The Muscular System
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards containing definition of muscular system from chapter 8.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Myology
The scientific study of muscles.
What are the three types of muscular tissue?
Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle.
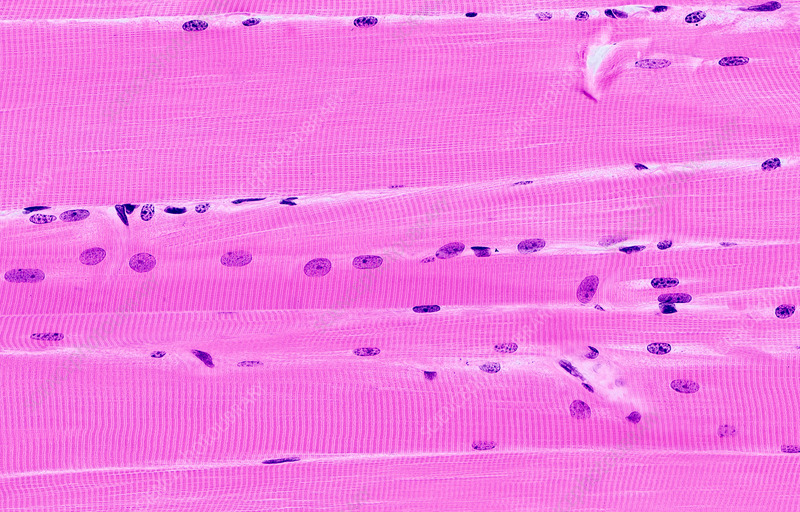
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Mostly attached to bones, striated, and voluntary.
