AQA A level Chemistry 3.1.6 Equilibria
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Under what condition can equilibrium be reached? (1)
Equilibrium can only be reached in a closed system, where reactants and products cannot escape
What are the features of a dynamic equilibrium?
- The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction
- The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant
What is Le Chatelier's principle? (1)
A system at equilibrium will react to oppose any change imposed on it
What are the three factors that affect the position of equilibrium? (3)
1. Concentration
2. Pressure
3. Temperature
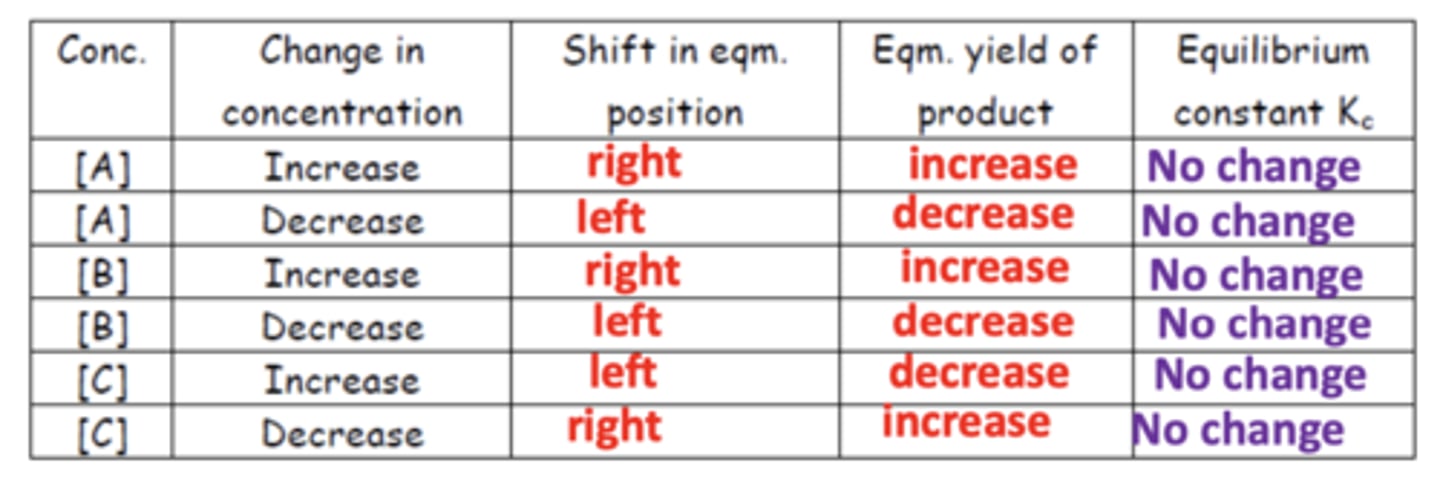
How does increasing the concentration of reactants or decreasing the concentration of products affect equilibrium? (2)
- Equilibrium will shift to the right.
- This happens to decrease the concentration of reactants/increase the concentration of products.
How does decreasing the concentration of reactants or increasing the concentration of products affect equilibrium? (2)
- Equilibrium will shift to the left.
- This happens to increase the concentration of reactants/decrease the concentration of products.
How does increasing pressure affect equilibrium? (3)
- Equilibrium will shift to the side with fewer moles.
- This can be to the left or right.
- This happens to decrease the pressure.
How does decreasing pressure affect equilibrium? (3)
- Equilibrium will shift to the side with more moles.
- This can be to the left or right.
- This happens to increase the pressure.
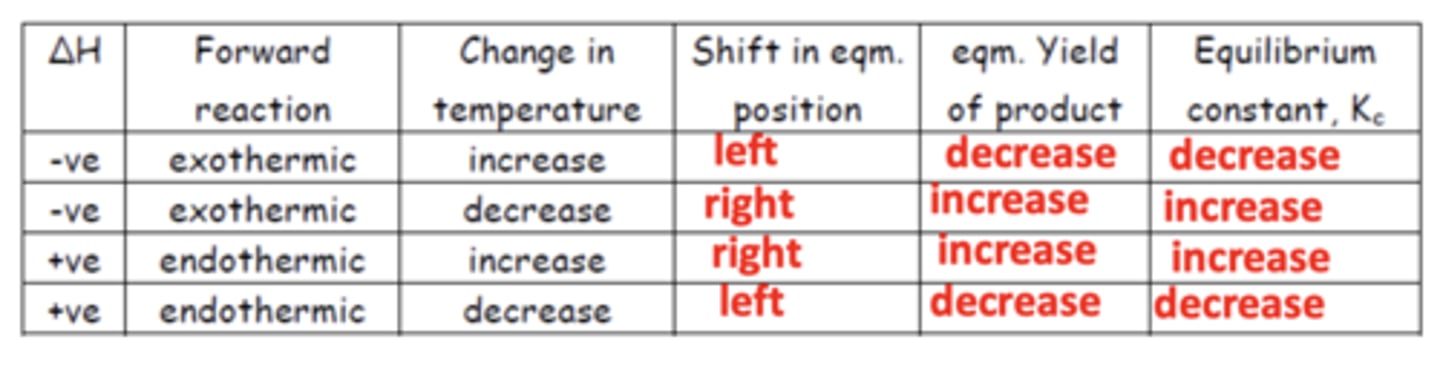
How does increasing temperature affect equilibrium? (3)
- If the reaction is exothermic/endothermic, equilibrium will shift in the endothermic direction.
