Week 12: Key Medical Terms and Definitions for Understanding Prinzmetal Angina and Related Cardiac Conditions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
ST/T wave
- ventricular repolarization
- crucial in identifying warning signs of ischemia and infarction (not the only conditions that cause changes in ST/T)
normal ST
typically isoelectric
normal T wave
upright in all leads except aVR and V1
left bundle branch block
- QRS abnormally wide
- QRS in V1
- appropriate discordance (ST elevation in leads with negative QRS complexes)
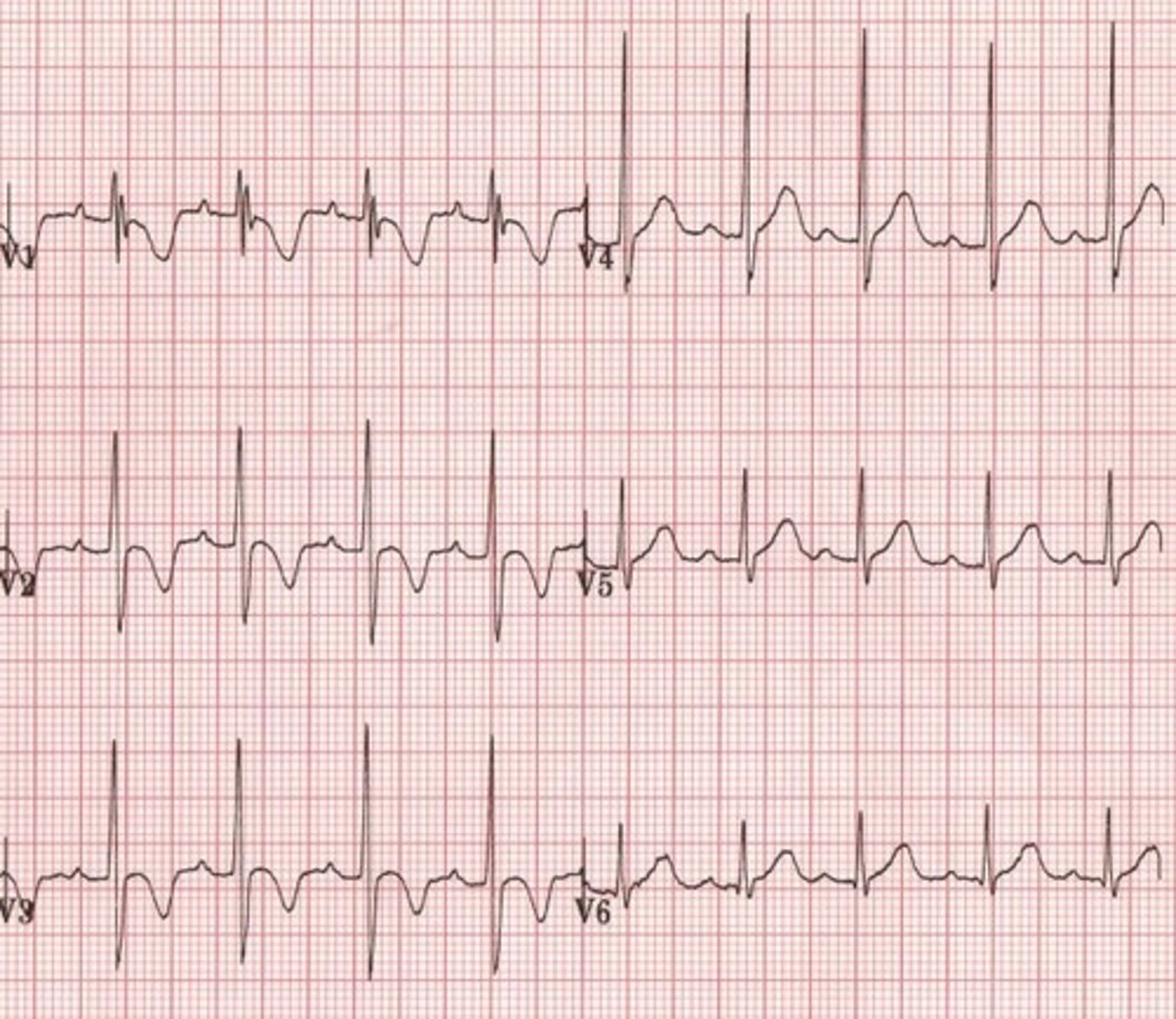
left ventricular hypertrophy
- sokolow-lyon criteria
