POD 3 Liposomes micelles
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
Surfactants are \___
amphiphilic
2
New cards
Many surfactants with pharmaceutical applications have a \___ chain and a \___ or \___ head
single hydrophobic
simple ionic
large non-ionic
simple ionic
large non-ionic
3
New cards
The head group of surfactant are classified as \___
Anionic
Cationic
Zwitterionic
Non-ionic
Cationic
Zwitterionic
Non-ionic
4
New cards
Example of non-ionic surfactants?
sorbitan esters - Spans
polysorbates - Tweens
polysorbates - Tweens
5
New cards
Pharmaceutical Applications of Surfactants?
Solubilisation (Solubilize poorly water-soluble drugs)
Detergency (Eg cleaning skin)
Wetting agent (Lower contact angle between surface and wetting liquid)
What's the difference below and above CMC?
Detergency (Eg cleaning skin)
Wetting agent (Lower contact angle between surface and wetting liquid)
What's the difference below and above CMC?
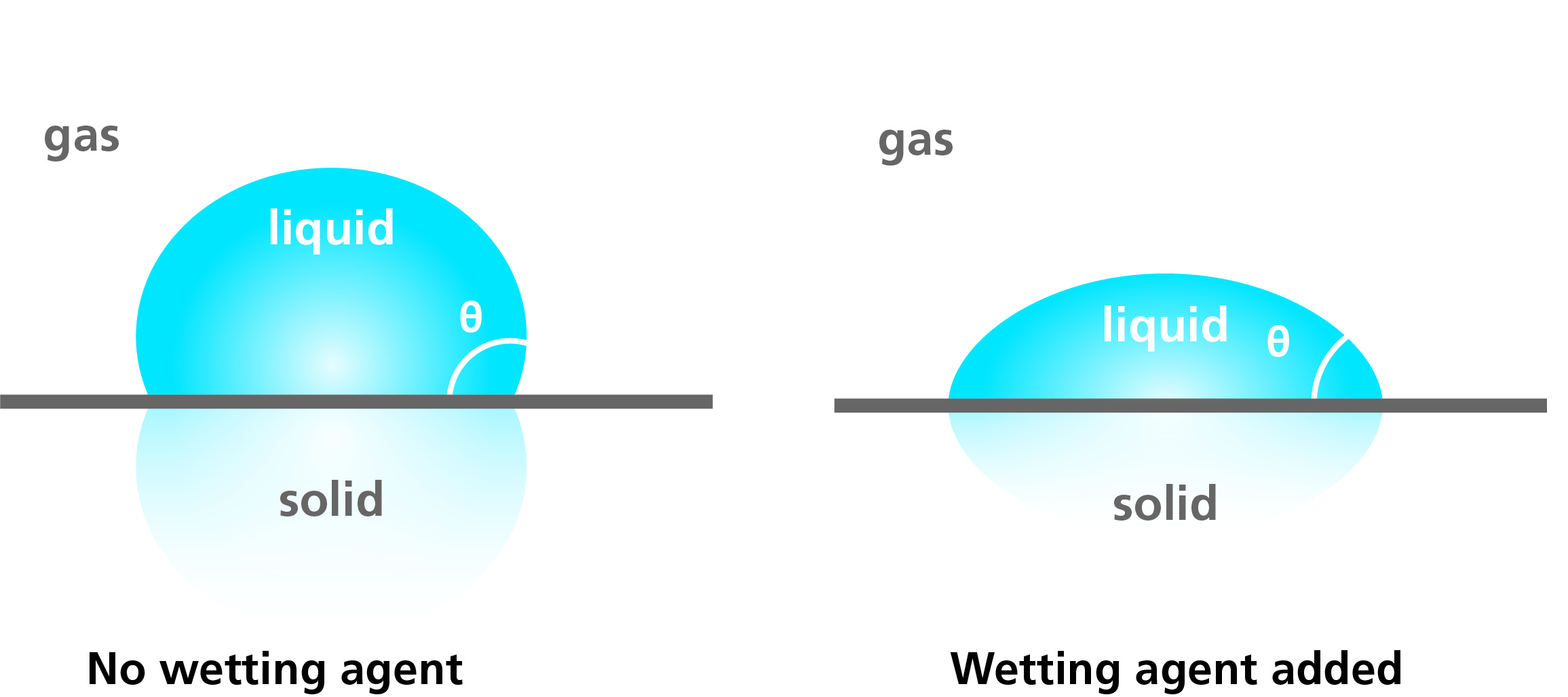
6
New cards
What's the main reason for micelle formation?
