BIO 101: Lab 7 - Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Cell Structures and Functions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
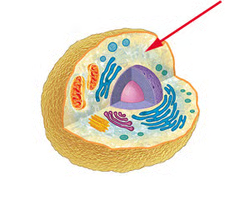
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
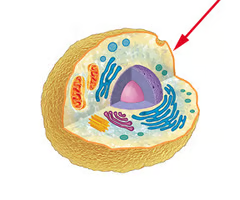
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
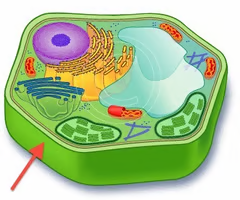
glycocalyx
The external surface of a plasma membrane that is important for cell-to-cell communication and identification
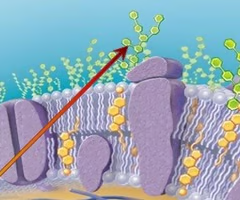
capsule
when the glycocalyx is bound more tightly to the cell and is denser and thicker
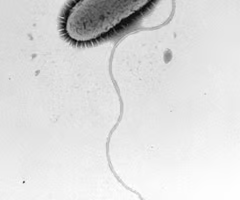
flagella
whiplike tails found on the exterior surface of some cells to aid in movement
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
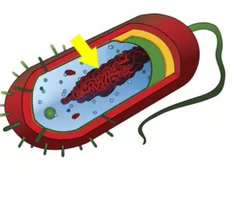
plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
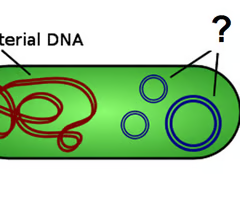
fimbriae
attachment structures on the surface of some prokaryotes
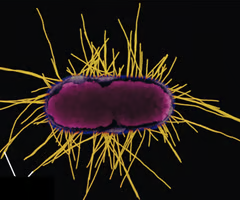
conjugation pili
in a bacterium, elongated, hollow appendage used to transfer DNA to other cells
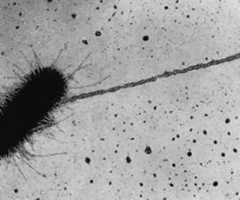
cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic, oxygen-producing bacteria (formerly known as blue-green algae).
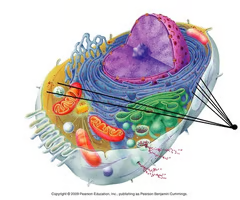
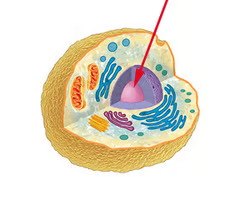
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for protein synthesis
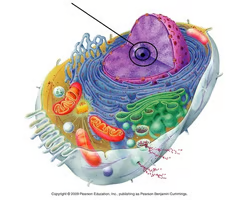
nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
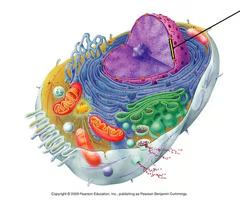
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
central vacuole
A membranous sac in a mature plant cell that stores water, solutes, toxins, and pigments
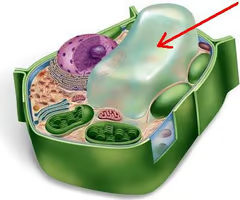
vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
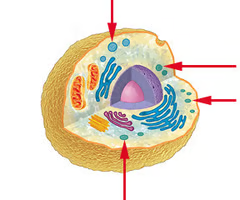
rough endoplasmic reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasmm; rough due to the presence of ribosomes; makes and modifies proteins
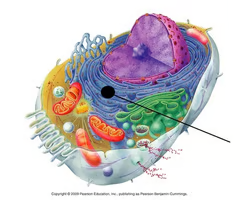
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
BIO 101: Lab 7 - Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Cell Structures and Functions
golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies, packages, and ships proteins and lipids
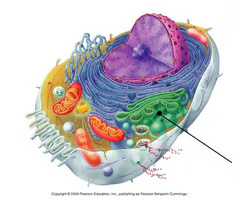
vesicle
A membrane bound sac that contains materials involved in transport of the cell.
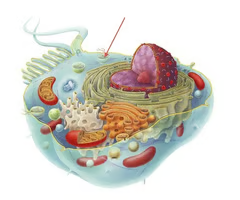
lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes that breaks down pathogens, macromolecules, and damaged cell parts
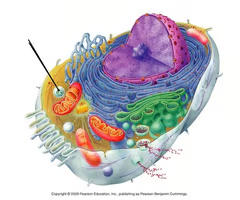
peroxisome
an organelle involved with lipid (fatty acid) metabolism; as it breaks down the lipids, it produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product, then converts it to water
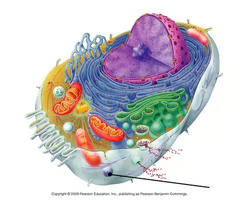
mitochondrion
Cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in food into energy available for cellular work (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration
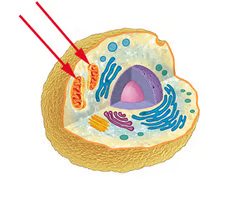
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
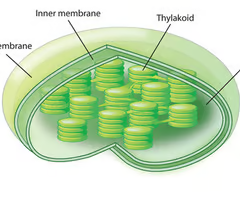
cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement and cell division
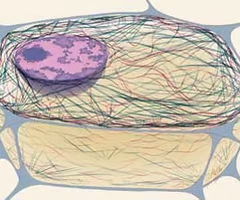
cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion and moving substances across the surface of the cell
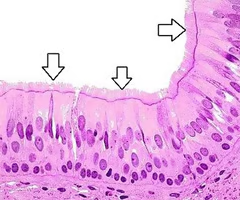
centriole
structure in an animal cell that helps to organize and produce microtubules for cell division
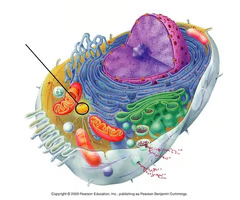
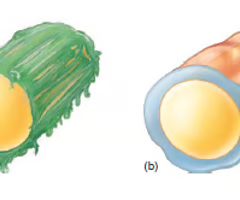
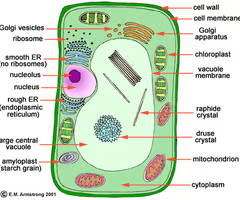
plant cell
What type of cell is this?
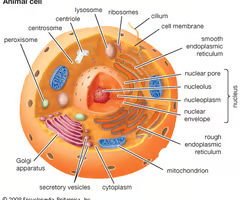
animal cell
What type of cell is this?
protozoan
An animal-like protist
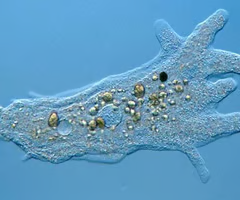
Amoeba
a kind of single-celled organism in kingdom Protista able to move by itself
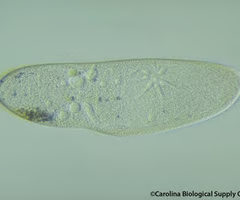
Paramecium
a single-celled freshwater animal that has a characteristic slipperlike shape and is covered with cilia.