- R wave taller than 11 mm in aVL
- appropriate discordance (ST elevation in V2-V3 most common)
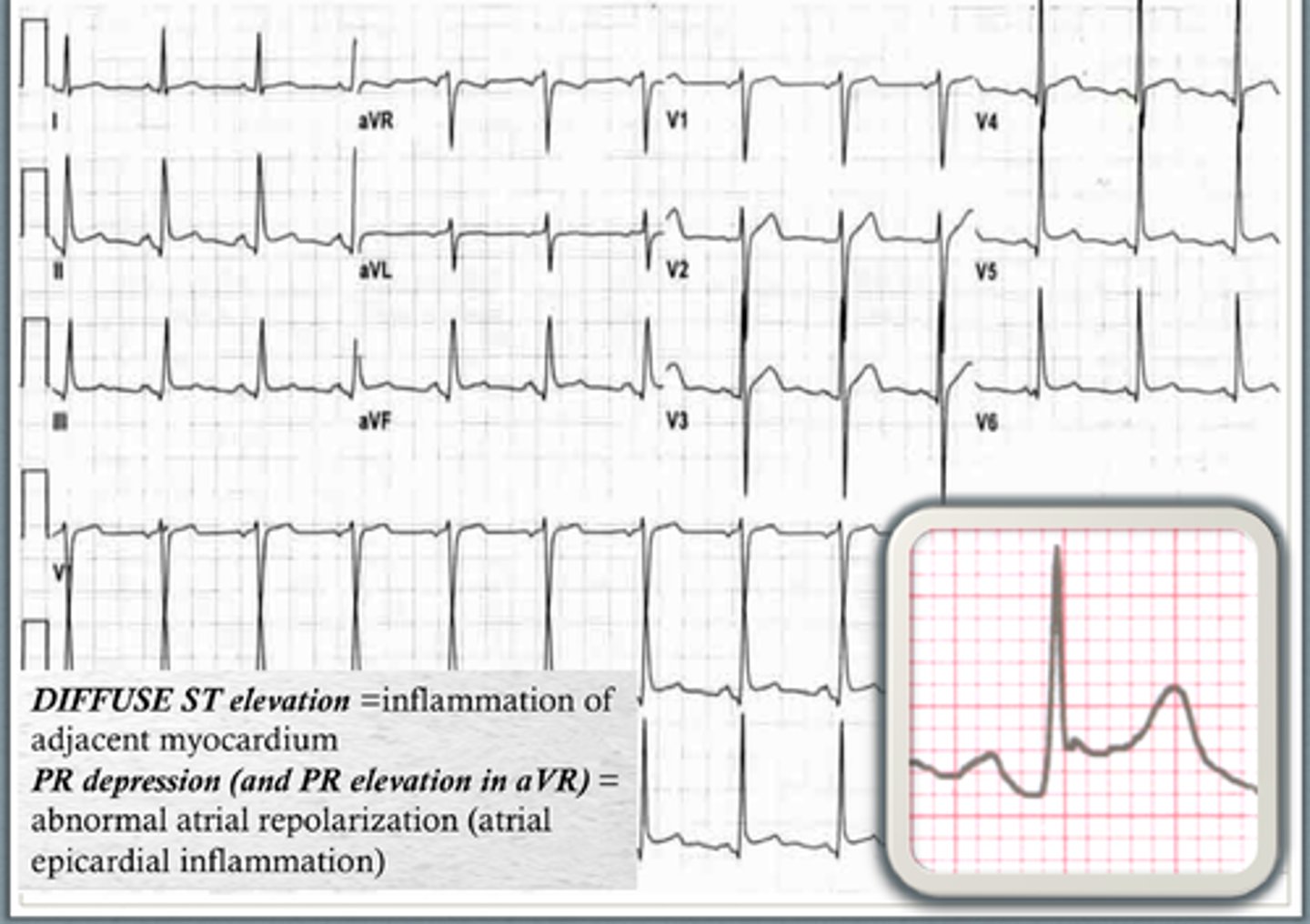
pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardial sac
S/S of pericarditis
pleuritic chest pain, patient sitting up and leaning forward, may have friction rub
characteristics of pericarditis
- widespread concave ST elevation
- ST/T ratio >0.25
- widespread PR depression
- sinus tachycardia
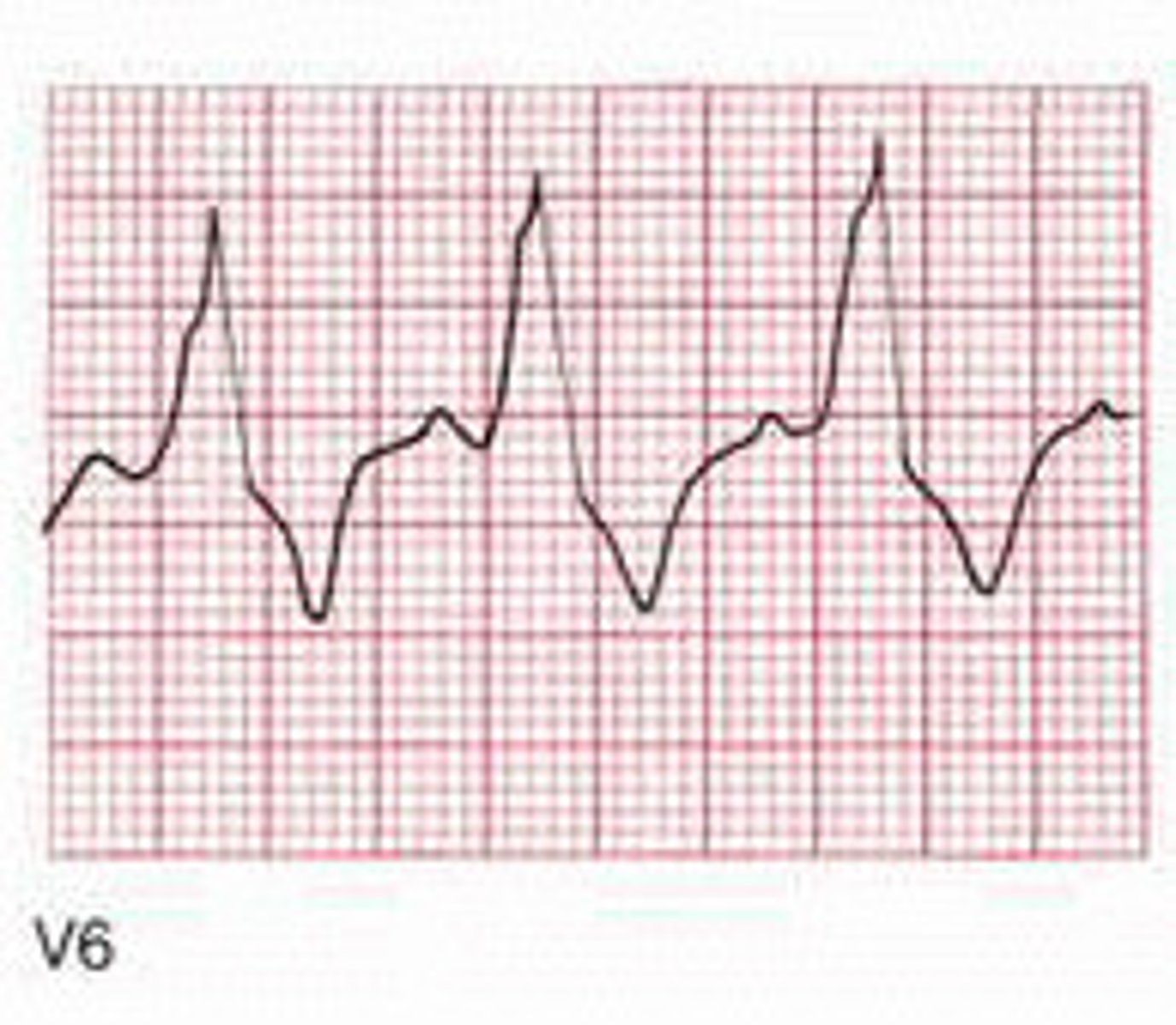
benign early repolarization
- normal EKG variant
- young men, typically under age 50
characteristics of benign early repolarization