To minimize free energy
7
New cards
Micelles continually form and don't break down in solution T/F
False they do break down
8
New cards
List some factors affecting CMC & micellar size?
Structure of the hydrophobic group (↑ chain length \= ↓ CMC)
Nature of hydrophilic group (non-ionic generally ↓ CMC)
Electrolyte addition ↓ CMC and ↑ the micellar size
Nature of hydrophilic group (non-ionic generally ↓ CMC)
Electrolyte addition ↓ CMC and ↑ the micellar size
9
New cards
Micelles are used to formulate \___ drugs in colloidal solutions
low solubility
10
New cards
At what critical packing parameter (CPP) can surfactants form spherical micelles?
< 1/3
11
New cards
Other than spherical micelles, what can surfactants can also form?
Cylindrical Micelles 1/3 < CPP < 1/2
Flexible Bilayers or Vesicles 1/2 < CPP
Flexible Bilayers or Vesicles 1/2 < CPP
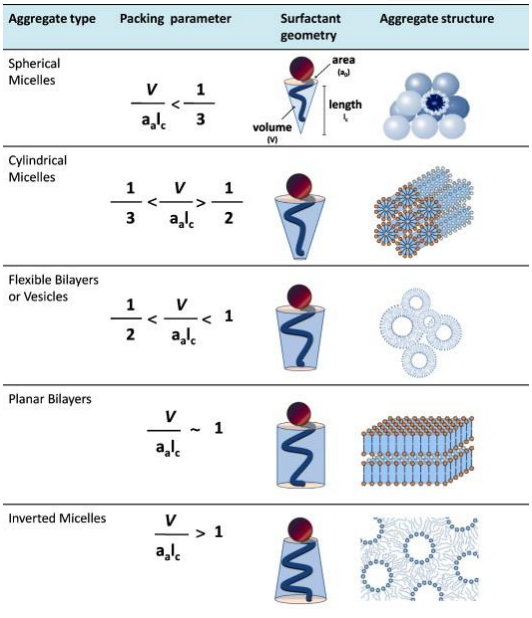
12
New cards
What determines the type of micelle formed?
Dispersed medium
13
New cards
Drug molecules are located differently in solution due to
polarity
14
New cards
Drug molecules can be located
In the core
On the surface
Palisade layer (in between core and the outside)
An intermediate position (dunno what the hell this is but amphiphilic drug can basically exist like picture b)
What is the main pharmaceutical interest in micelles?
On the surface
Palisade layer (in between core and the outside)
An intermediate position (dunno what the hell this is but amphiphilic drug can basically exist like picture b)
What is the main pharmaceutical interest in micelles?
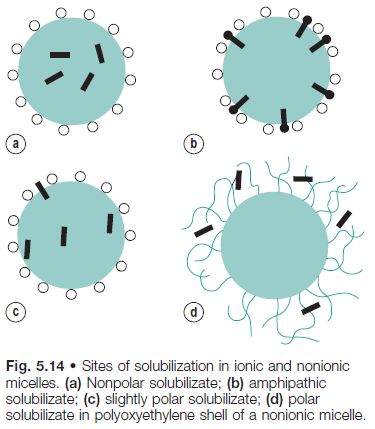
15
New cards
Solubilization influenced by
Nature of solubilisate (what u need to solubilize)
Surfactant chain length
Temp
Surfactant chain length
Temp
16
New cards
What is Maximum additive concentration (MAC)?
Max amount of drug that can be incorporated into a micellar system (at fixed surfactants conc and temperature)
17
New cards
Micelle instability can result due to
Change in temp, pH, addition of additives at change Hydrophilic-lipophilic balance of surfactant
18
New cards
What happens if the concentration of surfactant drops below CMC?
precipitation of the drug
19
New cards
List some application of Micelles
administration of steroids (where oily solution or suspension not suitable)
Dettol - Solution of Chloroxylenol B.P.
