Special Senses Review - Hearing/Taste/Smell
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are all of the special senses? Why are they considered special senses?
Sight, hearing, smell, taste, and balance (coincides with hearing).
They’re considered special senses because their receptors are clustered in specialized organs (like the eye) or in a small area.
What is the main goal of the ears? What kind of receptor does the ear use to accomplish this?
It’s to transfer sound vibrations to the auditory nerve.
The ear use mechanoreceptors to do this.
What structures make up the external ear?
The pinna (auricle), external auditory meatus (ear canal), and tympanic membrane (eardrum).
What structures make up the middle ear?
The ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), eustachian tube, and the tympanic cavity.
What structures make up the inner ear?
The cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
Describe how the organ of corti (cochlea) plays a role in hearing…
The cochlea has a basal membrane that vibrates from the ossicles, which then causes hair cells to move into the tectonic plate (rigid plate that cannot move). From there, cilia move which causes mechanosensitive channels to open and release neurotransmitters to create an electrical impulse that is sent through the auditory nerve to the brain!
How are sound waves FIRST captured? Think all of the external ear…
They are funneled in by the auricle (outer ear) and then are passed through the external auditory canal. Then, these sound waves vibrate and move the tympanic membrane (eardrum)
How are sound waves processed from the middle ear?
After sound hits the tympanic membrane (external ear), the vibrations from it cause the ossicles (malleus, incus, stirrup—in order) to amplify the sound to the inner ear through a membrane called the oval window.
How are sound waves processed from the inner ear?
After the ossicles amplify the sound, they hit against the cochlea, which is a bony-snail shaped structure that contains fluid called perilymph. With that, only a tiny impulse is made here, called the organ of corti. The fluid here vibrates, which then causes a basal membrane to vibrate (chain-reaction). The membrane contains tiny hairs that, as a result, move and stimulate the tectorial membrane, which creates an action potential which is sent through the auditory nerve and processed in our brain.
What are the structures that make up the vestibular organs?
It’s the vestibule and semicircular canals.
What is static equilibrium?
This is our body’s resting “balance.” So, it’s our balance whenever we are standing upright.
What are maculae?
These are nerve receptors in the vestibule that report on head position relative to gravity. Help with static equilibrium and keep our head upright.
What are otoliths?
These are calcium stones in the inner ear that drag the otolithic membrane when our head moves, causing hair cells to move as the membrane is dragged, sending a nerve impulse to our brain about our heads’ positioning.
What is dynamic equilibrium?
This is our balance while we’re moving.
What is the ampulla (exterior AND interior)?
Exterior: It is the swollen base of each semicircular canal that is filled with endolymph (fluid).
Interior: It contains crista ampullaris, which are tons of nerve receptors that report on angular + rotary movement to the brain.
What are the cupula of the crista ampullaris? How does this contribute to balance?
These are nerves covered in a gel-like substance.
When you move, the cupula drag against the endolymph fluid which stimulates hair cells to send an impulse to the brain via the vestibular nerve.
What are olfactory receptors, also called _____?
They’re also called chemoreceptors.
These receptors are responsible for responding to chemicals, like taste.
How do we actually detect taste?
Third-party molecules (like foods) contact the chemoreceptors in the olfactory bulb from sniffing.
What is Rhinitis? What causes this?
This is inflammation of mucous membranes that line the nasal passages. This is caused by Histamines.
What are Histamines? When are they activated?
These are molecules that trigger congestion and nasal drainage in response to an allergen or pathogen.
What are gustatory cells?
They are chemoreceptors on taste buds that detect taste!
What do olfactor receptors actually do?
They help to distinguish thousands of different molecules.
What does sniffing do?
It helps to bring outside molecules into contact with the olfactory receptors.
What happens when olfactory receptors contact a substance continually?
They become insensitive to the smell (accomidation).
What are papillae?
These are little bumps on the tongue that contain taste buds with have chemoreceptors.
What are gustatory cells?
These are chemoreceptors on the tongue that respond to molecules dissolved in saliva.
What happens when gustatory cells’ chemoreceptors respond to molecules?
When they respond to these dissolved molecules in saliva, they send depolarized signals to the brain through 3 facial nerves.
