AP Biology Review
1/434
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes weird ways I remember stuff.... this is literally everything... or as much as I could put.... godspeed.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
435 Terms
ionic bond
bond when electrons are transferred
covalent bond
co = share
bond when electrons are shared
polar
magnet poles are positive and negative, so they are…
not equal, hydrophilic
non polar
equal, hydrophobic
nonpolar covalent bond
covalent bond when electrons are shared equally
polar covalent bond
covalent bond where electrons are shared unequally
hydrogen bond
positive hydrogen and an electronegative atom
weak bond
used for water’s adhesion, cohesion, surface tension
most common elements of life
CHONPS
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
water
polar molecule/hydrophilic
universal solvent
less dense, so lakes don’t freeze solid
high specific heat (takes a lot to make it go up a degree)
causes transpiration in plants thanks to cohesion and adhesion
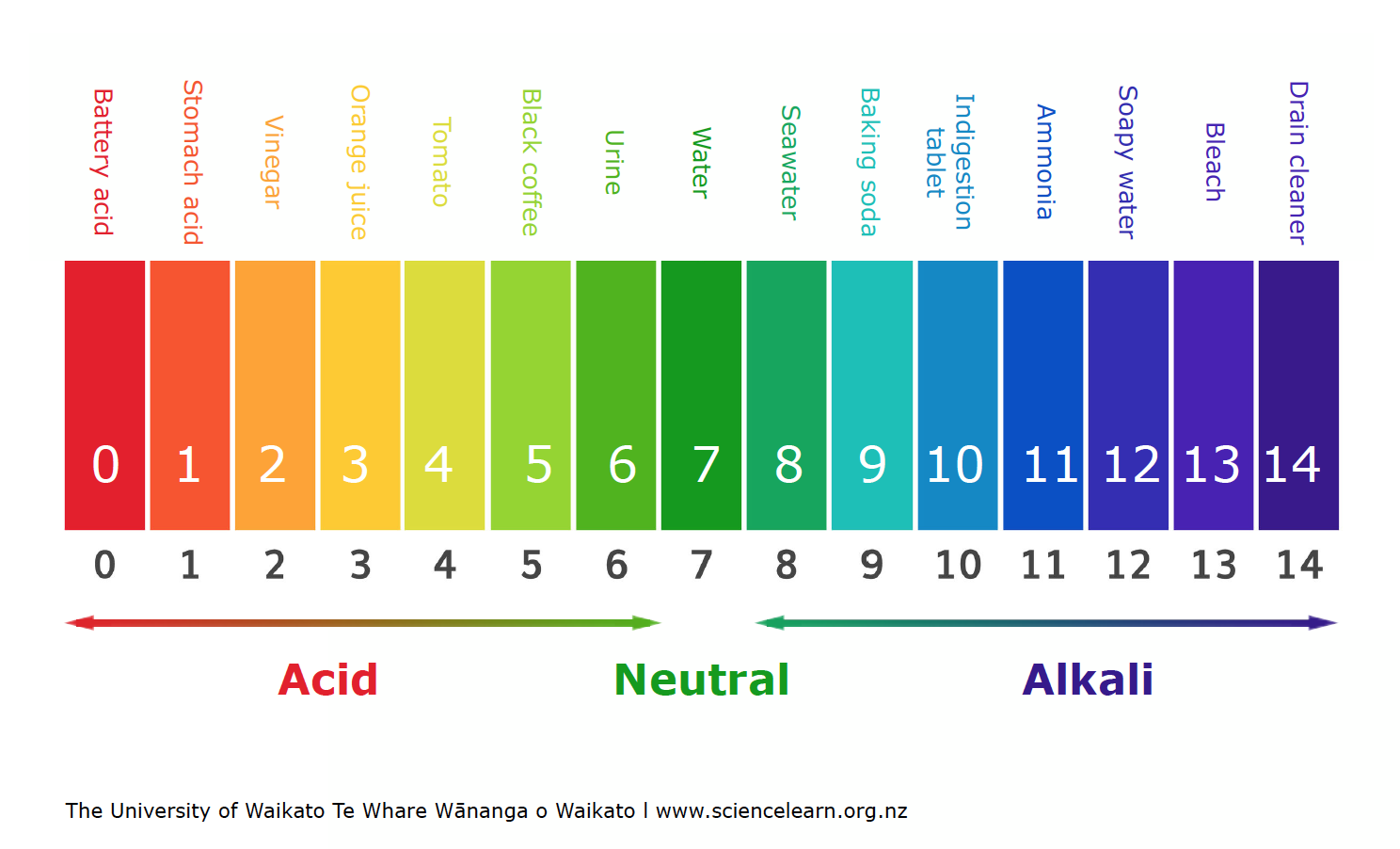
pH
pH level and amount of hydrogen ions are inverse
amount of hydrogen ions
acidic pH
dropping acid lowers pH
high amount of hydrogen ions
less than 7 pH
neutral pH
7 pH
basic pH
being based gets you more pH
low amount of hydrogen ions
more than 7 pH
about anabolic/catabolic and endergonic/exergonic reactions…
anabolic + endergonic: generally, creation takes energy
catabolic + exergonic: generally, destruction releases energy
anabolic
creating something
catabolic
catastrophes destroy
destroying something
endergonic
en = in
energy goes into the reaction
exergonic
ex = exit
energy exits the reaction
dehydration synthesis
dehydrate = get rid of water, synthesis = making something
releasing/getting rid of water to make a polymer
anabolic = creation
endergonic = energy into
hydrolysis
hydro = water, lysis = destruction
adding water to destroy something into monomers
catabolic = destroy
exergonic = energy exits
carbohydrates
CHO 1:2:1
quick energy
monosaccharides
monomers of carbohydrates
disaccharides
dimers of carbohydrates
polysaccharides
polymers of carbohydrates
ex: cellulose, starch, chtin, glycogen
lipids
CHO, not 1:2:1
cell membrane, energy storage, steroid hormones, insulation, myelin sheath
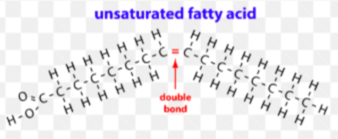
unsaturated fatty acid chains
lacking an extra hydrogen atom
double carbon bond causes kink
liquid at room temp
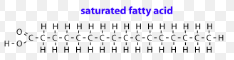
saturated fatty acid chains
has the full amount of hydrogen atoms
single carbon bond makes it straight
solid at room temperature
phospholipid head
touches the water so it’s hydrophilic
polar = hydrophilic
on the outside of the membrane
phospholipid tail
away from water so it’s hydrophobic
nonpolar = hydrophobic
