American Revolution vocabulary
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
John Locke
English philosopher who argued that governments should protect citizens' life, liberty and property, and that people should give their consent for any laws placed upon them.
Pontiac's War
Led by Neolin and Pontiac, AI rebellion that tried to push the British back to the Atlantic Ocean. Failed, but the British started using the middle ground tactics and started giving gifts -- 1763
Proclamation of 1763
Tried to prevent colonists from encroaching upon AI lands by saying that colonists couldn't move west of the Appalachian mountains.
Stamp Act
Passed by George Grenville's government, it imposed taxes on most legal documents in the colonies and on newspapers; the colonists did not like this -- 1765
Townshend Acts
Imposed taxes on tea, paper, glass, lead, and paint. Led to more nonimportation agreements. Repealed in 1770 except for the tea tax -- 1767
Sons of Liberty
Group in colonial cities, especially Boston, who organized sometimes violent resistance to British policies. Used peer pressure to make sure people didn't accept British policies. Involved in the Boston Tea Party -- 1765-1775
Boston Massacre
Confrontation between British soldiers and colonists in March 1770. Five colonists were killed and people were shocked at the violence.
Committees of Correspondence
Groups formed in each colony the exchanged ideas and information about what the British were doing to the colonies -- helped bring the colonists together -- 1772-1775
Tea Act
British tried to grant a monopoly on the tea trade to the British East Indian company that would cut out the colonial middlemen. Colonists threw the Boston Tea Party to show their displeasure -- 1773
Coercive/Intolerable Acts
Acts passed after the Boston Tea Party -- closed the port of Boston until tea was paid for, restricted town meetings in Massachusetts, and allowed the army to live among civilians -- 1774
First Continental Congress
Met in Philadelphia to organize resistance against the Coercive Acts. Petitioned the king and created the Association to enforce nonimportation -- 1774
Lexington & Concord
First battles of the American Revolution. The British wanted to destroy weapons that were in Concord, but the colonists confronted them at Lexington and drove them away from Concord -- 1775
2nd Continental Congress
Organized the colonial army and offered the Olive Branch Petition. It also approved the Declaration of Independence and the Articles of Confederation -- 1775-1781
Declaration of Independence
Justified independence to the rest of the world. Inspired by John Locke and condemned King George III -- 1776
George Washington
Commander in Chief of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, won battles at Trenton, Princeton, and Yorktown.
Battle of Trenton
Important American victory as it propped up sagging patriot morale. Washington surprised Hessian (German) troops on Christmas and took them prisoner. 1776
Saratoga
Turning point in the Revolutionary War as American forces stopped a British force from Canada that was trying to go to Albany, New York. This victory helped bring the French into the war on the side of the Americas -- 1777
French Alliance
After the battle of Saratoga, the French signed an alliance with the colonists and agreed to fight until the colonists got their independence. The French supplies were necessary to win the war -- 1778
Loyalists
People in the 13 colonies who remained loyal to Britain during the Revolutionary War.
Yorktown
Last major battle of the Revolutionary War. The American and French armies and the French Navy trapped Lord Cornwallis here and forced him to surrender -- 1781
Treaty of Paris 1783
Ends the Revolutionary War and gives the U.S. all the land to the Mississippi River and rights to fish off Newfoundland. The Americans still had to pay off their pre-war debts -- 1783
French and Indian war
Ranged from 1754-1763 and was the last of a series of wars fought between Great Britain and her allies and France and her allies.
Treaty of Paris 1763
Happened in 1763 and ended the French and Indian war and forced the French to turn over it's control of Canada to Great Britain.
Proclamation of 1763
Was an attempt to end the Americans settlement beyond the Appalachian mountains.
Stamp Act of 1765
This tax was collected on every document or newspaper printed or used in the colonies.
Committee of correspondence
This committee was made to communicate with the other colonies.
Sons of Liberty
Was organized by Samuel Adams to protest the Stamp Act
Intolerable Acts
Were designed to make an example of Massachusetts and hopefully stop the growing resistance to British authority.
Daughters of Liberty
Organized by the women of Boston and we're instrumental in maintaining the American boycott of British goods.
Common sense
Was published by Thomas Paine in January 1776. This short work helped to persuade many who were undecided to support the cause of independence.
Colony
A territory owned and run by another country.
King George III
King of England during the American Revolution.

