133 lec Lesson 1_Good Pharmacy Practice
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Joint FIP/WHO Guidelines on Good
Pharmacy Practice: Standards for Quality of
Pharmacy ServicesGood Pharmacy Practice International
Training Program by FAPA, FDA,
Pharmaceutical Society of Taiwan, Taiwan
YPG (Taipei, Taiwan)
References Used in GPP [2]
Discuss the mission of Pharmacy practice
Explain the elements of GPP
Enumerate roles of a pharmacists
Objectives [3]
📅 1986: WHO Meetings in Delhi, India & Tokyo, Japan
🔹 Recognized pharmacists' importance in healthcare
🔹 Discussed standard pharmacy practices
📅 1992: FIP Developed Pharmacy Service Standards
🔹 Introduced Good Pharmacy Practice (GPP) for both community and hospital settings
📅 May 1994: Adoption of WHA47.12
🔹 WHO recognized the pharmacist's role in healthcare
🔹 Supported better drug use policies
📅 1994: Submission of GPP Text to WHO
🔹 Reviewed by the WHO Expert Committee on Pharmaceutical Preparation
🔹 Final recommendations published in 1999
📅 1997 & 1998: WHO Meetings in Vancouver & the Netherlands
🔹 Emphasized the need to update pharmacy education
🔹 Highlighted pharmacists' role in self-care & self-medication
📅 1999: FIP/WHO Joint GPP Document Published
🔹 Established global pharmacy practice guidelines
📅 2006: Launch of "Developing Pharmacy Practice – A Focus on Patient Care"
🔹 Shifted focus to patient-centered care
🔹 Included automated dispensing, medication review, and clinical pharmacy
🔹 Recognized pharmacist prescribing rights (e.g., in the US)
📅 2007: FIP Initiative to Update GPP
🔹 Recognized the need for continuous updates
🔹 8 years since the first GPP document
📅 2008: FIP Consultation in Basel, Switzerland
🔹 50 experts reviewed GPP standards from 37 countries
🔹 Set global discussions with 120 FIP member organizations
📅 2009: WHO Expert Committee Meeting on GPP
🔹 GPP was developed to:
✔ Standardize global pharmacy practice
✔ Ensure safe & high-quality pharmacy services
✔ Promote effective patient care
✔ Adapt to new research & technologies
✔ Enhance patient safety
✔ Support continuous professional growth
Summary of Timeline
read
1986
India and Tokyo
(To know what should be included in the standard practice of pharmacy)
[GPP Background]
WHO organized 2 meetings to see the importance of pharmacy practice.
What Year and Where?
International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP)
🔉 Good Pharmacy Practice for both community and hospital setting
[GPP Background]
In 1992, _____ developed standards for pharmacy services
1994
[GPP Background]
What Year did adoption of WHA 47.12 happen
WHA: World Health Assembly Resolution
🔉 Each number in the WHA represents a specific resolution that addresses a specific health problem or issue.
🔉 Document that recognizes the role of a pharmacist and supports the plan of the WHO for a better drug use
WHO Expert Committee on the Pharmaceutical Preparation
🔉 Recommendations from this committee, along with the support of FIP, was incorporated in the published document in 1999
[GPP Background]
In 1994, Text in good pharmacy practice was submitted to _____
1999
[GPP Background]
What Year?
FIP/WHO Joint document of good pharmacy practice (GPP) was published
Vancouver, Canada and Netherlands
🔉 Highlighted the need to change the pharmacy education and show how pharmacists can help in self-care and self-medication
[GPP Background]
In 1997 and 1998, WHO organized 2 more meetings where?
2006
[GPP Background]
What Year?