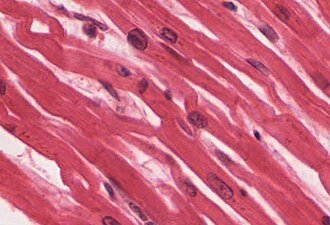
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Forms most of the wall of the heart, striated, and involuntary.
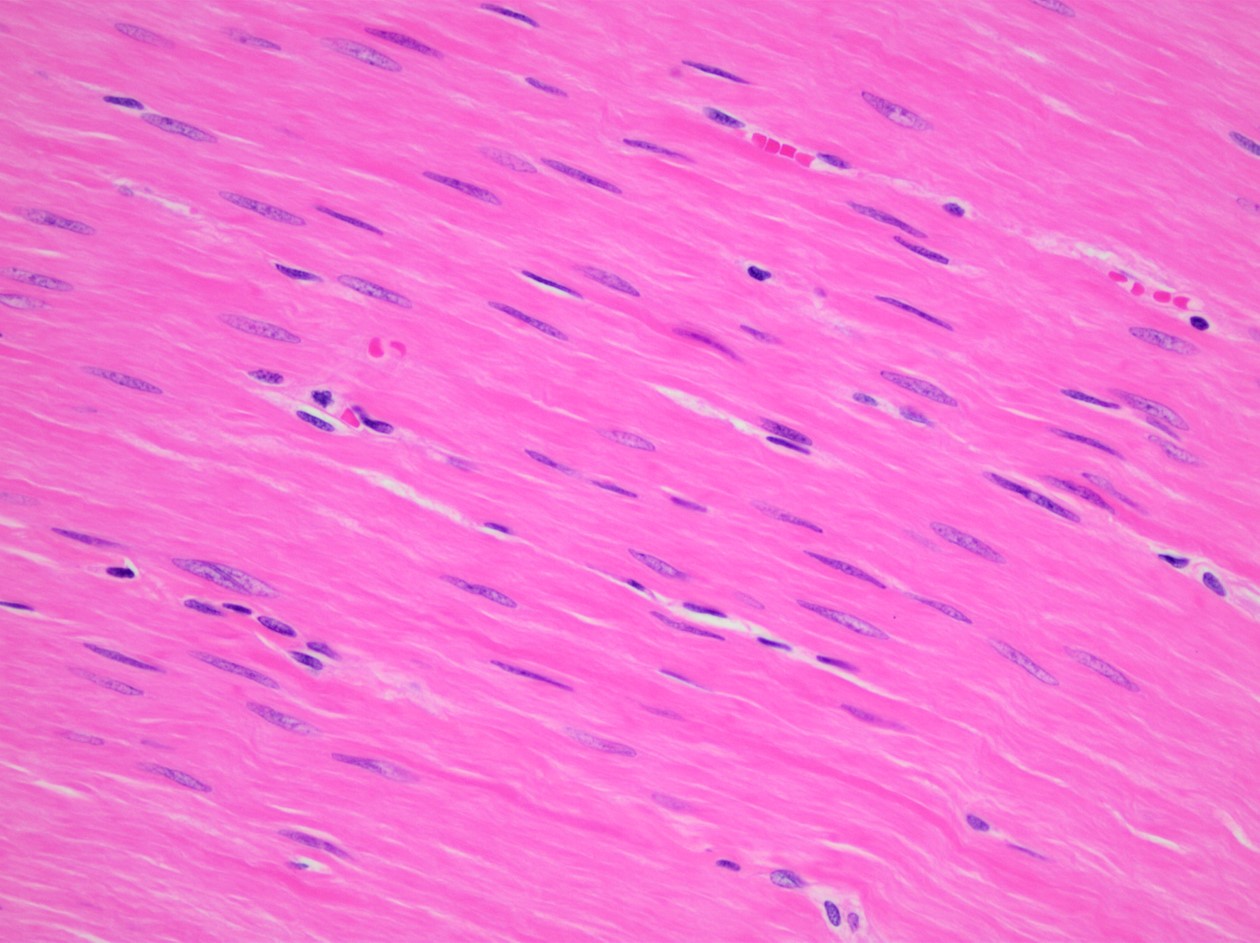
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Located in viscera, nonstriated, and involuntary.
What are the five key functions of muscular tissue?
