Geography Case Studies
1/79
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Location: Haiti (2010)
Caribbean, Capital Port Au Prince 15 miles away from the epicentre
What were the magnitudes of both the Haiti (2010) and the Christchurch, New Zealand (2011) earthquakes?
Haiti- 7.0
New Zealand- 6.3
Primary Impacts: Haiti (2010)
316,000 died
300,000 injured
1/3 buildings destroyed
1.5 million homeless
Prison destroyed
Secondary Impacts: Haiti (2010)
Cholera outbreak 10 months after the earthquake (the bodies were left to decompose)
4000 prison inmates escaped
Immediate Responses: Haiti (2010)
Food aid, water, shelter sent BUT took 48 hours to arrive
USA sent 10,000 troops
The UK government donated £20 million
Long Term Responses: Haiti (2010)
98% of rubble remained unclear 1 after
Rebuilding homes to a stronger standard
1 million people were still living in tents after 1 year
The port was rebuilt after 1 year
Cash-for-work Programme
Why was Haiti so badly affected?
Placed 145/169 on the HDI
Less than 10% of total population had access to water
Less than 1/3 had access to electricity
Over ½ lived on less than $1 a day
No seismic networks
Location: New Zealand (2011)
South Island, close to 2nd largest city Christchurch
Centred near Lyttelton 6.2 miles SE of Christchurch
Primary Impacts: New Zealand (2011)
181 died
2000 injured
Cathedral Collapsed
Liquefaction
Secondary Impacts: New Zealand (2011)
Schools closed for two weeks
Could not hold the Rugby World Cup
Land that suffered liquefaction could not be built on again
Immediate Responses: New Zealand (2011)
300 Australian Police Officers flown in to help with the rescue effort
30,000 residents provided with chemical toilets, bottled water and supplies
Temporary housing
Long Term Responses- New Zealand (2011)
10,000 affordable homes built
Earthquake-resistant library built
Water and sewage systems restored by August 2011
Location: Hurricane Ida (2021)
Caribbean Sea
USA, Cuba, Venezuela
Category: Hurricane Ida (2021)
Category 4 (150)
Primary Impacts: Hurricane Ida (2021)
115 died
250,000 cars destroyed
Roads/Bridges collapsed
Secondary Impacts: Hurricane Ida (2021)
95% of population had no power 9 days after
Fishing industry collapsed as the port way destroyed (no oyster catch for a year)
Immediate Responses: Hurricane Ida (2021)
FEMA provided food, medicine, blankets
The Army rescued those trapped in cars