First edition of a practical handbook Developing pharmacy practice – a focus on patient care was launched
Meet the changing needs of pharmacist
Setting out a new paradigm for pharmacy practice
Presenting a step-by-step approach to pharmaceutical care
In 2006, In collaboration with WHO, first edition of a practical handbook Developing pharmacy practice - a focus on patient care was launched. This handbook was designed to: [3]
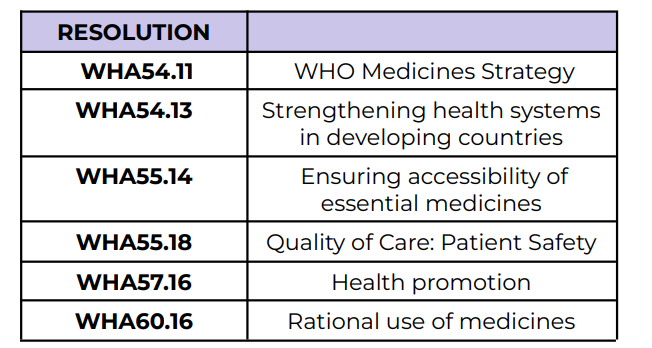
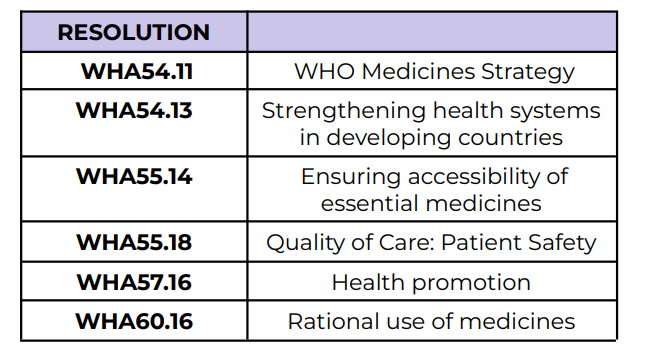
WHO Medicines Strategy
WHA54.11
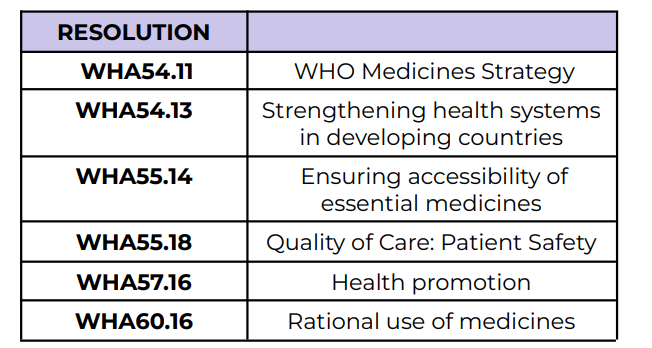
Strengthening health systems in
developing countries
WHA54.13
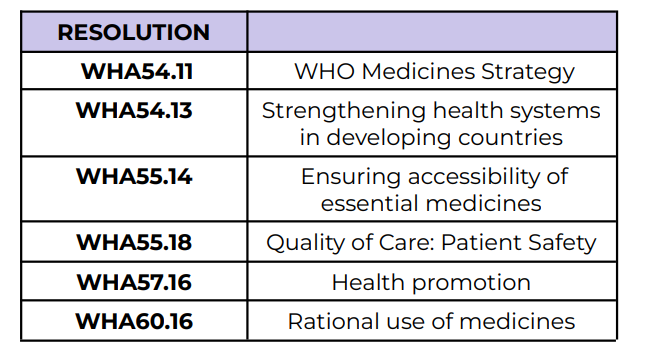
Ensuring accessibility of essential medicines
WHA55.14
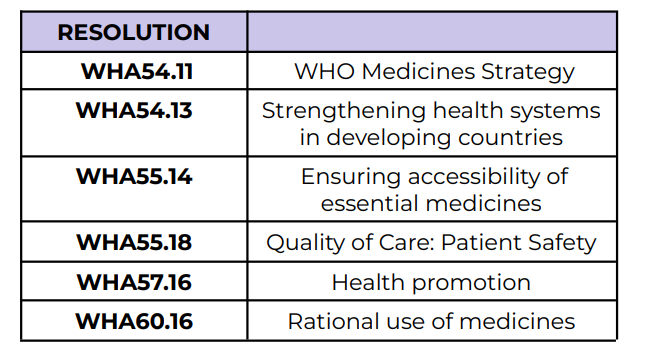
Quality of Care: Patient Safety
WHA55.18
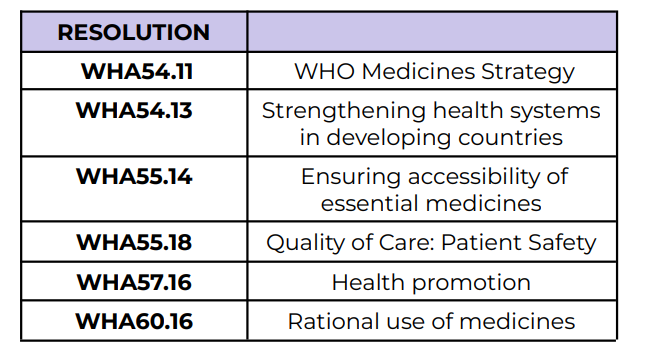
Health promotion
WHA57.16
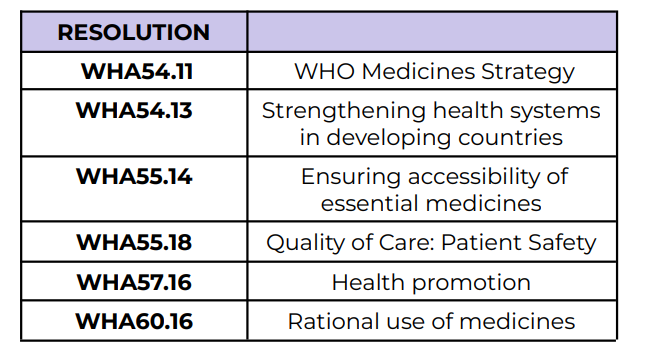
Rational use of medicines
WHA60.16
2007
[GPP Background]
What Year?
FIP established an initiative to investigate the need to update the guidelines on GPP
🔉 The practice evolves through time.
🔉 8 years since the FIP Joint document was published
🔉 Updates to match the current practice and ideas
2008
[GPP Background]
What Year?
FIP organized an expert consultation in Basel, Switzerland during its 68th World Congress
In the consultations, they shared it in the 44th meeting of WHO
2009
[GPP Background]
What Year?
44th meeting of the WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
2011
[GPP Background]
What Year?
Joint FIP/WHO guidelines on good pharmacy practice: standards for quality of pharmacy services.
🔉 Standardized practice of pharmacists around the world
🔉 Ensure the safe and high quality pharmacy service
