Bio Final
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
What does CHNOPS stand for?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur
What are the 4 macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Which macromolecule provides quick energy?
Carbohydrates
Which macromolecule provides storage of energy in the form of body fat?
lipids
What is the monomer of proteins?
Amino acids
Enzymes are made from which major macromolecule?
Proteins
Which organelle stores DNA?
Nucleus
Where are proteins made?
ribosomes
What organelle takes food and turns it into ENERGY for plant and animal cells?
Mitochondria
The site of photosynthesis is…
chloroplast
What is the gel-like substance inside of cells called?
cytoplasm
A rigid layer that lies outside the plant cell's membrane is…
cell wall
What organelle helps with cell digestion?
lysosome
Which organelle is directly involved in the transportation of materials inside/within the cell?
endoplasmic reticulum
One of the principle compounds that living things use to store energy is…
ATP
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
Glucose and oxygen
What are the products of cellular respiration?
Carbon dioxide and water
Cellular respiration occurs in both plants and animals. True or False?
True
What does cellular respiration do?
Releases energy from complex organic molecules.
What does photosynthesis do?
It converts glucose and oxygen into energy.
Enzymes are made from which major biomolecule
Proteins
Which molecule is the best source of short term energy??
Glucose
What is the right chemical reaction for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2,
What is not right chemical reaction for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 12H0 -> C6H12O6 + 6O2,
Where in the cell does cellular respiration occur?
mitochondria
What is a product of cellular respiration
Carbon dioxide and water
Where in the cell does photosynthesis occur.
chloroplast
What molecule is considered an enzyme
Amylase
What cell structure produces ATP
Mitochondria
What type of maromolecule stores, transmit, and express genetic information.
Nucleic acid
What is the monomer of nucleic acid
nucleotide
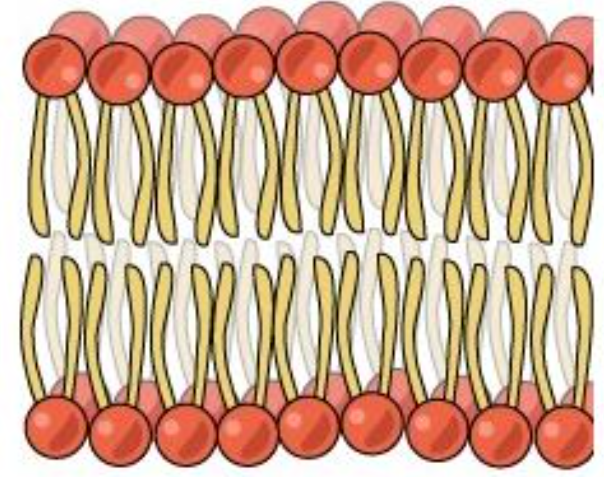
What type of macromolecule makes up this Membrane
phospholipid
In an isotonic solution, which way dose the water flow
It flows both ways in at equal rates
DNA stands for
deoxyribonucleic acid
The sugar found in DNA is known as
deoxyribose
What are the parts of a nucleotide
phosphate group, sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
— Is the process by which DNA is copied
DNA replication
What type of bond holds bases together in DNA
Hydrogen bonds
What is the enzyme that unzips DNA
Helicase
Where does DNA replication take place?
Nucleolus
Why does DNA replication occur.
To make new cells.
What is protein synthesis?
Making proteins
The process in which DNA is copied to make RNA is known as..
Transcription
—- is the process in which the mRNA messages is decoded and proteins is made
Translation
A chain of — makes up a proteins.