Producing body movements, stabilizing body positions, regulating organ volume, moving substances within the body, and producing heat.
Muscle Fibers
Skeletal muscles are separate organs composed of hundreds to thousands of cells called:
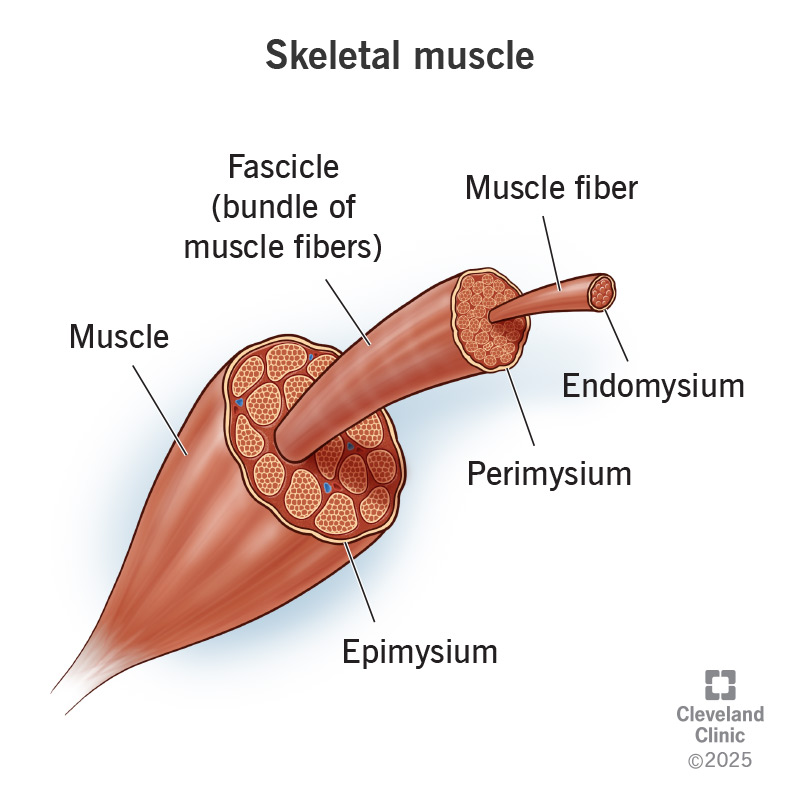
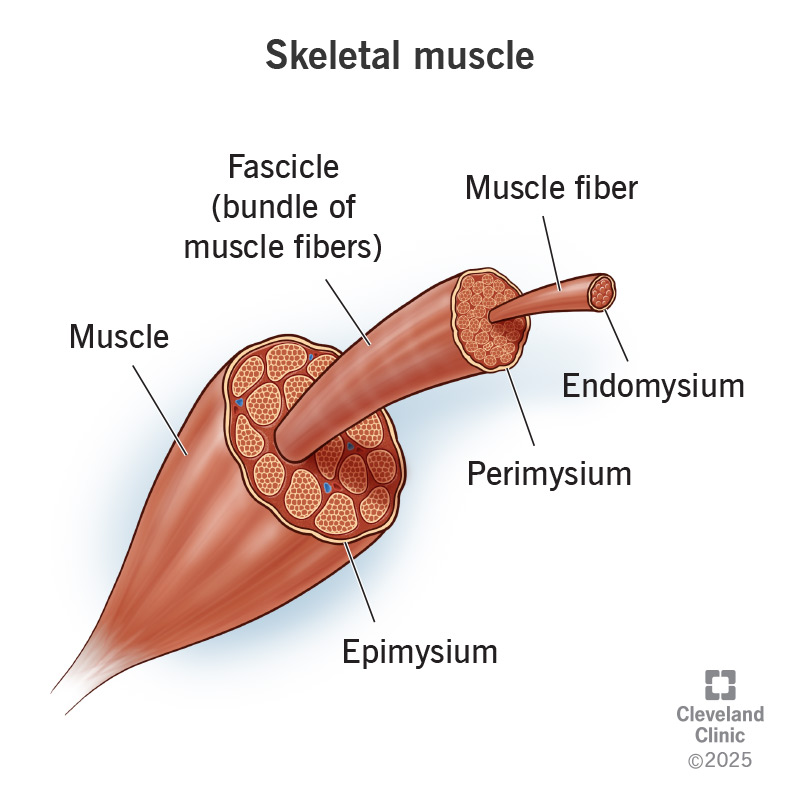
Epimysium
Connective tissue covering an entire muscle.
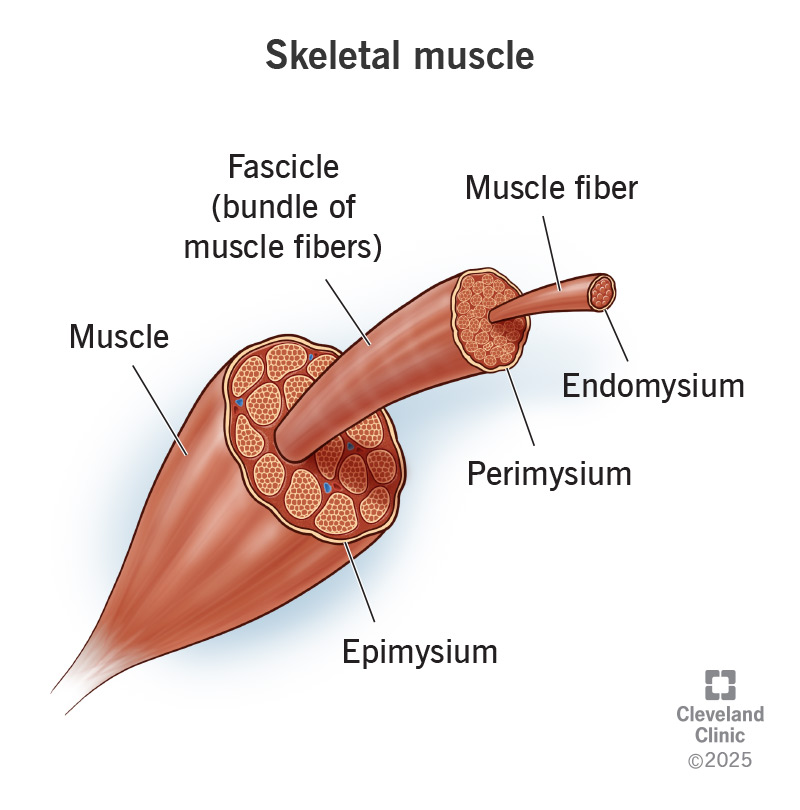
Perimysium
Connective tissue covering fascicles.