- widespread concave ST elevation
- notching or slurring a J point "fishhook"
- tall asymmetric T waves
- no reciprocal ST depression
- ST changes remain constant (STEMIs evolve)
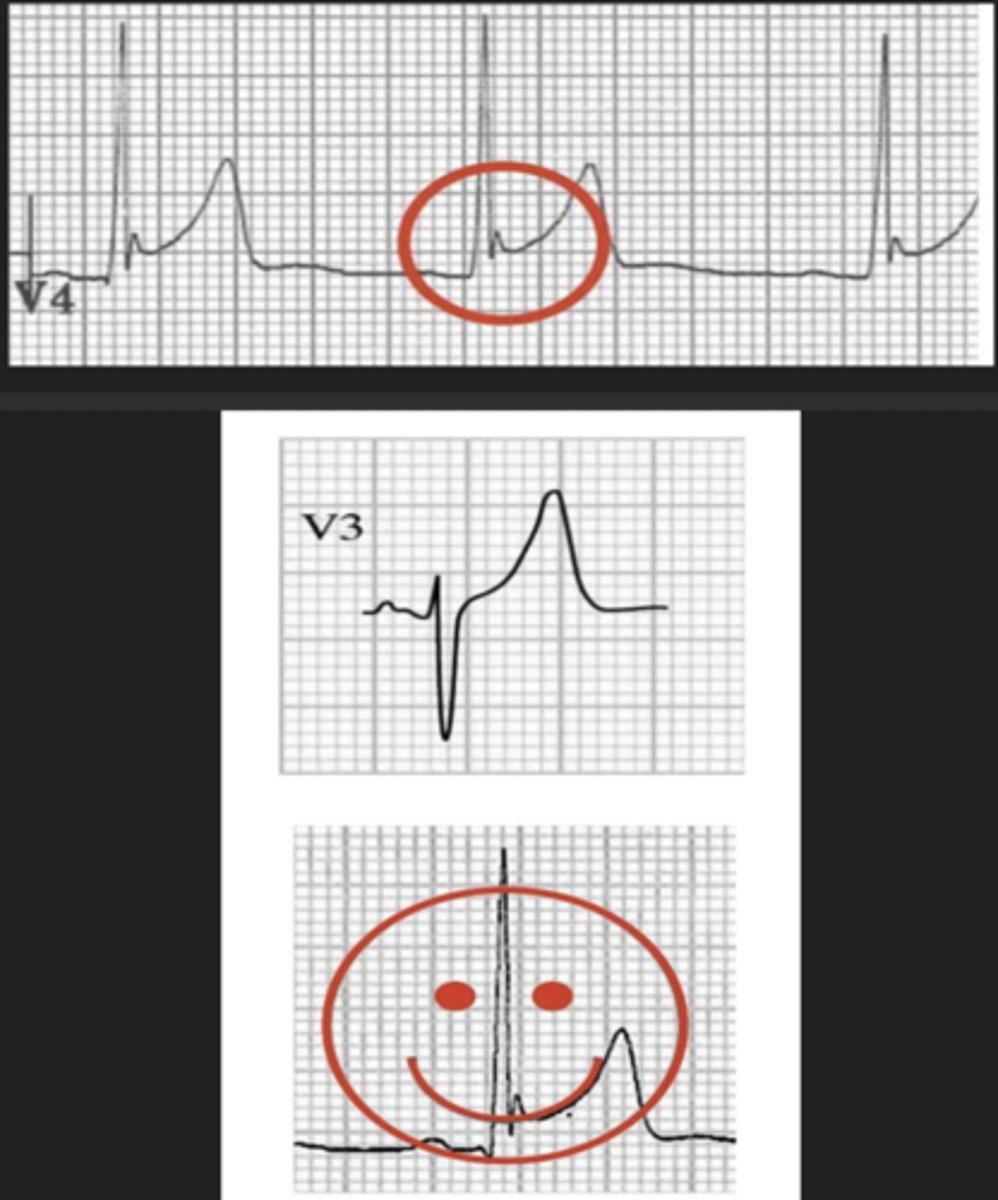
brugada syndrome
- autosomal-dominant sodium channelopathy
- can cause ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death (estimated 40-60% idiopathic V. fib)
characteristics of brugada syndrome
may be intermittent and revealed by conditions (i.e., fever, ischemia, medications, hypokalemia)
- pseudo RBBB
- coved ST segment elevation >2 mm in right chest leads
- T-wave inversion in right chest leads
