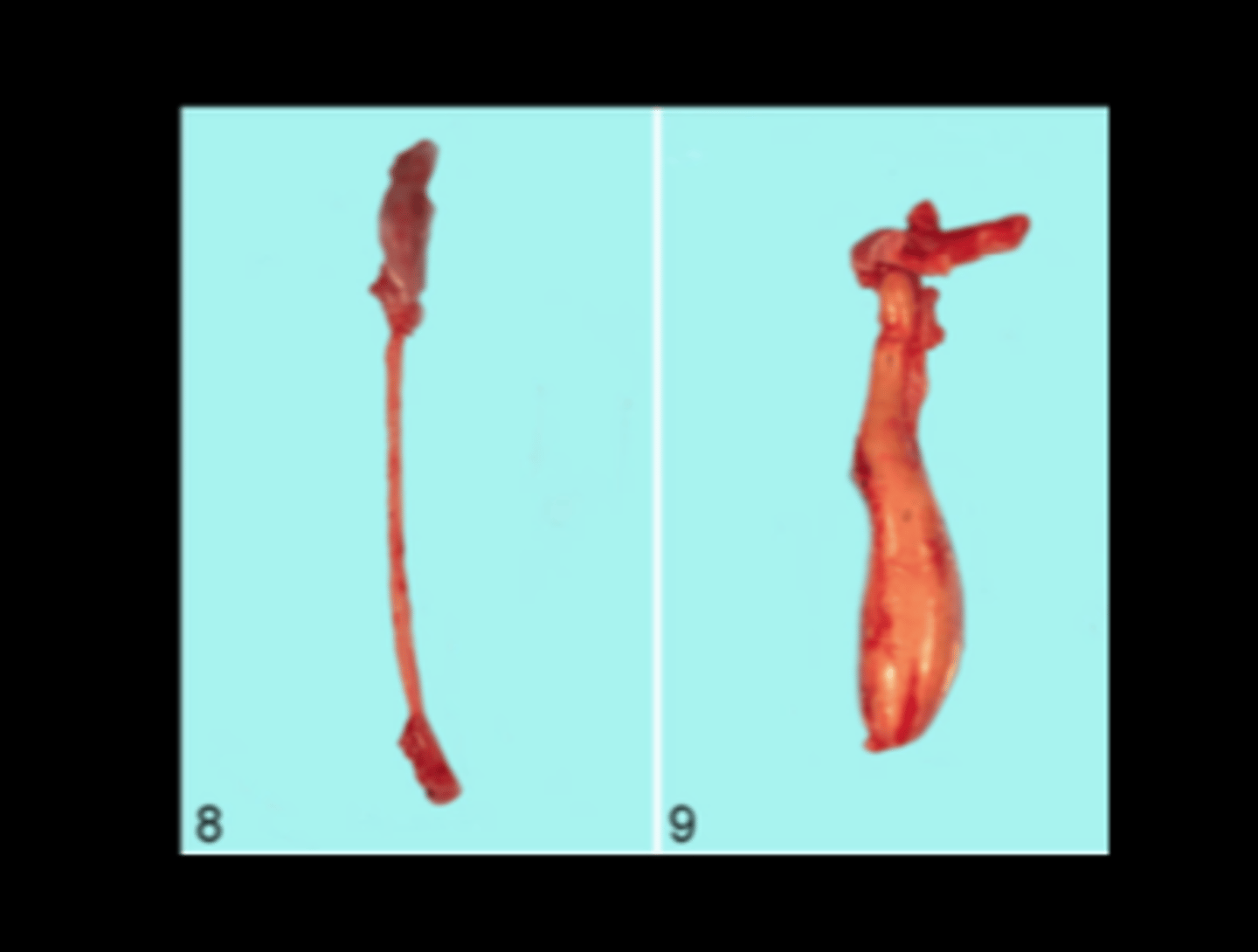
Esophagus
Megaesophagus (normal to compare)
Transgenic (Pvrl3- Cre) rat
Vet Pathol 2014;51(6):1187-1200. Report of 90% prevalence in transgene- positive animals.
Gross: megaesophagus containing compacted food and saliva.
Histo: muscle degeneration, inflammation, and reduced number of myenteric ganglia.
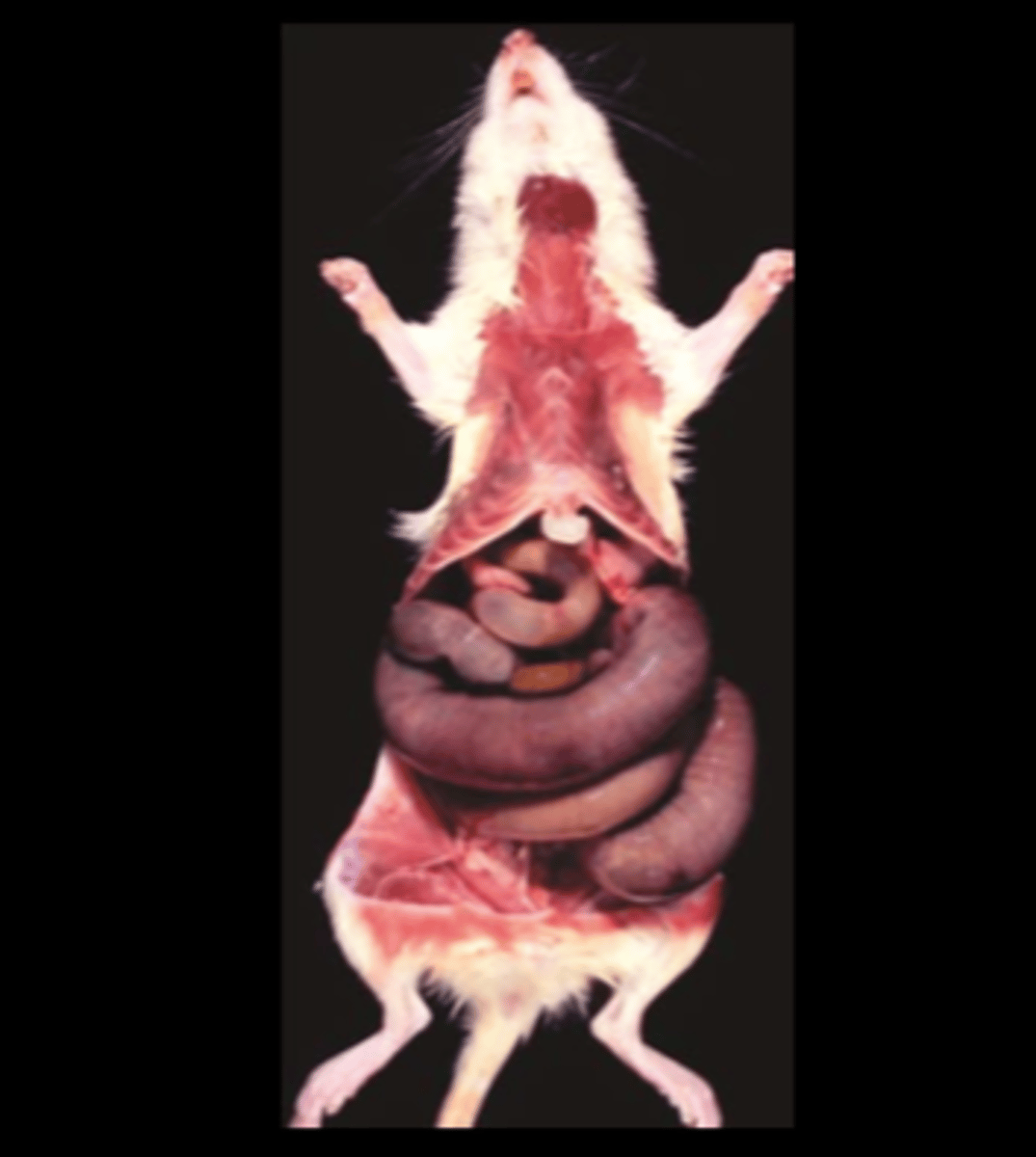
Small intestine
Adynamic ileus
IP chloral hydrate anesthesia
May not be apparent until up to 5wks after administration. DDx: megaloileitis with Tyzzer's disease
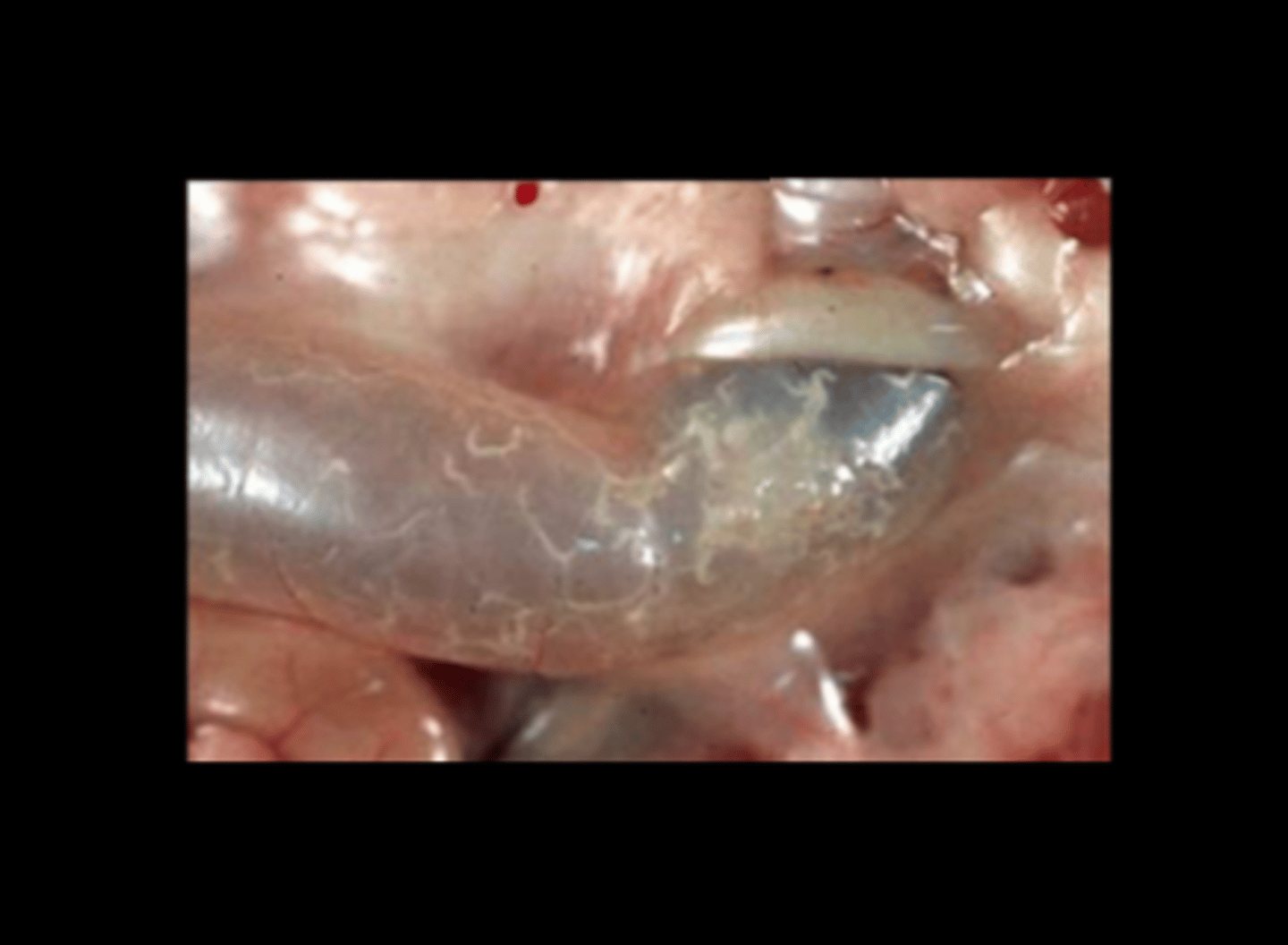
Large intestine
Intraluminal pinworms
Pinworms
Syphacia obvelata, Syphacia muris, Aspiculuris tetraptera
Found in cecum and colon. Direct life cycles. Often subclinical but young animals with heavy infestations can have diarrhea, poor weight gain, impaction, rectal prolapse, intussusception.
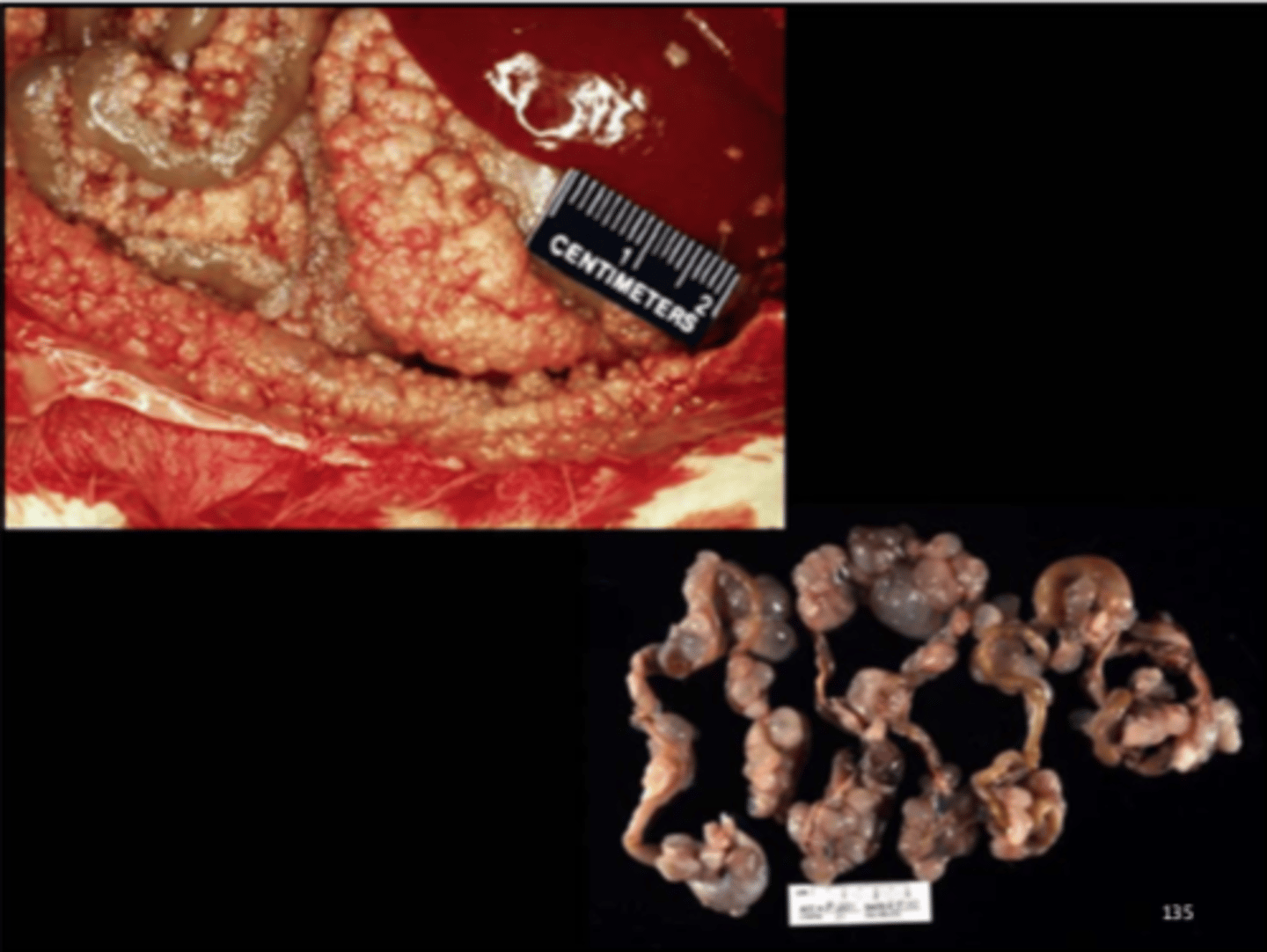
Abdomen
Peritoneal mesothelioma
Mesothelioma
Common neoplasm in rat (esp males, F344). All considered malignant. Primary site is often the tunica vaginalis of the testes
Gross: pale tan nodules/plaques on tunica vaginalis or abdominal surfaces; spread throughout the peritoneum is common; ascites
Histo: complex papillary fronds of stroma covered by mesothelial cells; often have epithelioid and mesenchymal components
IHC+: cytokeratin and vimentin
DDx (neoplastic): peritoneal sarcomatosis associated with telemetry implants (Toxicol Pathol 2012;40:113-121), ovarian yolk sac carcinoma (Vet Pathol 2014;51(3):659-662), metastatic ovarian adenocarcinoma or biliary carcinoma, mesenteric liposarcoma
DDx (non-neoplastic): reactive/hyperplastic mesothelium, abdominal fat necrosis, chronic peritonitis from intraperitoneal injections, Cysticercus fasciolaris
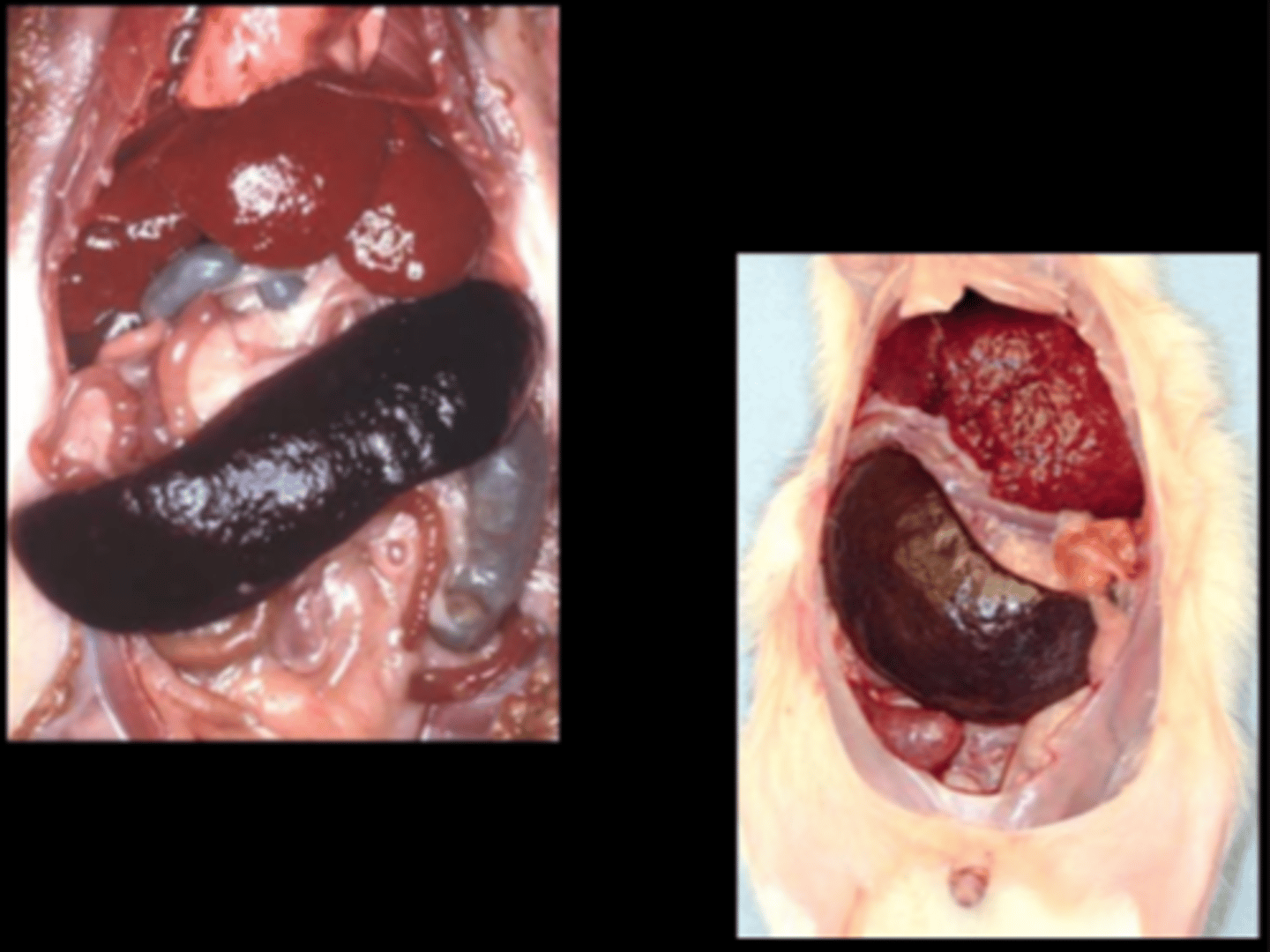
Liver, spleen, abdomen
Hepatic and splenic lymphoma;
Icterus
Large granular leukemia (LGL)
aka large granular lymphocytic leukemia, or LGL lymphoma
Classic disease of F344 (~33% males, 20% females), Wistar, Wistar-Furth. NOT retroviral associated. Blastic lymphocytes in all organs. Starts in splenic marginal zone with spread to liver, lung, lymph nodes.