800 evacuated from Cuba
Long Term Responses: Hurricane Ida (2021)
Disaster Relief Fund set up to help vulnerable and undocumented citizens
What is needed for tropical storms to form?
Warmth
Shear Wind
Pressure
Time of year
Coriolis
Access to water
Hurricane Ida vs Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was 16 years before Ida
1,833 deaths
Levees built in 2005 in New Orleans (less deaths in Ida)
Location: Boscastle (16 Aug 2004)
North Cornwall
Primary Impacts: Boscastle (2004)
75 cars and 6 buildings washed away
Trees uprooted
58 properties flooded
Secondary Impacts: Boscastle (2004
People made homeless
1 year for tourism to return
Management Strategy: Boscastle (2004)
Environmental Agency spent £10 million
Raised car parks and bridge
Widened and deepened the river Valency
Removed dead trees
Human Causes: Boscastle (2004)
Low bridges, debris got trapped
Building materials blocked downstream (like a dam)
Lots of impermeable surfaces (Concrete)
Physical Causes: Boscastle (2004)
Heavy rainfall (89mm in 2 hours)
Ground was already saturated from previous wet weather
Steep sided drainage basin (Boscastle was surrounded by mountains)
Impermeable rock at the confluence of rivers Jordan, Valency and Paradise
Rivers already full of sediment
Location: New Forest
South Coast on England in the county, Hampshire. Bournemouth is to the West and Portsmouth to the East
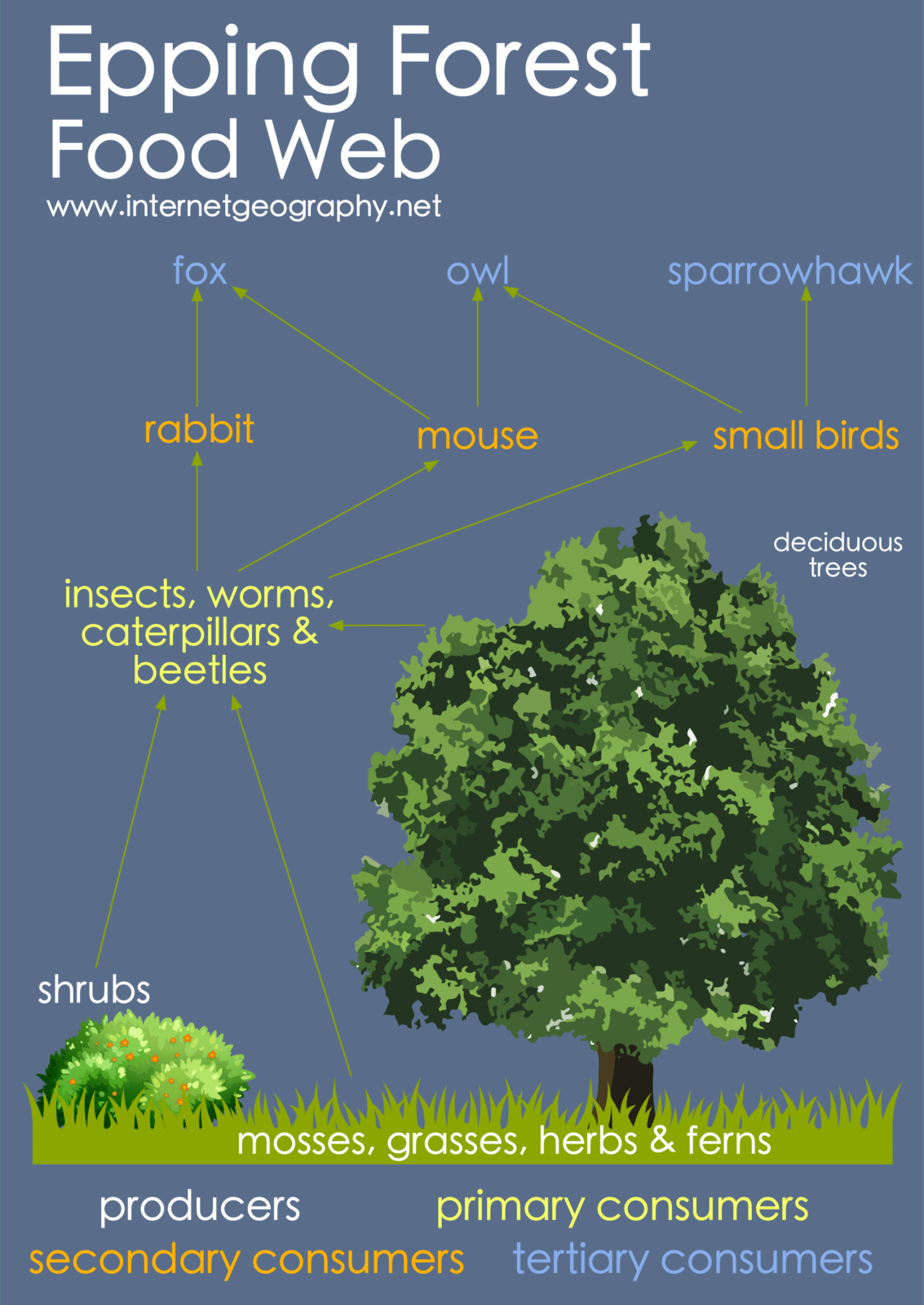
Location: The Amazon
Covers 40% (8 countries)
17% has been lost through deforestation
South America is home to 20 million people and 20% of the world's species. In the last 50 years
Characteristics: The Amazon
Hot (27oC)
Over 2000mm
Quick nutrient/water cycle
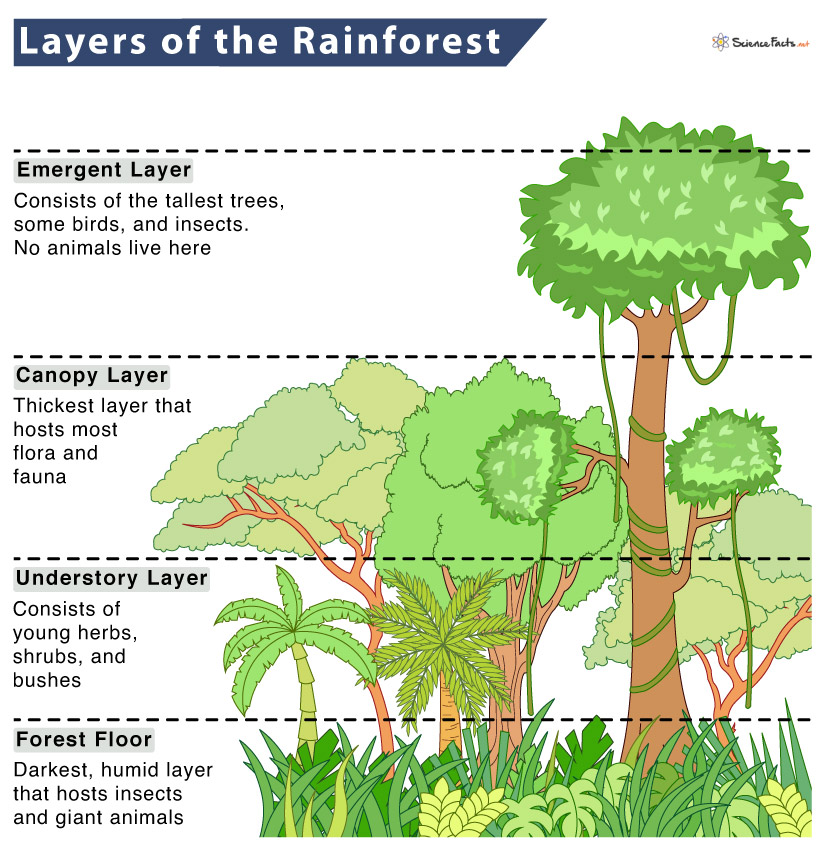
Plant Adaptations: The Amazon
Buttress roots
Liana
Epiphytes
Drip-tip leaves
Animal Adaptations: The Amazon
Leopard spots
Spider monkey arms
Causes of Deforestation
Pasture and cattle ranching- 63%
Small-scale, subsistence farmers- 12%
Fire- 9%
Commercial crop farming- 7%
Tree felling and logging- 6%
Management: The Amazon
Selective logging
Education
Ecotourism
International Agreements (WWF & Brazilian gov to protect 150 million hectares of forest)
Location: The Sahara
Stretches 3,000 miles across 11 countries in North Africa (Algeria, Tunisia, Egypt)
Covers 31% of Africa
Characteristics/Challenges: The Sahara
Extreme temperatures- 40oC — -10oC (diurnal range)
