Biology 1500 Test 4
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Explain how the circular processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration result in the cycling of carbon within ecosystems.
Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide into environment, photosynthesis pulls carbon dioxide out of atmosphere
. Explain the two reasons for an imbalance in this cycle that led to the increased O2 during the Carboniferous.
Increased photosynthesis
buried carbon-removed from cycle
Describe the hypothesized reasons for the decline in O2 during the late Permian
Because trees falling down caused carbon to become trapped underground, slowing down photosynthesis and celluyl
Explain the importance of Lignin and Lignin Decomposition on the rise and fall of O2 levels during the Carboniferous
Evolved in early trees and allowed for bigger plants because of the structural benefits
Could not be decomposed
allowed for coal formation from buried carbon
Explain where most of the matter in organic carbons comes from
AIR
Recall elevation of mt everest
8800 M
recall reason for death zone
Insufficient Oxygen
High winds and low temps
Body uses oxygen faster then it can replenish it
less O2 in atmosphere
Where does the death zone occur
8000m
Recall the migration path of Bar Headed Geese and which feat makes it remarkable
Migrate from India to Mongolia
Elevation at which they fly
Function of mammalian respiratory system
Oxygen moves into blood, co2 moves out of blood into air
List steps of mammalian respiratory system
Inhalation
O2 diffuses to red blood cells
O2 binds to hemoglobin
Co2 diffuses into blood
O2 used for Cellular respiration
Blood transports co2 to lungs
Co2 is exhaled
Gas exchange
Exchange of Co2 and O2 in an organism
Tidal Volume
Amount of air moving in and out of lungs with each respiratory cycle
Vital Capacity
Greatest volume of air that can be expelled from lungs after one deep breath
Alveoli
Air sacs in lung allows for rapid gas exchange
Describe how the structure of our respiratory system facilitates gas exchange
Large folded surface= large surface area for diffusion to take place
Explain what residual lung volume refers to and why it exists
Used air
there must always be air in lung, if no air, alveoli can stick together and won’t open back up to take in air
Compare the atmosphere we breathe (at sea level) and the atmosphere in our lungs, and explain the reason for the difference
Sea level: Po2= 21KPA. PCO2= 0.04 KPA
In lungs: Po2= 13KPA. PCO2= 5 KPA
All depends on volume of gas exchange
Describe differences in atmospheric gasses between sea level and the Himalayas
O2 at sea level is 3X higher then Himalayas
Differentiate between the concentration (or percentage) of a gas in the atmosphere and its partial pressure
Depending on the altitude the partial pressure of gas varies
Higher altitude= lower partial pressure
Explain similarities/differences among amino acids
Same bases
different R groups
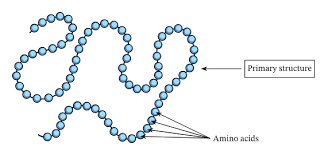
Primary protein structure
Linear Amino Acid sequence
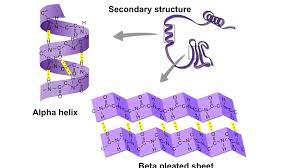
Secondary Protein Structure
hydrogen bonds between backbones of nearby Amino acids cause either a helix or sheet form
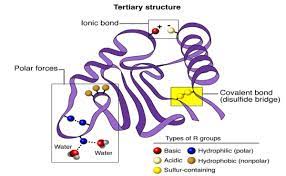
Tertiary Structure
Caused by interactions between R groups, determine 3D structure
Chemical bonds form between distant parts of chain causing the 3d shape
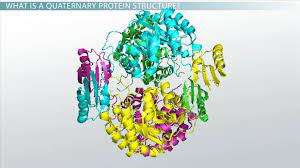
Quaternary Structure
Interactions between separate chains
Describe how classes of amino acids influence their chemical interactions
They have different repulsions and attractions based on their makeup
Hydrophobic Amino acids
Tend to aggregate, end up on interior of protien
Hydrophilic polar Amino acids
One end of R group slightly more negative then other
Form H bond with each other within water
Hydrophilic basic/ acidic amino acids
Strongly polar either + or -
Usually on outside of protein
form bonds with each other
Explain why a change in an aa-sequence may change the 3D structure of a protein
the AA sequence codes with what it will react with. Shape determines function
Basic Function of hemoglobin
Transports O2
Binds to O2
Structure of hemeglobin
Contains 4 globular subunits (2 alpha, 2 beta)
Contains 4 heme groups
explain the basic properties required of an O2 transport molecule, i.e. why transporters need to have complex affinity
High Affinity is needed to effectively bind O2 in lung
Low affinity is needed to release o2 in tissues
Complex affinity is needed because you need to have both high and low affinity
Interpret O2- Hb dissassociation curve
has a sigmodial shape, Hb affinity increases with increasing PO2 levels
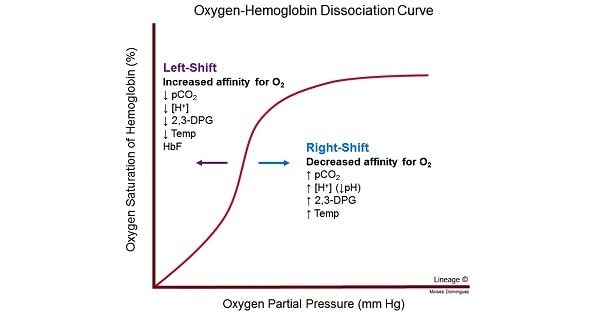
define high and low affinity in the context of Hb and O2
Low affinity O2 won’t bind easily
Gets released easily
explain how a left- or right-shift of the binding curve represents a change in affinity
Left is high affinity
Right is low affinity
connect molecular changes during O2 binding to cooperative O2 binding properties of Hb
The O2 and hemoglobin binding process starts out slow but as O2 bonds to hemoglobin it is easier for more O2 to bind (Party analogy)
Explain how the O2 affinity of Hb decreases in the body, incl. which factors contribute to this decrease and how this facilitates the release of O2 in the body
Decreases because of release of Oxygen
factors include lower partial pressure of O2
Lower affinity, cannot hold O2 easily
summarize how pH, PCO2, temperature, and 2,3-BPG change the tertiary and quaternary structure of Hb and thus its O2 affinity.
Co2, H+ and 2, 3 BPG are polar charged
When attached to charged AA on the outside of heme subunits they can change heme structure
change if single AA unit can change function
explain why human Hb does not work sufficiently at high altitude, by relating PO2 at low and high altitude to the O2 Hb dissociation curve.
Does not work at high altitude because PO2 is too low for heme to effectively bind
At 100m PO2 is 13 KPA in lungs vs 8000m PO2 is 4.6 KPA
Know key characteristics of a scientific explanation
1. Science is about understanding, not facts.
2. Science focuses on the natural world, not supernatural.
3. Science relies on testing ideas by figuring out explanations.
4. New evidence is being acquired and old ideas are being revised.
5. Science is for the community, relies on diversity and different prospective.
Differentiate between a hypothesis and a formal scientific theory
Hypothesis is made before research, theory uses evidence to support claim
Identify fields of science that rely on observations and modeling more than experiments.
Psych
Physics
Explain how/why diversity among scientists improves the quality of the science that is practiced
Diversity makes it so there are many different ideas and hypothesis
ventilation
Breathing process