C/S: pale (icteric) rat with watery blood
Clin path: blood leukocytes can exceed 400,000/ml3, mononuclear cells with azurophilic granules; thrombocytopenia, anemia
Gross: hepatosplenomegaly +/- lymphadenopathy, icterus
Histo: intravascular leukocytosis/leukemia; neoplastic cells are small, pleomorphic with a small amount of reddish cytoplasm
DDx on gross: lymphoma, histiocytic sarcoma
Toxicol Pathol 2015;43:852-864.
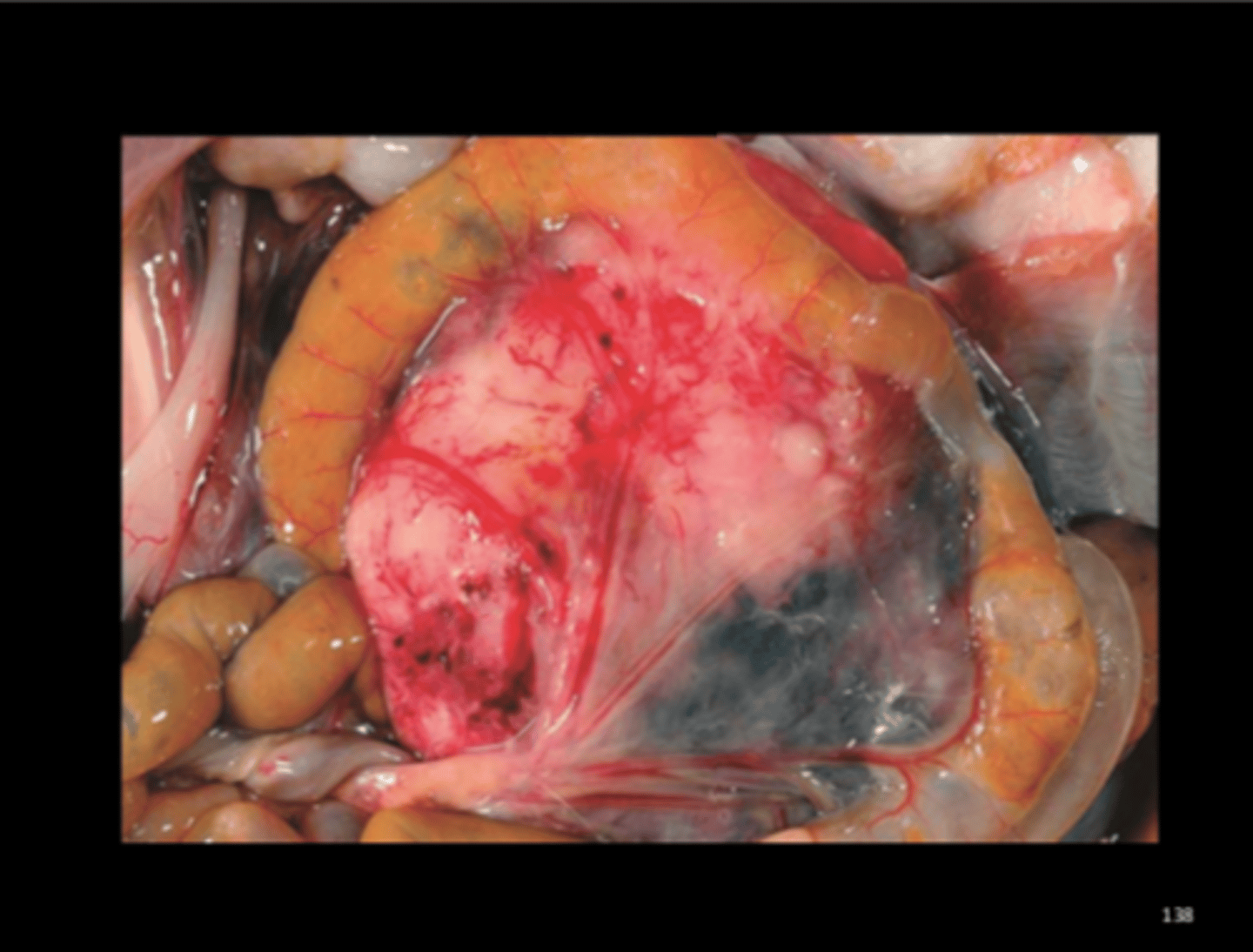
Mesenteric lymph node
Lymphoma
Other than LGL, lymphoid tumors are uncommon in rats. Usually result in enlarged lymph nodes and/or hepatosplenomegaly.
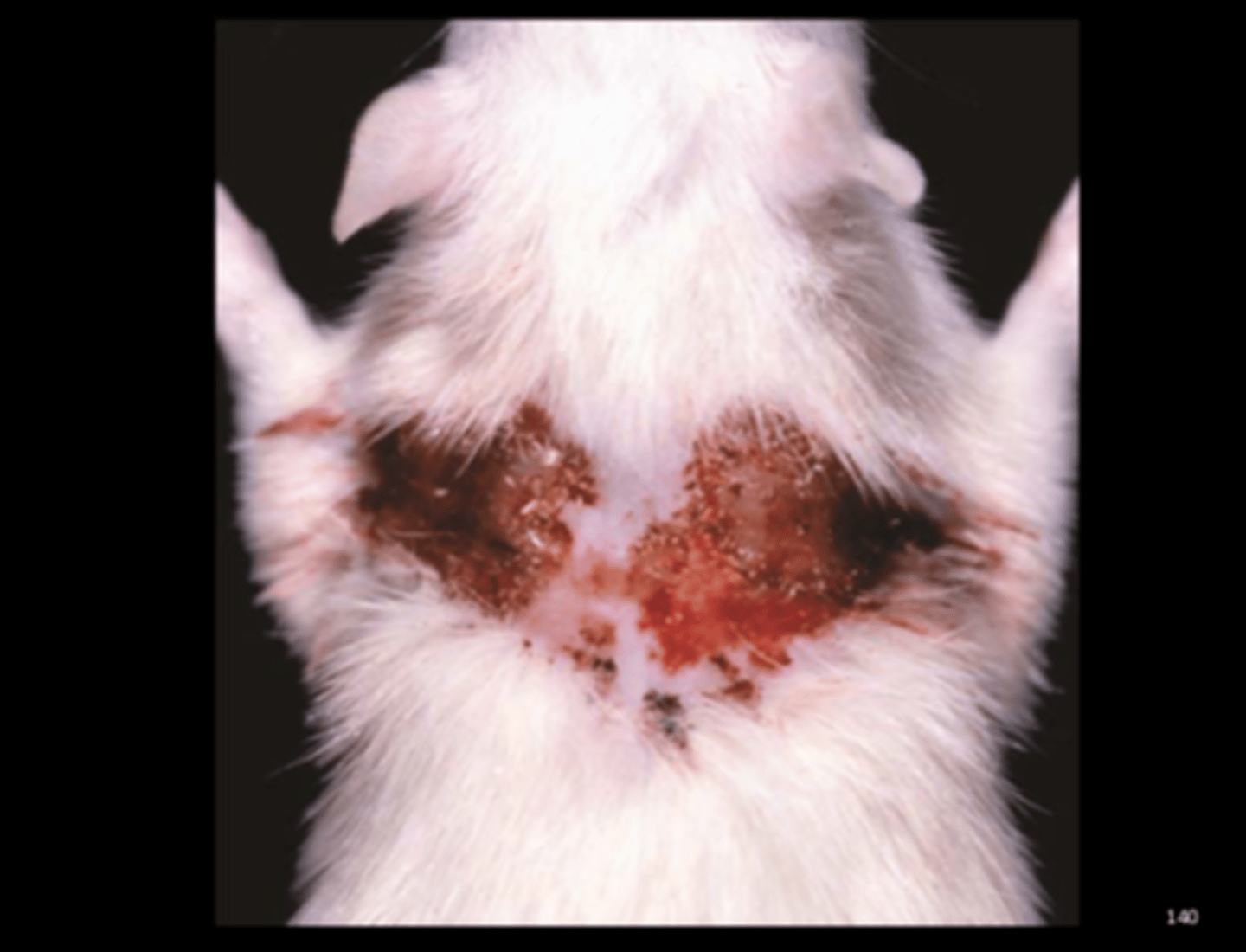
Haired skin
Ulcerative dermatitis
Staphylococcus aureus
Common commensal of skin and mucous membranes. Can be associated with ulcerative skin lesions, especially in NK-deficient beige rats. More often in males. Trauma by persistent scratching is important in disease.
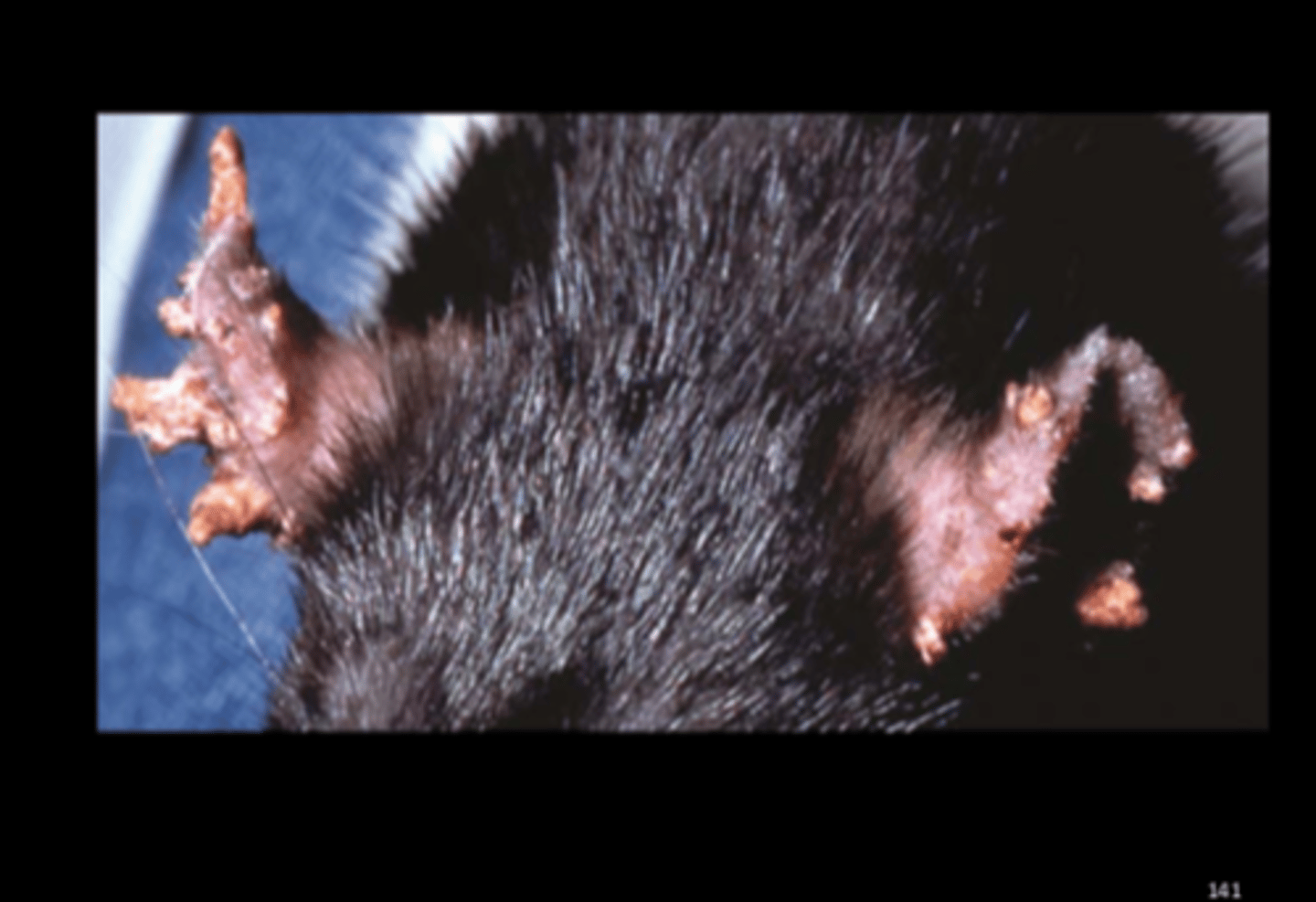
Ear
Proliferative dermatitis
Ear Mange
Notoedres muris
Proliferative dermatitis. Can result in disfigurement of ears. J Wildl Dis 2014;50(1):104-8.
Haired skin (flank)
Yellow crusting
Sucking mite
Ornithonyssus bacoti
Report of lesions in wild black rat (J Comp Path 2017;157:163-173). Histo: lymphoplasmacytic and eosinophilic dermatitis; mites attached

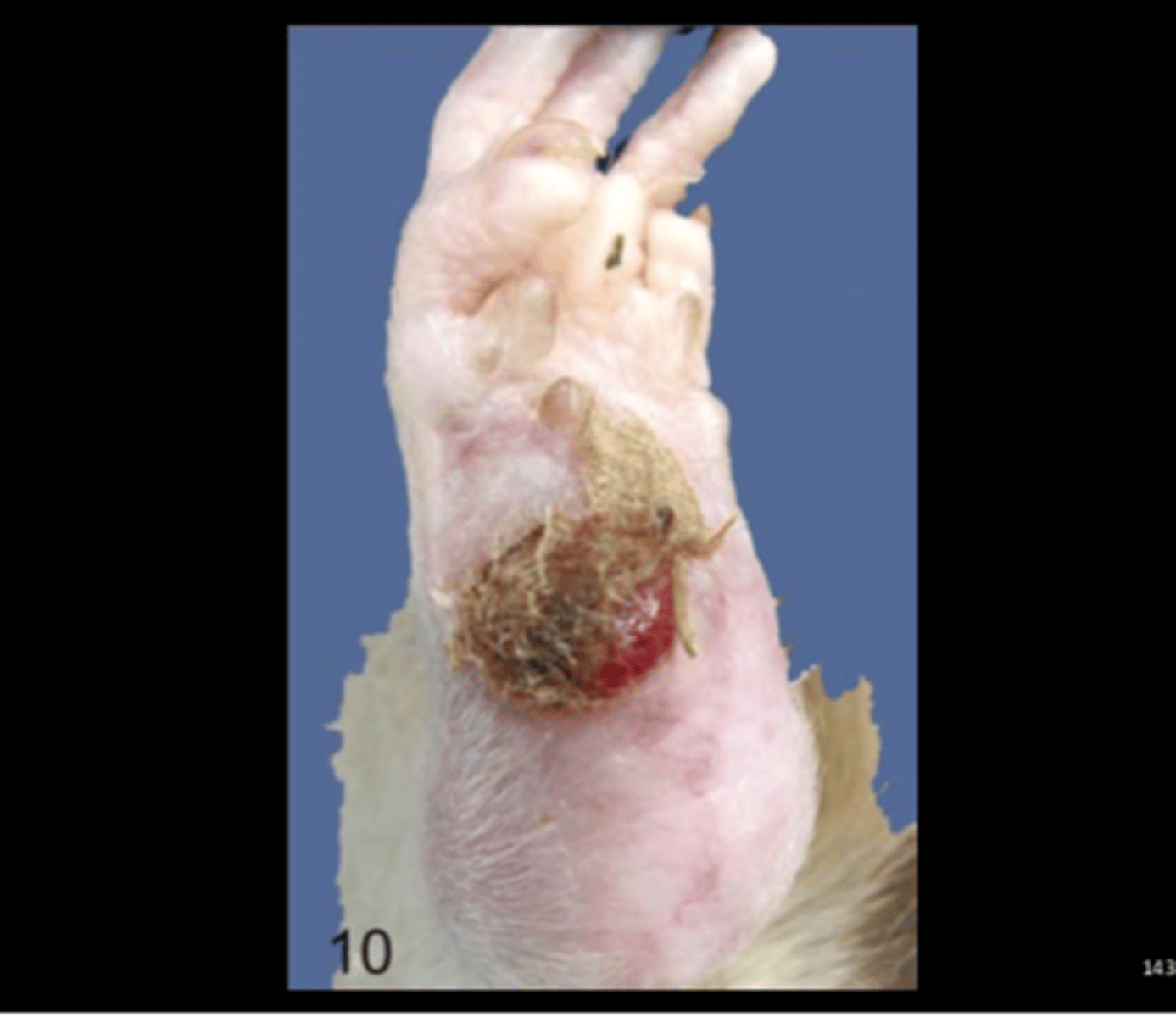
Feet
Ulcerative pododermatitis
Predisposing factors: aged, male, wire cages, ad lib diet.
Gross: ulceration and scabbing of the hock.
Histo: epidermal ulceration, chronic inflammation, granulation tissue; +/‐ hyperostosis of underlying bone. Vet Pathol 2016;53(2):233-243.