🔉 Essential not only in promoting effective patient care but also for adapting new research and technologies
🔉 Enhancing patient safety
🔉 Supporting the ongoing professional growth
🔉 Why do you think GPP was developed? [3]
Access to health care
Health promotion
Use of medicines
Joint FIP/WHO guidelines on good pharmacy practice: standards for quality of pharmacy services. WHO Technical Report Series, No. 961, 2011. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2011
This provides description to improve [3]?
Poor Access to quality medicinal products 💊
Lack of Trained Healthcare Professionals and care 🩺
Inadequate Health Workforce 👥
Poor Standard of Education leading to miscommunication 📚
Unaffordable Cost of Care 💰
💡 Barriers to good health which led to implementing these goals in GPP: [5]
Manages the distribution of medicines 💊
Ensures safe medication use through patient counseling 🗣
Enhances medicine-related services 📈
Closes the effectiveness gap ✅
⚠ Challenges Addressed:
Wrong administration 🚫💉
Non-compliance ❌💊
High cost of medication 💰
Roles of a Pharmacist [4]
Good Pharmacy Practice
Policy by FIP and WHO that will serve as a guide to the national pharmacy professional organization regarding the development of their standards in the GPP Guidelines
Good Pharmacy Practice
Examples:
Philippine Pharmacy Act
Philippine Practice Standards for Pharmacists
Guidelines developed as a reference to be used by organizations to set up standards of Good Pharmacy Practice
Good Pharmacy Practice
These are guidelines developed used as a reference to create laws and politics by organizations or the government
Practice of pharmacy that responds to the needs of the people to have pharmacy services that provide optimal evidence-based care.
