Chapter5. The skeletal system
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Perforating fibers
Made of collagen; anchors the periosteum firmly to the underlying bone surface by penetrating into bone matrix
What is Diaphysis?
The shaft of long bone.
What is periosteum?
The membrane made of dense irregular collagenous connective tissue; rich with blood vessels and nerves which surrounds outer surface of long bones
What does the skeletal system include?
Bones, joints, cartilage, and ligaments
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
Protection- certain bones protect the underlying organs
Mineral storage, electrolytes, and acid-base homeostasis- Bone stores minerals which are necessary for electrolyte and acid-base balance.
Blood cell formation- red bone marrow is the cite of blood cell formation
Fat storage- Yellow bone marrow is made of fat cells and store triglycerides.
Movement- when muscles contract they are pulling on bones generating movement
support- The skeleton supports the weight of the body.
What are the 5 classes of bone structure.
Long bones- bones longer than wide
short bones- bones is about as long as it is wide
flat bone- bones is broad, flat, and thin (sternum)
sesamoid bone- round, flat bone found within tendon.
irregular bone- bone’s shape does not fit into other classes(vertebra)
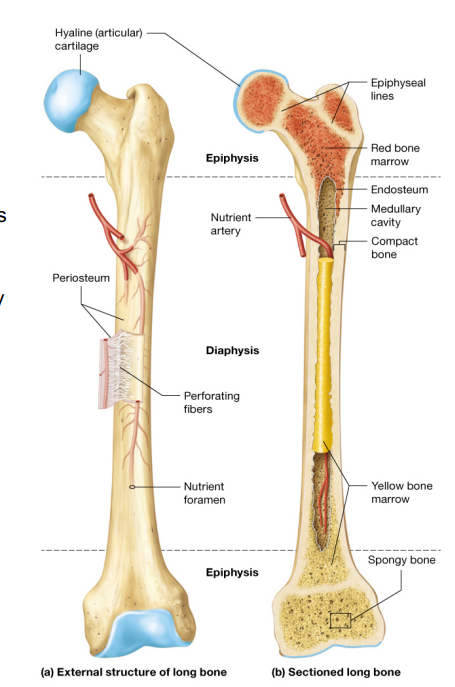
Structure of long bone
Periosteum- a membrane composed of dense irregular connective tissue, rich blood vessels, and nerves that surrounds the outer surface of long bones.
perforating fibers- made of collagen(protein fibers); it anchors periosteum firmly to underlying bone surface deep into the bone matrix
Diaphysis- Shaft of long bone; each end is epiphysis(Expanded part of the bone) and covered by hyaline cartilage.
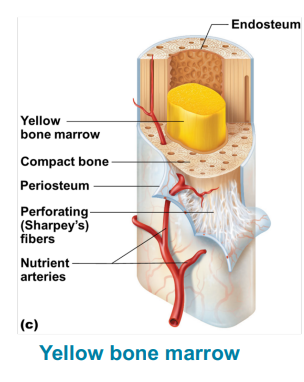
Medullary cavity- Within diaphysis contains either red or yellow bone marrow, depending on the age of the person.
Structure of long bone
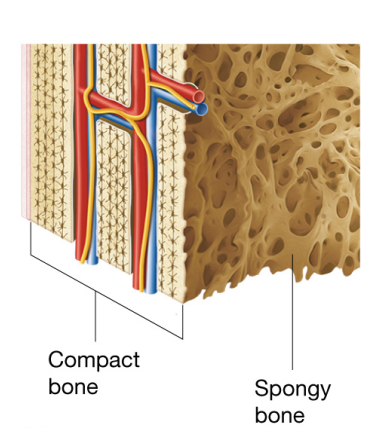
Compact bone- one of 2 bone textures with a hard and dense outer region; Allows bone to resist linear compression and twisting forces among other stresses
Spongy bone- The second bone texture found inside the compact layer; its a honey comb like framework of bony struts which allows long bones to resist forces from many directions , provides cavity for bone marrow, and reduces weight of the skeleton
Epiphyseal lines- separate both proximal and distal epiphyseal from diaphysis; remnant of epiphyseal plates, a segment of hyaline cartilage found in developing bones birth.
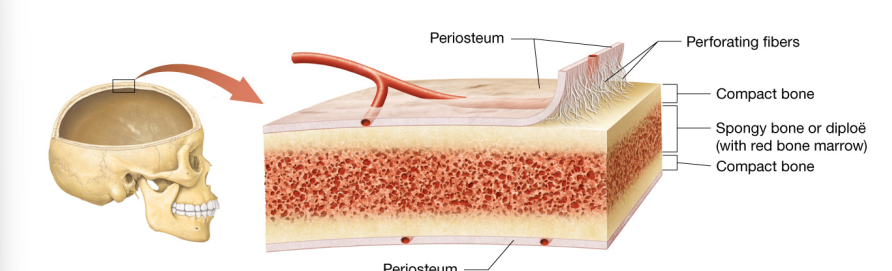
Bone structure of short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid bones
Do not have Diaphysis, epiphyses, medullary cavities, epiphyseal lines, or epiphyseal plates.
Periosteum- a membrane composed of dense irregular connective tissue, rich blood vessels, and nerves that surrounds the outer surface of long bones.
internal structure- two outer layers of thin compact bone with middle layer of spongy bone and associated bone marrow
Some flat and irregular bones of skull contain hollow, air-filled spaces (Sinuses) which reduce bone weight.
where do long bones get their blood supply
one third comes from the periosteum and the remaining two thirds comes from one or two nutrient arteries which enter through the nutrient foramen.