Limited water supply- 250mm of rain (Temporary & aquifers used quickly)
Poor accessibility- Limited roads, hard to transport goods (5 days to transport salt out of the desert)
Opportunities: The Sahara
Tourism- 14 million tourists visit the Egyptian pyramids each year, Star Wars set in Tunisia
Energy- Morocco built the world’s largest solar panel farm, Tunisia is building one that can power 2.5 million homes
Farming- Egypt is the largest producer of cotton
Mining- Contributes to 35% of Morocco’s exports
Management of desertification
Stone lines- slows runoff = infiltration
Afforestation- Great Green Wall, roots bind soil= nutrients gained (8,000)
Location: River Tees
Northeastern England, rising on cross fell in the northern Pennines and flowing 110km east to the North Sea
Source: River Tees
Cross Fell- 300m above sea level
Upper course
V-shaped valleys
Interlocking spurs
Tributaries and streams
Middle course: Waterfalls
High Force waterfall has a high Whin sill which lies above limestone. The limestone is eroded faster, creating an overhang
The overhang eventually falls which causes the waterfall to retreat
Middle course: Oxbow Lakes
When meanders form close together, they eventually meet each other and a new channel is formed. The meander gets blocked off and becomes an oxbow lake
Lower course
The river's estuary flows out to the North Sea. The mouth is located by Middlesbrough. It houses one of the biggest container ports in the UK
Opportunities: The Amazon
Cattle ranching is the main reason for deforestation in the amazon (63%)
2nd largest soybean exporter
Rosy Periwinkle cure for leukaemia found in the rainforest
2/3s of the world’s plant species found in the rainforest
Location: Rio de Janeiro
SE of Brazil on the Atlantic coast. 2nd most populated city of Brazil
Importance: Rio de Janeiro
Exports and industry as TNCs like VW & Pepsi have huge factories here and many Brazilian TNCs their HQs are here. 2 wonders of the world: Christ the Redeemer statue and Guanabara Bay making it a global tourist destination
Causes of Growth: Rio de Janeiro
People leave the rural NE of Brazil due to push factores…subsistence farming, lack of water, healthcare and education. They are PULLED into Rio by employment opportunities in docks,tourism, schools and further education, access to hospitals and medicines - a chance at a better life for their kids and to get their family out of poverty.