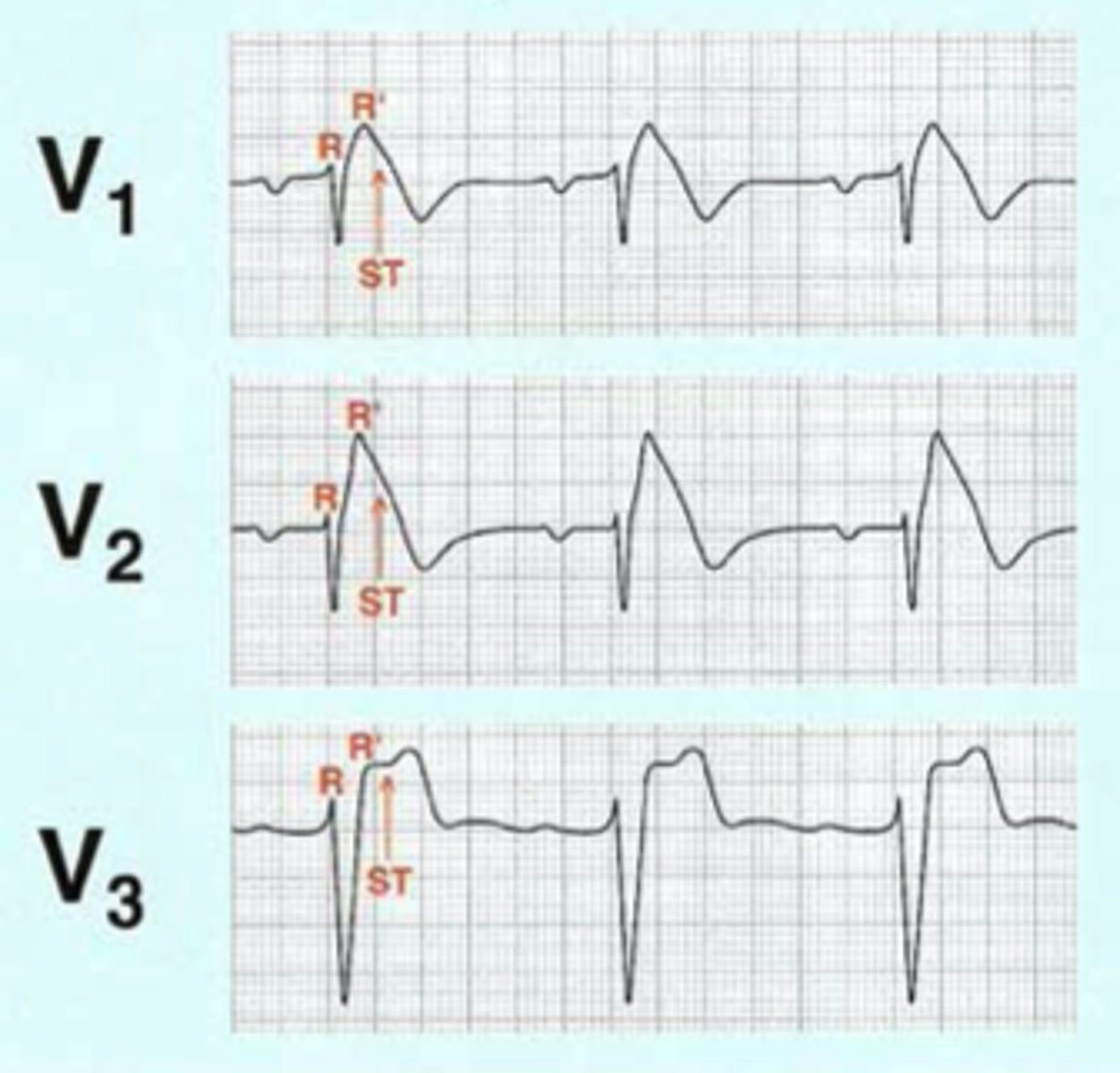
diagnosis of brugada syndrome
characteristic EKG changes plus one of the following
- documented V. fib or polymorphic V. tach
- family history of sudden cardiac death under the age of 45 years
- same coved ST morphology in family members
- VT can be induced by electrical stimulation
- syncope
- nocturnal agonal respiration
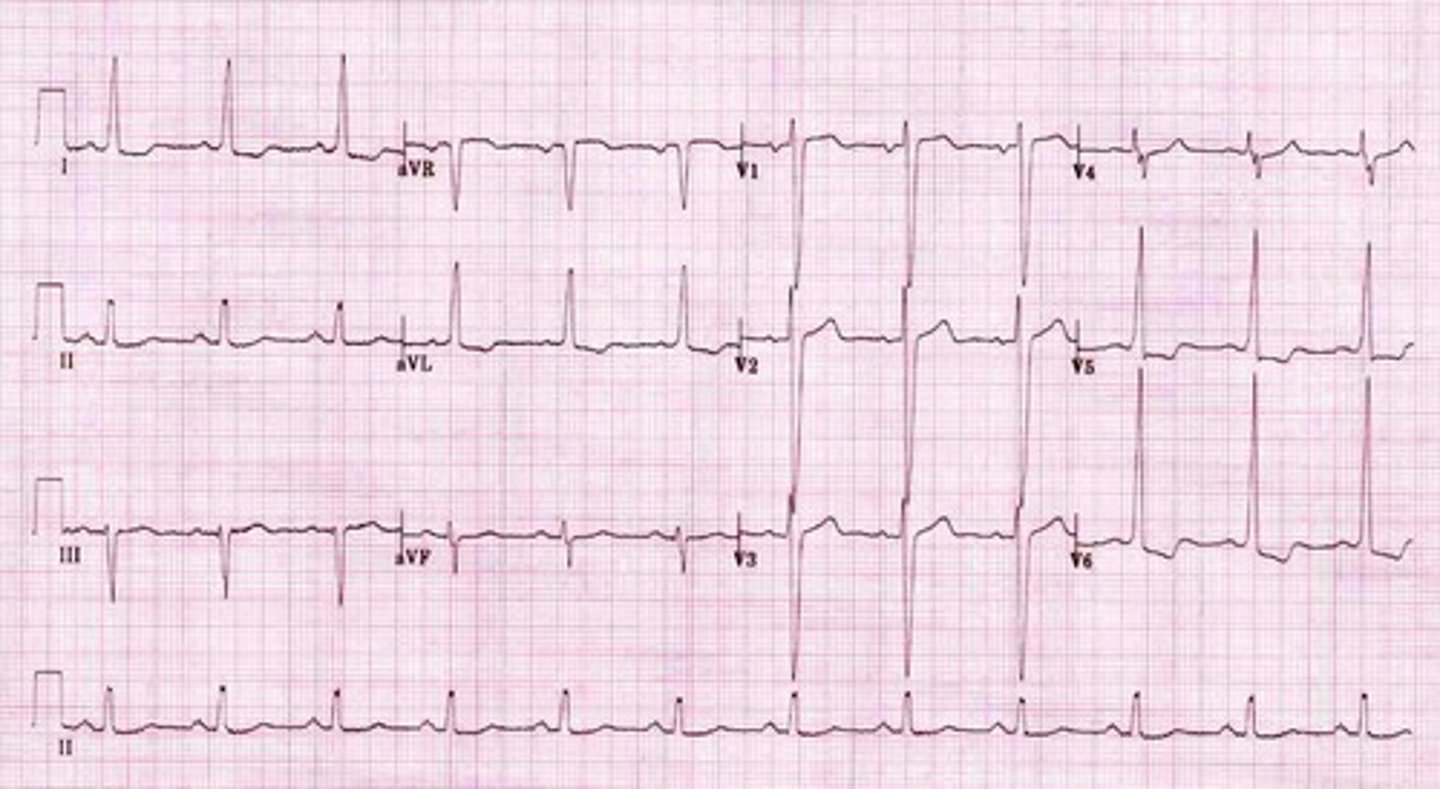
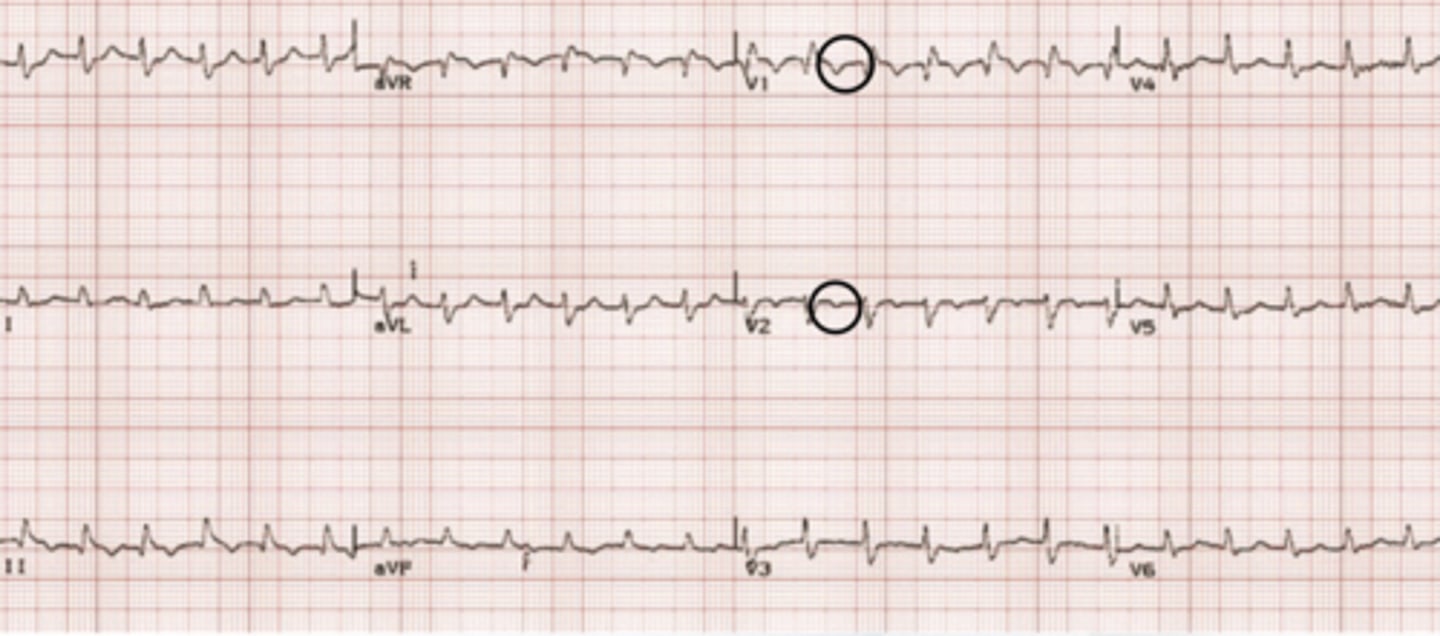
prinzmetal angina
vasospastic angina caused by coronary artery vasospasm
S/S of prinzmetal angina
- chest pain at rest (often occurs between midnight-early morning and lasts 5-15 minutes)