Amino acids
A change in the DNA sequences that affects genetics information
mutation
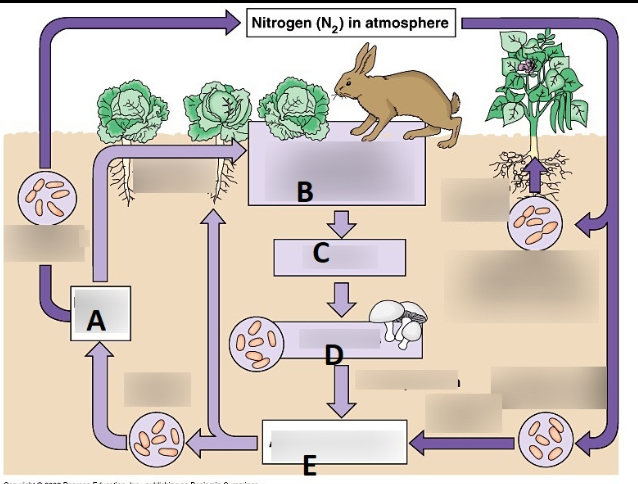
What does D represent?
Decomposition
What does A represent?
photosynthesis
What does B represent?
Animal respiration.
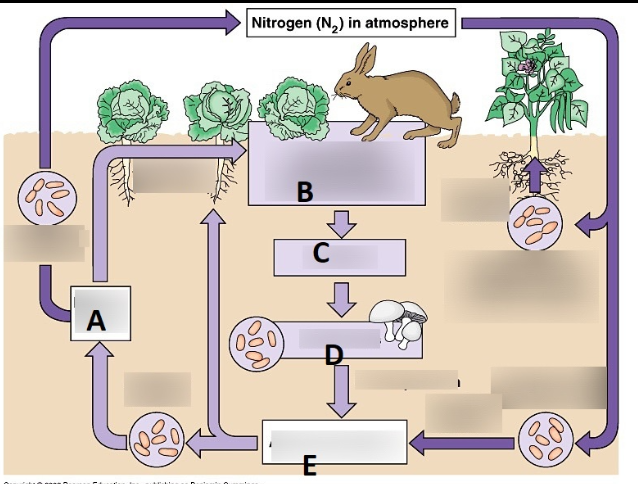
What does C represent?
Elimination
What is the term for each step in the transfer of energy and matter within a biological community?
Trophic levels
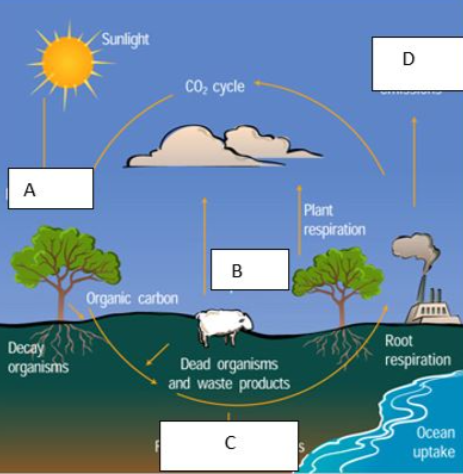
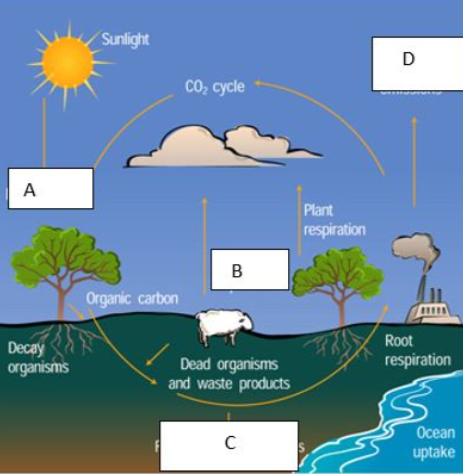
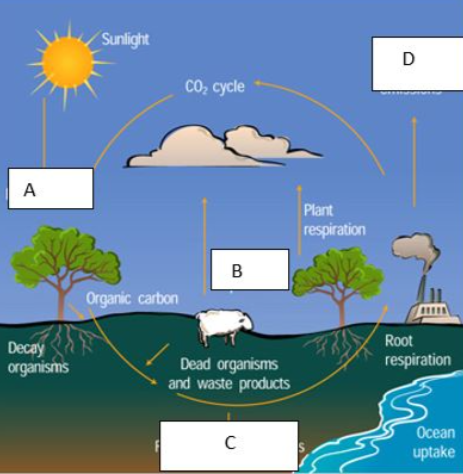
What does C represent?
