Programming and Analysis Study Items
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
characteristics for a hot-arid climate
thermal mass, shade, small windows, thick walls, water features, courtyards, low-e windows
bottom of the valley and south of a pond are best build locations
characteristics of hot-humid climate
large openings + orientation for breezes, long east-west dimension, tall ceilings, ceiling fans, sprawling building form
top of a hill and south of a pond are best build locations
vapor control layer on outside (warm-side) of insulation
characteristics of temperate climate
long east-west dimension, insulation, south-facing windows, buffers for winter winds, minimize north face of the building and maximize south facing of the building
plant deciduous trees on south side of building
¾ of the way up a hill is the best location to build
characteristics of a cold climate
compact building form to minimize heat loss (a little longer in the E-W direction), insulation, low u-value windows, airtightness, plant evergreen trees on the windy side of the building as a buffer
¼ of the way up a hill and the north side of a pond are the best sites to build on
vapor control layer on the inside (warm side) of the insulation
superfund
brownfield sites with toxic waste
soil capping
covers contaminated soil with asphalt, clay, concrete or membrane
bioremediation
microbes eat soil’s contaminants
phytoremediation
plant roots suck up contamination
soil washing
soil cleaned with water and detergents
soil mixing
mixing Portland cement with the soil to strengthen the perimeter of the excavation
slurry walls
use a watery clay mix to keep a trench from collapsing in on itself until concrete is poured and displaces the mix
then dig inside the resulting subterranean concrete wall
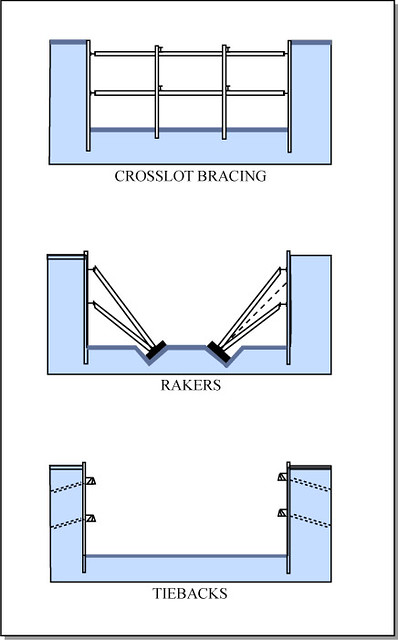
crosslot bracing
spans between excavation walls
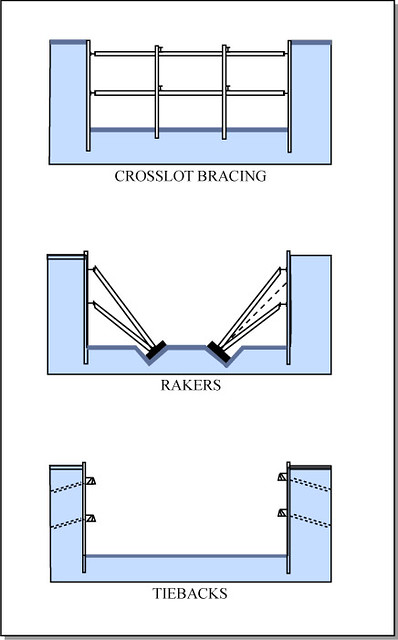
rakers
act as kickstand to hold up slurry walls
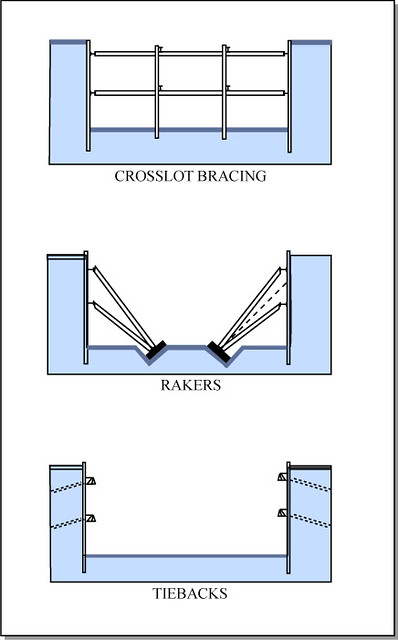
tiebacks
hold excavation walls back to the earth from behind
ciassons and end-bearing piles
engage (often deep) competent soil
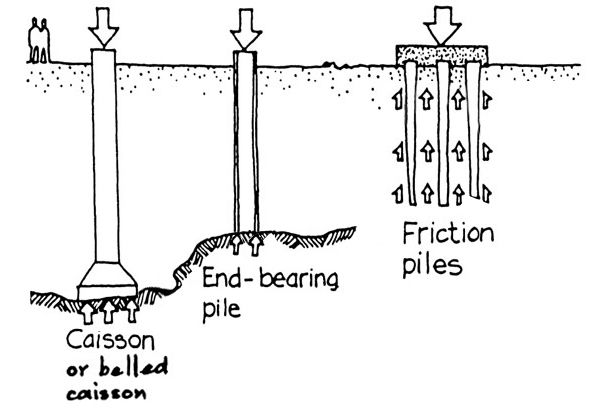
frictional piles
are used when hard soil or rock is too deep to be reached economically for an end-bearing pile, or when the soil is weak and cannot provide sufficient support at the tip
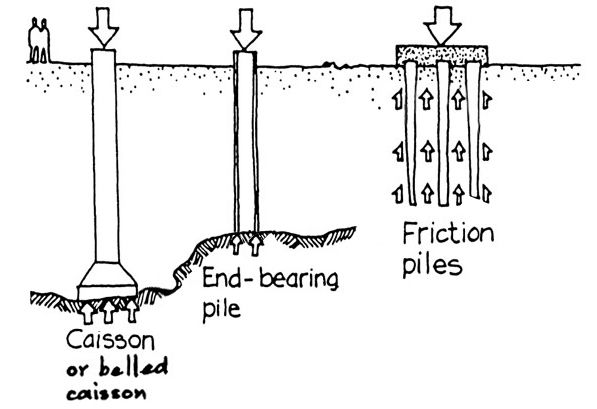
caissons
are drilled and then filled with concrete or drilled into bedrock
piles
are manufactured, brought to site and driven into the ground to either bear on bedrock/competent soil or can use the friction pile touching the soul around it to support the building
