IRE260 (starting frm lec 8, go over again w post class slides))
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Leadership
Influence that part. individuals exert on goal achievement of others in organizational context
effective leadership enhances productivity, innovation, satisfaction, commitment of workforce
Approaches to Leadership (3)
Structural: who is the leader? defined by organization
Trait: who are effective leaders? what do they bring to grp?
Behavioral/Situational: what behaviors caused them to become leaders? what fo we need in this setting?
Leadership Trait Theories
consider personality, social, physical, intellectual traits to differentiate leaders frm non-leaders (assume traits unchanged over time)
Styles of Leadership
no best style, successful leadership depends on leader’s behaviour and team members’ ability + confident of followers, contingency theory); leader behaviour change depending on person
Decision Making
developing commitment to some course of action
problem-solving (getting frm existing state → desired state)
involves making choice, a process, committing resources
can be impacted by strong emotions (may be hinderance) + mood (greatest impact on uncertain, ambiguous/crucial decisions)
Rational Decision Making Process
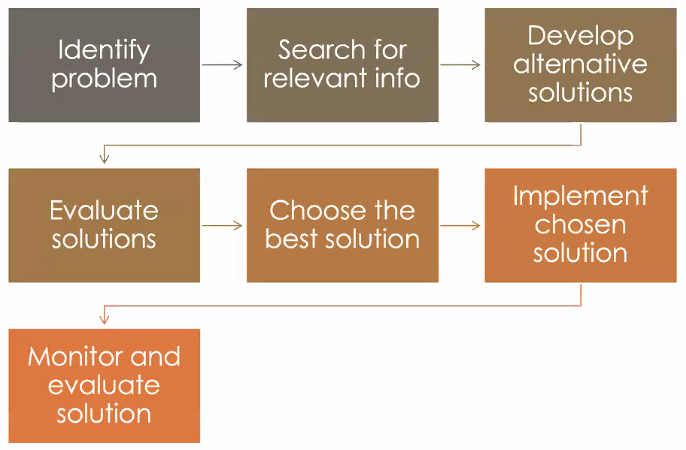
Perfect vs. Bounded Rationality
Perfect Rationality: decision strategy that is completely informed, logical, oriented towards economic gain.
Bounded Rationality: decision strategy relying on limited information
Economic Person
can gather info w/o cost + conpletely informed
perfectly logical
only one criterion for decision making
Framing
how info abt a problem is presented → powerfully impacts decision
what problem is
possible alternatives
Satisficing
stopping when you find a solution that exceeds your expectations
working under bounded rationality (satisficing > maximizing)
evaluation of alternatives ceases, solution chosen for implementation
problem: may miss solutions that could be better because you’ve stopped at one before seeing them
Narrow Framing
compares 2 options
focuses on tradeoffs
problem: miss hidden alternatives
Confirmation Bias
seeing information that proves us right
occurs when we hv preconcieved notions of what the ‘right’ answer should be
gives us overconfidence in judgement
ignores vital info
creates illusion of knowing
Sunk cost fallacy
based on an already made decision that results in a permanent loss of resources → may result in impacts in future decision making
irrational treatment
justification for faulty decisions
Escalation of Commitment
Nudge
aspect of choice architecture that alters behaviour in a predictable way without forbidding options/changing economic incentives
must be easy + cheap
Power + Its Bases (5)
ability to influence someone else’s behaviour
5 Bases of Power:
Legitimate Power: delegates/declares power to someone
Reward Power: influence others through rewards
Coercive Power: influencing others through negative consequences (if you don’t do this, then I will do this ___)
Referent Power: others doing nice things for you because they like you
Expert Power: from expertise + knowledge
High power → feelings of liberation frm social + normative pressures (“I don’t need to do this because I’m powerful”)
can cause us to be ethically lost
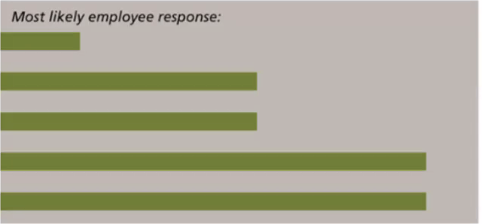
Political v.s Non-Political Behaviour