Fossil fuels
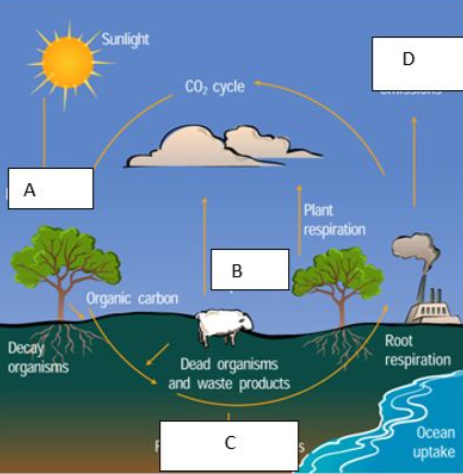
What does the letter D represent?
Factory emiss
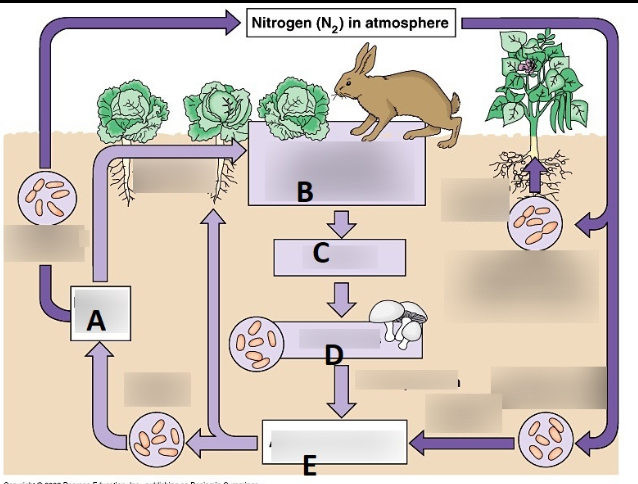
What does E represent?
Nitrification
When ATP is broken down in a chemical reaction, what is released?
Energy
What type of macromolecule stores, transmits, and express gentinc information?
Nucleic acid
What cell structure produces ATP?
Mitochondria
When ADP is converted to ATP ______________________. What happens?
a phosphate group is added
Enzymes speed up reactions within the human body by…
changing the pH level
A chain of many smaller subunits bond to form a larger molecule. What is the larger molecule called?
Polymer
The process which organisms keep their internal environment constant or equal is called __________.
Homeostasis
On a line graph where would the dependent variable go?
On the y-axis
Which of the following organisms would breathe in the gas produced from cellular respiration?
Plants
When ATP is broken down in a chemical reaction, what is released?
Energy
What is the principal pigment in green plants?
Chlorophyll
If the body can no longer make ATP, which type of transport would be impacted?
Active Transport
Osmosis is....
the movement of water from low water concentration to high water concentration.
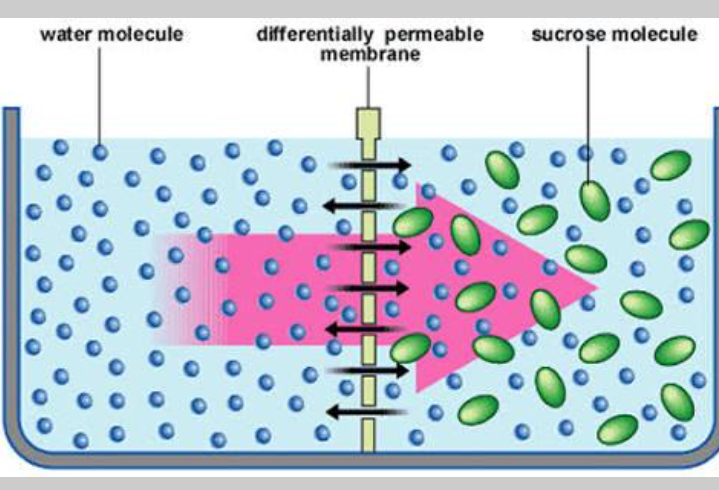
Which type of diffusion is represented?
