Oxidative Stress (Lecture 5, Exam 2 Content)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Radicals
O2 HO HO2
Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) Radicals
NO HNO
Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) Non-Radicals
NO2 ONOO- generally more stable
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Non-Radicals
HClO H2O2 HBrO O3 delta g
Supraoxide radical
O2*-
The addition a single electron to the ground-state
molecule (O2 + e- = O2.-)
Generation of superoxide (O2
.-)
Mitochondrial electron transport chain
• Enzymatic reduction of oxygen (O2 )
• Xenobiotic metabolism (redox cycling)
• Respiratory burst (phagocytes)
Superoxide radical
Hydroxyl radical
HO.
Highly reactive oxygen radicals
• Short-lived species with high affinity
toward other molecules.
• Formation of hydroxyl radicals in
biological systems:
• Ionizing radiation
• Formation of hydroxyl radical from ozone (O3)
• Reaction of metal ions with hydrogen peroxide
(Fenton Haber-Weiss reaction)
Hydroxyl radical (HO.)
Hydrogen peroxide
H2O2
not radical but reactive with metals (fenton rxn)
Supraoxide Dismutase H30 - H202 - H20
Nitric oxide
NO.
Endothelial derived-relaxing factor (EDRF) -
vasodilator
• Functions
• Vascular function, platelet aggregation,
immune response, neurotransmitter, signal
transduction
• Cytotoxicity
NO. + O2 =
.- ONOO- (highly toxic)
Role of free radicals
enzyme reactions
e- transport chain in mitochondria
signal transduction - gene expression
activation of nuclear transcription factors
oxydative damage of molecules, cells, tissues
antimicrobia,
aging and disease
Molecular effects of oxidative stress
Lipid peroxidation
• DNA damage
• Protein oxidation
• Inactivation of enzymes
• Release of Ca2+ ions from intracellular stores
• Cytoskeletal damage
• Chemotaxis
PUFAs
polyunsaturated fatty acids