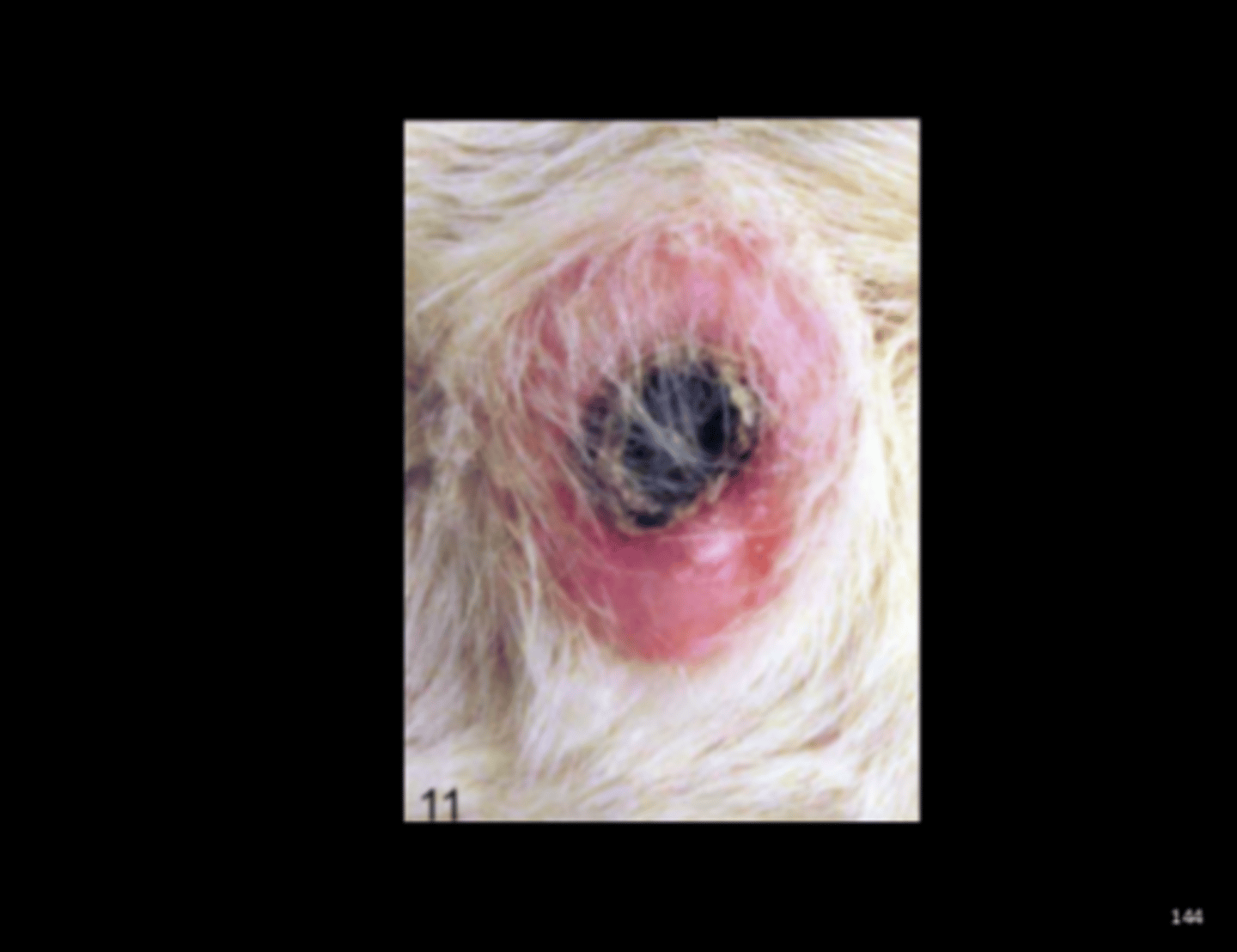
Haired skin
Fibroma (with central ulceration)
Age-associated lesion (Vet Pathol 2016;53(2):233-243).
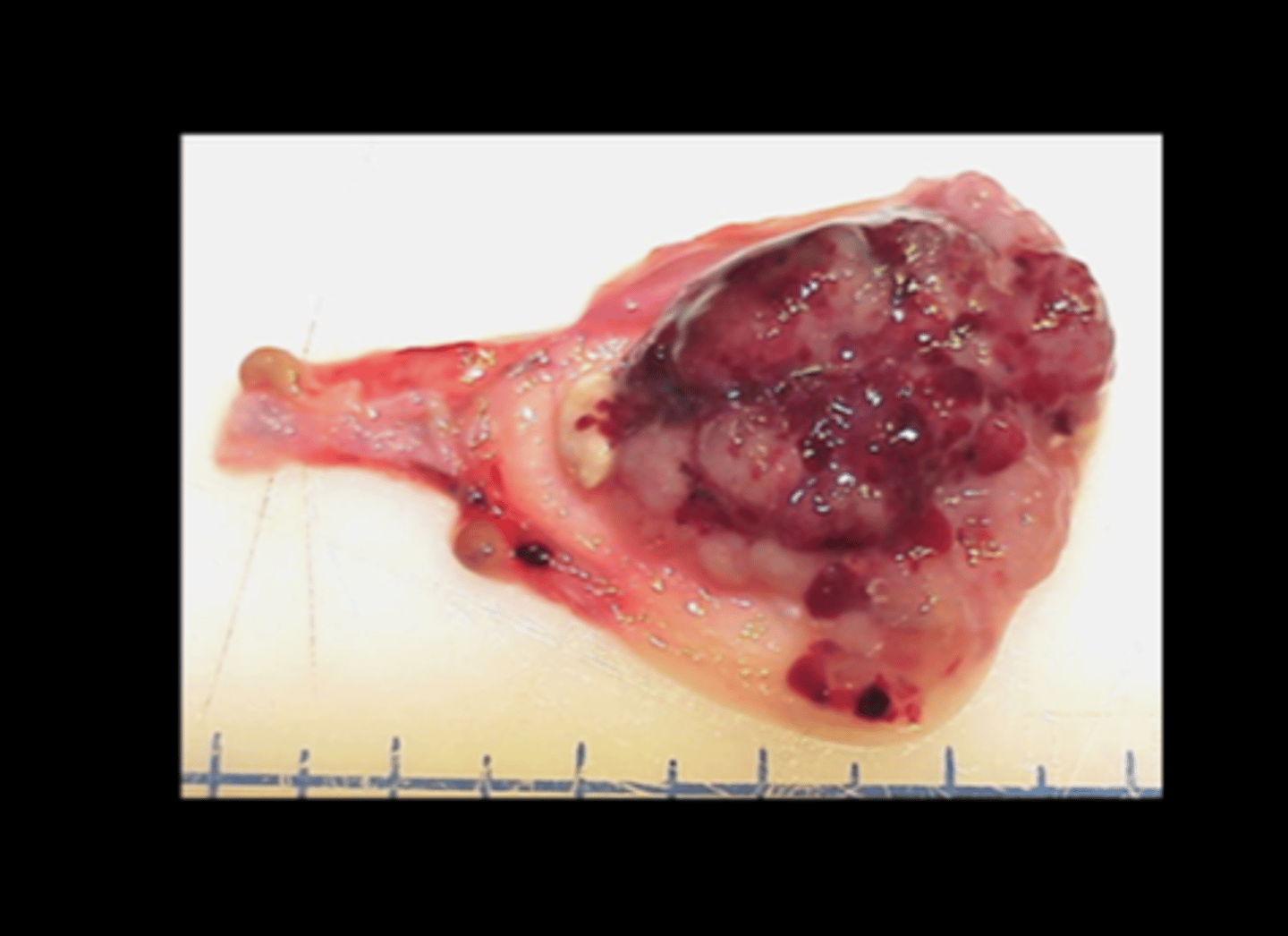
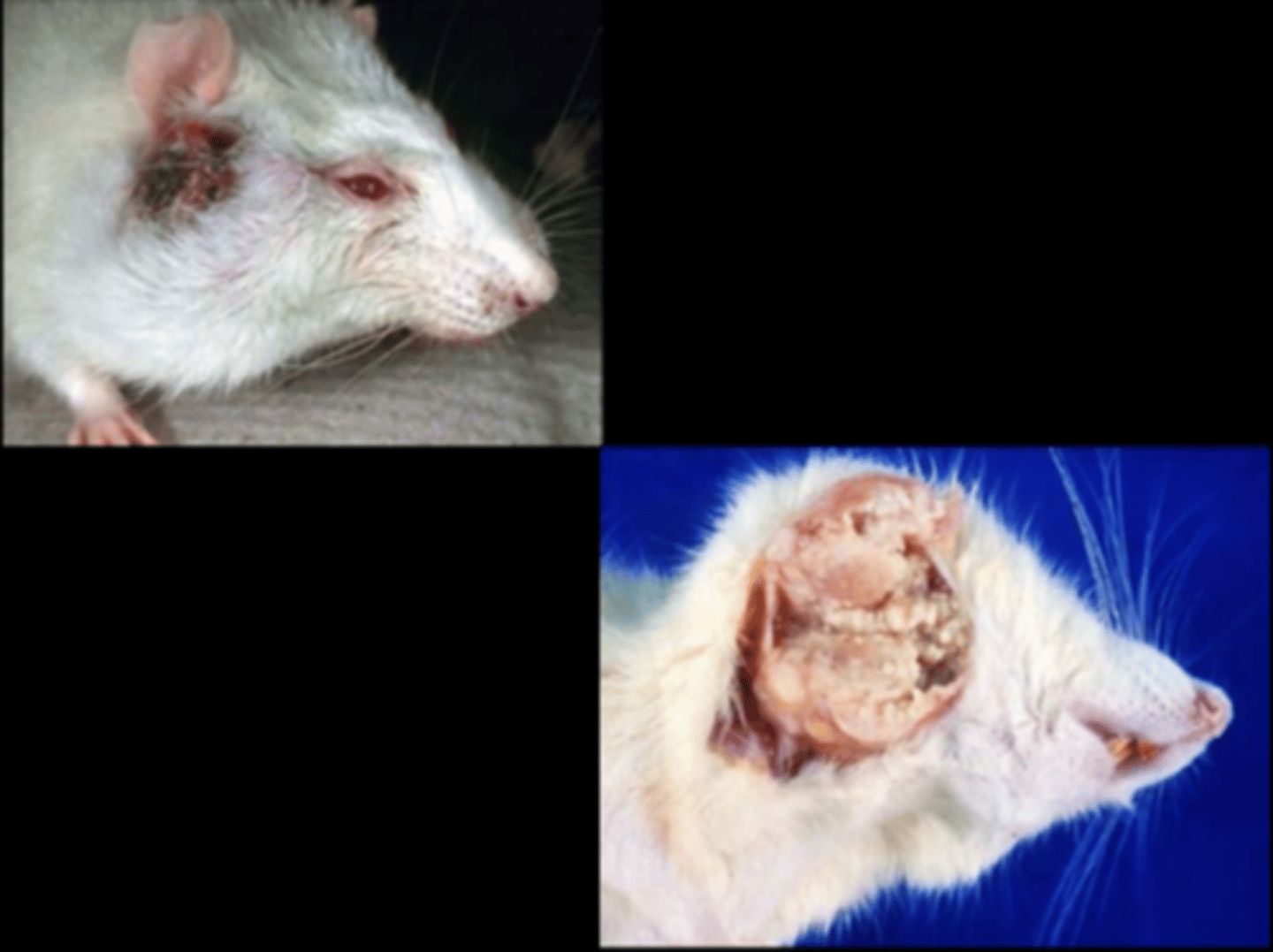
Zymbal's gland
Adenocarcinoma
Zymbal's gland tumor
Zymbal's gland is an external auditory sebaceous gland at ear base. Tumors can grow very large very quickly, locally invade and may invade into brain. Mets to lungs very rarely.
Gross: resemble abscesses, can express caseous material
Histo: proliferative sebaceous and squamous elements
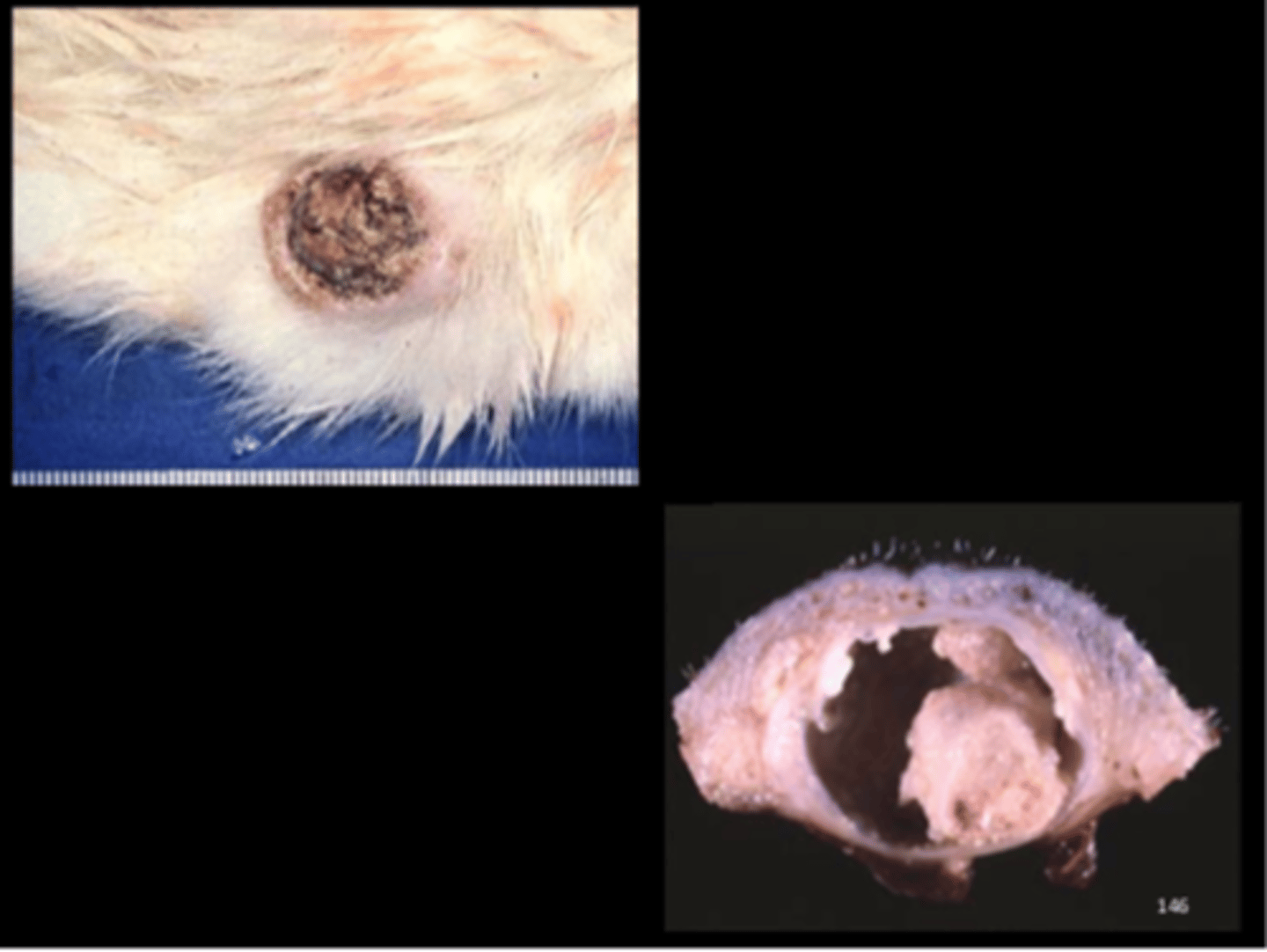
Haired skin
Keratoacanthoma
Common in rats. Derive from squamous epithelium of hair follicle infundibulum. Uncommonly progress to SCC.
Gross: nodular mass, communicates with surface via pore
Histo: well-demarcated mass with large central keratin-filled cavity surrounded by hyperplastic squamous epithelium; central pore
DDx: squamous cell carcinoma, squamous papilloma, squamous cyst
J Toxicol Pathol 2013; 26(3):27S-57S.
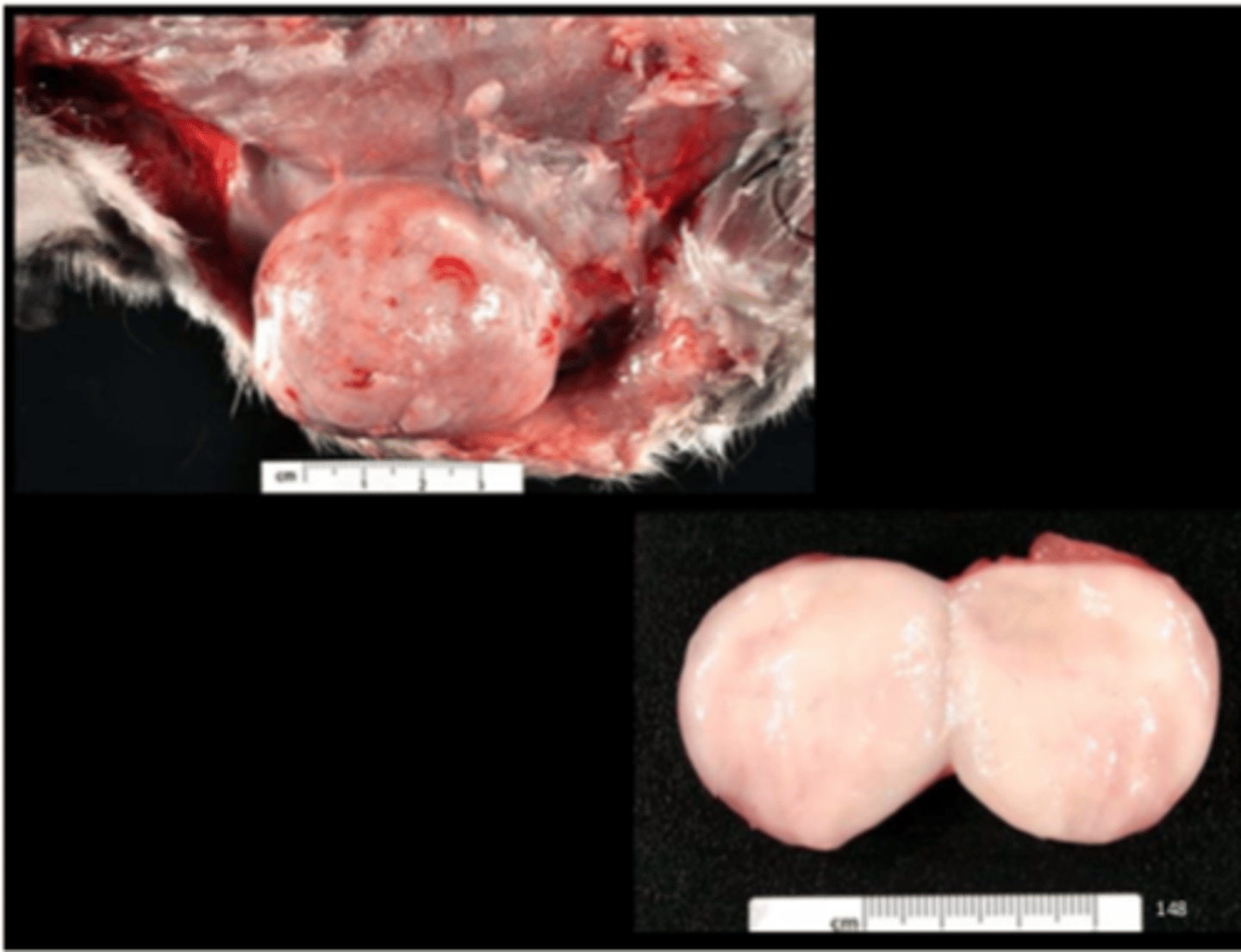
Mammary gland
Mammary fibroadenoma
Most common mammary neoplasm (SD > F344, Wistar). Fibroadenoma >>> carcinoma. Can occur in males also (uncommon).
Predisposing factors: age, genetic, dietary (delayed with caloric restriction), environmental, prolactin level. NO retroviruses implicated. Can occur anywhere except head, tail and distal extremities.