Osmosis
Maintaining a constant internal state in a changing environment.
Homeostasis
Which of these is not a form of passive transport?
Endocytosis
Whats thee formula for water
H₂O
Whats the formula for oxygen
6O₂
whats the formula for Carbon Dioxide
6CO₂
Whats the formula for Glucose
C₆H₁₂O₆
What is the formula for cellular respiration
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
What is the formula for photosynthesis
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
What does aerobic mean
organisms that require oxygen
The purpose of meiosis is to produce...
Haploid gametes cells
Meiosis occurs in what type of cells?
Gametes
In which organelle does translation occur?
ribosomes
What are the 4 bases found in a RNA molecule?
Adenine, Cytosine, Uracil, Guanine
The uncontrolled growth of cells is called?
Cancer
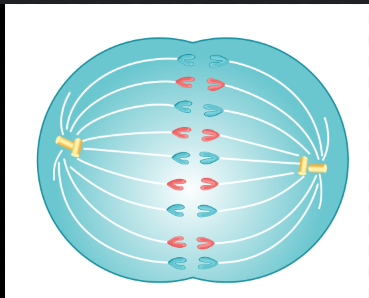
Which description best describes what is happening in the diagram below?
Anaphase
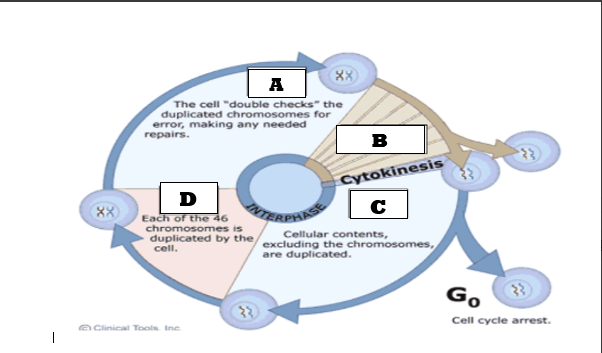
Which of the following represents letter B in the cell cycle
Mitosis
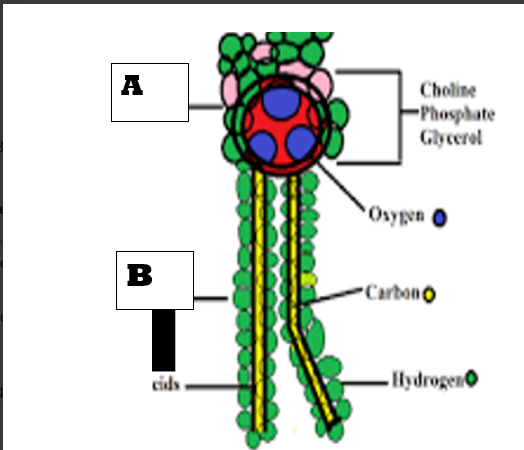
Which structure of the phospholipid is hydrophobic?
B
What does active transport need?
ATP
What does passive transport need?
Not ATP
The cell membranes acts like the "door" to cell allowing certain molecules and nutrients in or out. What is the cell membrane made mostly of?
Lipids
What is the type of passive transport where larger molecules move through a protein carrier and are moving from high concentration to low concentration?
Facilitated diffusion
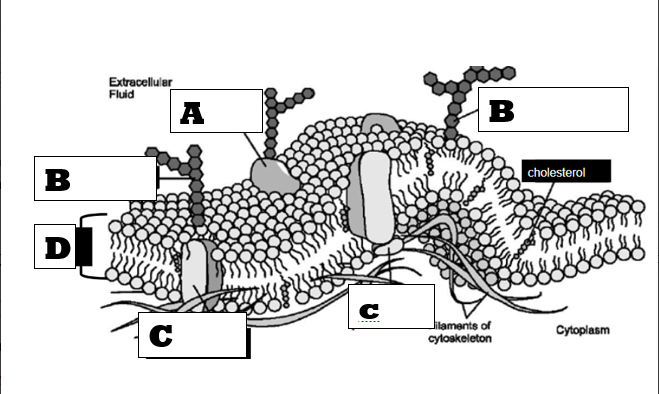
On the diagram below, the letter "D" represents what molecule?