potential toxic effects
antioxidants
cellular defense mechanisms against
oxidative stress: Antioxidants
• Enzymes and repair systems
• Superoxide dismutase
• Catalase
• Glutathione system
• DNA repair enzymes
• Macroxyproteinases – degrades oxidatively
denatured proteins in red blood cells.
• Sequestration of metals
• Transferrin, lactoferrin, ferritin, metallothionein
• Vitamins
• Vitamin A
• Vitamin B
• Vitamin C 26
Nrf2-ARE pathway
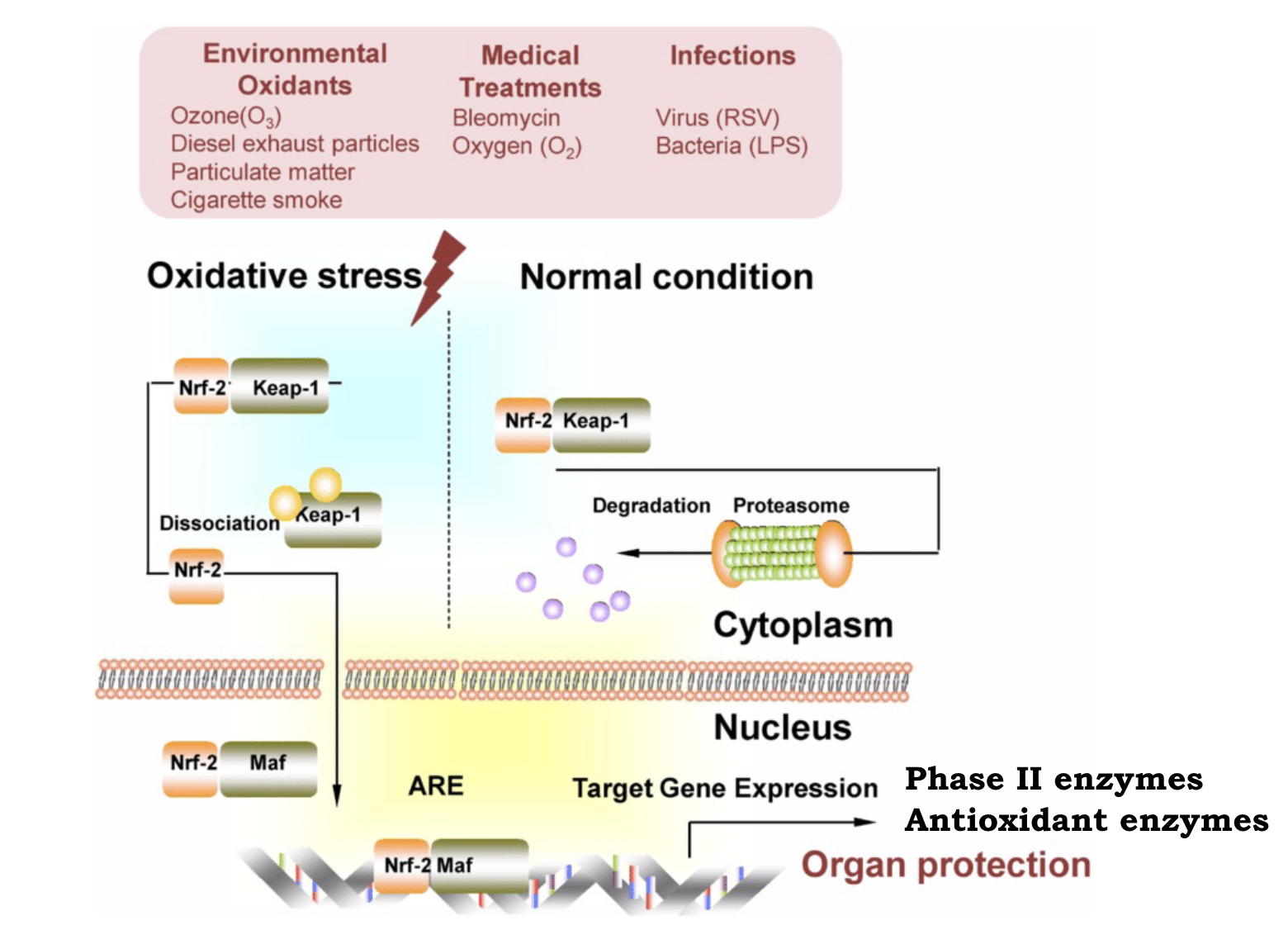
antioxidant response element
nrf2 is a multiorgan protector
Supraoxide dismutase
in the cytosol - SOD1 (Cu +Zn)
in mitochondria - SOD2 (MnSOD)
h30 - h2o2
Gluthathion Redox Cycle
Major reducing power - processes hydrogen peroxide
reduced form: GSH
Oxidized form : GSSG
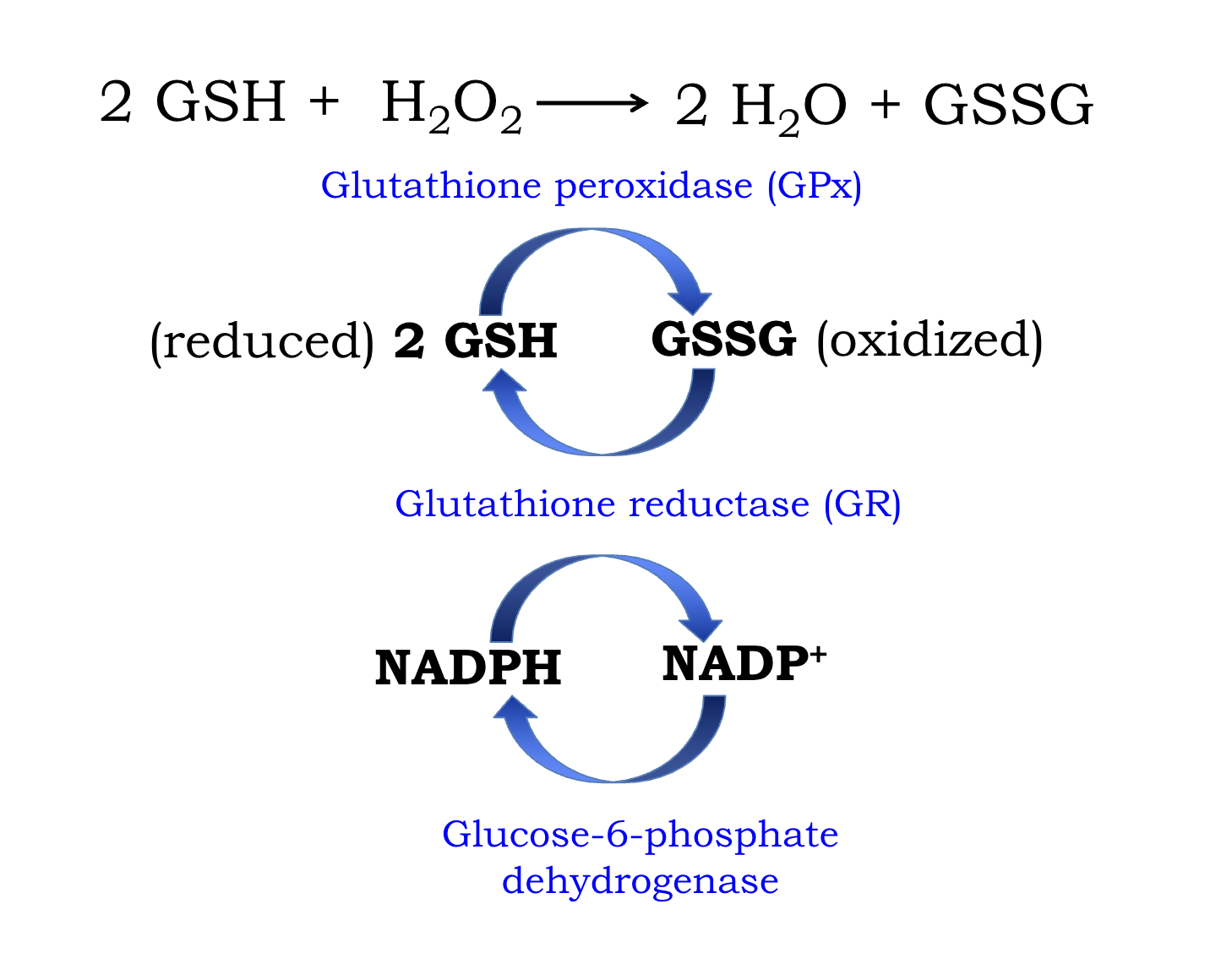
mediated by gluthathion peroxidase (GPx)
fascilitated by NADPH - NADP
Metal sequestration agents
• Ferritin, transferrin, and ceruloplasmin:
