Death and Decomposition
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is Death in Biology and who clarifies death?
a process in which the cells and tissues of an organism cease to function
When a qualified individual pronounces that a life is now extinct; recorded on a death certificate
What are the Mortems
Ante- mortem
peri-mortem
Post-mortem
Agonal period
Post-mortem interval
Before death (What mortem)
Ante-mortem
At around time of death (What mortem)
Peri-mortem
After death (What mortem)
Post-mortem
The moment of death (What mortem)
Agonal Period
Post-Mortem Interval
Time Since Death
What is Death in Forensic Science? What is the terminology for humans
Differentiate between normal and abnormal processes
• Estimate cause and manner of death
• Estimate PMI
• Establishing if a crime did or did not occur
(Usually by the medical examiner, Coroner, foresnic pathologist, forensic anthropolgist)
Term: Corpse, cadaver, body, individual, remains, skeleton
What is Decomposition?
Act or process of the reduction of matter into simple forms
Process involves physical changes, intracellular and chemical changes
What are the stages of Decomposition?
• complex, chaotic, non-linear, systematic continuum
-Fresh, bloat, putrefaction, putrid dry remains
What factors impact decomposition?
• Intrinsic versus extrinsic • Biotic versus abiotic
• Microbes, insects, scavengers
• Individual, environment, behavior
What are the immediate first changes?- Somatic/somatic death
• Somatic: relating to the body
Somatic death: cessation of at least one of the main bodily systems • Respiratory, circulatory, nervous
Somatic death initates celluar death
What are the fresh changes: Early? and the different rates cells die
Cellular death: death of cells due to lack of oxygen and other nutrients
Brain cells: 3-7 minutes
Skin cells: up to 24 hours
What are the different mortis
• Pallor = pale/ Paleness of death
• Livor = bluish color, bruise/Blueness of death
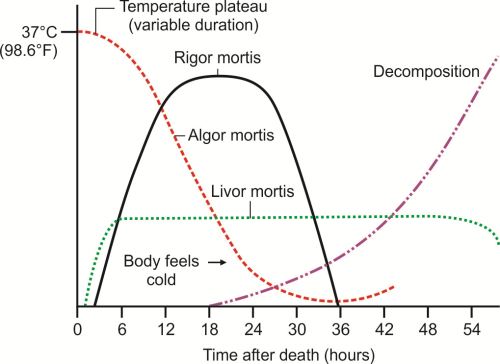
• Algor = cold /Coldness of death
• Rigor = stiff • Stiffness of death
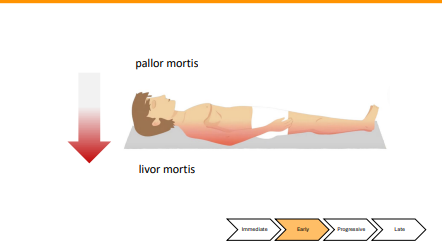
What happens in Pallor Mortis
• Somatic death = cessation of bodily systems
Without blood pressure, gravity causes blood to settle
-Creates Pallor Mortis
-Begins 20 minutes after death
Opposite of where the blood settles is pale, from lack of blood in capillaries under the skin the
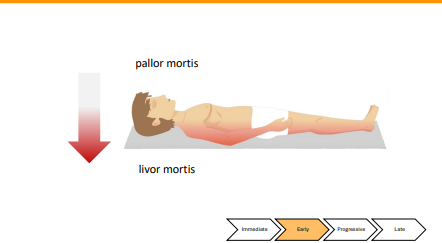
What is Livor Mortis
Somatic death = cessation of body systems → gravity pools blood
• Blood pooling is livor mortis, or hypostasis
• Skin where blood pooled underneath appears red to blue/purple/green
• Begin with patches or blotches
• Move to full development, confluence
• Maximum intensity
• Become fixed
What are the color changes in Livor Mortis?
• Red → Blue/purple → Green tint
Red color comes from oxygenated blood • Oxygenated blood = oxyhemoglobin → bright red in color
Blue/purple color comes from deoxygenated blood • Deoxygenated blood = deoxyhemoglobin → blue/purple in color
Over time, cells will lyse (breakdown) • Revert oxyhemoglobin to deoxyhemoglobin
Green color comes from sulfhemoglobin
Cell lysis causes oxygen to separate from hemoglobin
• Cell lysis also releases cytoplasm into the surrounding tissue
• Released oxygen reacts with hydrogen sulfide
Creates sulfhemoglobin → greenish color
What is Livor Mortis timing?
• Blood pulled by gravity immediately after loss of blood pressure
• Moves slowly
• Visible patches: 30min to 2hr
• Complete confluence: 4hr to 6hr
• Maximum intensity: 6hr to 10hr
• Fixed: 12hr to 24hr
What is Algor Mortis and the influential factors
Thermoregulation stops— moves to ambient temperature
Normal body temperature (98.6 F). Ambient temperature is below this (cooling)
• Body weight
• Body position
• Body mass index in relation to surface area
• Sex of deceased
Environmental conditions
Surface insulations
What is Rigor Mortis and the steps?
First: total relaxation of all muscles immediately after death
• Then: Rigor Stiffening and shortening of muscles
• Rigor develops across all muscles at roughly same time and speed
• Stiffening begins in eyelids and jaw
Fully developed 6 to 18 hours after death
What is loosening rigor?
Fully developed rigor can be called the rigid stage
After the rigid stage, the process will reverse
• Muscles will lose rigidity in the order it appeared
• Small to large • After another ~12 hours, the body will lose all rigor
Process can begin 24 to 36 hours after death/ • After this, rigor cannot be assessed to estimate PMI
What is Rigor Mortis Influential Factors
• Rigor impacted by extrinsic and intrinsic factors
• Environment
• Higher temperature = earlier/faster development
• Lower temperature = later/slower development
• Individual •
Body mass, muscle mass • Activity prior to death
What is Cadaveric Spasm?
Complete and instantaneous rigor
Cadaveric rigidity or Instantaneous rigor
Occur in deaths with extreme physical/ emotional stress (rare)
Fill in the blanks