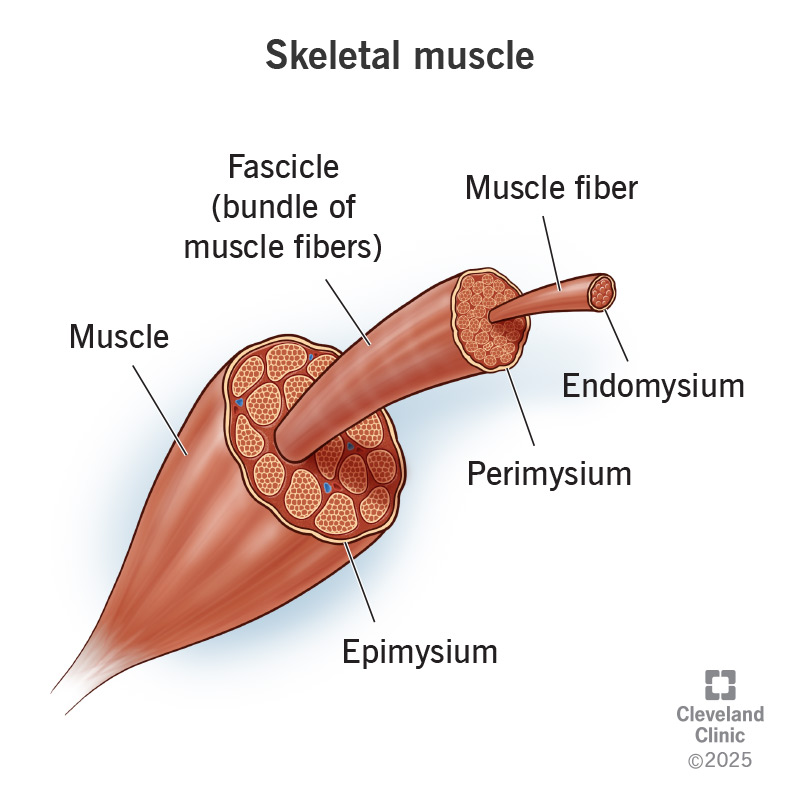
Endomysium
Connective tissue covering individual muscle fibers.
Tendons
Extensions of connective tissue beyond muscle fibers that attach the muscle to bone.
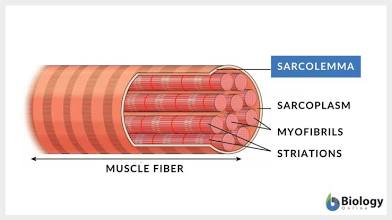
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane that covers the skeletal muscle
Transverse Tubules (T-tubules)
Tunnel in from the surface toward the center of each muscle fiber.
