Marketing Final Celly
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Service
intangible offering involving a deed or performance
Hierarchy of Value
fundamental shift in how we experience the world from primarily function to primarily emotional (product-based economy) (example we pay more for Starbucks coffee than regular)
Service Marketing is…
intangible, inseparable, heterogenous, and perishable
The 7ps
product, price, promotion, place, presentation, personnel, processes
Knowledge Gap
understanding customers’ expectations (to reduce the gap…)
Standards Gap
difference between the firm’s perceptions of customer perceptions and the service standards it sets
Delivery Gap
gap between the delivery and service quality
Communication Gap
gap between the actual service provided and the service the firm promises/communicates
What is the Main Gap?
The service gaps model: difference between the customer expectations and the actual service delivered
Voice of Customer (VOC)
program that collects customer input and integrates them into managerial decisions
Zone of Tolerance
the area between customer’s expectations regarding their desired service and the minimum level of acceptable service
Service Recovery Paradox
When a company messes up but does so much to redeem itself that the customer is more loyal to the brand than they would’ve been if they never had a problem
Pricing
customers decide it (incentive to purchase = perceived value - price) (firm’s incentive to sell = COGS - price)
5cs of Pricing
company objectives, customers, costs, competition, and channel members
Profit Oriented
maximize the money made
Sales Oriented
focused on increasing sales, premium pricing could be pursued, more concerned with overall market share
Customer Oriented
pricing strategy based on how the firm can add value to its products and services to match prices to customer expectations (a lot of different prices)
Competitor Oriented
price similar to competitors
Status Quo Pricing
only change the prices to meet the competitors’
Monopoly
one firm controls the market
Monopolistic Competition
many firms selling differentiated products at different prices
Oligopolistic Competition
a handful of firms control the market
Pure Competition
many firms sell commodities for the same prices
Price Elasticity of Demand
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Elastic Demand
price sensitive (ex. slippers)
Inelastic Demand
price insensitive (necessities) (gas)
Income Effect
as people’s income increases their spending behavior changes
Cross-Price Elasticity
% change in the quantity of product A demanded compared to product B
Substitution Effect
customer’s ability to substitute other products for it
Complementary Goods
goods that go well with each other (pb and jelly)
Razor Blade Strategy
they give away the razor body for really cheap then make you pay a lot for the razor blades (complimentary good)
Break-Even Point
total revenue = cogs so that they are coming off even
Every Day Low Pricing (EDLP)
creates value for the consumers in different ways, it reduces the search costs
High/Low Pricing
provides the thrill of the chase for a low price
Internal Reference Price
what you think you spend on it last time
External Reference Price
what is the actual price you spent on it last time on the shelf
Penetration Pricing
set the initial price low for the introduction of the product or service
Price Skimming
set a higher initial price for the segments of consumers who are willing to pay premium price to have the innovation first
Anchoring and Adjustment
make up a number and anker them in then they will adjust away from it (like the coach bag)
Lewin’s Equation
behavior is a function of people and their environment, b = f(pe)
Priming
things that you have seen (stimuli) earlier in the decisions making process that influence your decisions later (banner ads)
Prospect Theory
You feel losses and gains differently (loss more than gain) loss aversion
Attraction Effect
inferior product (a decoy) increases the change the change they will buy the other product
Extremeness Aversion
customers don’t pick the cheapest or priciest option they will choose the moderate one because it is in between quality and value
Bundling
selling multiple products or services together to increase the perceived value (5 dollar meal deal)
Unbundling
Separating goods and services so customers can have more flexibility (airlines charging tickets and luggage separately)
Charm Price
ending prices in 99 cents because it round (you think its cheaper than it is_ or using a random number so it seems more fair (John Deere)
Legal and Ethical Aspects of Pricing
deceptive/illegal advertising, predatory pricing (charging a little less than competitors ex. DG) price discrimination (legal, special deals for certain groups but others get mad a lot), price fixing (colluding with other companies)
Merchandise is Produced and Distributed
in the right quantities, right locations, at the right times
Supply Chain
network of suppliers that works to deliver products to consumers
Wholesalers
firms that buy products from manufacturers and resell them to retailers (retailers cn act as wholesalers too)
Distribution Center
facility for the receipt, storage, and redistribution of products
Fulfillment Center
used to ship directly to individual consumers (Amazon)
QR (quick response) / JIT (just in time)
less merch on a frequent basis (no holding costs) (think about Toyota’s production system)
Kaizen
Japanese philosophy of continuous movement (flow state) (cars are on a convey belt) (how can we constantly be improving better) (troubleshooting)
Direct Channel
manufacturer to customer (becoming more popular because we want relationships with customers)
Indirect Channel
one intermediary (manufacturer to retailer to customer) or two intermediaries (manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer)
Franchising
contractual agreement between a franchisor and a franchisee to operate a retail outlet using a name and format developed and supported by the franchisor
Vertical Channel Conflict