Aqueous injections of water insoluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
Anti-cancer drug Paclitaxel
Dettol - Solution of Chloroxylenol B.P.
Aqueous injections of water insoluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
Anti-cancer drug Paclitaxel
20
New cards
What are Polymeric Micelles?
Micelles formed from block copolymers
21
New cards
Diameter of polymeric micelles
10-80 nm
22
New cards
Polymeric micelles compare to surfactant micelles?
more stable, lower CMC
23
New cards
Application of polymeric micelles in drug delivery
Solubilised (poorly soluble drugs) in hydrophobic micelle core
Conjugation to micelle polymer (drug stick to polymers)
Conjugation to micelle polymer (drug stick to polymers)
24
New cards
Polymeric micelles also serve as ligands (sometimes)
I can’t make a question out of this one
25
New cards
Polymeric micelles shell is
hydrophilic
26
New cards
Polymeric micelles shell forms barrier which
Reduce aggregation and protein binding
27
New cards
main component of liposomes?
phospholipids (amphiphilic -\> exhibit surfactant behaviour)
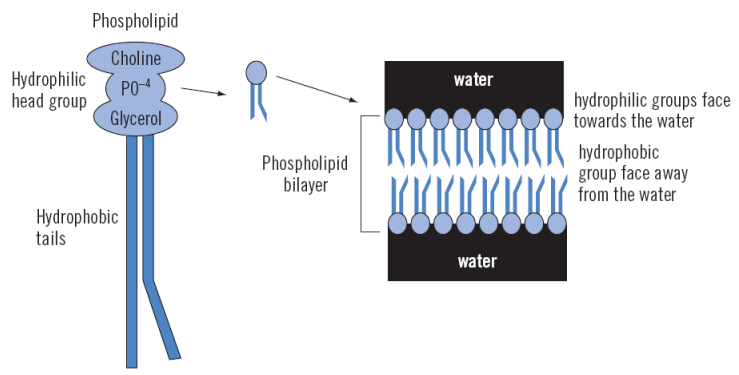
28
New cards
In liposomal system, drug can dissolve in
Within the aqueous core
Within bilayer
Adsorbed on surface
Within bilayer
Adsorbed on surface
29
New cards
Types of liposomes?
Multilamellar vesicle (MLV) ⦾
Large unilamellar vesicle (LUV) O
Small unilamellar vesicle (SLV) o
Oligolamellar vesicles (OLV) ⦾ (2-5 bilayers)
Large unilamellar vesicle (LUV) O
Small unilamellar vesicle (SLV) o
Oligolamellar vesicles (OLV) ⦾ (2-5 bilayers)
30
New cards
In an aqueous medium, the phospholipid molecules self-assemble into
bilayer sheets
31
New cards
Liposome formation does not require energy T/F
False
32
New cards
Liposome typically size
20 nm to 10µm
33
New cards
Liposome stability and surface charge can be influenced by
Phospholipid composition
Addition of cholesterol
Addition of cholesterol
34
New cards
What charge is on surface of liposome?
negative, positive or neutral
35
New cards
What influences the distribution of liposomes?
Modifying the size, lamellarity (how many layers), charge or surface FGs
36
New cards
Why are drugs encapsulated in liposome?
Prolong drug activity, protect drug from enzyme
37
New cards
What does similarity with the cell membrane mean for liposomes?
They can interact with cells
38
New cards
Liposome can be designed to \___ the encapsulated drug to \___
direct/ specific biological targets
39
New cards
Liposomes can be used for which ROA?
orally, topically, transdermally and parenterally
40
New cards
What can happen to Liposomes after IV administration?
Disintegrate in the circulation
Cleared by macrophages
Escape from the circulation via leaky blood vessels
Cleared by macrophages
Escape from the circulation via leaky blood vessels
41
New cards
The leaking of liposomes from the systemic circulation to sites of inflammation and tumour can be \___ for the delivery
advantageous
42
New cards
What is AmBisome®?
Amphotericin B (single bilayer) liposome for infection
43
New cards
Where is Amphotericin B in AmBisome®?
Within the membrane