cell membrane quick flashcards
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
what does compartmentalization allow for
allows for efficiency and specialization of function
what is the plasma membrane
separates living cell from external environment
response
what is the plasma membrane made of
made of a phospholipid bilyaer
phospholipids are amphipathic molecules - hydrophobic tails, hydrophilic tails
what are integral proteins
stably attached to the biological membrane
span the phospholipid bilayer
what are peripheral proteins
temporarily adhered to the biological membrane
either attached to an integral protein or penetrating peripheral regions of the bilayer
what is the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane
phospholipids in plasma membrane move
most lipids and some proteins drift laterally
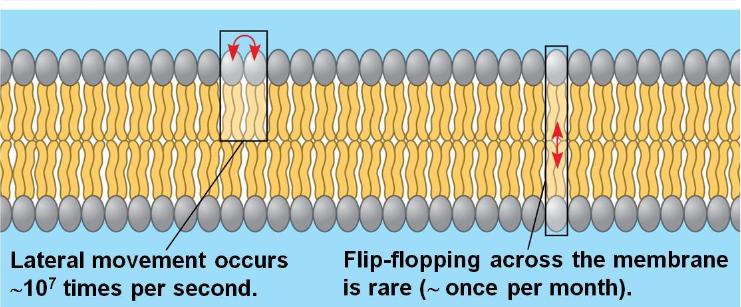
why must membranes be semipermeable
to be sufficiently compact: avoid uncontrolled trafficking
to be sufficiently fluid: remain biologically active
what do usnaturated hydrocarbon lipid tails allow for
allows the membrane to remain fluid at low temperatures
what does cholesterol allow for
prevents membranes from solidifying in low temperatures
prevents membranes becoming too fluid in high temperatures
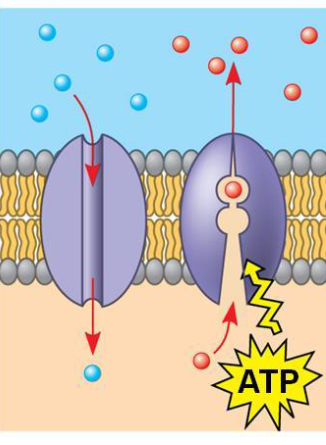
what are membrane transport proteins
allow passage of select solutes across membrane
some transport proteins shuttle substances across membrane through a change in shape
may provide hydrophilic channel
what does passive transport involve
small, non polar molecules
slow
what is diffusion
movement of molecules across a membrane from region of high to low concentration
what is facilitated diffusion
involves charged hydrophilic solutes
polar molecules enter cell at high rates
ion channels and gated channels
no ATP required
what is osmosis
movement of water molecules from a region of high to low concentration across a semi permeable membrane
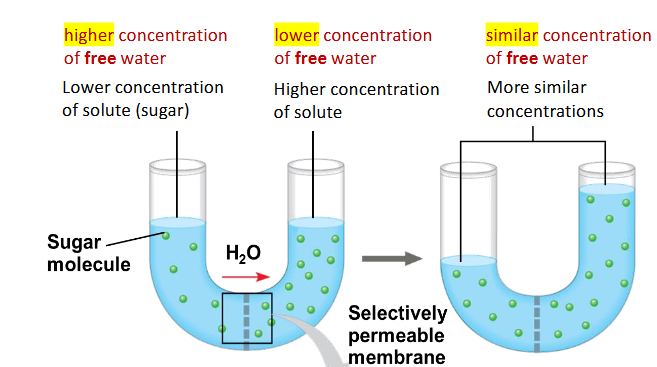
what is the tonicity of a solution
its ability to move water in/out of a cell through osmosis
what is an isotonic solution
does not move water
eg cells without cell wall are healthy in this
what is a hypotonic solution
moves water in (less concentrated solutes)
eg cells with a cell wall are healthy in this
what is a hypertonic solution
moves water out (more concentrated solutes)
what do channel proteins allow for
water or specific hydrophilic molecules to pass through:
in both directions
down their gradient
what are gated channels
open in response to an electrical or chemical stimulus
what are aquaporins
selectively conduct water in/out, preventing passage of charged species
what is active transport
requires ATP & is against the gradient
eg Na+/K+ pump
what is the Na+/K+ pump
Shape of pump has affinity for Na+, 3 Na+ ions bind → phosphorylation causes the shape to change and Na+ is released outside
Shape of pump now has affinity for K+, 2 K+ bind → loss of phosphate group causes pump to go back to original shape and K+ is released
what is exocytosis
large molecules are secreted when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
transport from the cell
what is endocytosis
large molecules are taken in when plasma membrane pinches inward
transport to the cell
what is bulk transport
moves large molecules
requires energy
what is phagocytosis
ingestion of solid food particles (engulfed bacteria, virus, debris)
what is pinocytosis
ingestion of fluids containing small solutes (ie vitamins, toxins)
what is rec-mediated
small/macro molecules bind to receptors before being engulfed
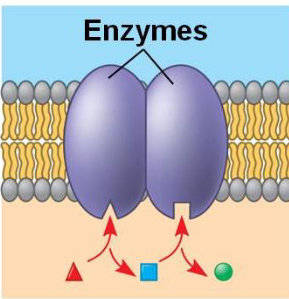
what are membrane enzyme proteins
lowers activation energy of reaction, making it faster
when substrate binds, enzymes undergo a conformation shift which makes them more reactive
high specificity to substrates (lock and key)
why are membrane enzyme proteins membrane bound?
allows precise position, orientation and proximity with other enzymes
catalyse reactions in specific locations
coordinated catalysis in metabolic pathways
what are membrane receptor proteins
the external signaling molecule may cause a shape change of the receptor protein, passing a message into the cell
has a binding site with a specific shape that fits a molecule
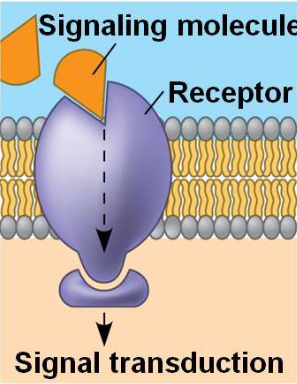
what does cell to cell recognition involve
glycoproteins:
serve as identification tags
recognised by membrane proteins of other cells
short lived interactions
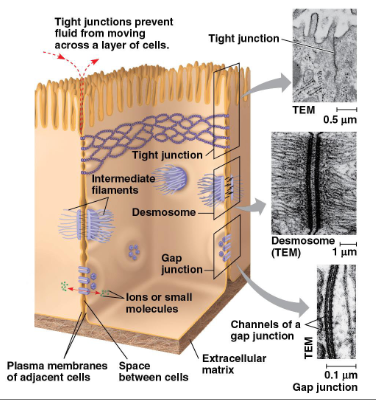
what does intercellular joining involve
tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions:
neighbouring cells in tissues, organs or organ systems often adhere, interact and communicate through direct physical contact
what does attachment to cytoskeleton and ECM involve
integrins:
bind ECM and cytoskeleton
important during development for cell migration
can coordinate cellular changes in response to environmental signals