Gross: large, lobulated, firm, usually non‐ulcerated, SQ mass
Histo: well circumscribed, firm, lobular mass with variable amounts of mature collagen and ductular/glandular elements
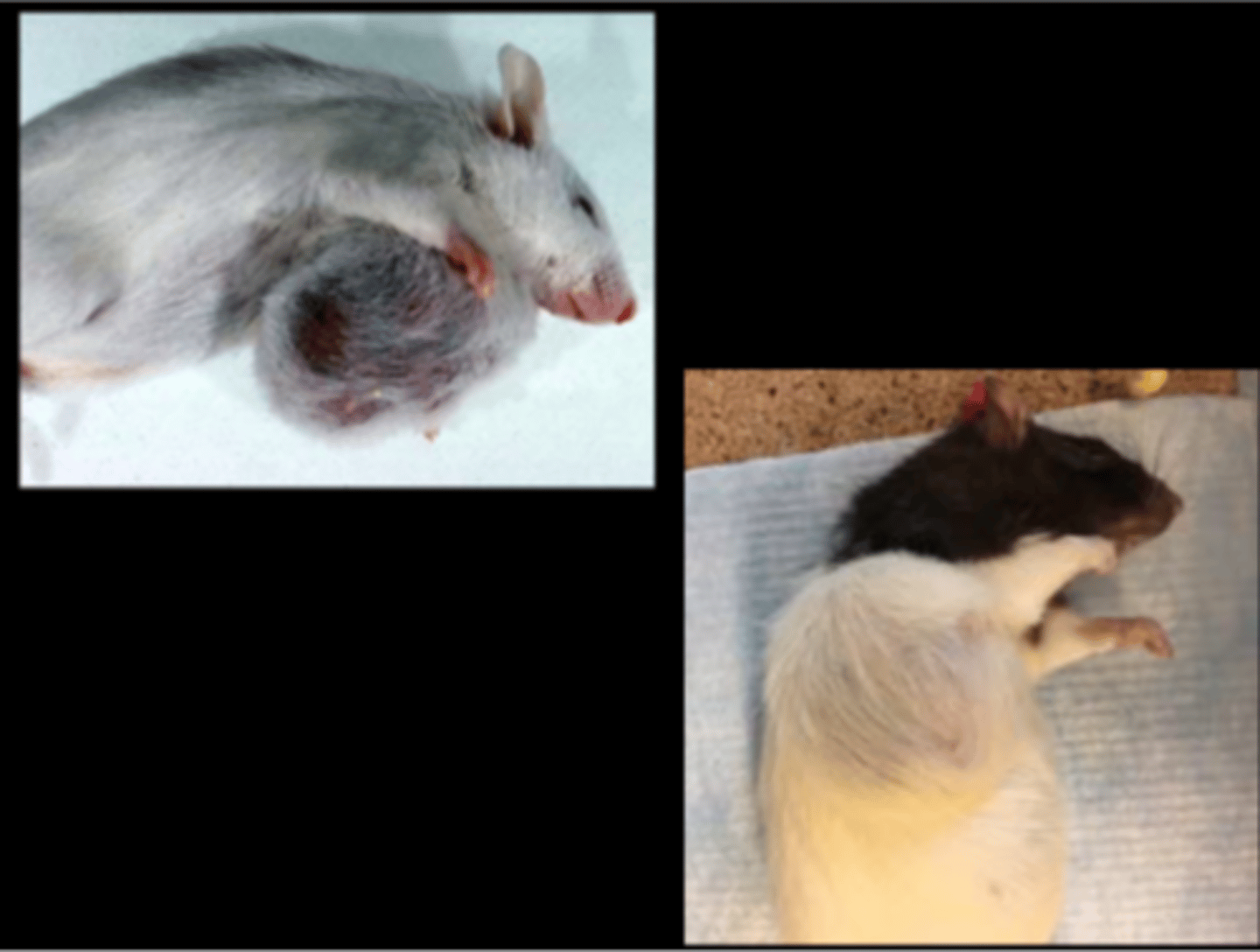
Mammary gland
Mammary fibroadenoma
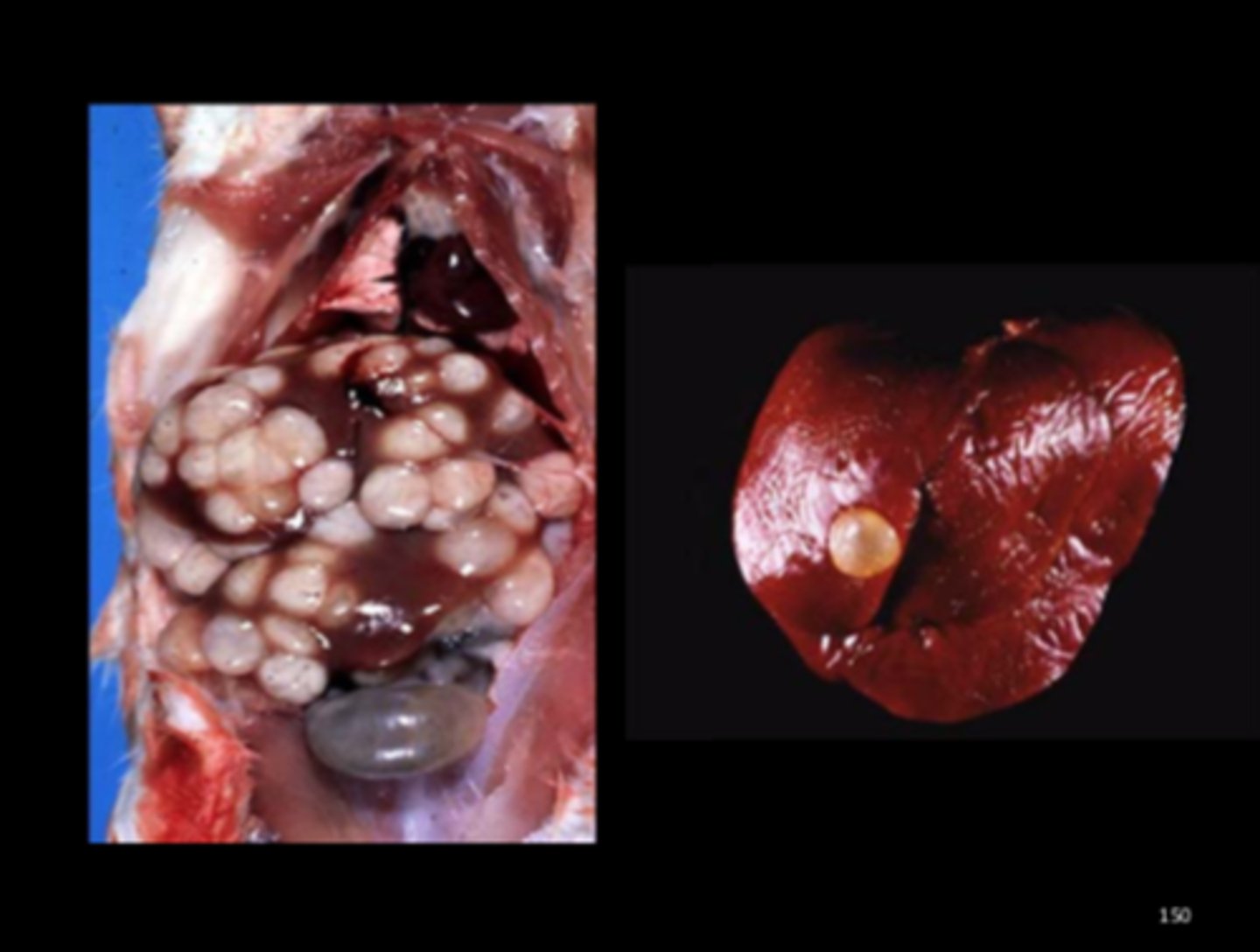
Liver
Multiple hepatic cysticerci
Cysticercus fasciolaris
Rare in lab, occasional in pets, common in wild rats (J Comp Path 2017; 157:163-173). Larval stage of cat tapeworm (Taenia taeniaformis). Transmission: ingestion of eggs in cat feces. Gross: cysts in liver.
Histo: granulomatous inflammation, fibroplasia
Associated lesions: pulmonary arteriolar hypertrophy (Vet Pathol 2010;47: 292-297); fibrosarcoma around the cyst
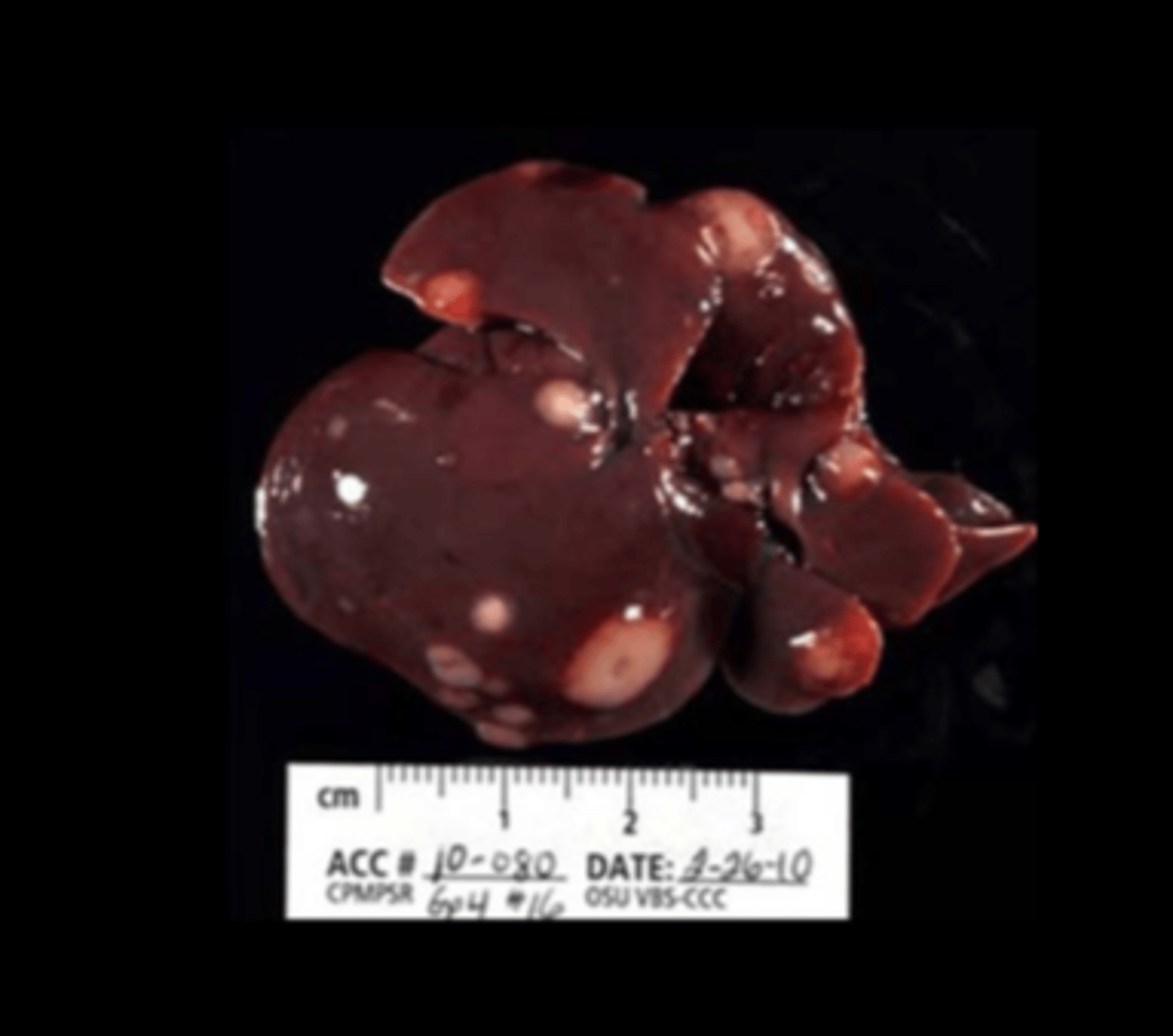
Liver
Histiocytic sarcoma
Most often in SD rats >1yr old.
DDx: lymphoma, fibrosarcoma, metastatic carcinoma, granulomas, abscesses (C.kutscheri, S.pneumoniae, K.pneumonia and P.aeruginosa)
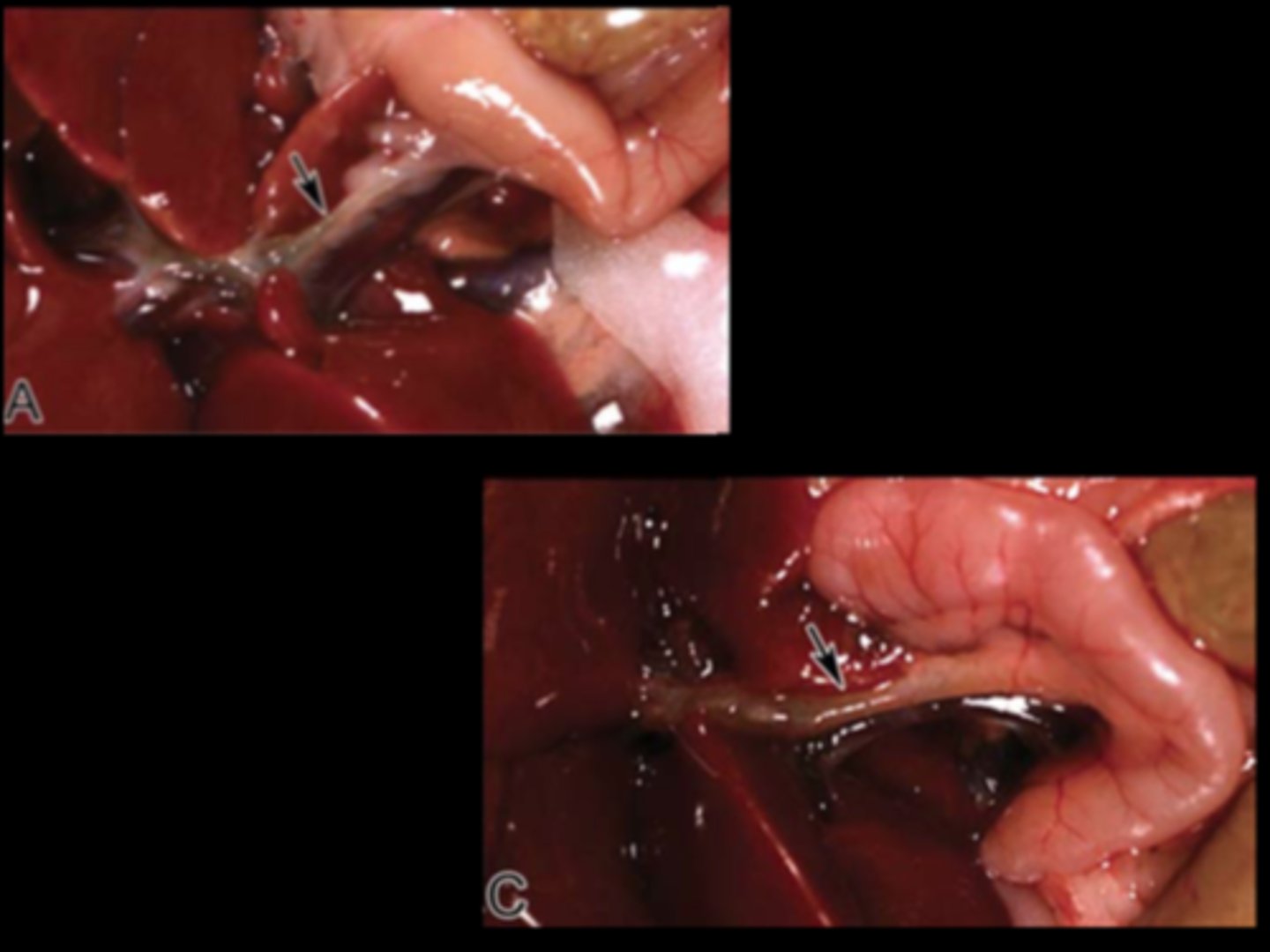
Common bile duct (arrow)
Ectasia and cholangitis (normal in A)
Experimental manipulation
Toxicol Pathol 2015;43:651-661. Recall that rat lacks a gall bladder.
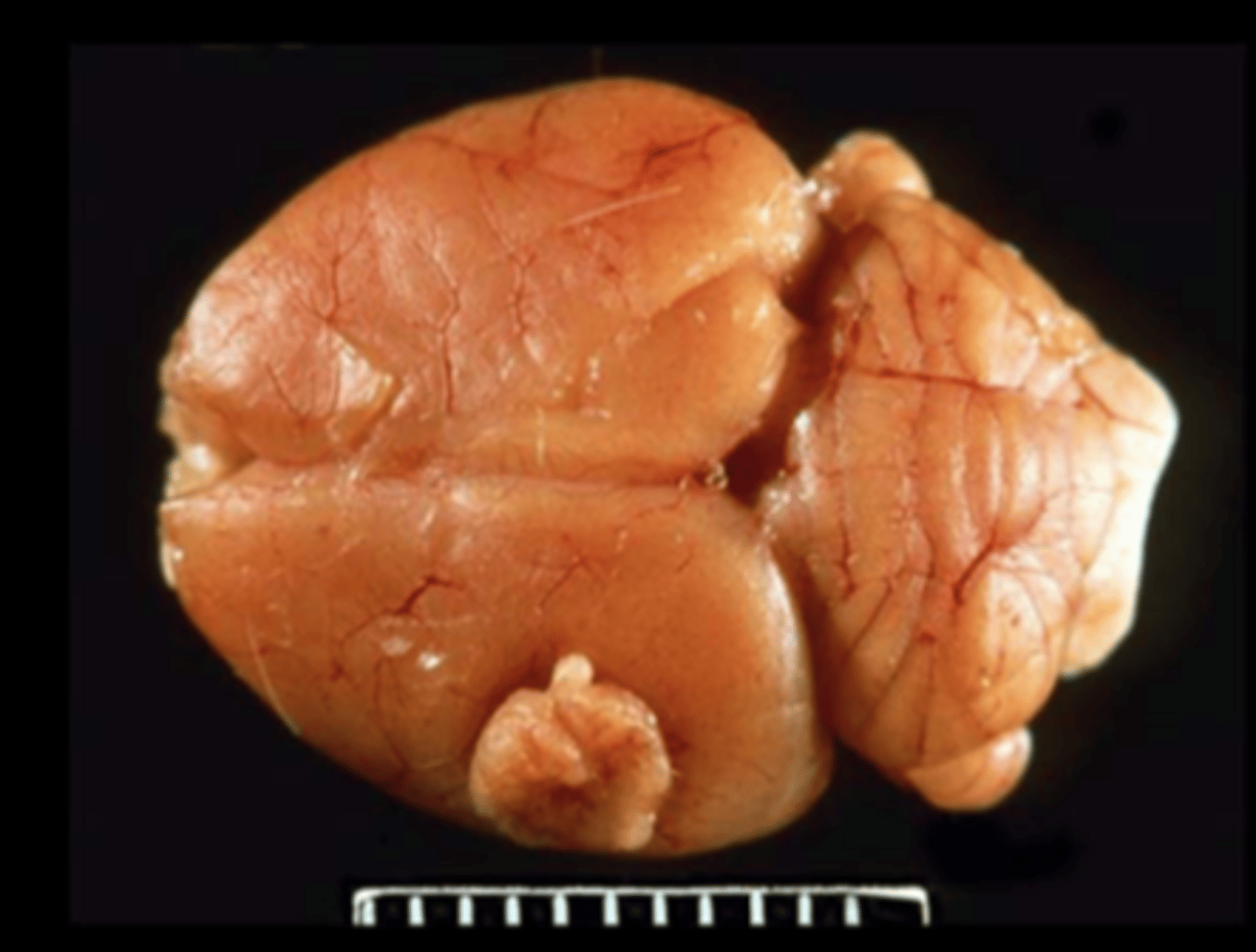
Brain (fixed)
Meningeal granular cell tumor
Granular cell tumor
Most common primary CNS tumor. Can also be in female repro tract. Gross: single or multiple nodules, expansile, compressive, non-invasive Histo: PAS+/diastase resistant granules in neoplastic round cells
IHC+: vimentin, ubiquitin, Iba-1
IHC-: GFAP, synaptophysin
EM: Neoplastic cells containing phagolysosomes
Other species: uterus of mouse; lung/bronchi of horse; tongue and meninges of dog; brain/meninges of ferret
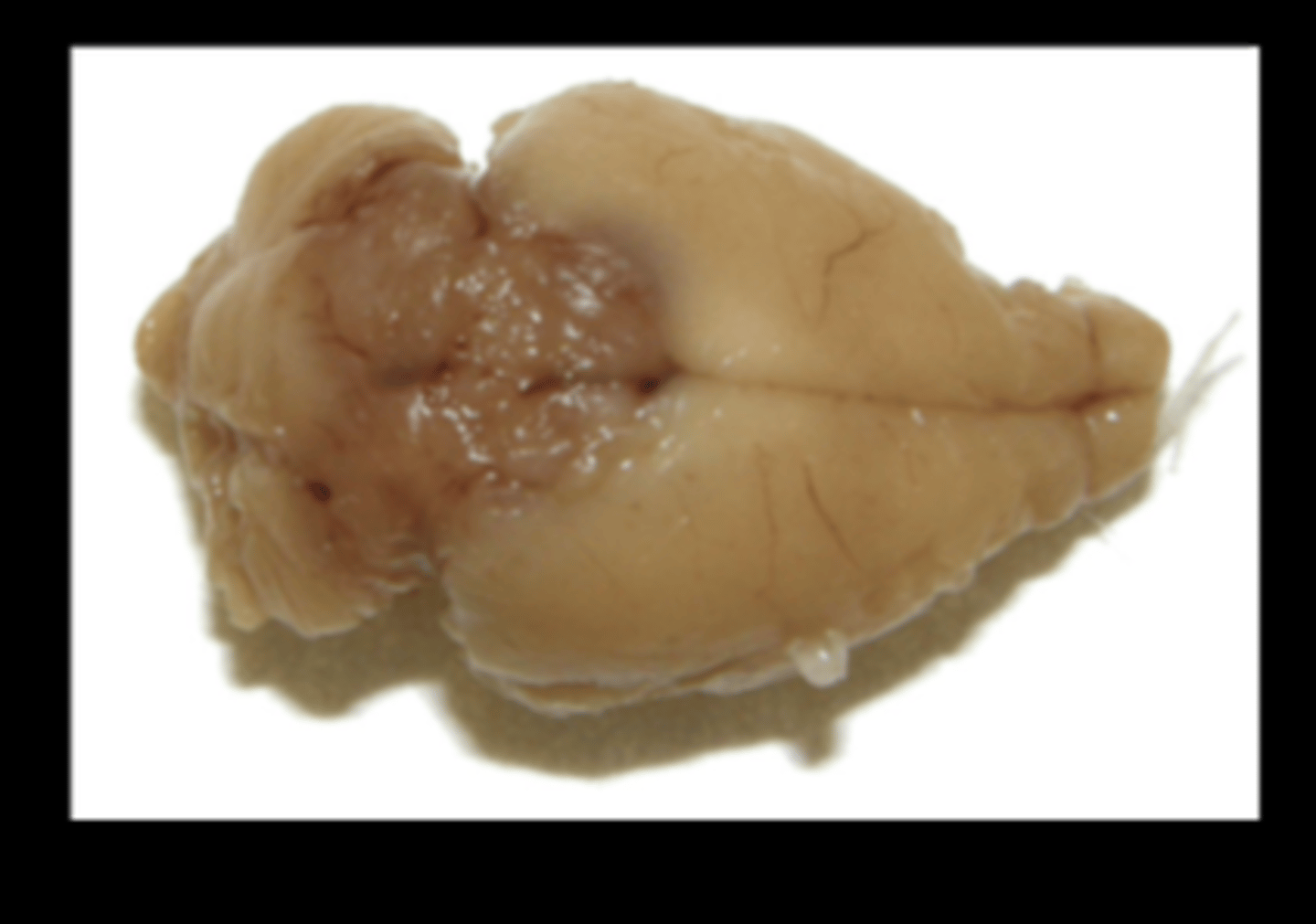
Brain/ pineal gland (fixed)
Malignant pinealoma
Very rare spontaneous lesion in rats and other species. Report of 8 cases (Toxicol Pathol 2015;43:838-843).
