Physics 2- study
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Sound
produced by vibrating objects.,
Compression
a region of slightly higher pressure where the air molecules are closer together than usual.
wavelength
is equal to the distance between the centres of two successive compressions.
Ultrasound
high frequency sound, above 20 000 Hz, too high to be heard by humans.
Infrasound
low frequency sound, inaudible to human, although we may feel the very slow vibrations.
Sound waves in different materials
Sound travels quickest through solids.
Sound travels well through liquids.
Sound travels slowest through gases.
echo
reflected sound wave.
Echo eqwuation
speed = distance / time
SPEED
Speed = distance / time.
oscilloscope
device that with a microphone attached can be used to display a sound wave.
amplitude
height of the wave (measured from the centre of the screen)
frequency
number of entire waves that appear on the screen
wave
means of transferring energy and information from one point to another without there being any transfer of matter between the two points.
Transverse waves
waves where the direction of vibrations is at 90° to the direction in which the wave travels.
example: water waves
Longitudinal Waves
waves where the vibrations of the particles are along the direction in which the wave travels.
Wavelength
distance between one wave peak and the next wave peak along the path of a wave. metrees
Average Speed
Average Speed = Distance moved / Time taken
Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Time taken
Frequency
number of wave peaks that pass a point in one second, measured in hertz (Hz)
frequency = 1 / time period
Time period
time taken for a source to produce one wave.
time period = 1 / frequency
Wave Equation
speed = frequency x wavelength
Refractie index
refractive index, n= speed of light in a vacuum, c / speed of light in that material, v
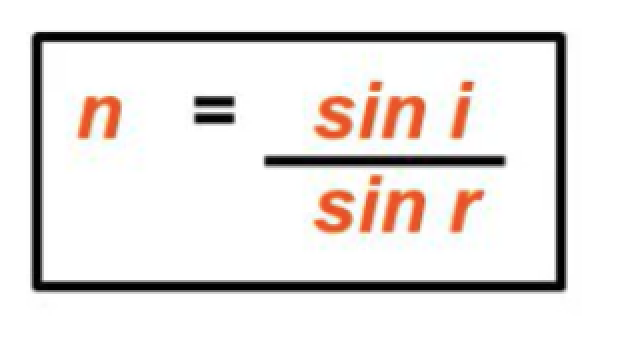
Refraction occurs
when a wave changes speed as it passes from one region to another.
angle of incidence
The angle of the wave approaching the boundary
Angle of reflection
The angle of the wave leaving the boundary
Reflection occurs
A wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but instead stays in the original medium
electromagnetic spectrum
continous spectrum of waves which includes the visible spectrum.
velocity
speed in a given direction.