Forensic Science DNA/Fingerprinting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study this and the slides! Hope this helps!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Fingerprints are a result of oil and secretions that are transferred to a surface by the ridges of one’s fingers. true or false
true
Fingerprints are considered to be a form of class evidence. True or false
false
It is necessary to obtain a full print from a crime scene in order for it to be used as evidence. true or false
False
Plastic/impression prints are dusted in order to identify ridge patterns. true or false
false
Loops are the most common form of fingerprints. true or false
true
With the aid of CODIS, it is possible to obtain a “match” of a fingerprint. true or false
false
There is only one method that can be used to collect fingerprints from a crime scene. true or false
false
A fingerprints examiner looks for similar minutiae patterns between a suspect print and a crime scene print. true or false
true
Cyanoacrylate fuming (or glue fuming) is a fingerprint extracting that uses reactions to make prints visible. true or false
true
Fingerprints are formed
during pregnancy
Fingerprints that are actual indentations left on a soft material such as putty or clay are referred to as
plastic/impressions prints
The use of fingerprint identification is not perfect because
the current technology depends on humans to input and analyze the information and humans make mistakes.
The lines on a fingerprint are known as
ridges
What does CODIS stand for?
Combined DNA index system.
What is the current theory?
No 2 people have the same fingerprints. But not always believed by the community.
When were fingerprints discovered?
1792
What are the 3 patterns of fingerprints?
Loops, whorls, arches
What is a core?
The center of a loop or whorl.
What is a delta?
A triangular region near a loop.
What is edge counting?
Counting from the core to the edge of the delta.
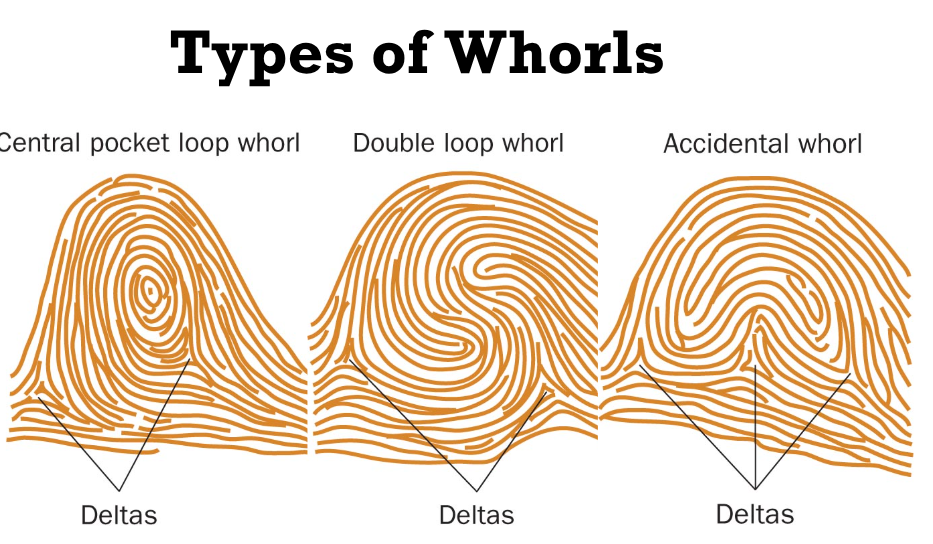
Types of whorls?
Central pocket loop, double loop, accidental whorl
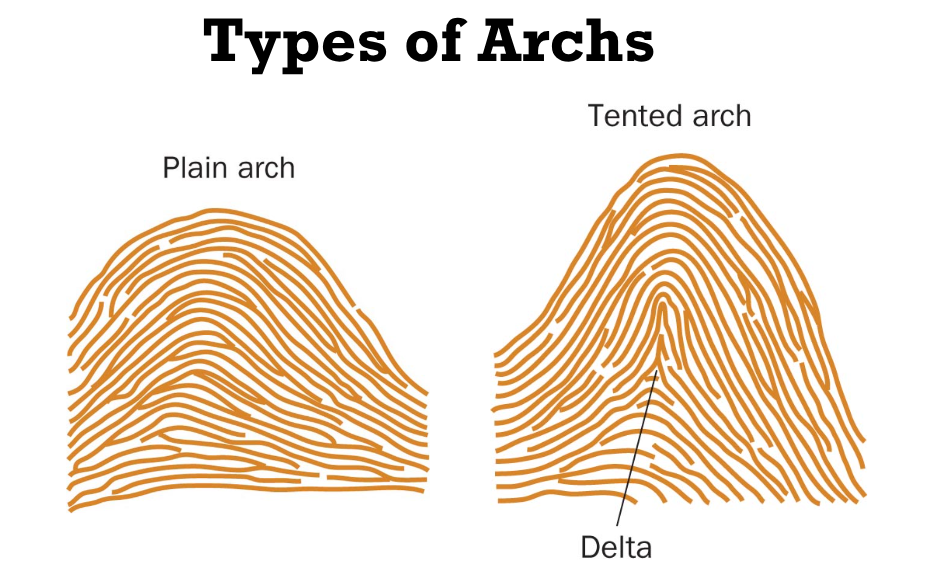
What are the types of arches?