Gross: red-brown mass in area between cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum (infiltrating both).
Histo: cellular atypia, high mitotic index, giant cells, necrosis, rosettes and pseudorosettes. IHC+ for synaptophysin, NSE.
Testis
Interstitial cell tumor (Leydig cell tumor)
Very common neoplasm in aged rats, especially F344. Almost all considered benign (malignant if invade structures adjacent to testis or met). Can be bilateral or multiple within one testis.
Associated clin path finding: hypercalcemia in F344
Gross: circumscribed, yellow or white masses, often hemorrhagic
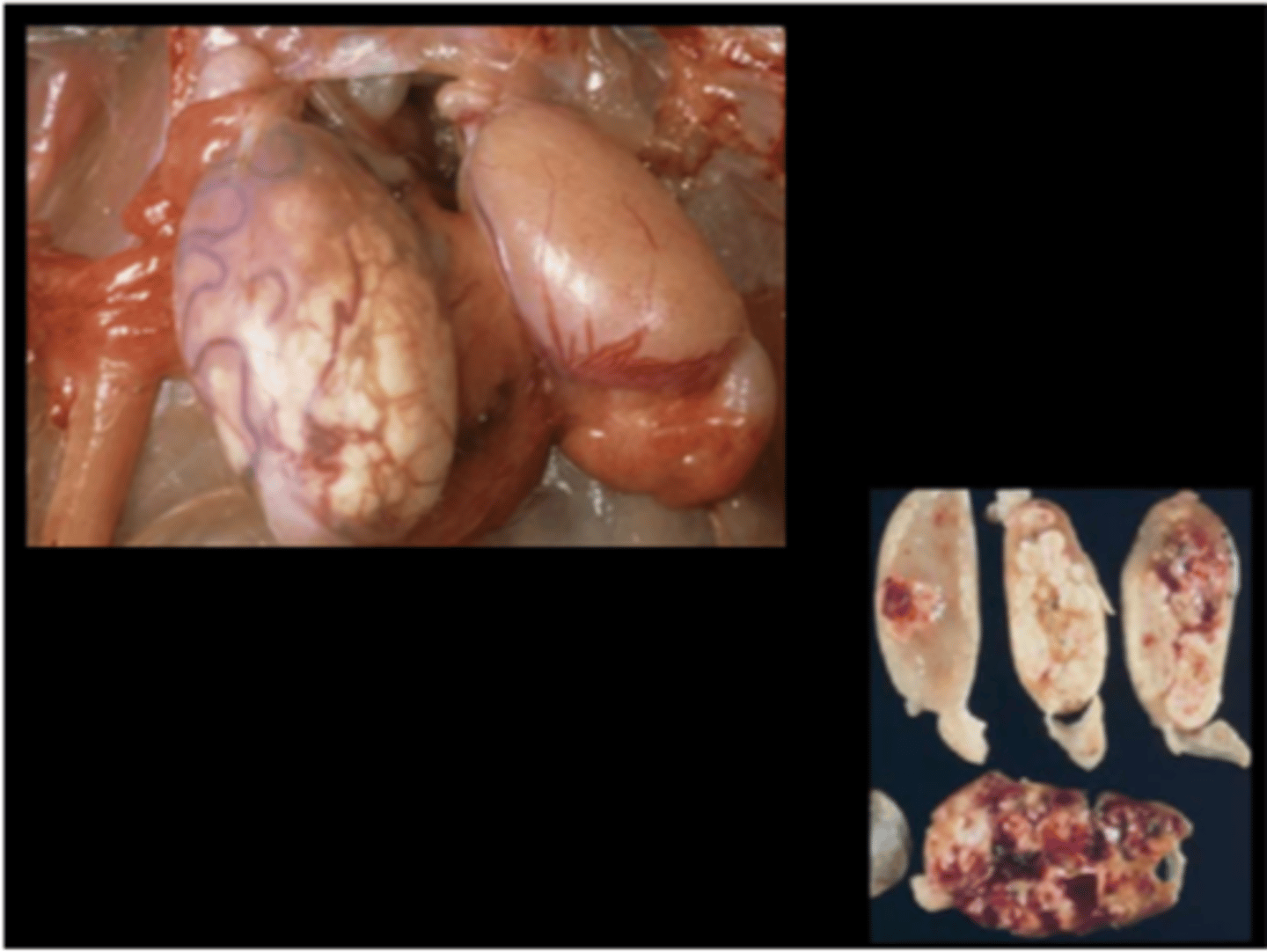
Testis
Bilateral mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis; Unilateral interstitial cell tumor with contralateral testicular atrophy
Interstitial cell tumor and mesothelioma
Look for mesothelioma and interstitial cell tumor concurrently, especially in F344.
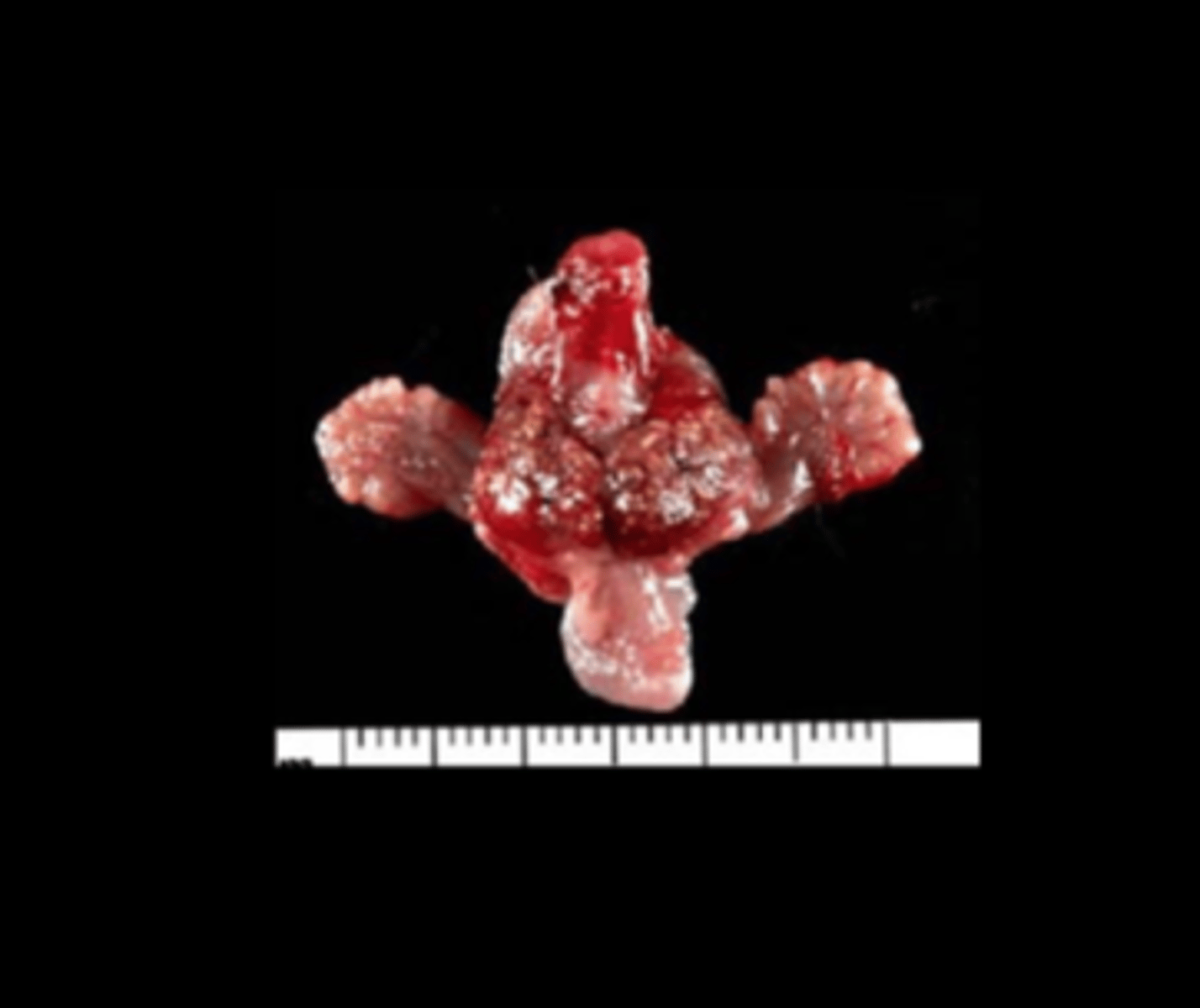
Prostate gland
Normal
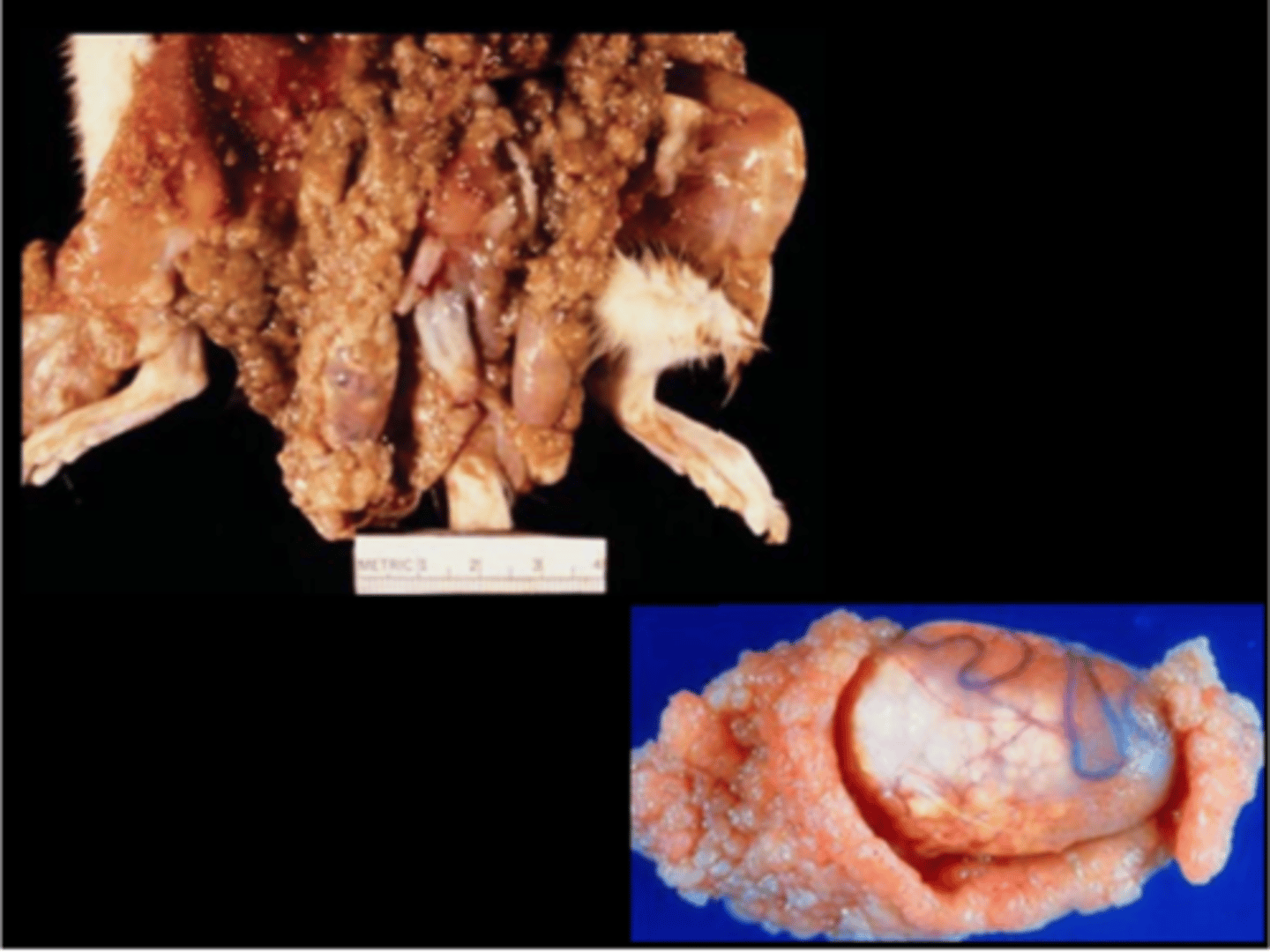
Prostate gland
Diffuse suppurative prostatitis
E.coli
Induced model of bacterial prostatitis.
Lung (fixed)
Diffuse interstitial pneumonia
Sendai virus (Parainfluenza virus-1)
Rare in lab rodents (mice, rats) now. Transmission: aerosol, direct contact. Additive effect with M. pulmonis. Can be zoonotic.