- drugs and alcohol
- male smokers
characteristics of prinzmetal angina
- widespread ST elevation
- quick resolution of ST elevation
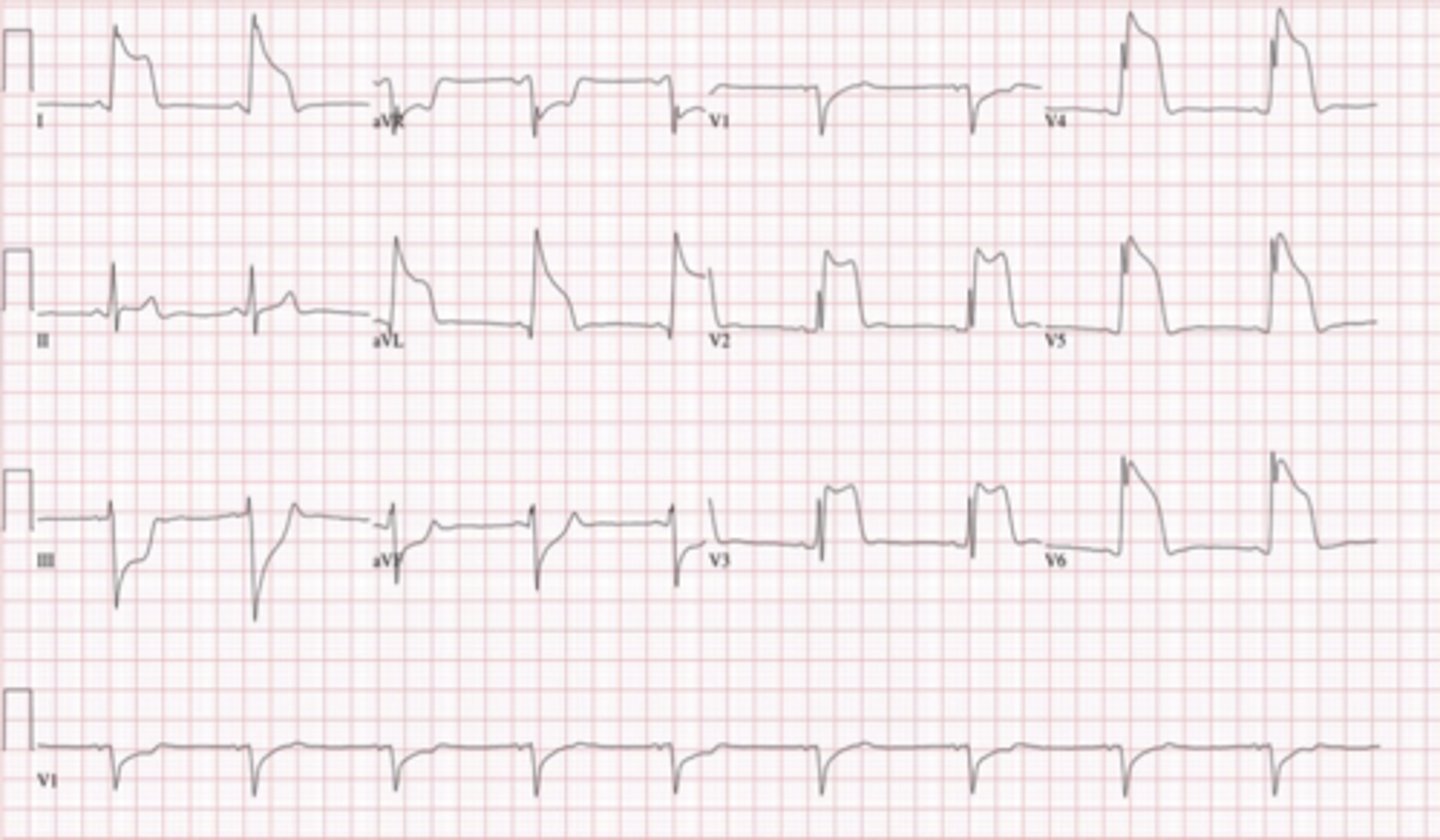
takotsubo
aka "broken heart syndrome;" ballooning shape of the left ventricle due to emotional stress
characteristics of takotsubo
- widespread ST elevation with no reciprocal depression
- reversible Q waves indicative of Purkinje cell death (usually disappear within 30 days)
- T wave inversion
- QT prolongation
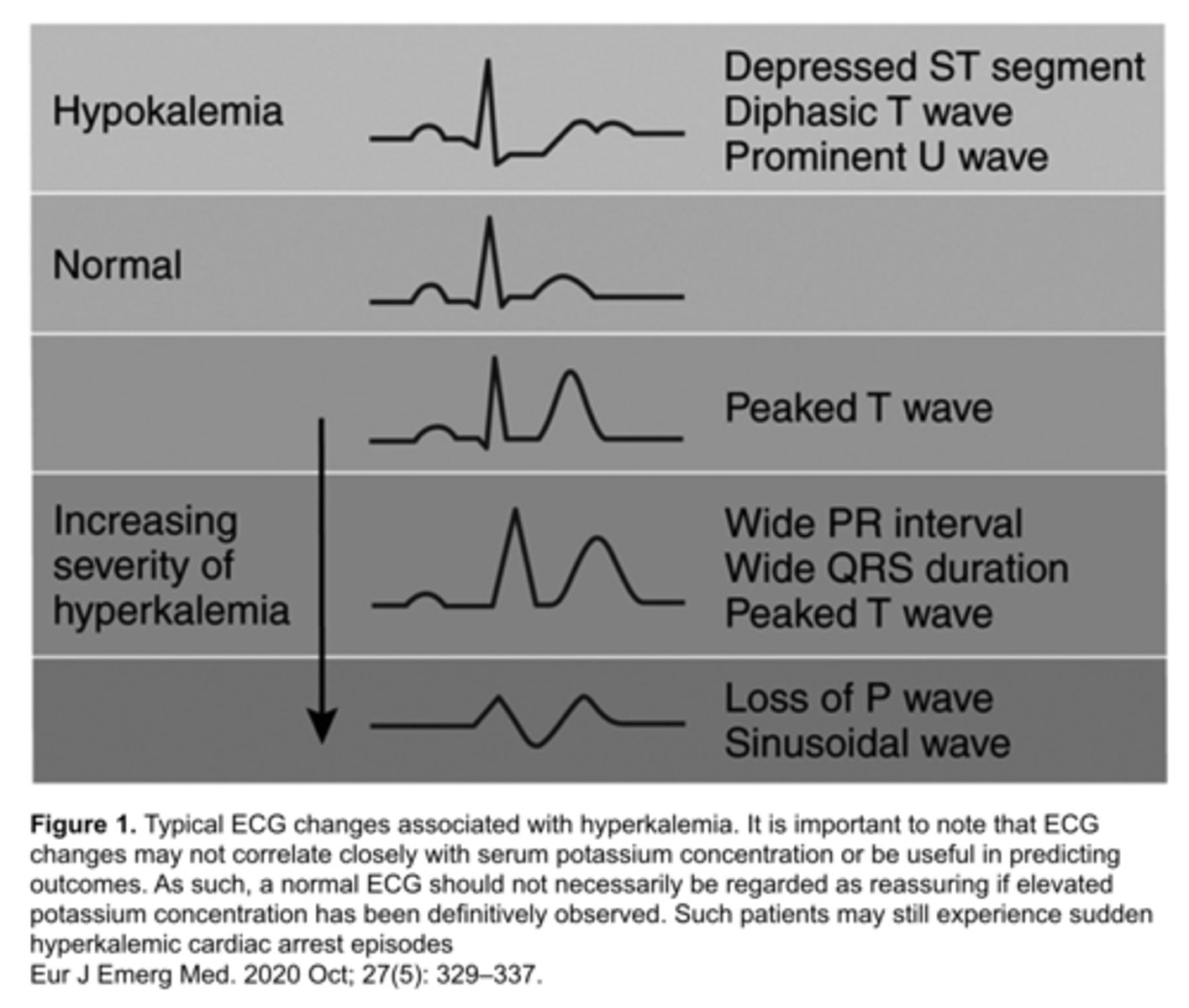
hyperkalemia
potassium level >5.5
characteristics of hyperkalemia
- can lead to ST elevation that mimics STEMI