ALTA/ASCM Surveys
show improvements to land, easements, rights-of-way, that impact land ownership
Topographical surveys
show contours of the land
plats
demarcate divisions of land, like property lines
metes and bounds surveys
older and more rural - include start points and may reference landmark
ex of a right-of-way
a shared driveway
ex of an easement
a linear strip of land used for a powerline
eminent domain
government forces you to sell your land for a highway project
step-back
upper floors have a smaller footprint to allow light to reach the street
set-back
can’t build too close to property line
stormwater pollution prevention plan (SWPP)
required for large projects that disturb at least one acre of land
defensible space theory
holds that homes with personal spaces are safer
1 acre = ? SF
43,560
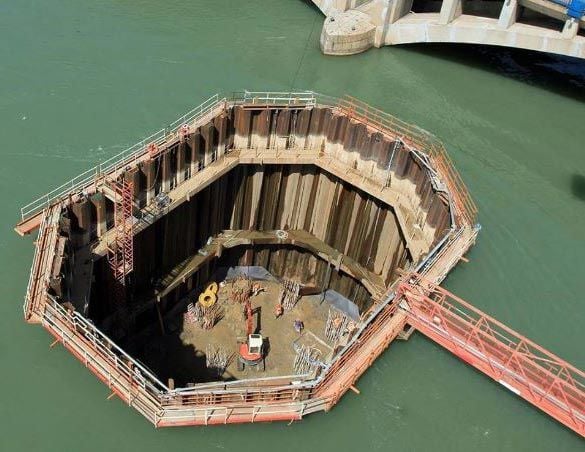
cofferdam
temporary enclosed area in a body of water

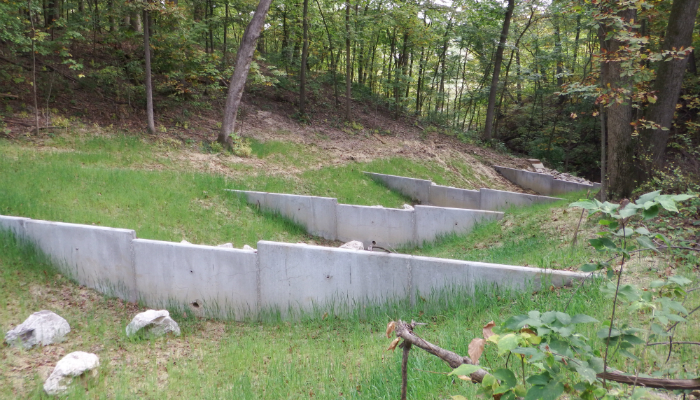
check dam
small obstruction to slow down water in a stream

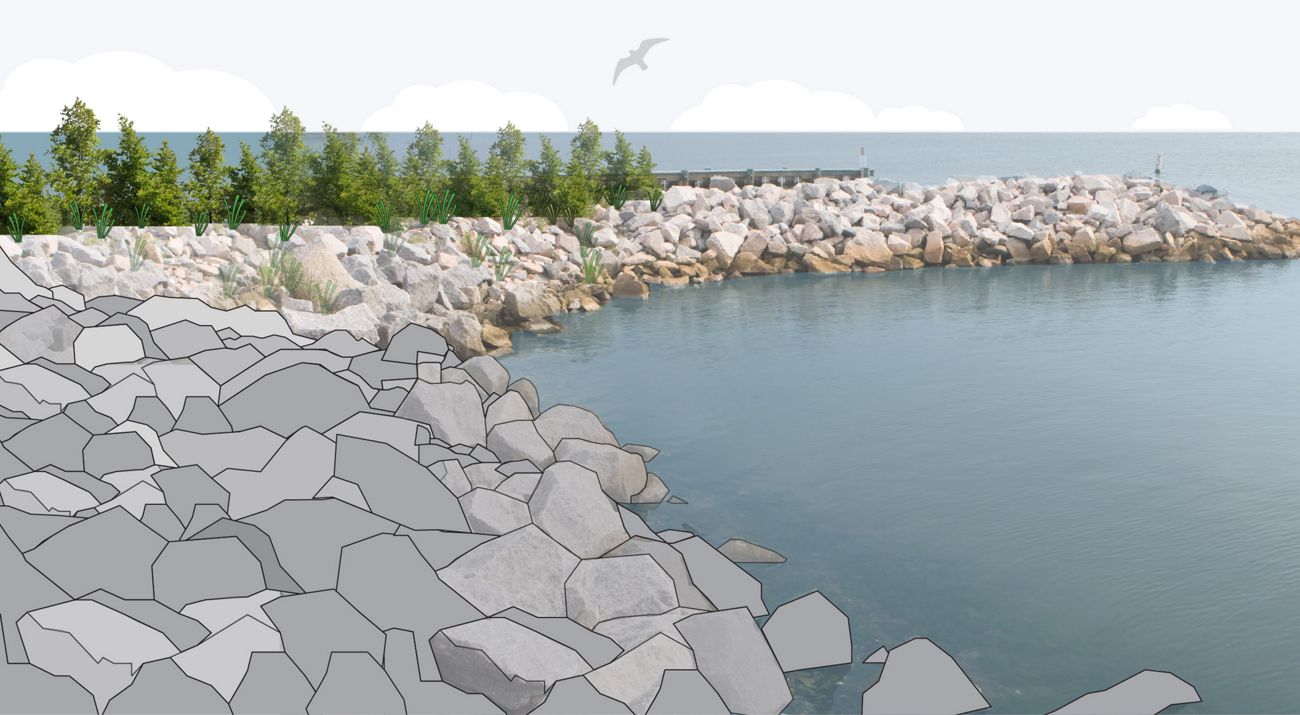
riprap
rock used to protect shorelines

max slope for an ADA ramp
1:12 with uninterrupted runs no longer than 30’ (that rise no more than 30”)
max cross-slope for an ADA ramp
1:48 or 2%
how to find the slope angle with percent/ratio slope
tan(-1) (rise/run)