Histo: inclusions in airway cells and syncytia are very suggestive; rhinitis, bronchiolitis, alveolitis with epithelial proliferation, lymphoid cuffing, interstitial fibrosis
DDx: Rat coronavirus, Parainfluenza Virus 3, Pneumonia Virus of Mice
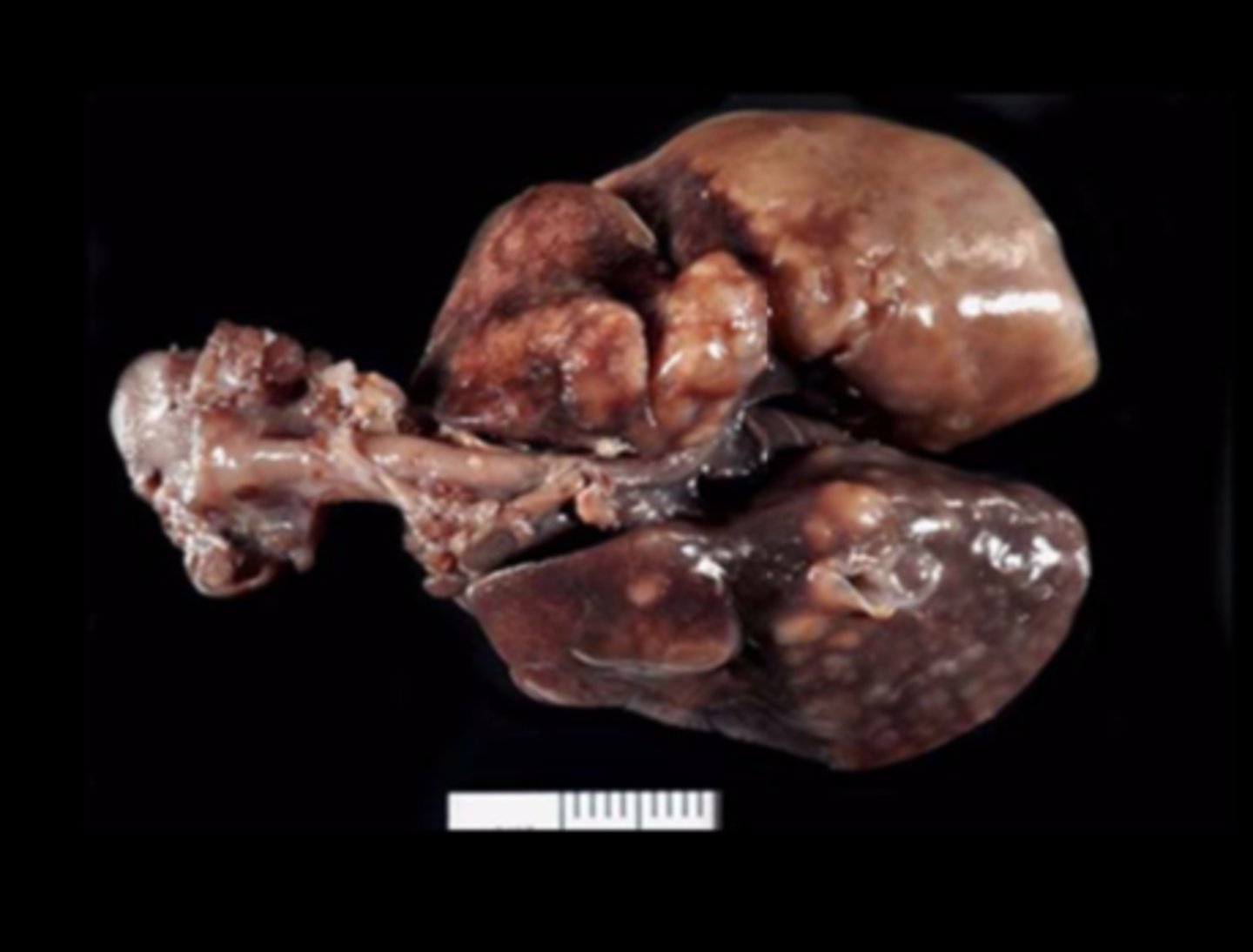
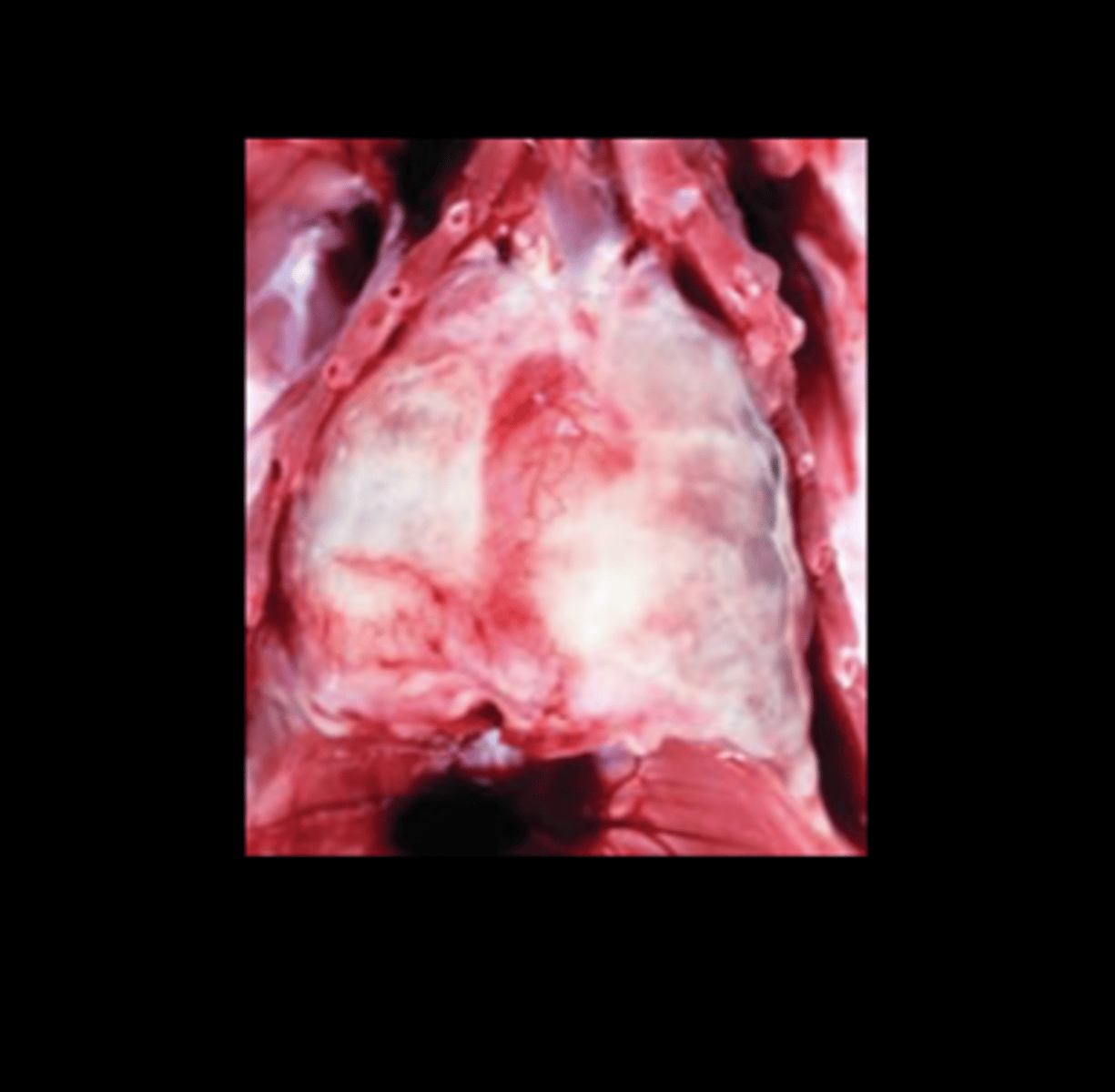
Thorax
Diffuse fibrinous pleuropneumonia
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Can be asymptomatic carriers but concurrent infections or environmental changes may precipitate disease.
Transmission: contact, aerosol, human carriers (ZOONOTIC).
Lesions
- Fibrinosuppurative polyserositis (always consider Strep with fibrin) - Suppurative to fibrinosuppurative bronchopneumonia
- Fibrinosuppurative meningitis, rhinitis, otitis media
- Embolic suppurative lesions (liver, spleen, kidney)
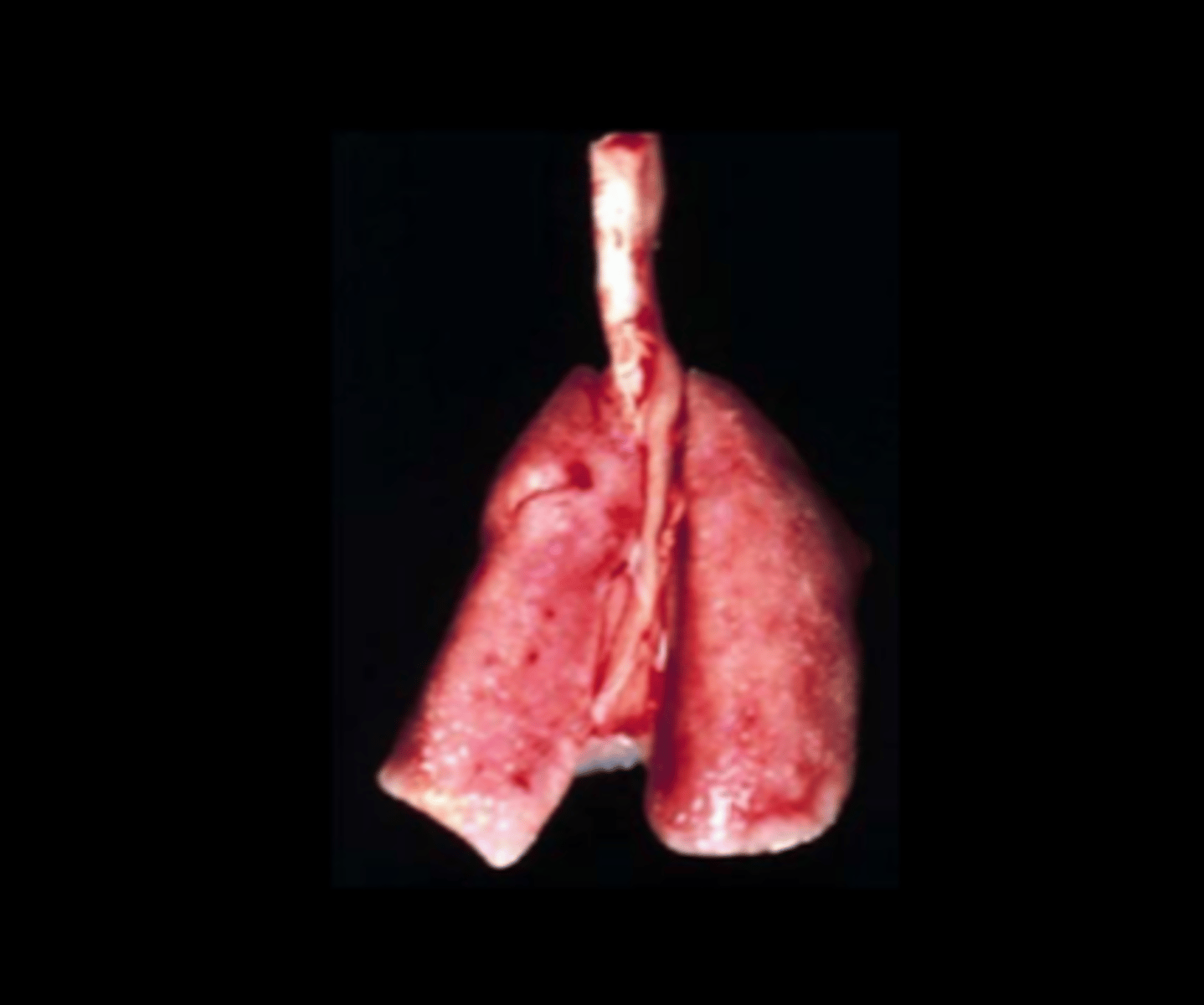
Lung
Diffuse granulomatous interstitial pneumonia
Pneumocystis carinii, Pneumocystis wakefieldiae
Transmitted by contact, dirty bedding, fomites. Disease in immunocompetent and immunodeficient animals.
Lesions depend on immune status:
- Immunodeficient: lungs fail to collapse; raised subpleural foci; intra- alveolar, foamy eosinophilic material with intralesional trophozoites, cysts
- Immunocompetent: lymphohistiocytic interstitial pneumonia and perivasculitis (formerly "rat respiratory virus"; Vet Pathol 2009;46:992- 999; Comp Med 2011;61:45-59; Vet Pathol 2012;49:440-452).
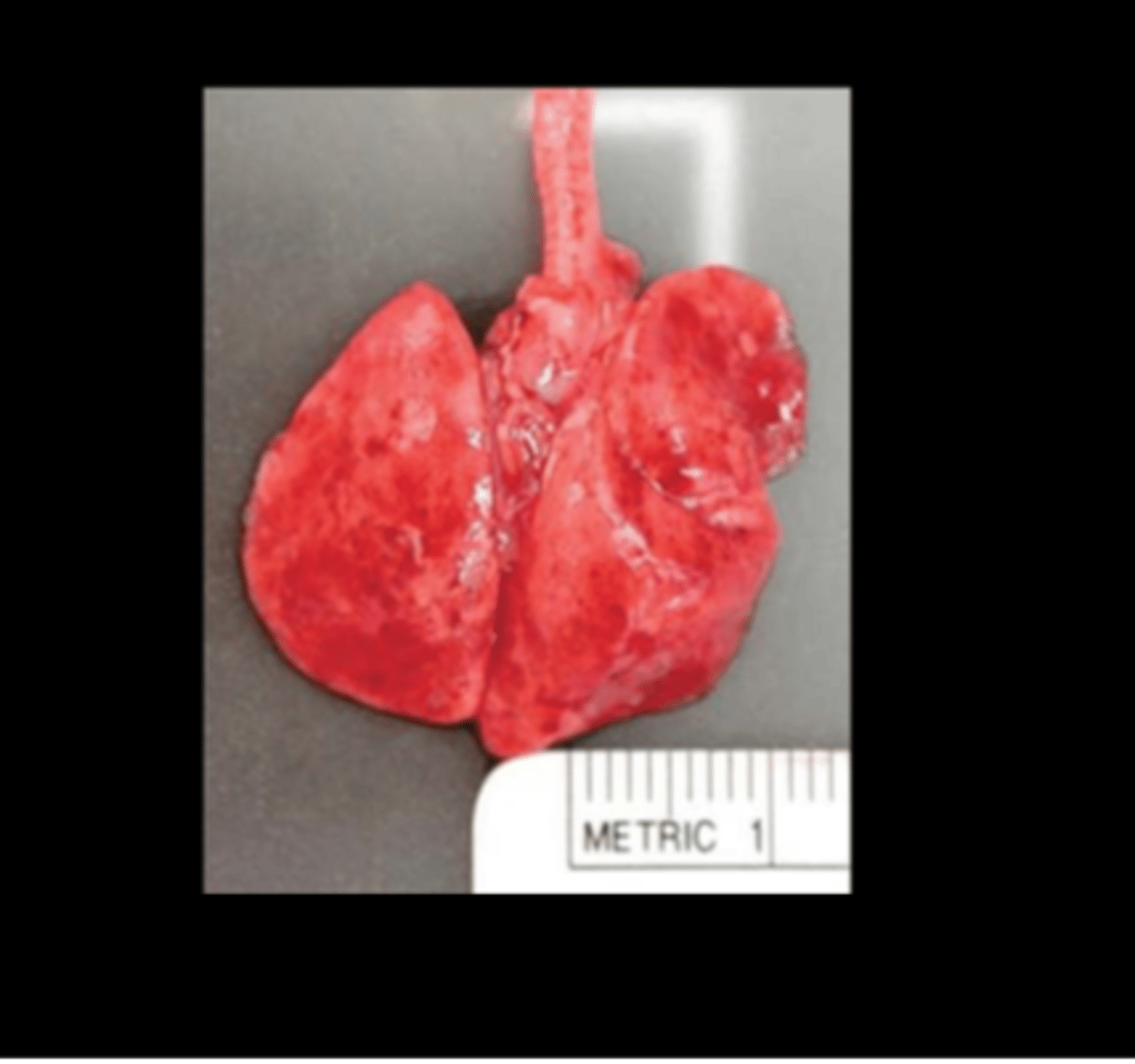
Lung
Granulomatous to eosinophilic pneumonia
Eosinophilic Granulomatous Pneumonia of Brown Norway Rats
Very high prevalence in Brown Norway rats of all ages, from multiple locations, and of any health status, including gnotobiotic.
Cause unknown, may be related to a hypersensitivity reaction.
Gross: multiple pale tan/gray foci throughout parenchyma
Histo: granulomatous pneumonia with epithelioid cells and/or multi- nucleated giant cells; edema; perivascular and peribronchiolar eosinophils Special stains are negative, as are cultures and serology.
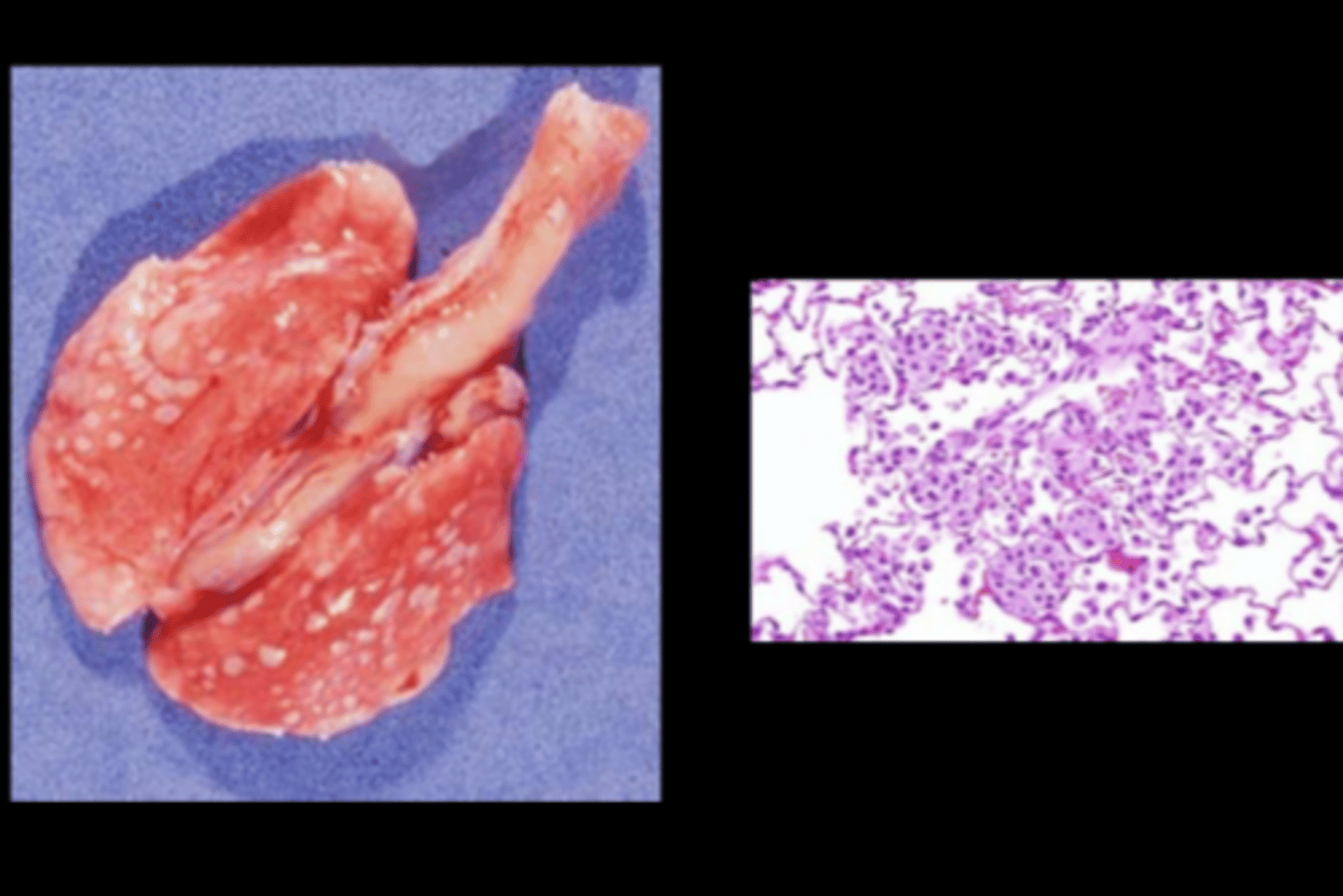
Lung
Alveolar histiocytosis
Common in old rats (esp F344 and SD) and reported in wild rats (J Comp Path 2017;157:163-173). Cause unknown but increased with high fat diet. Histiocytes contain FFA, cholesterol, phospholipids. NOT thought to be infectious.
Gross: 1‐3mm pale tan/yellow foci on pleural surface
Histo: subpleural clusters of foamy macrophages in alveoli
DDx: clusters of foamy macs seen in inhalation or gavage studies
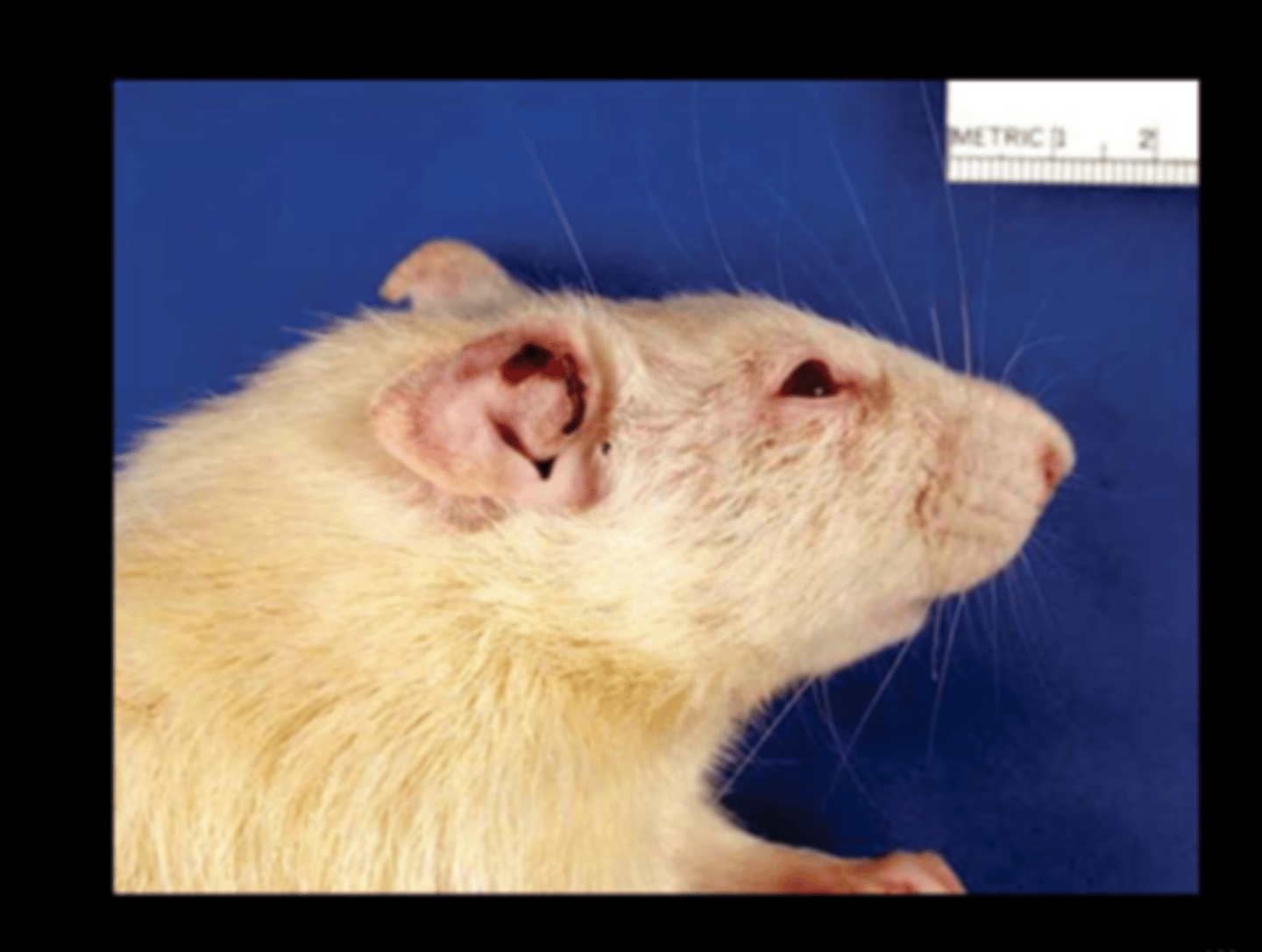
Ear
Granulomatous auricular chondritis
Auricular chondropathy
Can be spontaneous or associated with metal ear tags or trauma. Presumed immune‐mediated reaction (to Type II collagen?).
