Ethnography Flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Ethnography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Ethnography
Describing and understanding a cultural world from the point of view of its people.
Emic Perspective
An insider's perspective.
Etic Perspective
An outsider's perspective.
characteristics of ethnographic research
conducted in natural settings
provides holistic and systematic overview of context
done within field site
documents native perspective
descriptive and interpretative
guided by general research questions not hypotheses
focuses in meaning of word and images rather than numbers
How do researchers collect data during ethnographic fieldwork
focus groups - group of people chose for shared characteristic to be involved in discussion
surveys
interviews
archival research
participant observation
Participant Observation
A qualitative research method in which the researcher not only observes people but actively engages in social activities.
Principles of participant observation - Ethnographic Humility
Acknowledging the complexity of social activity.
Principles of participant observation - ethnographic ‘dazzle’
tendency for outsiders when observing other cultures to be focused on difference they fail to notice or appreciate similarities
Types of participant observation - Complete Participant
Researcher fully immersed in the community; activities as a researcher may be concealed.
Types of participant observation - Participant-as-Observer
Researcher participates fully in activities; status as researcher is known.
Types of participant observation - Observer-as-Participant
Researcher participates in key activities for research purposes; status as researcher is known.
Types of participant observation - Complete Observer
No contact with those being observed; covert observation.
Types of ethnographic research methods - Field Ethnography
Observing people in their normal lives for a deeper insight.
Types of ethnographic research methods - Digital Ethnography
Using digital tools to speed up the ethnographic process.
Types of ethnographic research methods - Photo Ethnography
Giving a person a camera to capture images of their life with accompanying notes.
How to do ethnography
identify research q —> determine location —> formulate presentation method —> acquire permission and access —> observe and participate —> interview —> collect archival data —> code and analyse data
Implanting the method
who to observe
when to observe - access, safety, practicality
frequency of visits
alone or accompanied ?
what to take with you
mode of transportation ?
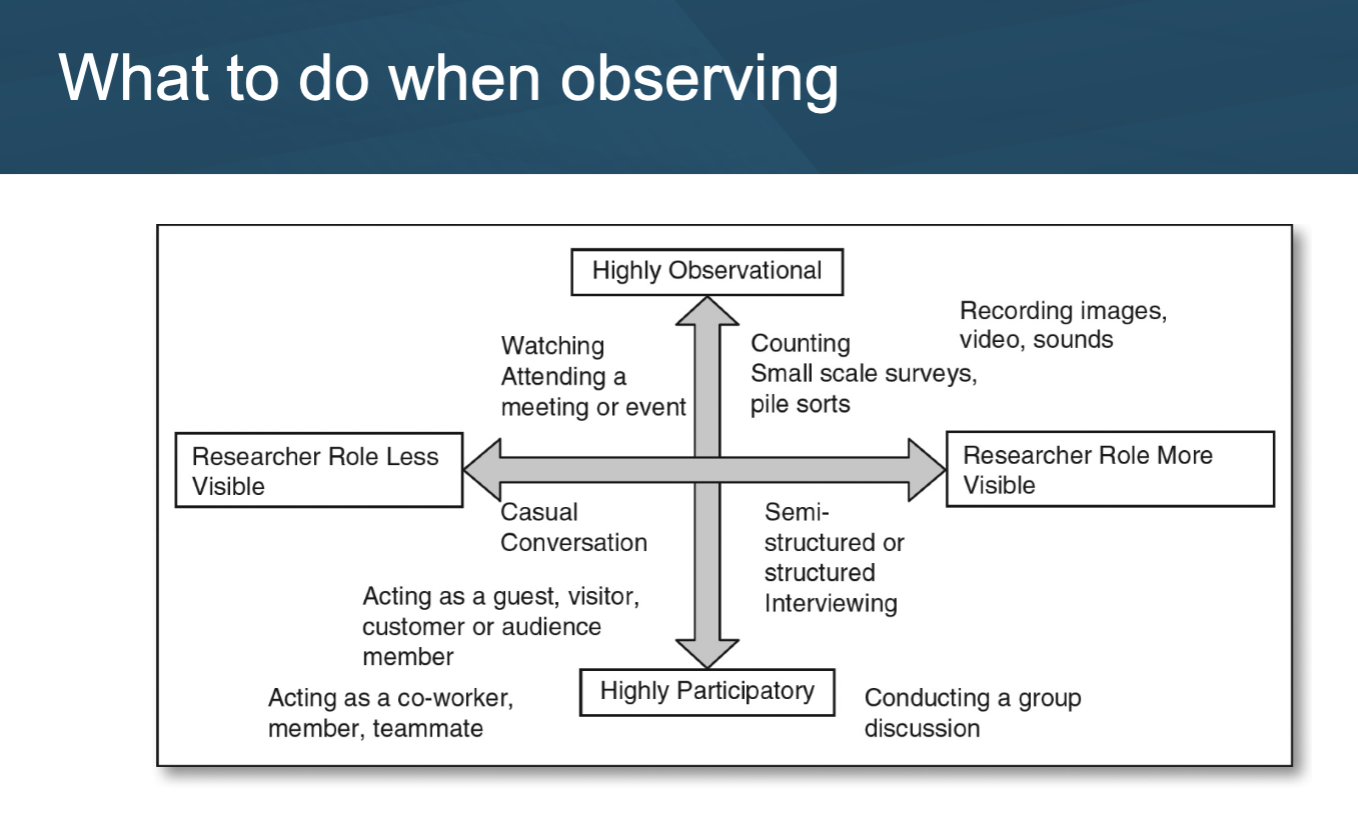
what to do when observing
Field notes
decide note-taking style and level if detail
decide in theme / coding
experimental style - writing postponed
participating-to-write or observing-to-write : writing begins earlier
what to write
W: who, what, when, where, how
R: reaction
I: inaction (silence ?)