Challenges in Favelas: Rio de Janeiro
Unsafe- Buildings made from waste materials like metals,
10% no access to water, sickness
50% lack sanitation
High crime rates - gun/drug cartels
Unemployment high -large % in informal sector
Landslides- Favelas built on hillsides, heavy rain makes for little protection
Budget: Favela Bairro Project
$1 million for the Local Authority to improve quality of life for the urban poor.
Positives: Favela Bairro Project
+Paved and named roads- added to maps. Enables easy access for emergency services and rubbish removal trucks
+Adult education night classes/training schemes. Free education programme for children in favelas
+Health centres introduced to support with drug and alcohol abuse.
+26,000 residents with access to a clean water supply and drainage systems reducing the impact of water borne disease such as cholera
+Day care centres for young children set up to allow parents to work. - 40,000 day-care places for children under 4
+Police pacifying unit set up with 300 police offices to reduce crime
Negatives: Favela Bairro Project
-Crimes moved to different neighbourhood
-Only 60/600 fevelas benefited. The project has benefitted just 400,000 of the 11 million
- Cable car which was installed (cost $64 million) had to be shut because of budget cuts
-97% of properties increased in value due to the project.
Location: Southampton (HIC)
Southampton is a city located in the county of Hampshire in the South East of England. Located between the New Forest to the West and Eastleigh and Fareham to the East.
Importance: Southampton (HIC)
-The port: Cruise ship destinations as we are a major cruise terminal with over 1.4 million passengers a year and ship to countries all over the world 95% of trade arrives from the sea
-Universities: Solent and Southampton Uni -over 35,000 students. They need places to live so will rent & improve the economy
Causes of Growth: Southampton (HIC)
Natural increase & migration (Poland)
Opportunities: Southampton (HIC)
-Dock employs 15,000, redevelopment of West Quay South/above bar/ showcase cinema = new businesses
-Green spaces- St James Park/Riverside awarded Green Flag awards 2019, good links to main cities 1hr 15 → London, ‘Go Travel card’ Solent Go, science park
Challenges: Southampton (HIC)
-Loss of greenland due to urban sprawl, air pollution 100 deaths a year, too much waste- only 40% recycled, increased congestion due to growing pop, inequalities in housing (10,000 on social housing list) education(Redbridge fewer GCSE’s), closure of manufacturing e.g Ford Van loss of 500 jobs
Describe the Regeneration of Southampton
West Quay was needed after the Pirelli factory was closed in 1990. The ground was derelict, polluted with Mercury attracting crime/graffiti. Unsightly for tourists when they arrived in the ports. Built on a brownfield site in 2000. Created 130 shops & 3000 jobs. West Quay South then created 500 jobs→ in 1st year 16 million visited.