Gross: nodular thickening and distortion of pinna (often bilateral)
Histo: granulomatous inflammation with destruction of cartilage, nodular cartilage hyperplasia, osseous metaplasia
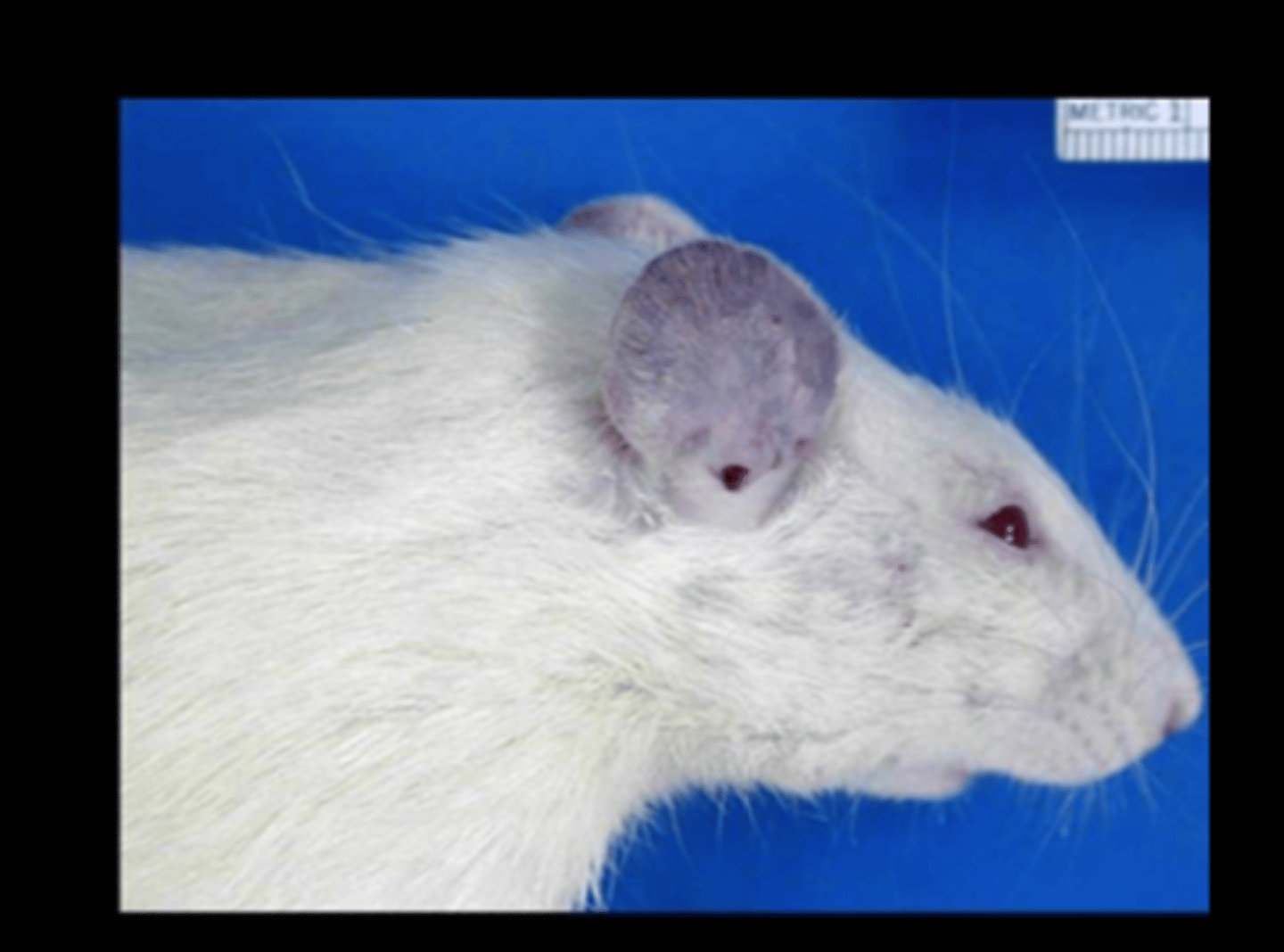
Ear
Granulomatous auricular chondritis
Auricular chondropathy
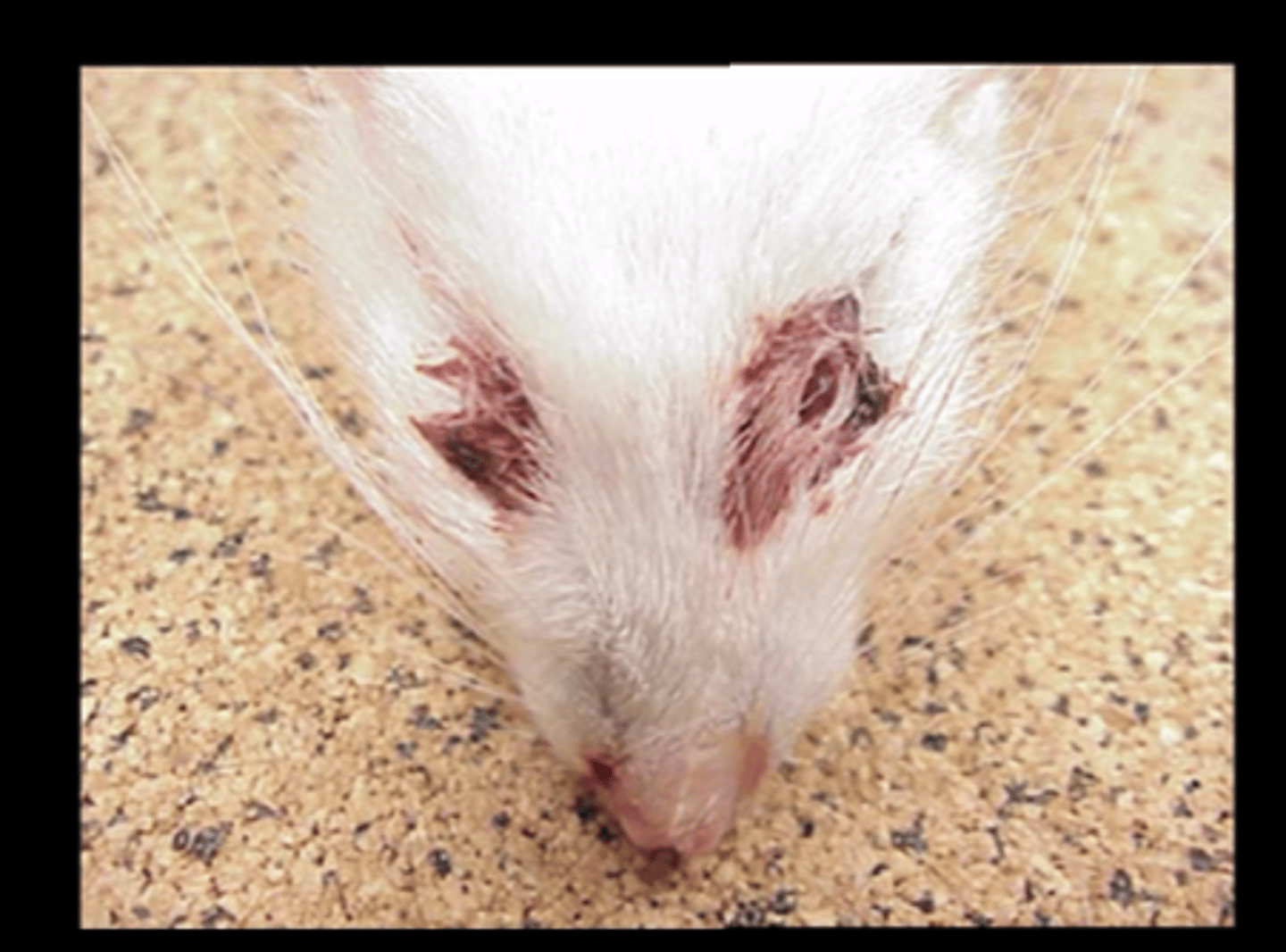
Eye
Chromodacryorrhea
Common response to stress and illness. Due to porphyrin pigments from Harderian gland.
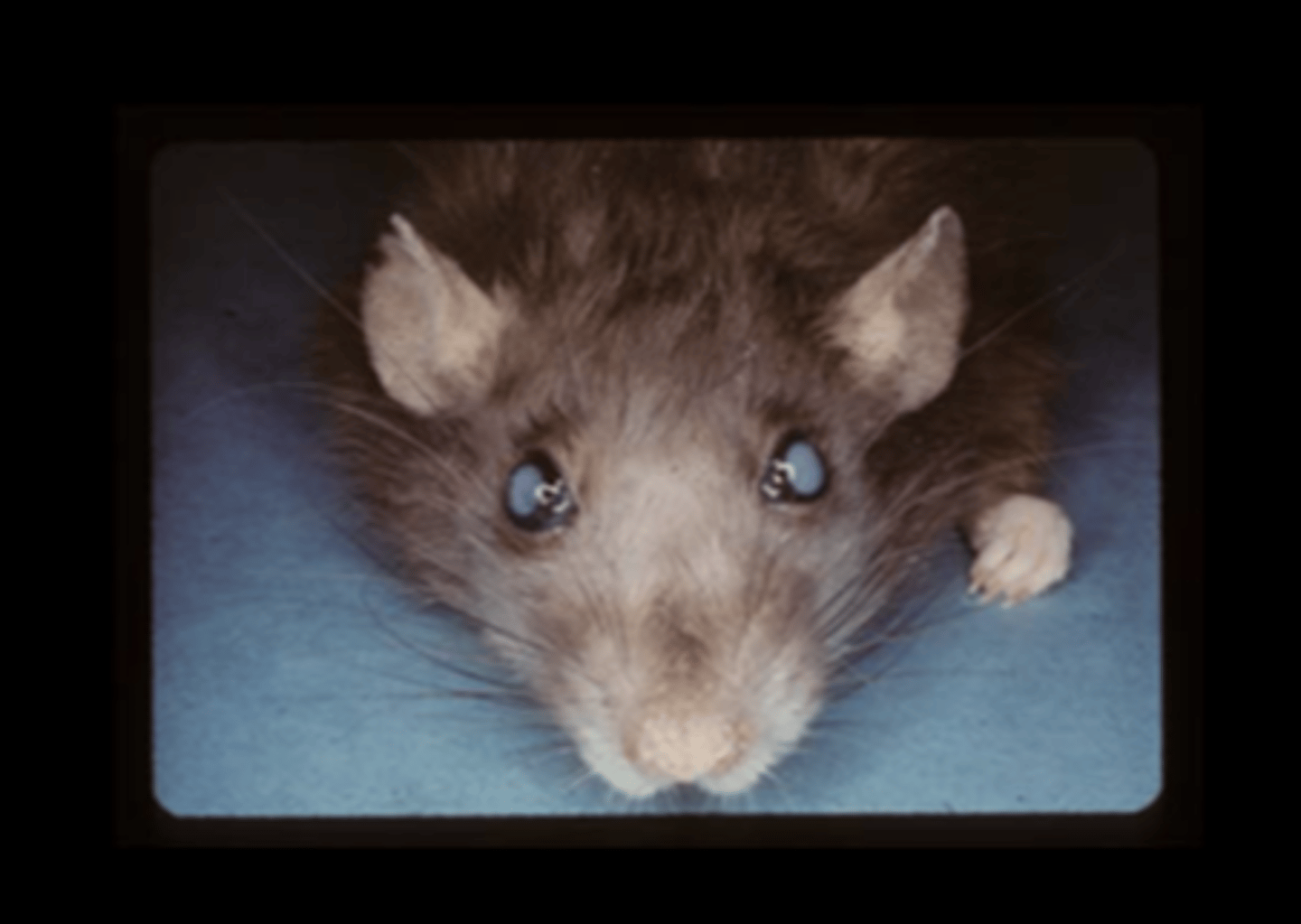
Eye
Cataracts
Inherited (ICR or inherited cataract rat is a model) or associated with aging, radiation, excessive light exposure (albino r

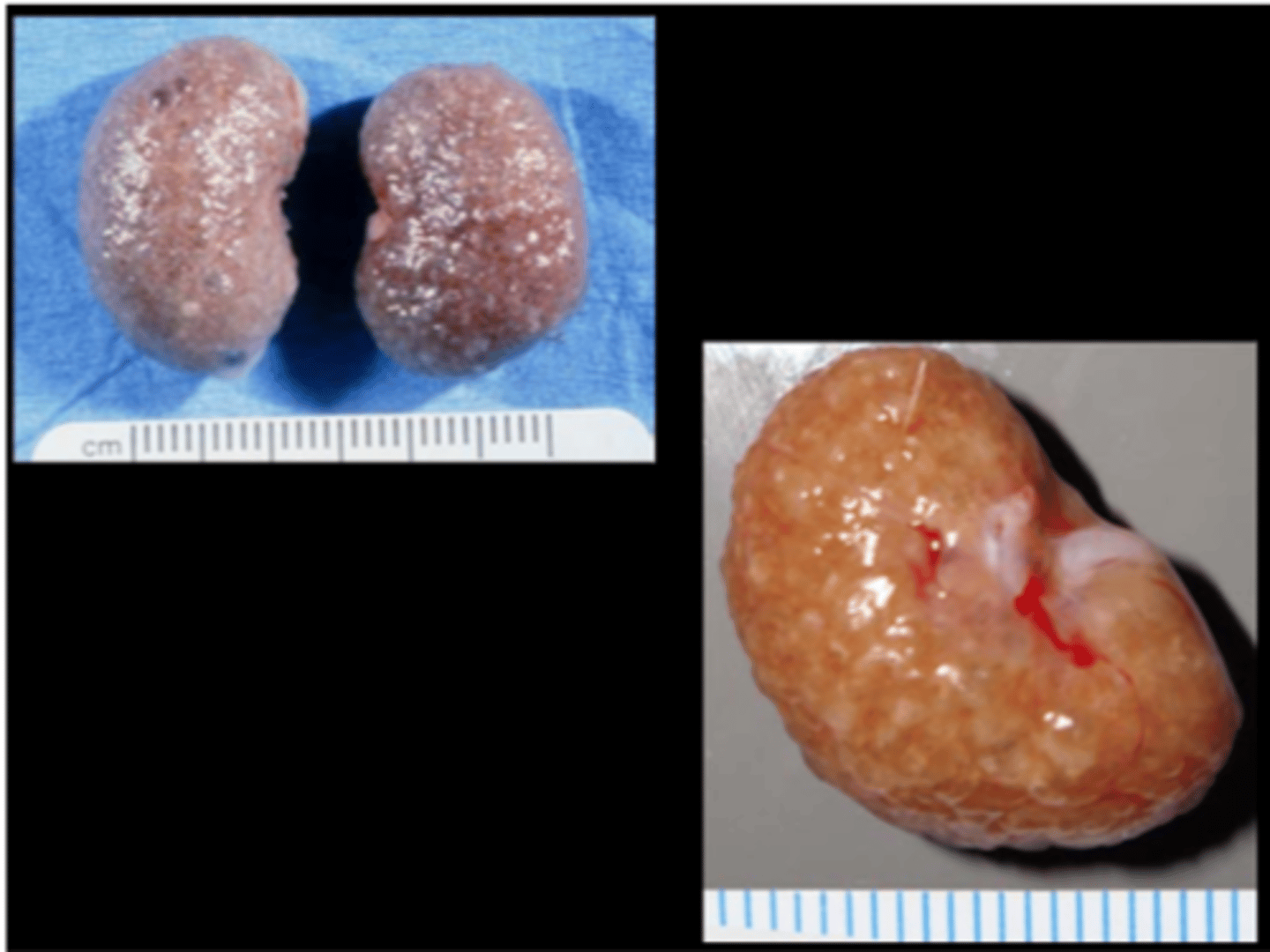
Kidney
Chronic fibrosing interstitial nephritis
Chronic progressive nephropathy (CPN)
aka Chronic Renal Disease, Old rat nephropathy
Most important disease of rat kidney. Common cause of early death on carcinogenicity studies and can be difficult to distinguish from drug‐ related effects in toxicity studies. Prevalence very high, especially in males (earlier onset, more severe). Lesions may begin by 3-6 months of age in some strains (F344, SD, hypertensive strains).