- usually in right chest leads (V1-V3) with tall, pointed T waves
right bundle branch block
- wide QRS
- rSR' morphology in right chest leads (V1-V2)
- ST/T wave discordance (T wave inversion in right chest leads)
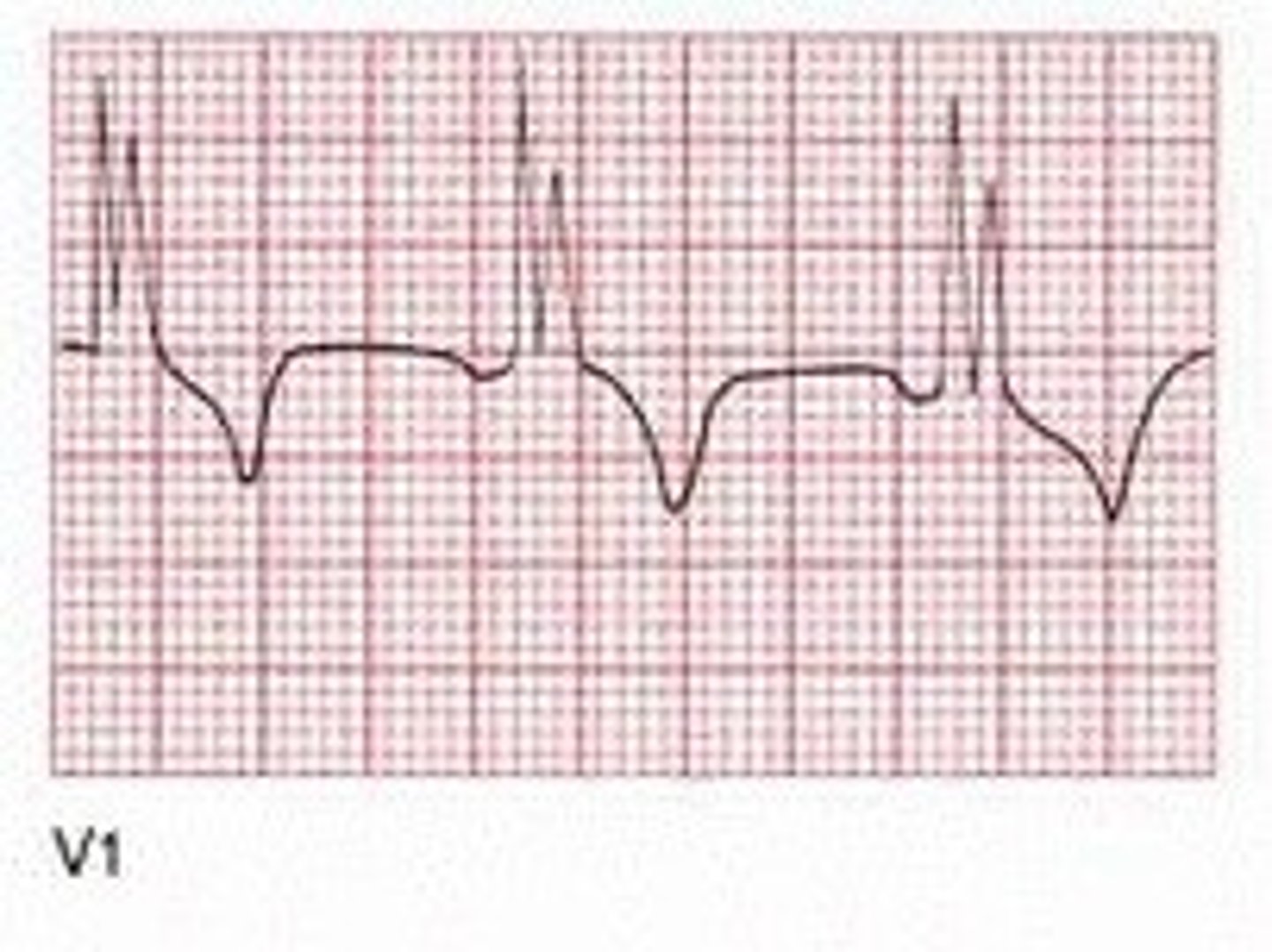
right ventricular hypertrophy
- tall R waves followed by ST depression and T wave inversion in V1-V3
- formerly called "strain pattern"
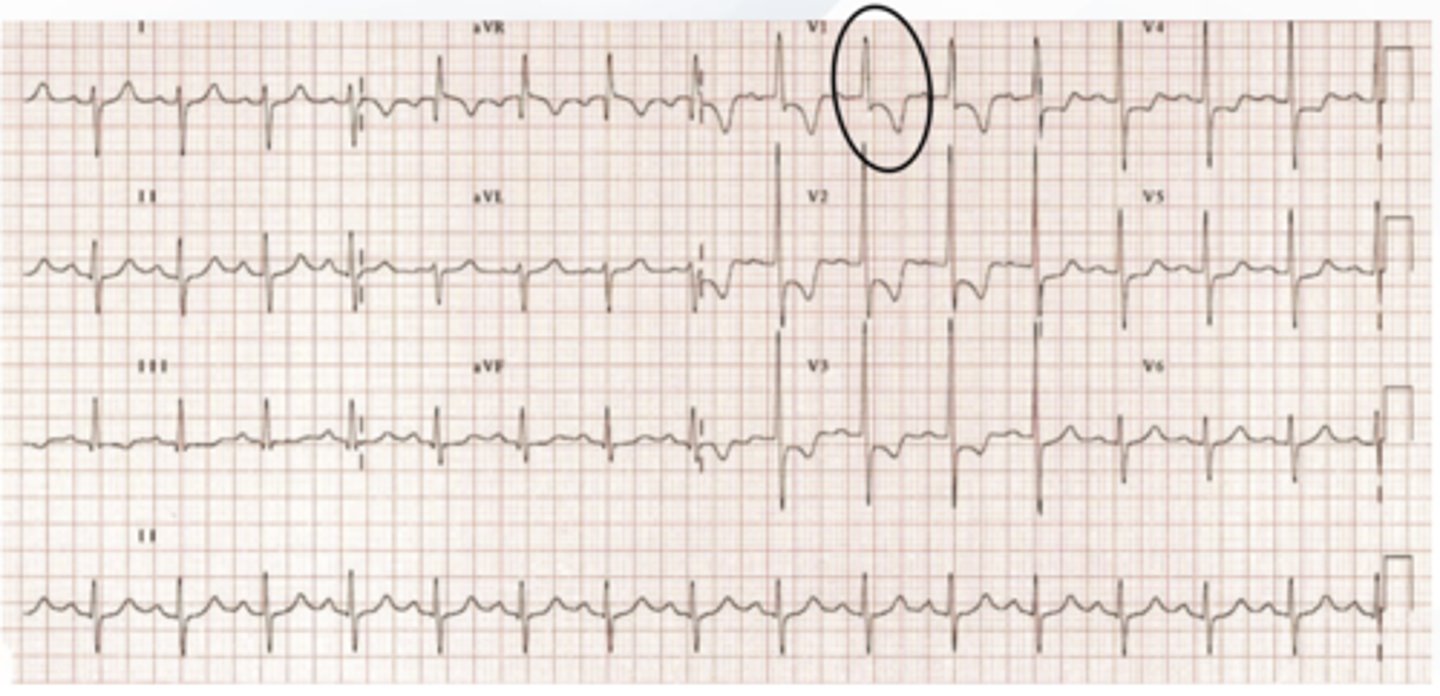
arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
- fibrotic tissue that can result in ventricular arrhythmias
- 3x more common in men than in women (Greek or Italian)
characteristics of ARVC