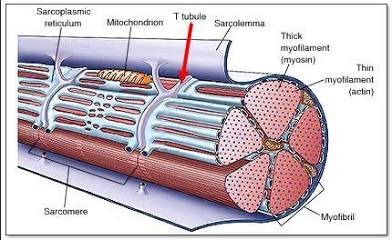
Sarcomeres
Functional units that filaments are arranged in
Myosin
Thick filaments consist of:
Actin, Tropomyosin, and Troponin
Thin filaments are composed of:
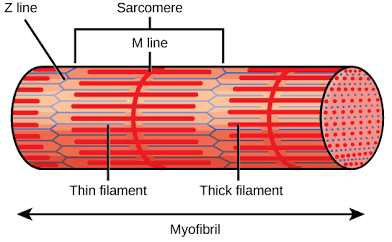
Z discs
Sarcomeres are separated from one another by zig-zagging zones of dense protein material called:
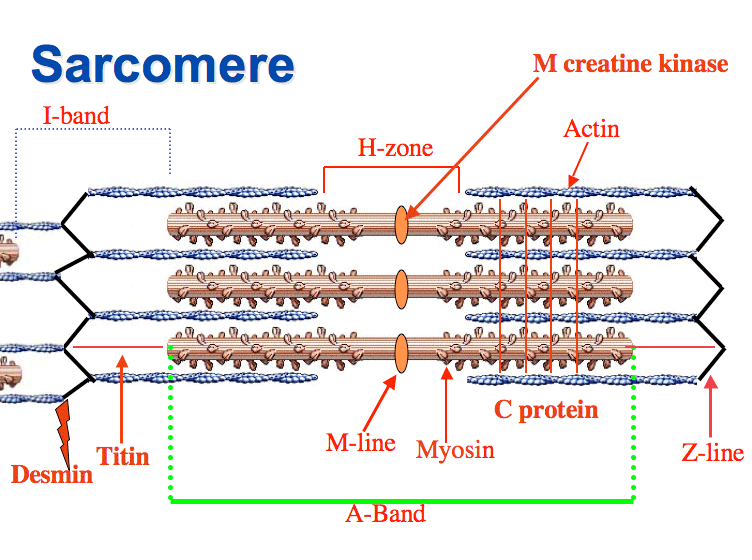
A band
A darker area within each sarcomere that extends the entire length of the thick filaments.
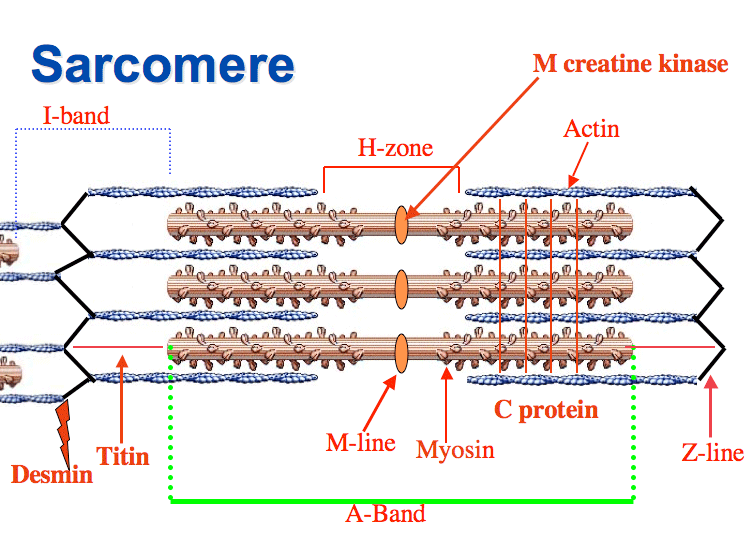
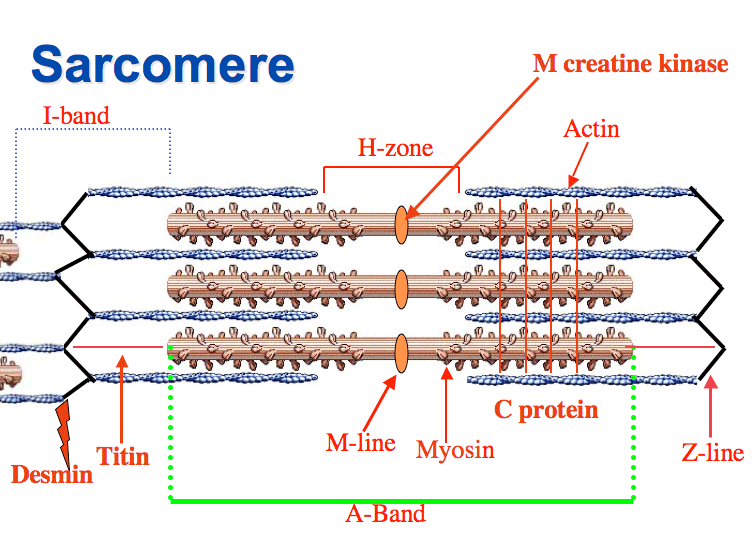
H zone
A narrow zone at the center of each A band, which contains only the thick filaments.