Sustainability Solent Go: Southampton
Promotes public transport reducing traffic congestion and C02 to stop lateness to work. Cycle lanes (£25 million invested) promoted introducing bike lanes and e-scooters
Sustainability Water Conservation: Southampton
Grey water recycling scheme, onsite wastewater treatment, smart water meters for each property, drainage system to collect runoff
Sustainability Energy Conversation: Southampton
Southampton District Energy Scheme (geothermal plant). Saves 10,000 tonnes of C02 a year- powers TV studio, hospital, uni, and shopping centre
Location: Nigeria (NEE)
West Africa bordering Benin, Niger, Chad and Cameroon
Political Context: Nigeria (NEE)
Colony of UK but gained independence in 1960
Corrupt Government
Contributes troops to UN peacekeeping organisations
Economic Context: Nigeria (NEE)
Inequalities between North and South
88,000s live in extreme poverty
80% work in farming
Rural-urban migration
Social Context: Nigeria (NEE)
500 ethnic groups
Conflict between North (Muslim) and South (Christian)
Life expectancy
Importance: Nigeria (NEE)
2nd biggest film industry ‘Nollywood‘
Highest GDP within Africa
7th largest population in the world (200 million) with 70% population under 30 = higher % working age
Why is Nigeria growing so quickly and industry changed?
Growth of manufacturing industry (textiles, leather goods, processed foods) and oil exports now 52% of GDP- cheap and plentiful labour
Discovered large supplies of oil (Niger Delta) which can be exported
10th largest supplier in the world
TNCs Positives (Shell): Nigeria (NEE)
Niger River Delta: one of world’s most difficult places to extract oil from
$200 million in tax paid to government
85,000 nigerians employed directly and 250,000 in other related sectors
TNCs Positives (Shell): Nigeria (NEE)
Water pollution contaminating water supplies and crop growth reduced
Corruption and fighting
Fisherman livelihood impacted
Water Aid (Nigeria): Why is it needed?
Only 10% have access to water
68 million have no access to drinking water
23% practice open defecation
Water Aid (Nigeria): Positives
300,000 have access to toilets
Hand pump so women and girls can collect water without leaving the villages
119 communities declared free from open defecation
Water Aid (Nigeria): Negatives
Nigeria gov known for corruption it may affect the aid they receive
Nigeria has become dependant on aid
May not be appropriate or sustainable as it does not reach all
Tourism in Jamaica
4th largest island in the Caribbean, tropical climate, high temperatures, sandy beaches = ideal tourist location
Numbers grown although this was impacted during COVID, 1 in 4 work in tourism
People in Montego bay have improved quality of life
Habitat loss, pollution, coral reef damage and locals cannot afford amenities built for tourists (poverty still exists)
Why is it growing?: South Cambridgeshire
Close to M11 for access to London, good uni’s, highly skilled workforce, population increased by 9% (148,800 to 162,100)
Why is it declining?: Outer Hebrides
Lewis (larger island) has reduced, journey from OH is 2 hours from mainland, flights are expensive
Location: Kielder Reservoir
Located in the Pennines (high land). It receives more rain than areas to the East which lie in the rain shadow.
What happens? Water is transported southwards and released into rivers that flow to Newcastle-upon-tyne, Sunderland, Durham and Middlesbrough
Advantages: Kielder Resevoir
+450,000 jobs created, 250,000 visit the reservoir for water sports/scenery around the lake.
+HEP generated, reliable/clean energy source saving 8,500 tonnes of carbon dioxide a year.
+Water insecurity has been reduced
+50% England’s native red squirrel live here
Disadvantages: Kielder Resevoir
-Breeding patterns of fish disrupted through blocking the dam
-58 families moved from homes to make room for the dam/reservoir
-2,700 acres of farmland/many habitats lost. 1.5 million trees cut down
-Cost £167 million to build the dam
Location: South-North Water Transfer
Water is diverted from Southern regions of China to Northern cities such as Beijing and Tianjin where there are water deficits through 3 routes (Central, Eastern and Western)
Advantages: South-North Water Transfer
+China has 20% world pop, and only 7% water
+Provides water to irrigate farmland so crops can grow to support the agricultural economy. Only 12% of China is arable
+Provides 44 billion cubic metres of water every year for people in the cities of Beijing and Tianjin, reducing water stress
Disadvantages: South-North China Water Transfer
-Cost $62 billion extremely high to taxpayers
-345,000 people in villages lost their home as they have been flooded to create new reservoirs for projects
-Water stress in southern areas will increase as water is being diverted. There won’t be enough drinking water for 30 million locals