on the inside of the membrane
proteins
CHON (sometimes S)
enzymes, structure, transport, signaling, protein carriers, antibodies
amino acids
monomer of proteins
carboxyl + amino group + central carbon + variable R group
carboxyl group
COOH
one end of amino acid
amino group
NH2
other end of amino acid
central carbon
main part of amino acid
variable R group
hydrophobic or hydrophilic
determines chemical properties of the amino acid
protein folding
shape determines function
primary structure of protein
amino acid sequence
secondary structure of protein
chain/polypeptide backbone
beta pleated sheet
alpha helix
beta shape
who gives a sheet about betas
pleated sheet
alpha shape
helix
tertiary structure of protein
3d protein, a single polypeptide
quaternary structure of protein
multiple polypeptides/proteins
nucleic acid
CHONP
storage and transmission of genetic info
nucelotide
monomer of nucleic acid
nitrogen base + phosphate group + 5C deoxyribose sugars
DNA and RNA
polymers of nucleic acid
DNA function
carries genetic code
eukaryotes: in nucleus on multiple linear chromosomes
prokaryotes: single circular chromosome
DNA structure
double helix
deoxyribose sugars
antiparallel strands
3’ to 5’
5’ to 3’
made of nucleotides connected by hydrogen bonds
RNA
single stranded
ribose sugars
ribonucleic acid
AGCU
mRNA
copies genetic message
tRNA
transfers amino acids
rRNA
attaches mRNA by helping form peptide bonds
makes up ribosomes
purines
Pure As Gold, gold is strong = double ringed
As = adenine
Gold = guanine
double ringed
pyrimidines
C.U.T. the Pie, get one slice = single ringed
C = cytosine
U = uracil
T = thymine
single ringed
nitrogen bond pairs
AT, AU, GC
DNA: adenine + thymine
RNA: adenine + uracil
guanine + cytosine
GC base pair
3 bond group chats are strong
stronger due to 3 hydrogen bonds
AT/AU base pair
A is the weakest letter
weaker due to 2 hydrogen bonds
DNA transcription
DNA > RNA
by RNA polymerase
in nucleus
initiation of transcription
after TATA box, promoters binds to RNA polymerase
elongation of transcription
adds RNA nucleotides
termination of transcription
when RNA reaches a termination sequence
RNA polymerase reads…
DNA from 3’ to 5’
RNA polymerase synthesizes…
complementary mRNA in 5’ to 3’
mRNA editing
splice out introns
add polyA tail to 3’
add GTP cap to 5’
go to ribosome
intron
spliced out of mRNA
exon
expressed in final mRNA
translation
mRNA is ready and matched with tRNA (brings amino acids) to make a protein using the ribosome
DNA replication
exact copies of DNA for mitosis/meiosis
semi-conservative by copying the original strand
DNA polymerase
helicase
enzyme unzips DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds
replication fork
splits strands into 5’ to 3’ and 3’ to 5’
RNA primers
made by RNA primase, starts replication process