- This can be to the left or right.
- This happens to decrease the temperature.
How does decreasing temperature affect equilibrium? (3)
- If the reaction is exothermic/endothermic, equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction.
- This can be to the left or right.
- This happens to increase the temperature.
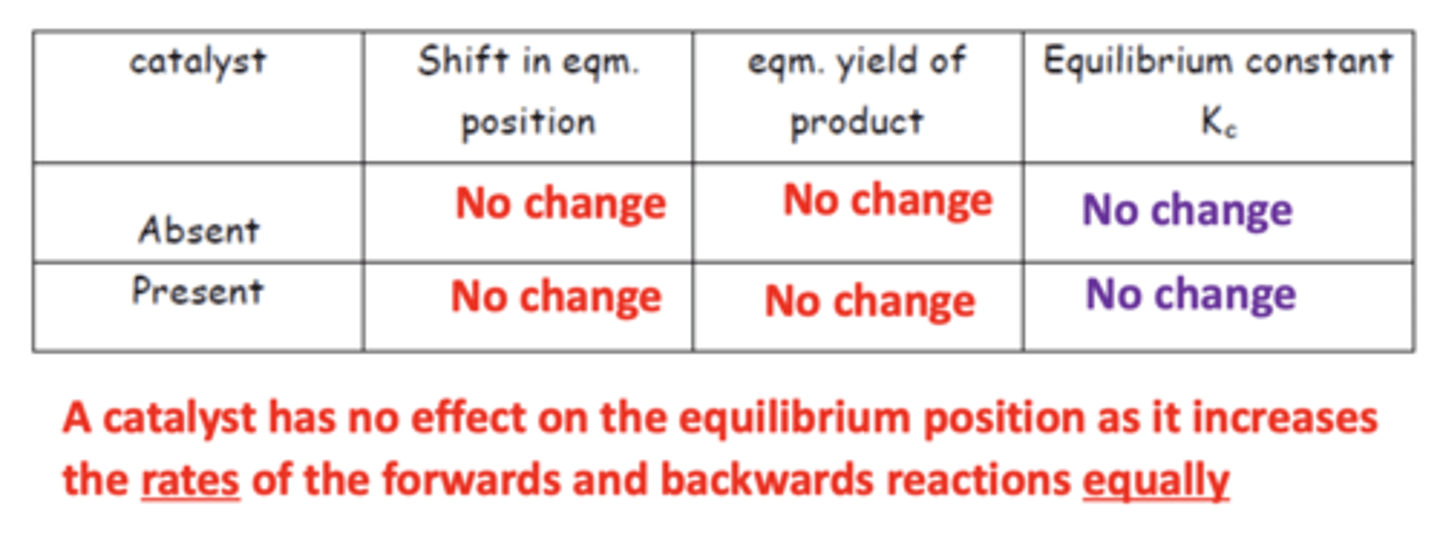
How does a catalyst affect equilibrium and yield? (2)
- A catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium position or yield.
- It increases the rates of both the forward and backward reactions equally.
How does the position of equilibrium affect yield? (2)
- If equilibrium shifts to the right, yield increases.
- If equilibrium shifts to the left, yield decreases.
What is the primary goal of equilibrium in industrial processes? (3)
- Achieve the highest possible yield.
- Complete the reaction in the shortest possible time.
- Maintain the lowest possible cost.
Why are very high temperatures and pressures in industrial processes unfavourable?
Because the cost is too high
Why are very low temperatures and pressures in industrial processes sometimes unfavourable?
- Low yield (for some reactions)
- Low rate of reaction
Why are comprise conditions used in industrial processes?
Give balance to yield, rate of reaction and the cost
What is the expression for equilibrium constant, kc? (2)
[Products] / [Reactants]
Where [ ] = concentration in moldm-3
![<p>[Products] / [Reactants]</p><p>Where [ ] = concentration in moldm-3</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ca672ac1-421f-4bb0-baf3-5ceeeb8efbb8.png)
What is the only factor that affects kc? (1)
Temperature
Summary diagram for the effects of temperature on Kc (8)
Summary diagram for the effects of concentration on Kc (12)
Summary diagram for the effects of a catalyst on Kc (4)