T: timing (the pace of action / speaking)
E: emotions (nonverbal signs)
initial impressions, significant/ unexpected fieldworker, routine actions, variations and exceptions to emerging patterns
Styles of field notes
notes
jottings
dictation
journal entries
keywords
images / drawings
photos
creative genres
Post-oberservational field notes
jottings need to be translated into full, coherent, descriptive text
within 24hrs
use word processor can facilitates coding and sorting
be aware takes time
Ethnography and colonialism
colonial conquest - ethnographies assisted justification of evolutionist theories and social change
ethnography occurred during colonisation
situated in a history of radicalisation
Ethnocentrism
The view in which one’s own group is the center of everything, and all others are scaled and rated with reference to it.
glorify or exotify other cultures
Global Ethnography
Ethnography that considers global contexts and interconnections.
Multi-sited Fieldwork
Research conducted in multiple locations.
Patchwork ethnography
how changing working and living conditions are transforming knowledge production
Digital Ethnography
Using digital tools and online communities for ethnographic research.
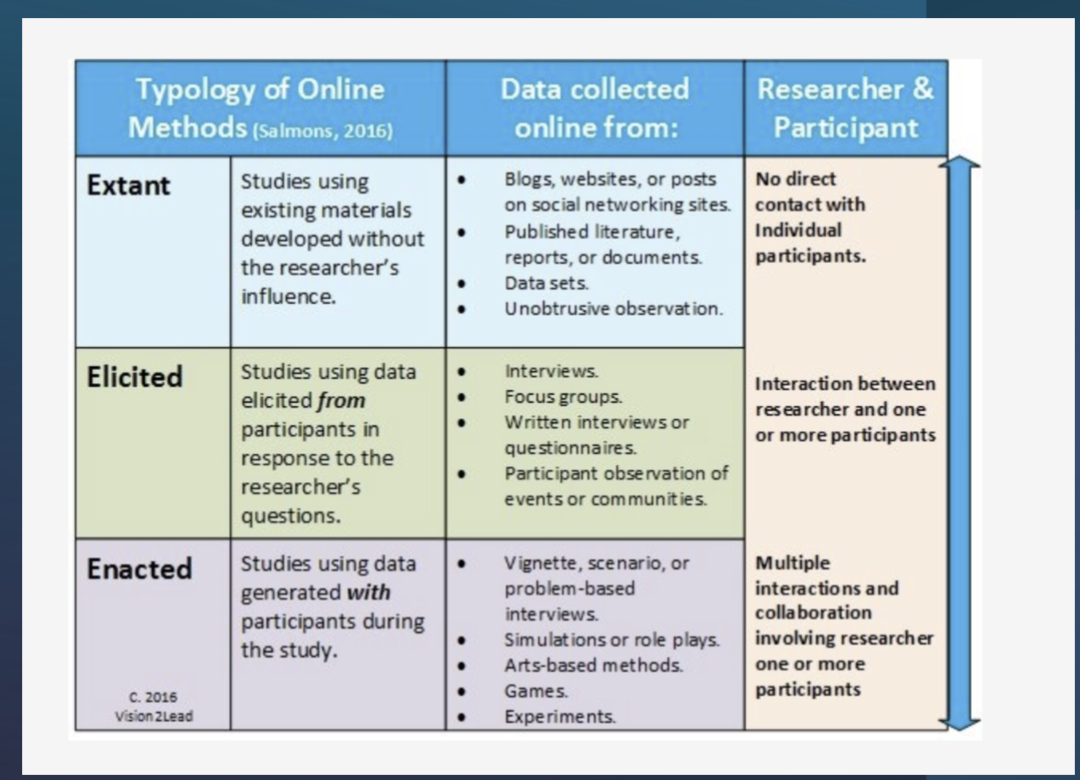
Extant - studies using exiting materials without researchers influence
elicited - studies using data from participants in response to researchers qs
enacted - studies using data generated with participants during the study
What is the field ?
distinction between home/ field problematic
feminist - argue fields - not isolated vessels
fields do not have to be far away
Auto-ethnography
A research method where the divide between participant and observer is blurred; the researcher examines their own experiences.
Anthropocentrism in Ethnography
The human subject as the privileged object of ethnography.
distinction between humans / animals ads a Eurocentric binary - does not reflect many cultures
rise of multi species - undo ethnographic as being solely about observation of human participants
Limits of observation
privileged method for accessing ‘truth’ about culture
moving participant observation away from positivist science
making space for history, context, positionally
we are not removed or detached from the world
Positionality
Recognition that people's perspectives and realities depend on their different positioning in society.
Reflexivity
Explicit recognition of the ethical and political dimensions of fieldwork and acknowledgement of how these may have shaped knowledge.
Ethical review
reliability of knowledge depends on explicit recognition of the ethical and political dimensions of fieldwork
permissions and consent -
purpose of activity, extent and scope of observation
topic and setting
type of research conducted