Chapter 7 The labour Market, Wages, and Unemployment
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TERMINOLOGY
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is working age population
people iver the age of 15 (15-65) who could work
what is employed?
people with a job including both full and part time
What is unemployed?
people WITHOUT a job BUT actively seeking work
what is the labour force?
people who are either employed or unemployed
How can you find labour force?
Labor force is found by adding employed people plus unemployed ones
ememployed + unemployed
or Lt= Et+Ut
how can we find unemployment rate?
Unemployment rate is a rate of people unemployed relative to the labour force, so it is unemployed people divided by the Total labour force
unemployed / labour force
u= Ut/Lt
how can we find participation rate?
The participation rate is found in the labour market by dividing the labour force by the working-age population
Labour force/working age pop
p= Lt/W
how can we find employment rate?
The employment rate is the rate of employed people who can work relative to an economy’s full population, so it can be found by dividing the employed by the working age population
employed/working age population
e= Et/W
what is cyclical unemployment?
cynical unemployment is unemplotment that comes from short run fluctuation in output such as recessions
What is the natural rate of unemployment? and its relation to cynical unemployment?
the natural rate is what remains when cynical unemployment equals 0
explain frictional and structural unemployment of natural rate of unemployment
frictional unemployment is when workers are stuck between jobs or searching
Structural unemployment is when there is a mismatch between a employees skill and the jobs
How do we calculate Actual unemployment?
actual unemployment is found when you add natural[frictional plus structural] and add it with cynical unemployment
![<p>actual unemployment is found when you add natural[frictional plus structural] and add it with cynical unemployment </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6d18ee51-6b27-4d01-a8ba-604f77035838.png)
What is the intuition of the bathtub model of unemployment?
The bathtub model, like the name suggest, you can think of it as a bathtub filled with water
There is an “inflow” of people losing jobs (This is denoted by an s variable cause you are separating the unemployed people from the employed)
and there is an “outflow” of people finding jobs (which is denoted by a f variable, which means finding job rate)
The relationship here is that if inflow is greater than outflow, there will be higher unemployment. However, if it’s the opposite and inflow is less than outflow then unemployment falls
what is the steady state in the bathtub model?
in the bathtub model the steady state is when inflow equals outflows
What is formula for the bathtub model?
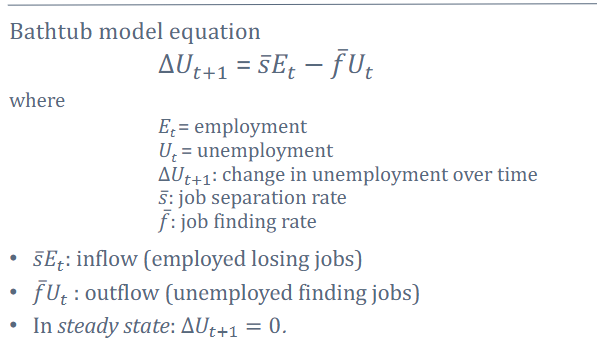
how do we set up steady state for the bathtub model?
we solve for the steady state by first setting the change in unemployment to zero and then you isolate for U*
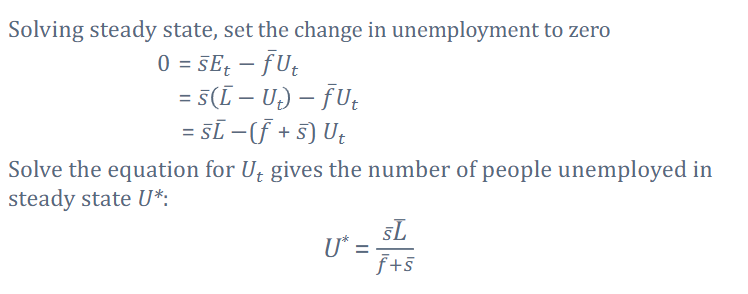
How do we express/ solve for the steady state of unemployment
We first start with the SS of unemployment then to make it into a natural rate of unemployment we divide each side by L
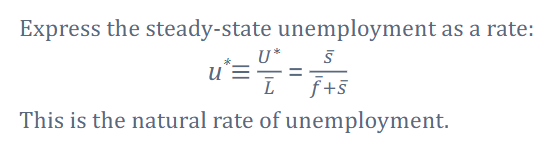
Which policies can affect the natural rate (2 of them)
the first policy is if there is an increase in job finding, f then it will lead to lower unemployment
the second is if there is reduce job separation, s, then there would be lower unemployment