Red Bone marrow
loose connective tissue which supports blood-forming hematopoietic cells
children need more red marrow to help support growth.
as you age red marrow is replaced with yellow marrow
adults only have red marrow in the pelvis, proximal femur, proximal humerus, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, clavicles, scapulae, and some bones of the skull
Bone/Osseous tissue
primary tissue found in bone
Composed mostly of ECM with a small population of cells scattered throughout
Extracellular matrix of bone is unique
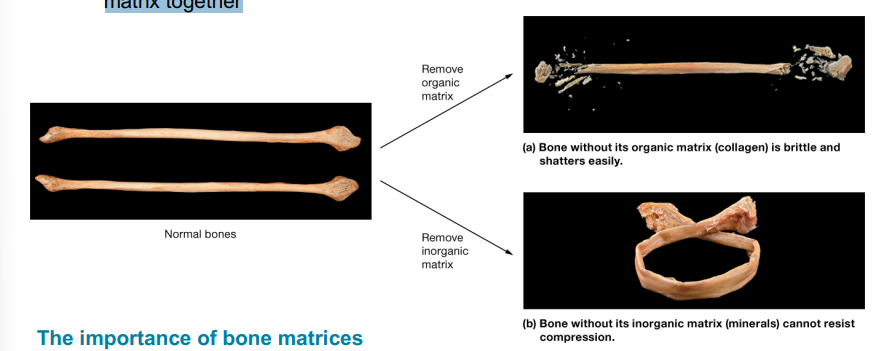
Inorganic matrix - minerals make up about 65% of bone’s total weight
Organic matrix- consist of collagen fibers and other standard ECM components.
makes up the remaining 35%
Inorganic Matrix
Storing around 85% of total calcium ions
mostly calcium, salts, and phosphorus
Crystalline structure makes bone one of the hardest substances in the body
(Allows bone to be both protective and supportive
Bicarbonate, potassium, magnesium and sodium are also in inorganic matrix
Organic matrix
Consist of protein fibersconsists of protein fibers, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins and bone-specific proteins
Collagen – predominant protein fiber enhances hardness of bone and helps bone resist twisting and pulling/stretching forces –
Glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans create an osmotic gradient; draw water into osteoid and help tissue resist compression –
AGlycoproteins in osteoid bind different components of osteoid and inorganic matrix together
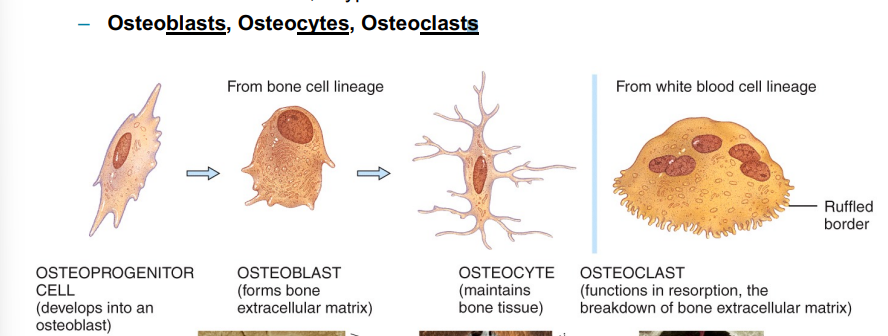
What are the 3 types of bone cells?
Osteoblast- forms bone ECM
Osteocytes- maintains bone tissue
osteoclast- Breaks down bone
structure of compact bone
compact bone is continuously subjected to a great deal of stress, which must be able to to withstand these forces of each region.
compact bone resembles a forest of tightly packed trees, where each tree is a unit called an osteon
rings of each osteon are made up of than layers called lamellae
Osteon structure
Each osteon contains 4-20 lamellae in layered ring structures, a very stress resistant arrangement
Callagen fibers of neighboring lamellae run in opposite directions, which resist twisting and bending forces from variety of directions
central canal- endosteum-lined hole in center of each osteon, containing blood vessels and nerves
lacunae- Small cavities between lamellae filled with extracellular fluid and osteocytes
neighboring lacunae are connected by network of small passageways called canaliculi;
Osteons are not permanent structures for osteo clast break down bone and osteoblast build bone matrix as needed.
Over all compact bone structure
interstitial lamellae- fill spaces between circular osteons; represent remnants of old osteons
Circumferential lamellae- outer and inner layers of lamellae that add strength, just inside periosteum at boundary with spongy bone
perforating canals- originate from blood vessels in periosteum
Structure of Spongy bone
Lighter, less densely packed, usually not weight bearing.
Network of struts reinforces compact bone and resist forces from variety of directions
provides protective structure for bone marrow tissue
Trabeculae
struts or ribs of bone which are covered with endosteum
what is ossification
process of bone formation
Bones form in what 4 situations?
During embryological and fetal development
• When bones grow before adulthood
• When bones remodel
• When fractures heal
bones formed by intramembranous ossification are bult on_____
Embryonic connective tissue
bones formed by endochondral ossification are built on model of____?
hyaline cartilage.
Intramembranous ossification
forms many flat bones during fetal development
Endochondral ossification
replaces cartilage with bone
longitudinal growth
continues at epiphyseal plate as long as mitosis continues in zone of proliferation