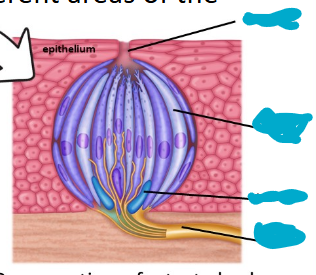
Label the following image from top to bottom…
Taste pore, gustatory cell, basal cell, cranial nerve fiber (afferent nerve).
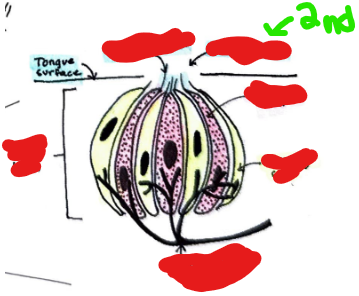
Label the following from top to bottom…
Gustatory hair, taste pore, gustatory cell, supporting cell, cranial nerve fiber (afferent nerve)
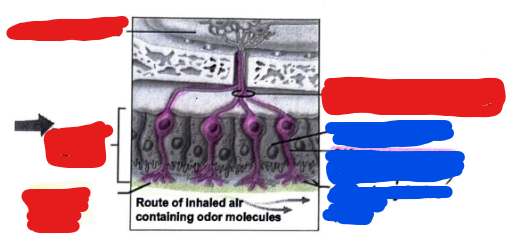
Label the following image. Start with the RED COLOR first and label that top to bottom. Then, label the BLUE COLOR from top to bottom.
Red Color: Olfactory bulb, olfactory nerve filaments, olfactory mucosa, mucus layer
Blue Color: Supporting cell, olfactory receptor cell (bipolar), olfactory hairs (cilia)

Label the following image from top to bottom…
Semicircular Canals, Vestibular nerve, maculae, vestibule, cochlea.
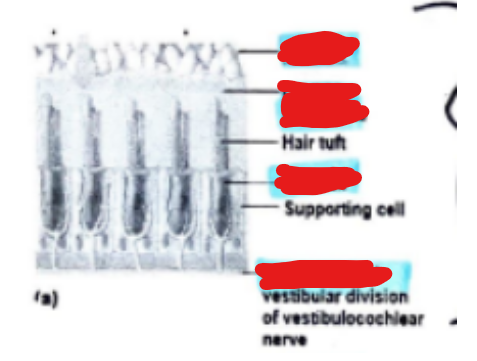
Label the different parts of a maculae from top to bottom…
Otoliths, otolithic membrane, hair cell, nerve fibers.
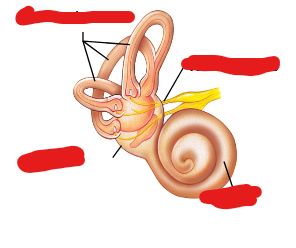
Label the following image from top to bottom…
Semicircular canals, vestibular nerve, vestibule, cochlea.
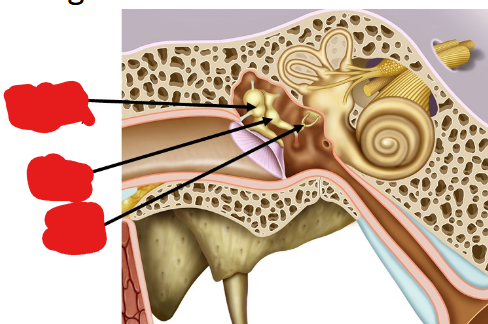
Label the following image from top to bottom…
Malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stirrup (stapes).
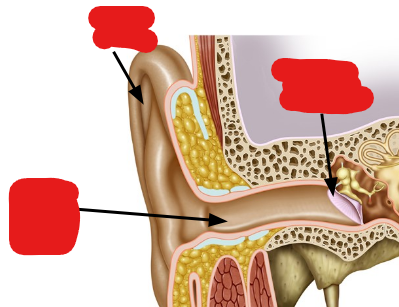
Label the following image from top to bottom…
Auricle (pinna), tympanic membrane, external auditory canal.

Label the following image from top to bottom…
Tectorial membrane, cilia, hair cells, basilar membrane.