Predisposing factors: male, age (>1yr), diet (ad lib, high protein), immune factors, high prolactin, microbial status
C/S: progressive renal malfunction/failure
Gross: initially enlarged then shrunken, pale, irregular‐shape, surface pitting, +/‐ small cysts
Histo
- Glomeruli: thickening of tufts by eosinophilic material, synechiae, basement membrane thickening, glomerulosclerosis
- Tubules: protein casts, dilated with flattened epithelium, degeneration/regeneration, mineralization
- Interstitium: fibrosis, lymphoplasmacytic aggregates
Secondary hyperparathyroidism may occur, with mineralization (lung, stomach, blood vessels, pleura), fibrous osteodystrophy
Kidney
Nephrocalcinosis
Deposition of calcium phosphate in renal tissue. High prevalence. Predisposing factors: female, strain (BDIX and F344 >> SD, Wistar), diet (high levels of Ca, phosphorus, low Ca:phosphorus ratios or Mg)
Gross: large deposits may appear as pale areas, may crunch when cut Histo: deposition most frequently at corticomedullary junction, in tubular epithelial cells and tubular lumina
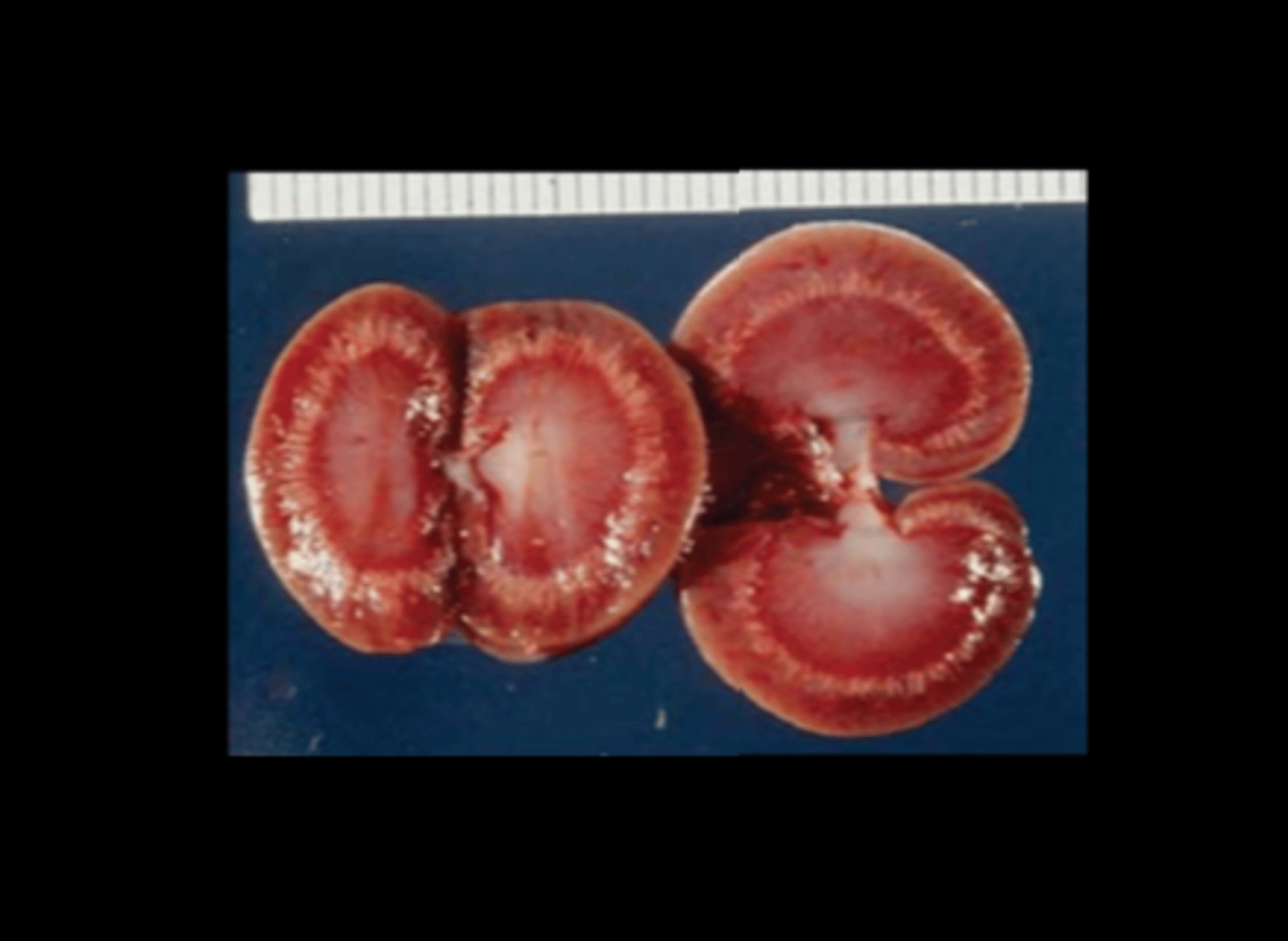
Kidney
Hydronephrosis
SD, Brown Norway, Zucker and Gunn strains especially. Often incidental. Often right kidney in males (due to passage of internal spermatic vessels across ureter?).
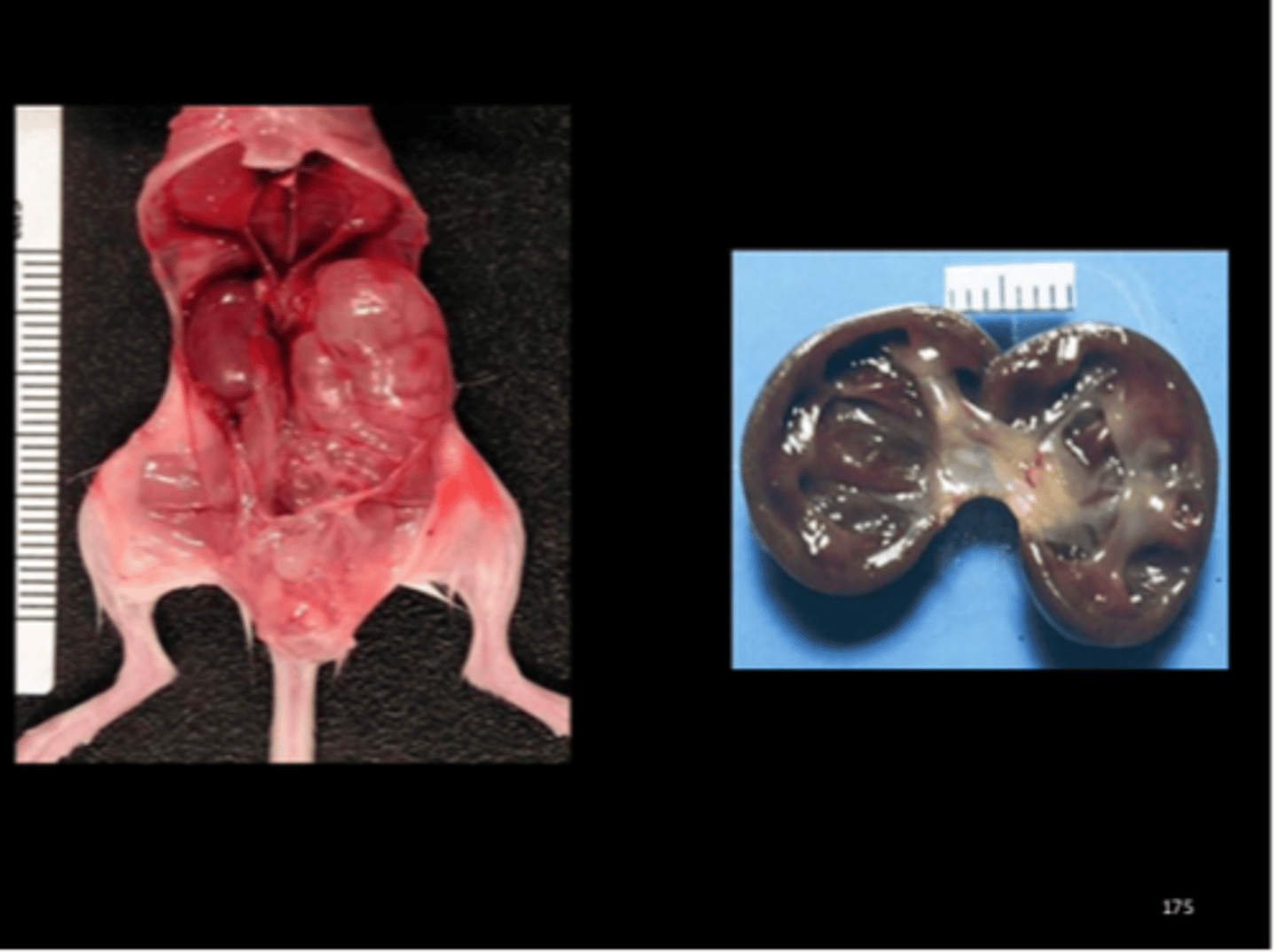
Kidney
Unilateral nephroblastoma
Model for Wilm's tumor in humans. Rare except in subline of SD (genetically predisposed, 14% incidence) but can be chemically-induced (ENU, MNU). Histo has 3 components (blastema, stroma, immature epithelium forming tubules). J Toxicol Pathol 2014;27:91-95.
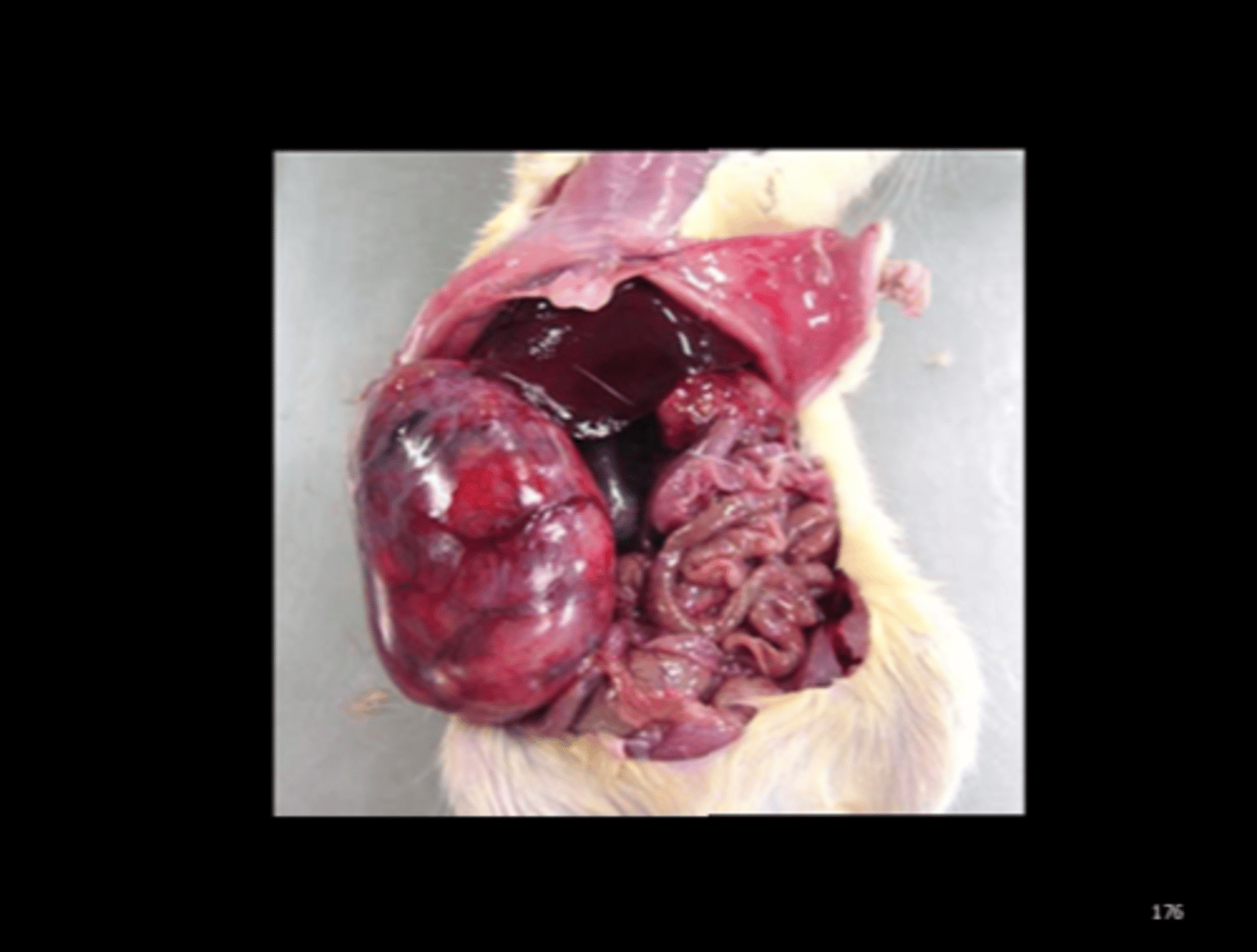
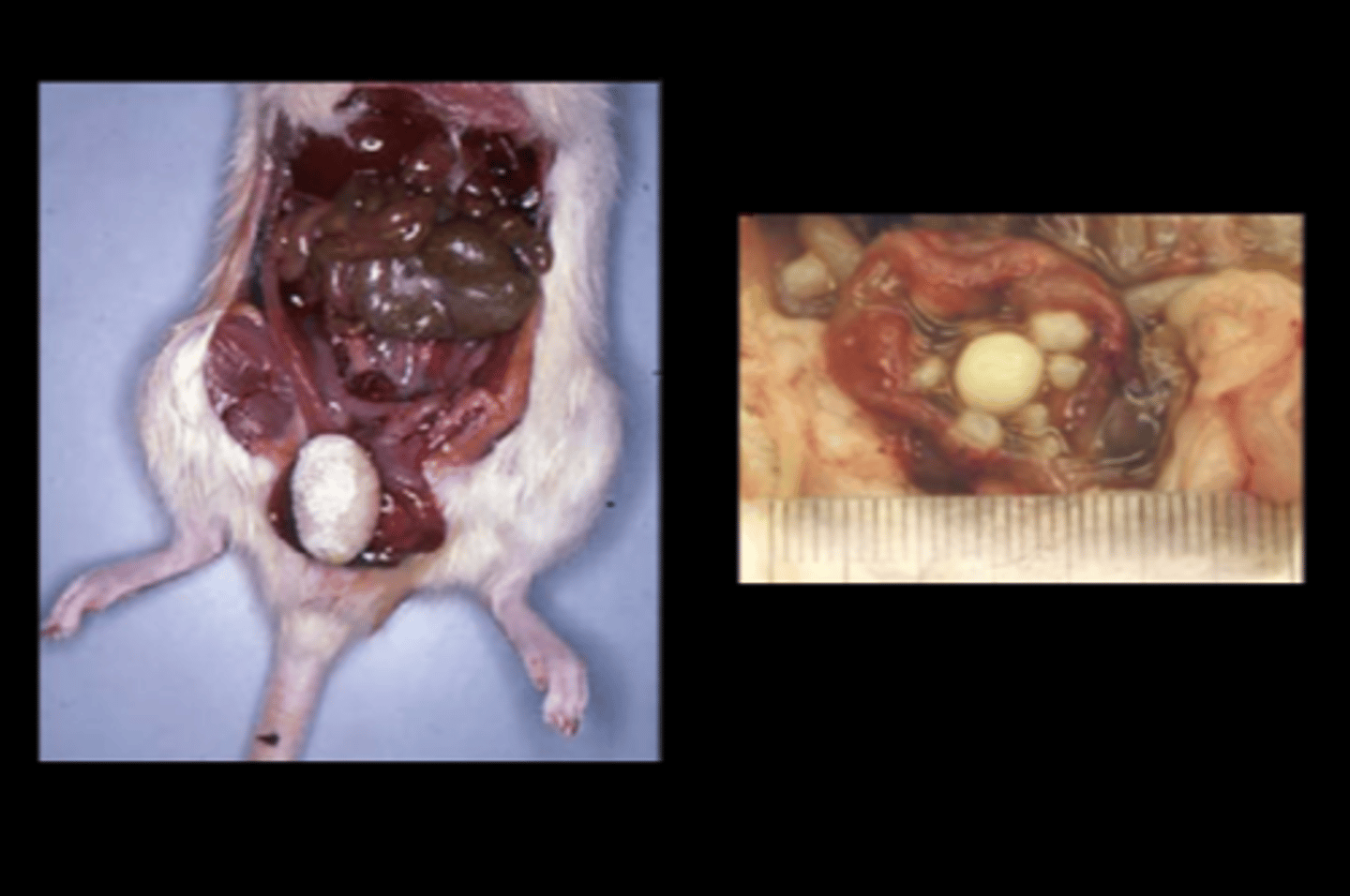
Urinary bladder
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Cystolithiasis
Ammonium magnesium phosphate (struvite), carbonate and oxalate are common. When in urinary bladder, can be associated with hemorrhagic cystitis, hematuria, urinary obstruction.
Comp Med 2015;65(6):486-491.
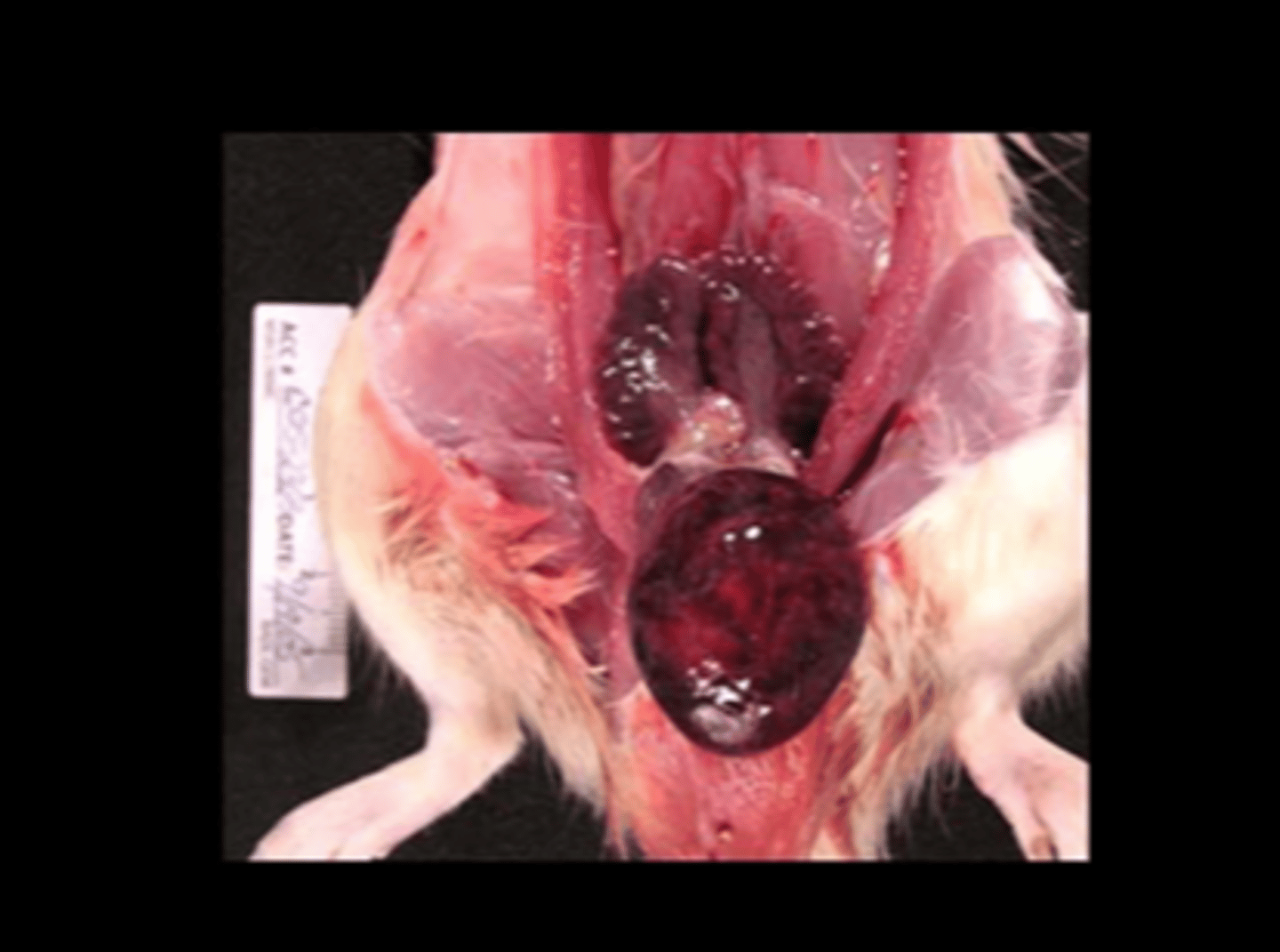
Urinary bladder
Hemorrhagic and proliferative cystitis with uroliths
Cystolithiasis
Ammonium magnesium phosphate (struvite), carbonate and oxalate are common. When in urinary bladder, can be associated with hemorrhagic cystitis, hematuria, urinary obstruction.
Urinary bladder
Transitional cell carcinoma
Can be spontaneous or experimentally induced.