I band
A lighter-colored area to either side of the A band, which contains the rest of the thin filaments but no thick filaments.
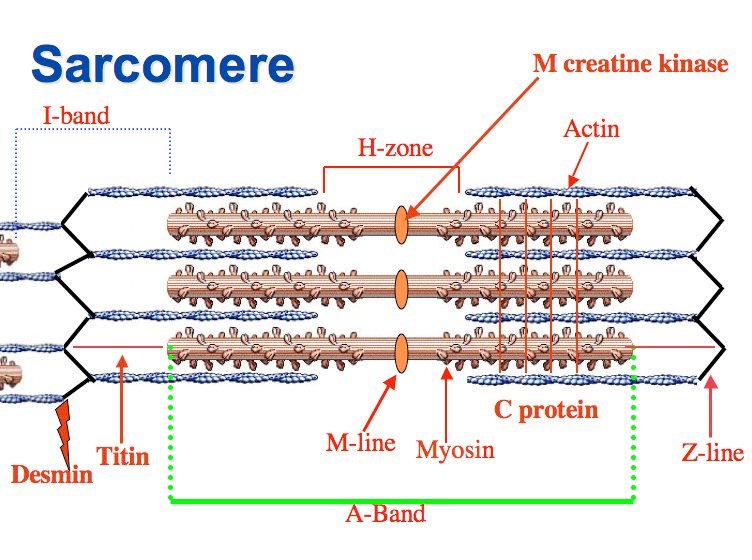
Motor Neuron
The neuron which delivers an electrical signal called a muscle action potential to a skeletal muscle fiber so it can contract.
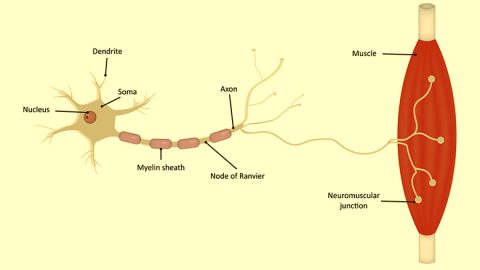
Motor Unit
A single motor neuron along with all the muscle fibers it stimulates
Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ)
The synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber.
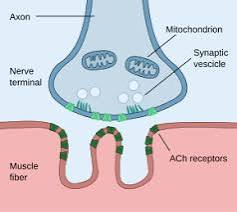
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Released from synaptic vesicles; diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to ACh receptors, initiating a muscle action potential.
Acetylcholinesterase
Breaks down ACh.
Sliding-Filament Mechanism
The sliding of filaments and shortening of sarcomeres that cause the shortening of muscle fibers.
What two things are needed for muscle contraction?
Ca2+ and energy, in the form of ATP
Name the 4 steps of the contraction cycle:
- Splitting ATP 2. Forming cross-bridges 3. Power stroke 4. Binding ATP & detaching
List the three sources for ATP production:
Creatine phosphate, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic respiration.
Creatine Phosphate
Provides enough energy for muscles to contract maximally for about 15 seconds.
Anaerobic Glycolysis
Glucose is converted to pyruvic acid in the reactions of glycolysis, which yield two ATPs without using oxygen and can provide enough ATP for about 2 minutes of maximal muscle activity.
Aerobic Respiration
Mitochondrial reactions that require oxygen to produce ATP; yields about 36 molecules of ATP from each glucose molecule.
Muscle Fatigue
The inability of a muscle to contract forcefully after prolonged activity.
Recovery Oxygen Uptake
Elevated oxygen use after exercise.
Twitch Contraction
A brief contraction of all of the muscle fibers in a motor unit in response to a single action potential in its motor neuron.
Myogram
A record of a contraction.
latent period, contraction period, and a relaxation period
A myogram consists of:
Wave Summation
The increased strength of a contraction that occurs when a second stimulus arrives before the muscle has completely relaxed after a previous stimulus.
Motor Unit Recruitment
The process of increasing the number of active motor units.
List the three types of skeletal muscle fibers:
Slow oxidative (SO) fibers, fast oxidative-glycolytic (FOG) fibers, and fast glycolytic (FG) fibers.