DNA polymerase reads…
DNA from 3’ to 5’
DNA polymerase synthesizes…
complementary DNA in 5’ to 3’
leading strand
continuous synthesis
5’ to 3’, towards replication fork
lagging strand
discontinuous/lagging synthesis in okazaki fragments
3’ to 5’, away from replication fork
ligase
enzyme that fuses okazaki fragments to lagging strand
topoisomerase
enzyme relieves tension of DNA by preventing tangles and knots
enzymes
proteins are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy
activation energy
how much energy is required for a reaction to happen
active site
enzyme region where substrates bond via enzyme/substrate complex
allosteric site
enzyme region where ligands bonds
substrate
the specifically shaped key to an enzyme
enzyme rate/function
based on enzyme and substrate collision
optimal pH
depends on the enzyme
temperature
increased temp means more collisions, so rate increases
too much heat denatures enzyme
enzyme concentration
more enzyme = faster rate
substrate concentration
if your job is to fold paper, getting passed paper is helpful, but too much paper won’t speed it up
helps increase reaction rate but can plateau
competitive inhibition
competes with substrate for active site
non-competitive inhibition
attaches at allosteric site
changes enzyme shape to make it not function
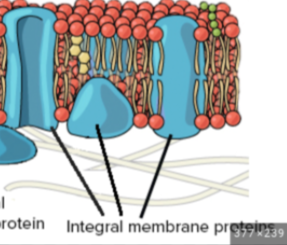
integral protein
permanently attached to the plasma membrane
transports ions and molecules
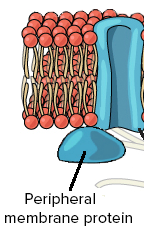
peripheral proteins
attached to the outside of the plasma membrane
usually enzymes or signal transduction

glycolipids
stabilize the cell membrane with hydrogen bonds

glycoproteins
used for cell recognition
molecules that can freely move through thanks to selective permeability
small
nonpolar/hydrophobic
not charged
molecules that cannot freely move through thanks to selective permeability
large
polar/hydrophilic
ionized/charged
passive transport
down the concentration gradient
high to low
no energy
active transport
against/up the concentration gradient
low to high
energy needed
simple diffusion
passive
no transport protein needed
facilitated diffusion
passive
channel/carrier proteins needed
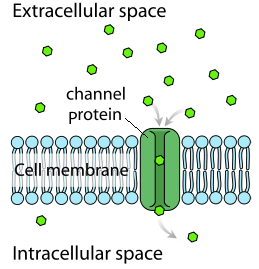
channel protein
passive transport
no energy
specific substances only
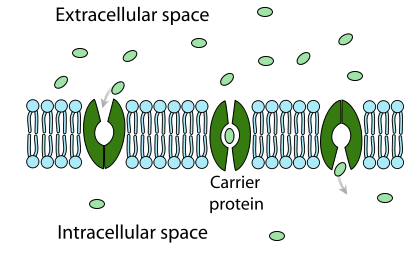
carrier proteins
passive or active transport
bind to molecules
changes shape to transport
osmosis
water always wants to balance/dilute
movement of water
high water concentrations to low water concentration
or, water moves from low solute concentration to high solute concentration

hypertonic solution
hyper people are thin
cell will lose water to the environment and shrink

hypotonic solution
hypo = hippo = fat
cell will gain water from the environment and swell