- prolonged S-wave upstroke
- epsilon wave: small positive deflection at end of QRS that is similar to a "fishhook"
- inversion of T waves in right chest leads
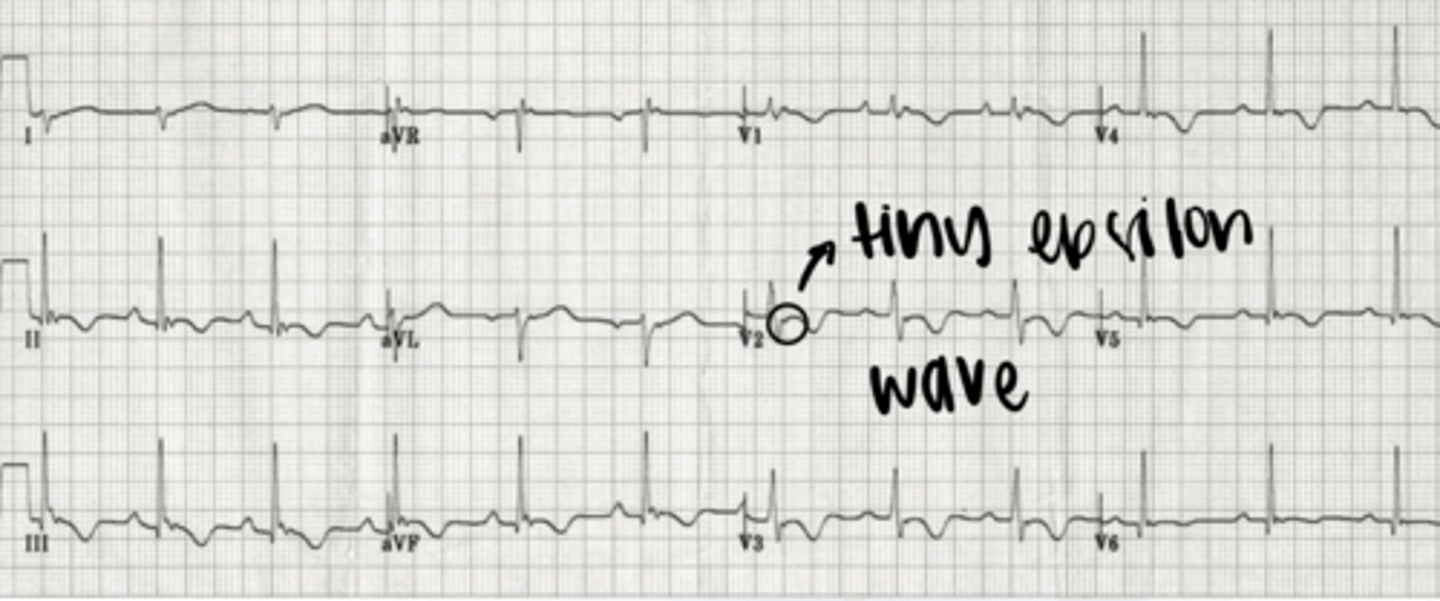
what is the most specific finding for ARVC?
epsilon wave
elevated ICP
can caused by tumors, infections, intracranial bleeds, etc.
characteristics of elevated ICP
- widespread giant T wave inversions known as "cerebral T waves"
- prolonged QT interval
- bradycardia
Cushing's triad seen in elevated ICP
bradycardia, respiratory depression, and hypertension
what is the most common EKG finding with a pulmonary embolism?