Plain and tented arches
What are the percentages of each fingerprint pattern?
arches 5%, whorl 30%, loop 65%
What does a fingerprint analyst do?
Compare common ridge patterns and minutiae patterns between suspect prints and evidence prints.
How minutiae patterns are required to find a match?
8-16
What are visible prints?
Made by fingers touching a surface after the ridges have been in contact with colored material
What Are plastic prints (impressions)?
Ridge impressions left on a soft material
What are latent prints?
Invisible prints left behind by a clear oils on the fingerprints
What light do you use to find latent prints?
Ultraviolet light
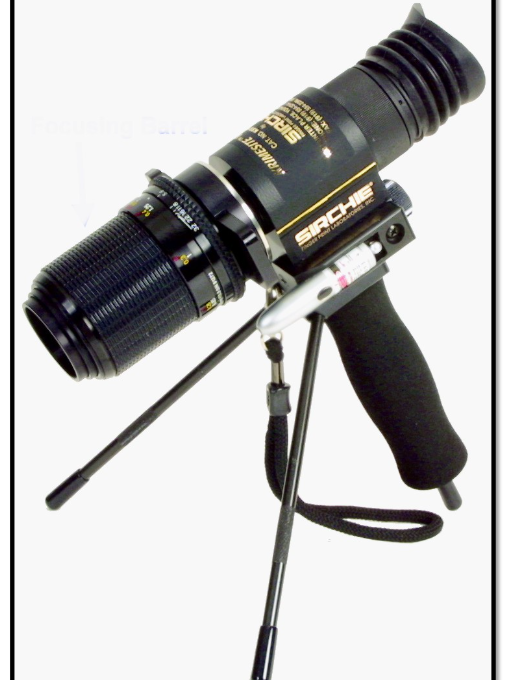
What device can locate most prints?
Reflected Ultraviolet Imaging system (RUVIS)

What powders are best to find latent prints?
Gray and black (darker surfaces need light powder)
What are the other methods for collecting fingerprints?
Iodine fuming, ninhydrin chemical reaction, superglue fuming.
What is the digital program where fingerprints go?
Automated fingerprint identification system AFIS
What can have the same DNA?
Identical twins
What is DNA considered as?
Individual evidence
Where can DNA be collected from?
Skin, blood, saliva, urine, semen, hair
Where is DNA located?
In the NUCLEUS, carries an organism's genetic information
What is DNA is a polymer that consists of many monomers?
Nucleotides
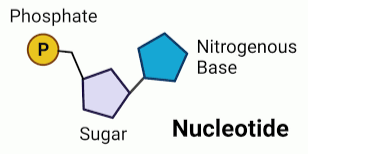
What are the 3 parts of nucleotides?
Phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base
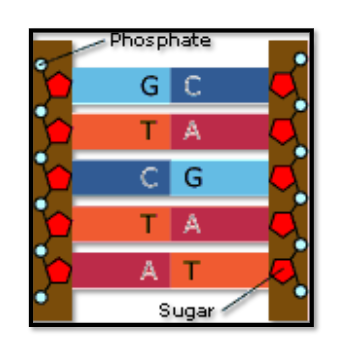
4 types of DNA???
Thymine (T), Cytosine ©, Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
Who made new DNA technology?
Sir Alec Jeffrey
What is considered the most useful form of evidence in obtaining convictions?
DNA
Where is the suspect's DNA collected from?
Hair, blood, saliva, cheek
What's the opposite of thymine?
Adenine
What is the opposite of guanine?
Cytonine
How is DNA fingerprinting used?
identity/profiling suspects
How many nucleotides comprise a single strand of DNA?
3 billion
What is the function of an allele?
Encode instructions for cell operation
What are the percentages of the mother and father?
50/50 for each
Why are alleles helpful to forensics?
To help identify matches in DNA profiles
In DNA fingerprinting, what do restriction enzymes do?
Cut a sample of DNA in segments
The process of using an electric current to create a DNA profile is called?
Gel electrophoresis.
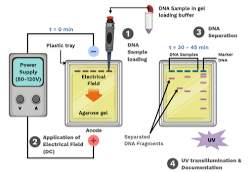
What is the purpose of CODIS?
To help find potential DNA matches.