a type of channel conflict in which members of the same marketing channel disagree (Walmart is mad at Heinz)
Horizontal Channel Conflict
members at the same level of a marketing channel disagree (target and Walmart)
Channel Power
one firm has means or ability to dictate the actions of another member at a different level of distribution (reward, coercive, referent, expertise, information, legitimate)
Reverse Merchandise Flow
total returns (has been 743 billion) growing becaue online sales are growing
Customer Lifetime Value
total profit a customer brings to the company during all of their purchases (lifetime revenue - lifetime costs)
Lifetime Revenue
revenue per sale * number of transactions
Lifetime Costs
Cost of acquisition + (cost to serve * number of transactions)
Margin
% of the selling price that you can take home from the profit (price - cost) / price
Mark Up
how much will you increase the cost of the product when you sell it to make a profit (will always be more than the margin) (gross profit = price - cost) ((price - cost) / cost
Romelle Morris
Uiowa grad who is a global marketing strategist for Estee Lauder
Retailing
adds value to products and services sold to consumer for their personal or family use (provides an assortment of p/s, breaking bulk, holding inventory, providing services)
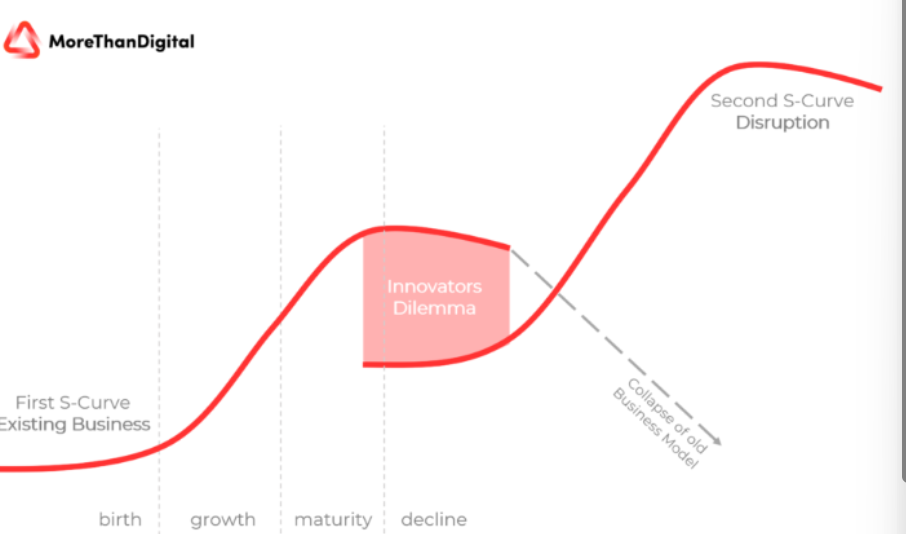
Innovators Dilemma
there is some new technology that comes out, and people have to decide if it is worth it to make it and sell it, will the new idea be worth our time and will it work out (sell)
Vertical Integration
business strategy where a company controls multiple stages of a supply chain including production, marketing, and distribution (streamline operations) ex. Tesla
Intensive Distribution
uses all available outlets (ex. beer, gum)
Selective Distribution
limited number of outlets to sell products, choosing the ones best fit to sell your product (Seiko)
Exclusive Distribution
only one wholesaler, retailer, or distributor in a specific geographical area (they have complete control)
Scrambled Merchandising
a retailer broadens their assortment to include items that are out of their general focus or are usually sold in a different format
Goods/Service Continuum
products can be a mix of goods and services and the line between them is blurry
Omnichannel
order online and pick up in store, buy online and return in store, buy in store and have it delivered at home (deeper and broader selection, more personalized, larger market presence and good brand image, reduction of channel migration, retailers can adjust prices (target))
Long Tail of Retailing
some books are super popular, and some are not so stores like Barns and Noble can only afford to have the popular ones, places like Amazon found a way to sell all books so that they could have more variety (must figure out what you are selling and to whom
Showrooming
people go to the store to see the product but then purchase it online (beds or like best buy electronics)
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
consumer, communication channels, and results of communication
The Communication Process
Sender (adjusts messages according to the medium and receiver’s traits (they encode the message)), transmitter, channel, receiver (decode differently), feedback, noise (interference or disruption)
AIDA Model
Awareness (senders must gain attention of the consumer), Interest (feelings and emotions, customer must want to further investigate), Desire ( I like it and now want it ), Action (goal)
Advertsing
most visible IMC strategy, placements of announcements, persuasive messsages
Public Relations
free media attention (ex. dance marathon)
Sales Promotion
aimed at end consumers or channel members, give people an incentive (maybe rebated)
Rebates
50% of rebates are not cash returned or used (same with gift cards)
Direct Marketing
communicating directly with target customers, email and mobile marketing (this is growing), must be able to target the right customers
Domino’s Points for Pies
introduced a rewards system so customers could get points on any pizza, by downloading the app users could scan any pizza and earn points towards a free Domino’s product, this promotion attracted many people to Dominos and got them to download the app
Burger King Geofencing
location based marketing to effect targeted consumers near local McDonalds locations, consumers in these locations would receive a special discount voucher designed to convince them to change their plans and drive to burger king instead, this gave incentive for consumers to download their app as well
Geofencing
setting an intangible barrier between other competitors and your brand
Offline and interactive IMC strategy
personal selling, sales promotions (contests), direct marketing (telemarketing)
Online and Interactive IMC Strategy
direct marketing (mobile marketing), online marketing (blogs/social media)
Offline and Passive IMC Strategy
advertising, sales promotions (coupons), public relations, direct marketing
Online and Passive IMC Strategy
direct marketing (email marketing)
Online Marketing
direct mobile marketing (blogs/social media), practice promoting products services, or brands using the internet and digital technologies
Competitve Parity
communication budget is set so the firm’s share of communication expenses = its share of the market (doesn’t allow firms to exploit unique opportunities or problems)
Percentage of Sales
communication budget is a fixed percentage of forecasted sales (assumes the same % used in the past and doesn’t consider new plans)
Available Budget
marketers forecast their sales and expenses without communication during the budgeting, forecast sales - expenses + desired profit is reserved for the budget (money available after operating costs and profits have been budgeted) (assuming communication expenses do not stimulate sales and profit)
Objective and Task Budgeting
say an objective then elaborate on what needs to be done to reach the goal (harder from a manager standpoint)
Rule of Thumb Budgeting
competitive parity, percentage of sales, and available budget