right ventricular strain can cause T wave inversions in right chest leads
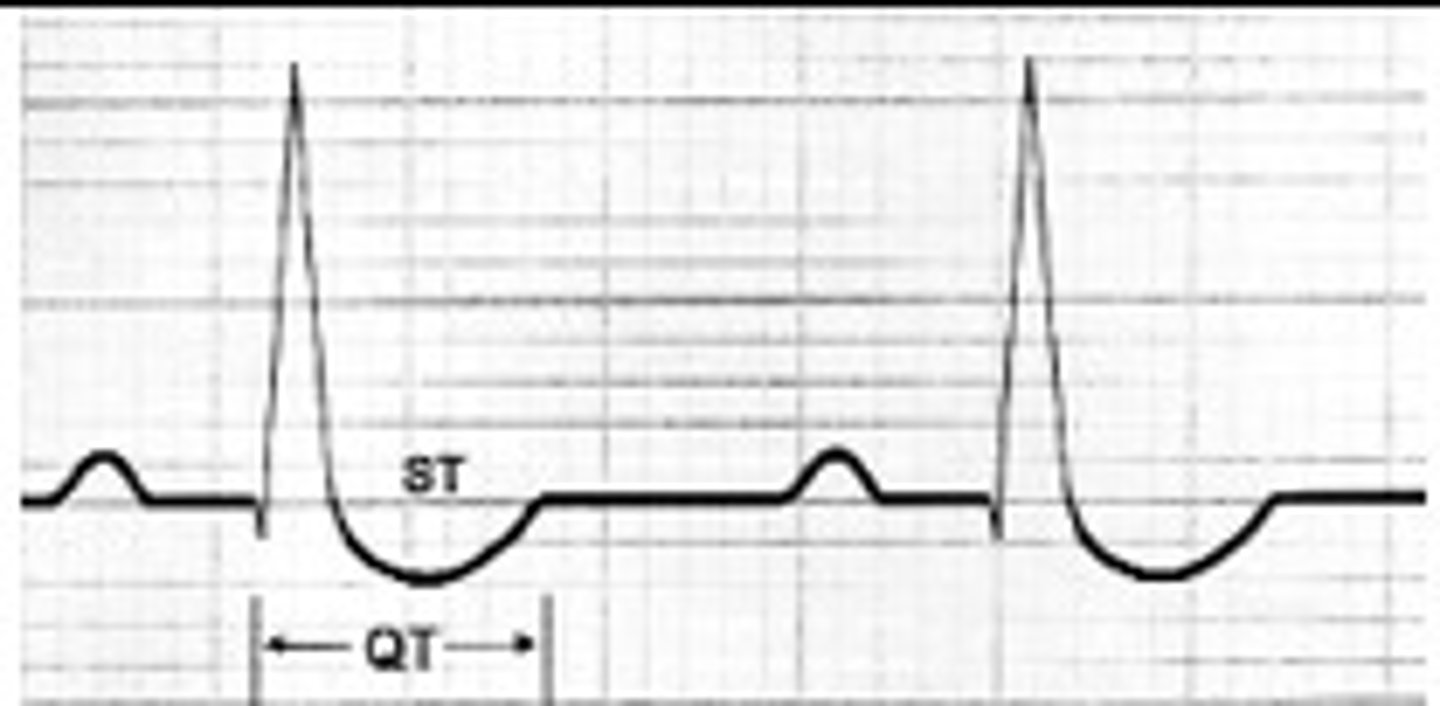
digitalis effect
slight sagging/swooping of ST
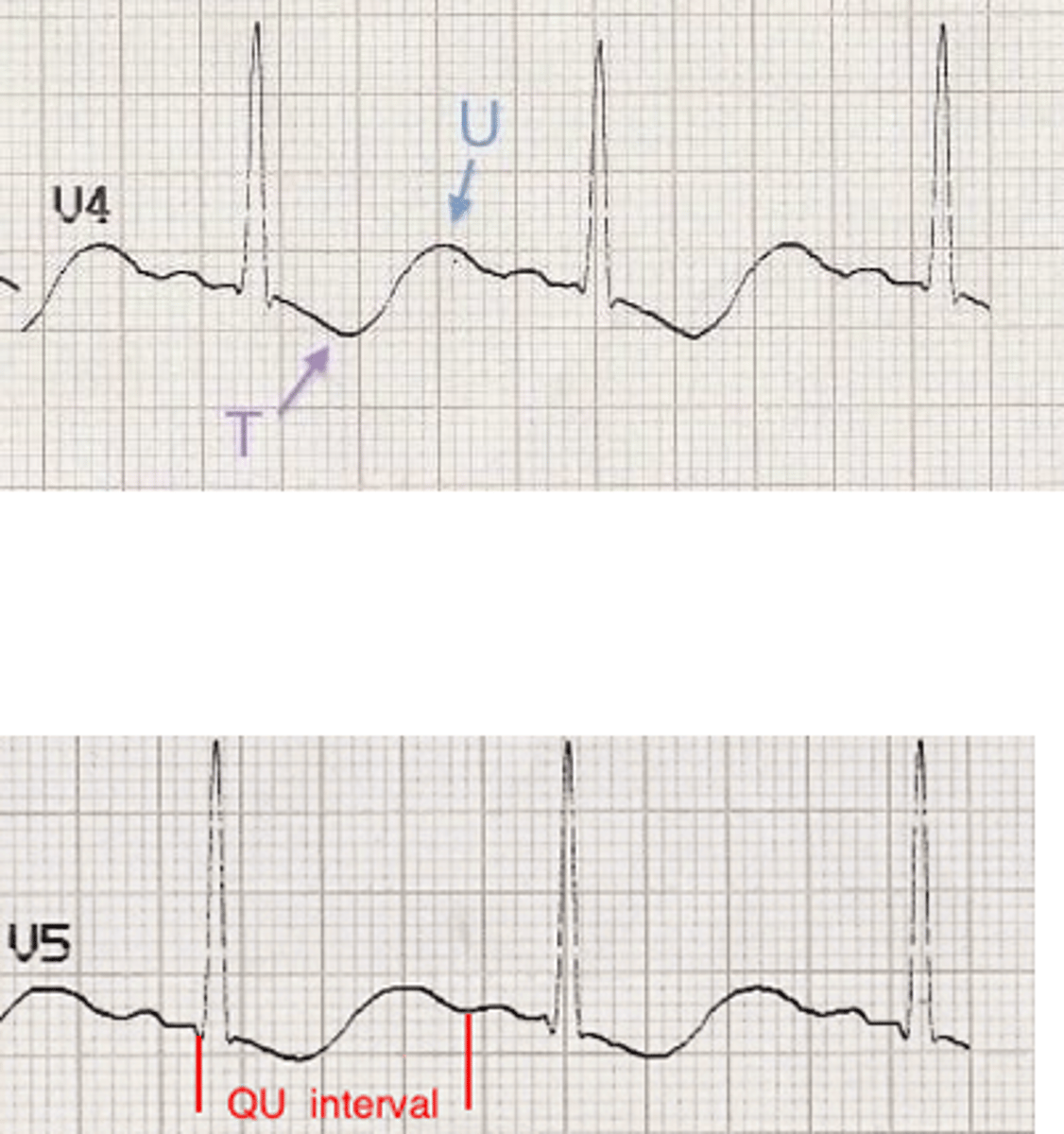
hypokalemia
potassium level <2.7
characteristics of hypokalemia
- ST depression
- flattened T waves
arrhythmias causing ST depression
- WPW
- SVT
persistent juvenile T waves
- children have asymmetric T wave inversions through right chest leads
- can persist in adults, particularly African-American women under the age of 30