Phospholipid bilayer
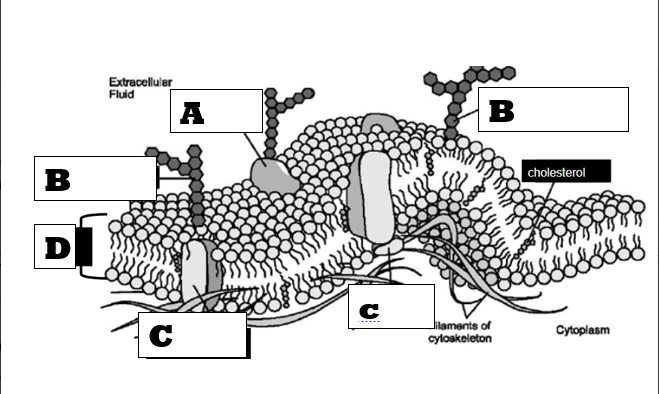
On the diagram below, the letter CAPITAL "C" represents what molecule?
Protein Channel
What does the term "selectively permeable" mean?"
Allows certain substances to pass through while restricting others
Oils, fats and waxes are forms of which of the following molecules?
Lipids
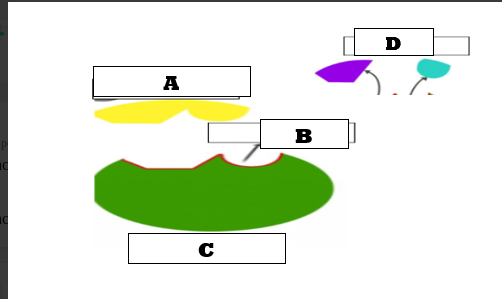
What does letter A represent?
Substrates
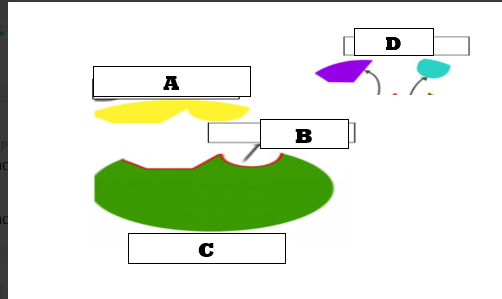
What does letter C represent?
Active site
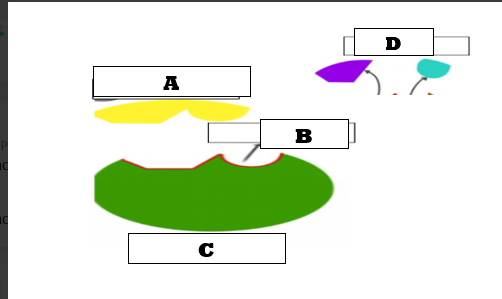
What does letter B represent?
What does letter D represent?
Diffusion is a form of __________ transport.
Passive
_____________ is the free movement of particles across the membrane with the concentration gradient
diffusion
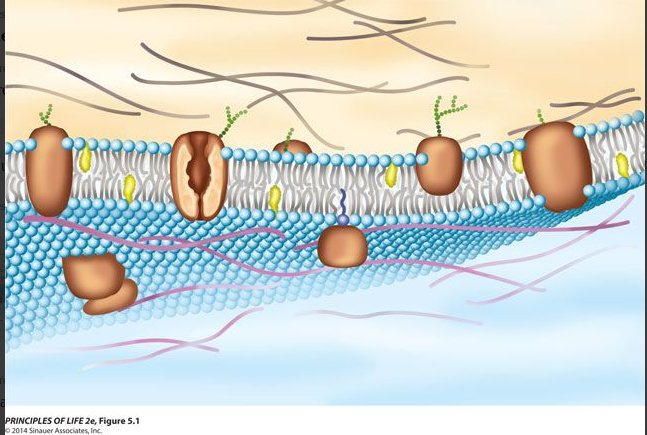
What do the brown structures represent?
Channel Proteins