- Ensures extremely low levels of free cytosolic metals with a potential for valence changes.
• Metallothioneins:
- Sequester several metals with a high affinity for –SH groups (e.g., mercury and cadmium).
32
Measurement of oxidative stress
Oxygen consumption
• Activity and levels of antioxidants
• Oxidative markers
– Lipid peroxidation products (TBARs, lipid hydroperoxides,etc.)
– DNA hydroxylation products
– Protein hydroxylation products (nitration products)
Free Radical detection
Single photon counting
• Chemiluminescence
• Fluorescent probe
• Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR)
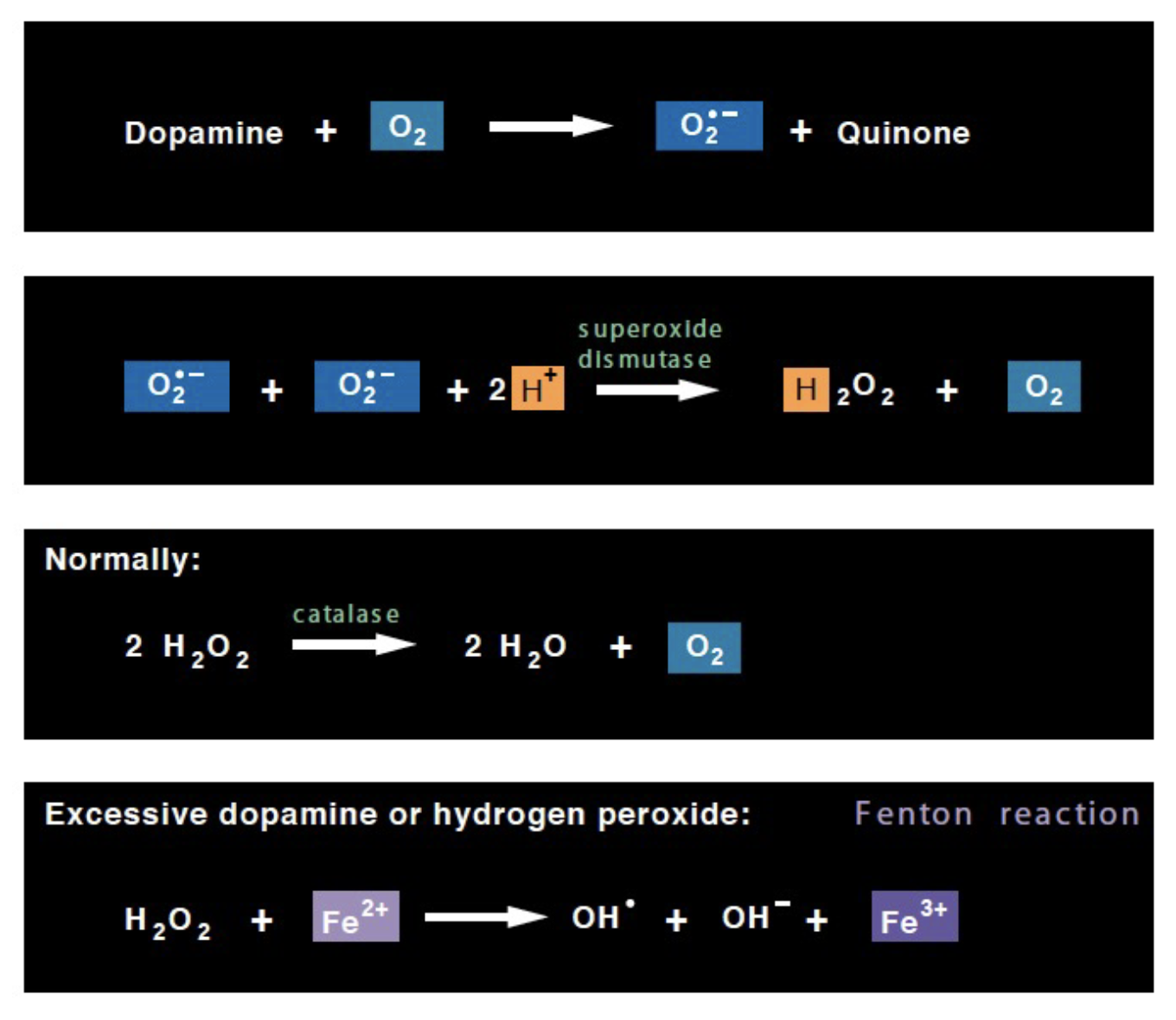
Dopamine oxidation
mediated by monoamine oxidase MAO) to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
(DOPAC or DPA) and H2O2
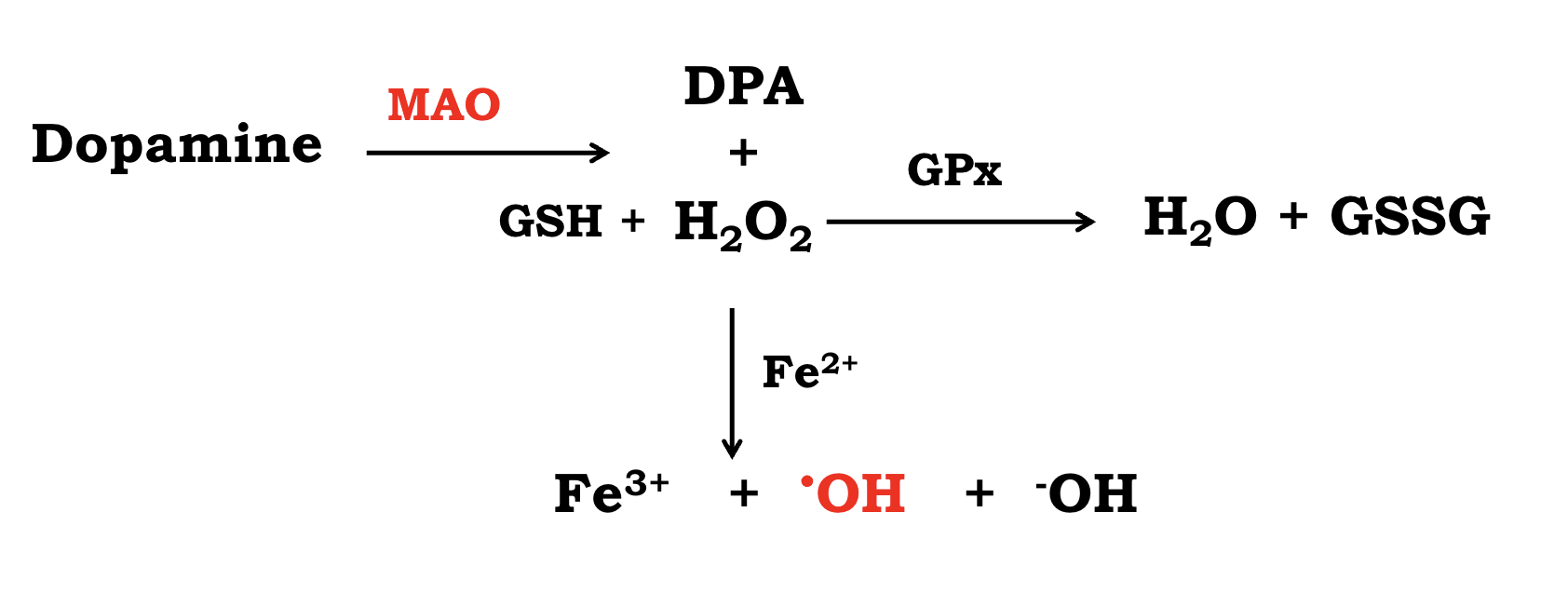
Dopamine auto-oxidation
Auto-oxidation in the presence of O2 or trace
multivalence metal ions