🔉 Backed by studies
🔉 Prioritizes the patient’s welfare
🔉 Ensuring the quality medication supply
🔉 Promoting rational prescribing
🔉 Effective communication with patients and health teams
To contribute to health improvement and to help patients with health problems to make the best use of their medicines
🔉 Teach patients medication on proper use to get the best effect
🔉 E.g. -statins: cholesterol
🔉 Simvastatin, Atorvastatin
🔉 Drink at night since synthesis of cholesterol is faster at this time.
🔉 Rosuvastatin: long acting (but for good practice, still taken at night
Mission Statement of Pharmacy Practice
Being readily available to patients with or without an appointment;
Identifying and managing of triaging health-related problems;
Health promotion;
Assuring effectiveness of medicines;
Preventing harm from medicines;
Making responsible use of limited health-care resources
6 Components of the Mission of Pharmacy Practice
Professional Health Consultant
We are the nearest and most accessible health professional
Manage health-related problems (e.g. fever, cold, cough)
Referral and Collaboration
Pharmacists aim to be acknowledged for: [3]
Pharmacist’s first concern in all settings is the welfare of patients
Core of the pharmacy activity is to help patients make the best use of medicines. Fundamental functions include:
The supply of medication and other healthcare products of assured quality
The provision of appropriate information and advice to the patient
Administration of medication when required
Monitoring of the effects of medication use
An integral part of the pharmacist’s contribution is the promotion of rational and economical prescribing, as well as dispensing.
Objective of each element of pharmacy service is relevant to the patient, is clearly defined and is effectively communicated to all those involved. Multidisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals is the key factor for successfully improving patient safety.
Requirements of GPP [4]
Pharmacists should have input into decisions about the use of medicines.
The relationship with other health professionals, particularly physicians, should be established as a therapeutic collaborative partnership that involves mutual trust and confidence in all matters relating to pharmacotherapy;
The relationship between pharmacists should be one of the colleagues seeking to improve pharmacy service, rather than acting as competitors;
A system should exist that enables pharmacists to report and obtain feedback about:
Adverse events
Medicine-related problems
Medication errors, misuse or medicine abuse
Defects in product quality
Detection of counterfeit products
Organizations, group practices and pharmacy managers should accept a share of responsibility for the definition, evaluation and improvement of quality
Pharmacist should be aware of essential medical and pharmaceutical information (i.e. diagnosis, laboratory test results and medical history) about each patient
Pharmacist needs evidence-based, unbiased, comprehensive, objective, and current information about therapeutics, medicines and other healthcare products in use, including potential environmental hazard caused by disposal of medicines’ waste
Pharmacists in each practice setting should accept personal responsibility for maintaining and assessing their own competence
Educational programmes for entry into the profession should appropriately address both current and foreseeable changes in pharmacy practice
National standards of GPP should be specified and should be adhered to by practitioners
Prerequisites to Requirements of GPP [10]
Legal Framework
Workforce Framework
Economic Framework
Necessary Frameworks to Establish Implementation of GPP [3]
Legal Framework
[Frameworks to Establish Implementation of GPP]
Defines who can practice pharmacy;
Defines the scope of pharmacy practice
🔉 Philippine Pharmacy Law (RA 10918)