The order in which motor units of a muscle are recruited:
first SO fibers, then FOG fibers, and finally FG fibers
Which type of muscle tissue contracts when stimulated by its own autorhythmic fibers?
Cardiac
Smooth Muscle Tone
A state of continuous partial contraction of smooth muscle tissue.
Origin
The attachment to the stationary bone
Insertion
The attachment to the movable bone
Prime Mover (Agonist)
Produces the desired action.
Antagonist
Produces an opposite action.
Synergist
Assists the prime mover by reducing unnecessary movement.
Fixator
Stabilizes the origin of the prime mover so that it can act more efficiently.
Rectus
Parallel to midline.
Transverse
Perpendicular to midline.
Oblique
Diagonal to midline.
Maximus
Largest.
Minimus
Smallest.
Longus
Longest.
Latissimus
Widest.
Longissimus
Longest.
Magnus
Large.
Major
Larger.
Minor
Smaller.
Vastus
Great.
Deltoid
Triangular.
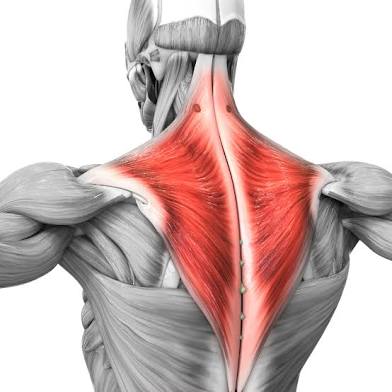
Trapezius
Trapezoid.
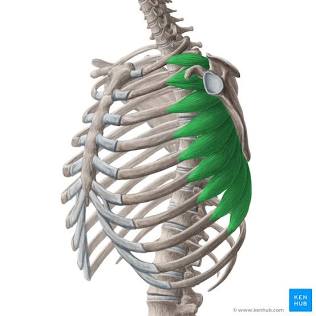
Serratus
Saw-toothed.
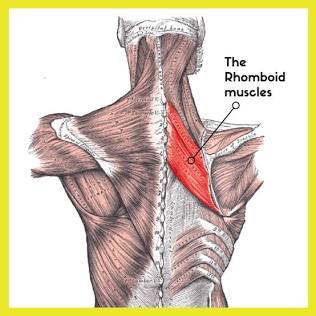
Rhomboid
Diamond-shaped.
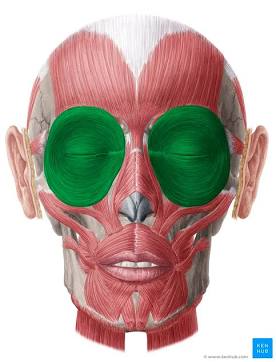
Orbicularis
Circular.
Pectinate
Comblike.
Piriformis
Pear-shaped.

Platys
Flat.
Quadratus
Square.
Gracilis
Slender.
Flexor
Decreases joint angle.
Extensor
Increases joint angle.
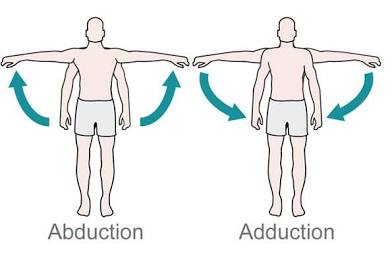
Abductor
Moves bone away from midline.
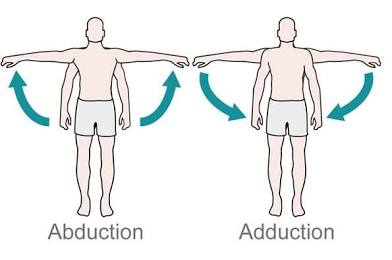
Adductor
Moves bone closer to midline.
Levator
Produces superior movement.
Depressor
Produces inferior movement.
Supinator
Turns palm anteriorly.
Pronator
Turns palm posteriorly.
Sphincter
Decreases size of opening.
Tensor
Makes a body part rigid.
Biceps
Two origins.
Triceps
Three origins.
Quadriceps
Four origins.