Cognition: Selective Attention - Hearing
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are issues in attention?
We cannot attend to everything, so we only attend to some things and not others
Cherry (1950s) - The cocktail party problem
we cannot understand or remember the contents of two concurrent spoken messages, the best we can do it alternate between attending selectively to the speakers
What are the three stages where this bottleneck in attention could occur
where we perceive the sounds - cannot process two speech sounds simultaneously
at lexical access - cannot retrieve two meanings in parallel
at interpretation - cannot interpret what two people saying
How did Colin investigate focused attention in hearing?
Played two different speech messages using headphones
What did Colin find
Repeating one of the messages aloud is
successful if the messages differ in physical properties such as location, voice and amplitude
not successful if they only differ in semantic context such as novel vs recipe
Also found that words repeated 35 times in the unattended message were not remembered better than a word heard once
What kind of changes do participants notice in the unattended message?
they notice physical changes such as location, voice and gross phonetics, including language change but not semantic changes such as meaningful to meaningless, words to pseudowords or language change where pronunciation of first language maintained
What did Colin’s work suggest?
That the bottleneck occurs at the meaning stage, people cannot attend to the meaning of two words simultaneously
unattended words filtered out early before access to identity/meaning
if required to extract identity P needs to switch attention filter
Broadbent’s (1958) dichotic split-span experiment
found that switching the attention filter between two sources is slow and effortful - one switch from left to right ear easier to report than three switches

Broadbent’s (1958) filter model
Sensory features of all speech sources are processed in parallel and stored briefly in sensory store - echoic memory
A selective filter is directed to only one source at a time, this is early in processing
Information that passes through the filter achieves higher level processing (recognition, activation)
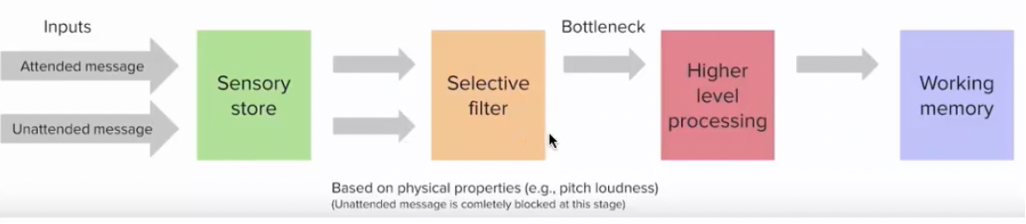
What are the two assumptions of Broadbent’s (1958) model?
filter is all-or-none
filter is obligatory structural bottleneck
What is the issue with Broadbent’s model’s assumptions
filter is not all or none
Moray (1959)
own name often noticed in unattended speech
Lackner and Garrett (1972)
interpretation of lexically ambiguous words in attended message are influenced by the meaning of words in unattended message - suggest some element of semantic processing
Corteen and Wood (1974)
Can condition a galvanic skin response to a word through mild shock
GSR evoked by word in unattended message though P does not notice or remember word being said
but GSRs to unattended message weaker than to attended names - semantic activation attenuated not blocked
Breakthrough demonstrations inspired late selection theories (Deutsch, 1963; Norman, 1968; Shiffrin & Schneider, 1977)
both attended and unattended words processed up to and including identification and meaning activation - relevant meanings then picked out on basis of permanent salience or current relevance
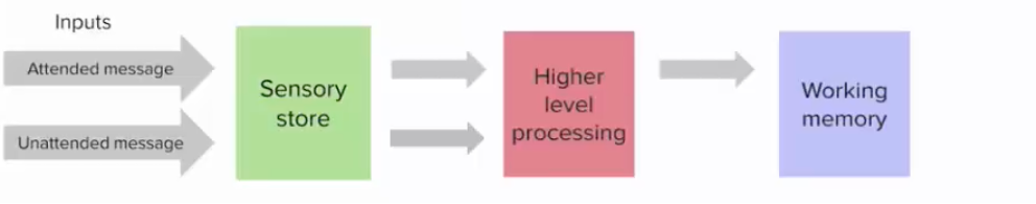
What are the issues with late-selection theories
selection on the basis of sensory attributes is more efficient than selection on basis of meaning
GSR to unattended probe words weaker than to attended
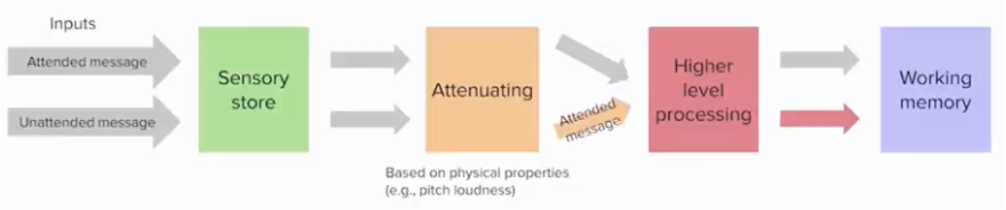
Treisman (1969) - filter-attenuation theory
there is a filter but
it is not all-or-none, instead it attenuates input from unattended sources, but with support of top-down activation unattended words if salient or relevant can still activate meanings
early filtering is an optional strategy not a fixed structural bottleneck

Ostry et al. (1976)
People can monitor for meaning from two channels
after practice target detection as accurate when a word target must be detected on either ear as only on one
support that early selection only an option
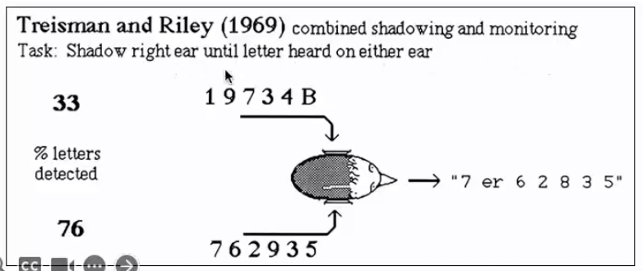
Treisman and Riley (1969)
can attend to both sources if then don’t have to do anything with info, can’t attend to both when processing more difficult
suggest that meaning from two channels can be monitored unless selective understanding or repetition of one message is required
also support that early selection is option