Ensures the integrity of the supply chain and the quality of medicines
(in time that we need to procure drug, procure immediate to prevent stock out)
Workforce Framework
[Frameworks to Establish Implementation of GPP]
Ensures the competence of pharmacy stuff through continuing professional development (CPD or CE) programmes
🔉 Attend seminars and training programs to stay updated in the practice of pharmacy
Defines the personnel resources to provide GPP
🔉 A pharmacy can designate a number of pharmacists and pharmacy technicians they need based on the volume of prescription they handle to ensure they can provide timely service and patient counseling
Economic Framework
[Frameworks to Establish Implementation of GPP]
Provides sufficient resources and incentive that are effectively used to ensure the activities undertaken in GPP
National Pharmacy Professional Association
Sets standards required for GPP;
Quality management framework
Strategic plan for developing services
Attention must be paid to:
Needs of the users of healthcare services
Capacity of national healthcare systems to support these services
Nations
Practice locations
Community pharmacy
Hospital pharmacy
🔉 Different needs lead to different standards
Pharmacy Practice is vary among: [2]
FIP emphasizes the importance of:
Defining the roles played by pharmacists, as expected by patients and society
Relevant functions for which pharmacists have direct responsibility and accountability need to be determined within each role
Minimum national standards should then be established, based upon the need to demonstrate competency in a set of activities supporting each function and role.
Minimum Standards on GPP [3]
Role 1: Prepare, obtain, store, secure, distribute,
administer, dispense and dispose of medical products
Role 2: Provide effective medication therapy
management
Role 3: Maintain and improve professional performance
Role 4: Contribute to improve effectiveness of the
health-care system and public health
4 expected roles of Pharmacists
Function A: Prepare extemporaneous medicine preparations and
medical productsFunction B: Obtain, store and secure medicine preparations and
medical productsFunction C: Distribute medicine preparations and medical products
Function D: Administration of medicines, vaccines and other
injectable medicationsFunction E: Dispensing of medical products
Function F: Dispose of medicine preparations and medical products
Role 1: Prepare, obtain, store, secure, distribute, administer, dispense and dispose of medical products
Function A: Assess patient health status and needs
Function B: Manage patient medication therapy
Function C: Monitor patient progress and outcomes
Function D: Provide information about medicines and health-related
issues
Role 2: Provide effective medication therapy management
Function A: Plan and implement continuing professional
development strategies to improve current and future performance
Role 3: Maintain and improve professional performance
Function A: Disseminate evaluated information about medicines
and various aspects of self-careFunction B: Engage in preventive care activities and services
Function C: Comply with national professional obligations,
guidelines and legislationsFunction D: Advocate and support national policies that promote
improved health outcomes
Role 4: Contribute to improve effectiveness of the health-care system and public health
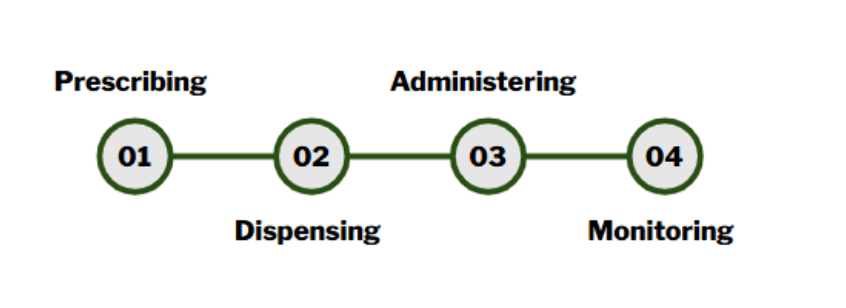
Prescribing
Dispensing
Administering
Monitoring
Medication Use Process [4]
Collaborate with the health professional team and educate prescribers as needed.
Educate nurses on how to administer the drug in a hospital setting.
Educate the pharmacy team on the proper inventory process in the pharmacy, storage conditions, and how to check for quality medications.
🔉 Know that the job is for the benefit of the patient
🔉 Improve their health outcome
Responsibilities of the Pharmacist [3]