42. Antimicrobial Therapy: Antiviral and Antifungal Agents
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
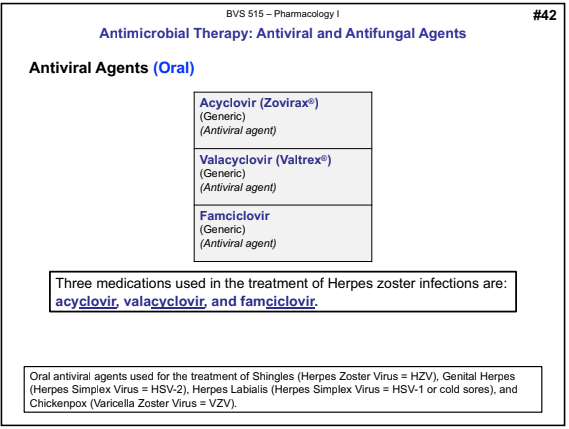
Antiviral Agents (Oral)
Three medications used in the treatment of Herpes zoster infections are:
acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir.
Viruses replicate by co-opting the host cell’s metabolic machinery.
Antiviral Treatment Overview: Herpes Virus
Herpes viruses are associated with a broad spectrum of diseases, cold sores, genital infections
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus that causes varicella (chickenpox).
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) comes in two forms: HSV-1 (oral herpes) and HSV-2 (genital herpes).
The drugs that are effective against Herpes viruses exert their actions during the acute phase of viral infections and are without effect during the latent phase.
Overview of Microbiology: Viruses
DNA (DNA virus) or RNA (RNA virus)
Contain the genetic information for their own replication but need to utilize the host’s machinery for reproduction.
Viral Pathogens include:
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV-1: oral and HSV-2: genital)
Herpes Zoster Virus (HSV): shingles
Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV): chicken pox
Enveloped DNA
Antiviral Agents: Acyclovir (Zovirax®)
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits DNA synthesis and viral replication.
Indications(all four)
Shingles (Herpes Zoster Virus or HZV)
Chickenpox (Varicella Zoster Virus or VZV)
Genital Herpes (Herpes Simplex Virus or HSV-2)
Herpes Labialis or Cold sores (HSV-1)
Pharmacokinetics
Poor bioavailability (need to take 5 times a day)
Adverse Effects
CNS and GI < valacyclovir, famciclovir
Antiviral Agents: Valacyclovir (Valtrex®)
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits DNA synthesis and viral replication.
Valacyclovir is a prodrug; converted to acyclovir
Indications (all four similar to acyclovir)
Pharmacokinetics
Better bioavailability (need to take 3 times a day)
Adverse Effects
both CNS and GI > Acyclovir
Antiviral Agents: Famciclovir
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits DNA synthesis and viral replication.
Famciclovir is a prodrug biotransformed to penciclovir.
Indications (missing chickenpox)
Pharmacokinetics
Better bioavailability (need to take 3 times a day)
Adverse Effects
both CNS and GI similar to valacyclovir, > acyclovir
Antifungal Treatment Overview
Fungi are yeasts or molds
All fungi are eukaryotic organisms
Immunocompromised hosts are at the greatest risk
Amphotericin B, the azoles, echinocandins are the primary drugs used in systemic infections.
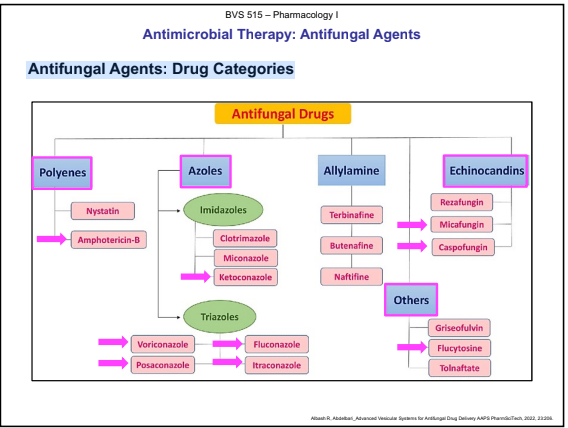
Antifungal Agents: Drug Categories
Polyenes
Amphotericin-B
Azoles
Imidazole: Ketoconazole (CYP-450 inhibitor)
2 nitrogens
Triazole: Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole, Posaconazole
3 nitrogens
Eichinocandins
Caspofungin
Micafungin
Miscellaneous
5-Flucystosine
Inhibitors of Fungal Membrane Stability (Polyenes)
Amphotericin B
Binds to ergosterol disrupting cell membrane
Is a polyene antibiotic
Used IV to treat serious disseminated yeast and fungal infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
widest antifungal spectrum of any agent
Inhibitors of the Ergosterol Synthesis Pathway: Inhibitors of 14α- Sterol Demethylase, a microsomal cytochrome P450 enzyme
Azole Antifungal Agents
are broad-spectrum disrupt the fungal cell membrane by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, a CYP450 enzyme.
imidazoles and triazoles.
The azoles antifungals can inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes.
This class of drugs, particularly ketoconazole, is a significant inhibitor of hepatic CYP450 isozymes and susceptible to clinically significant drug interactions.
5-Flucystosine
blocks nucleic acid synthesis.