Stamp Act (1765)
British tax in America on wills, licences and other documents

No Taxation without Representation
Slogan shouted by Americans angry at the British as they had to pay tax but had no say in how the country was run.
Townshend Acts
British taxes in America on items such as glass, paint & paper.

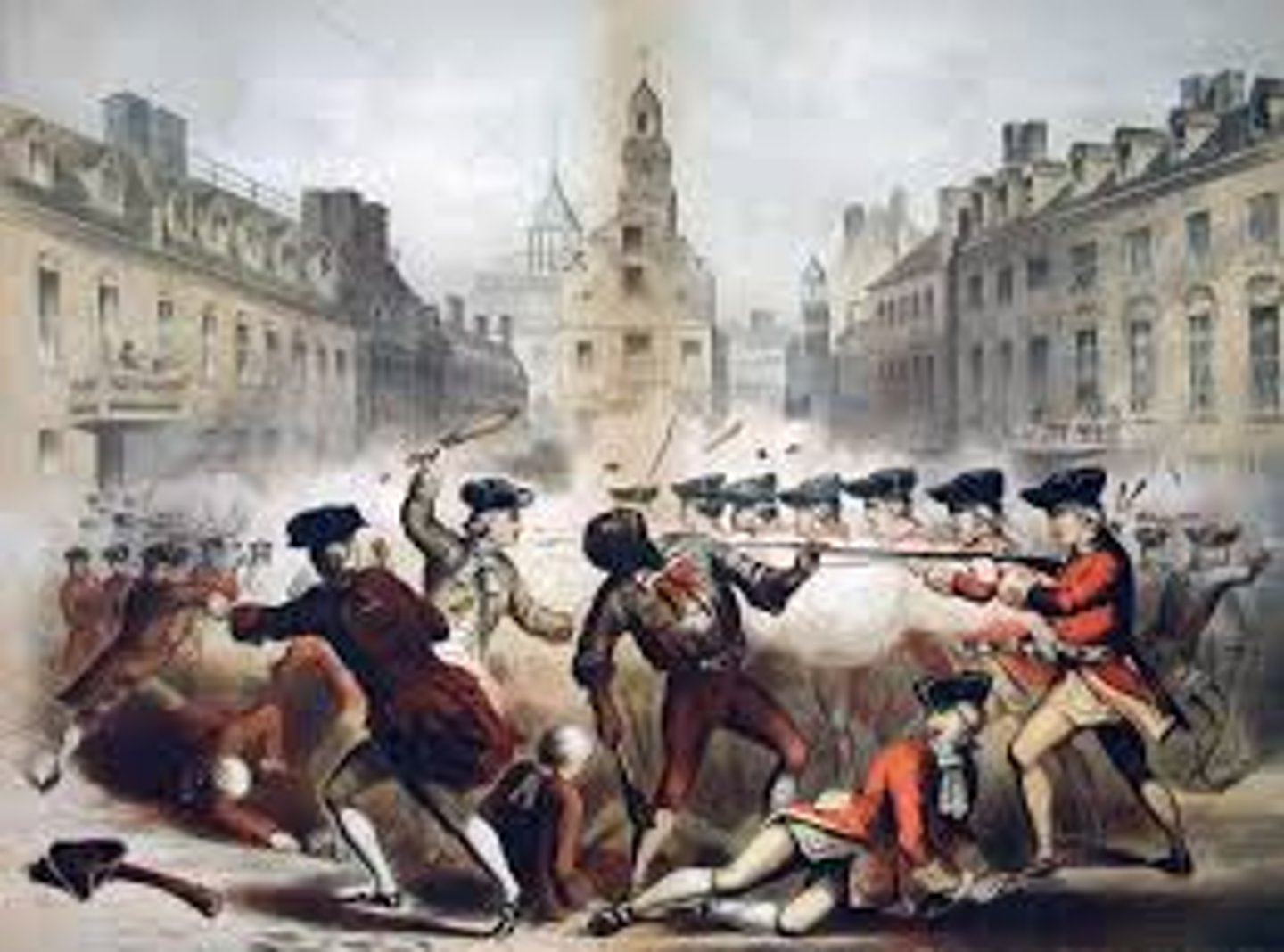
Boston Massacre
The shooting dead of 5 Americans protesting against British taxes.

Tea Act
British law that made American companies pay tax on tea but not British ones.

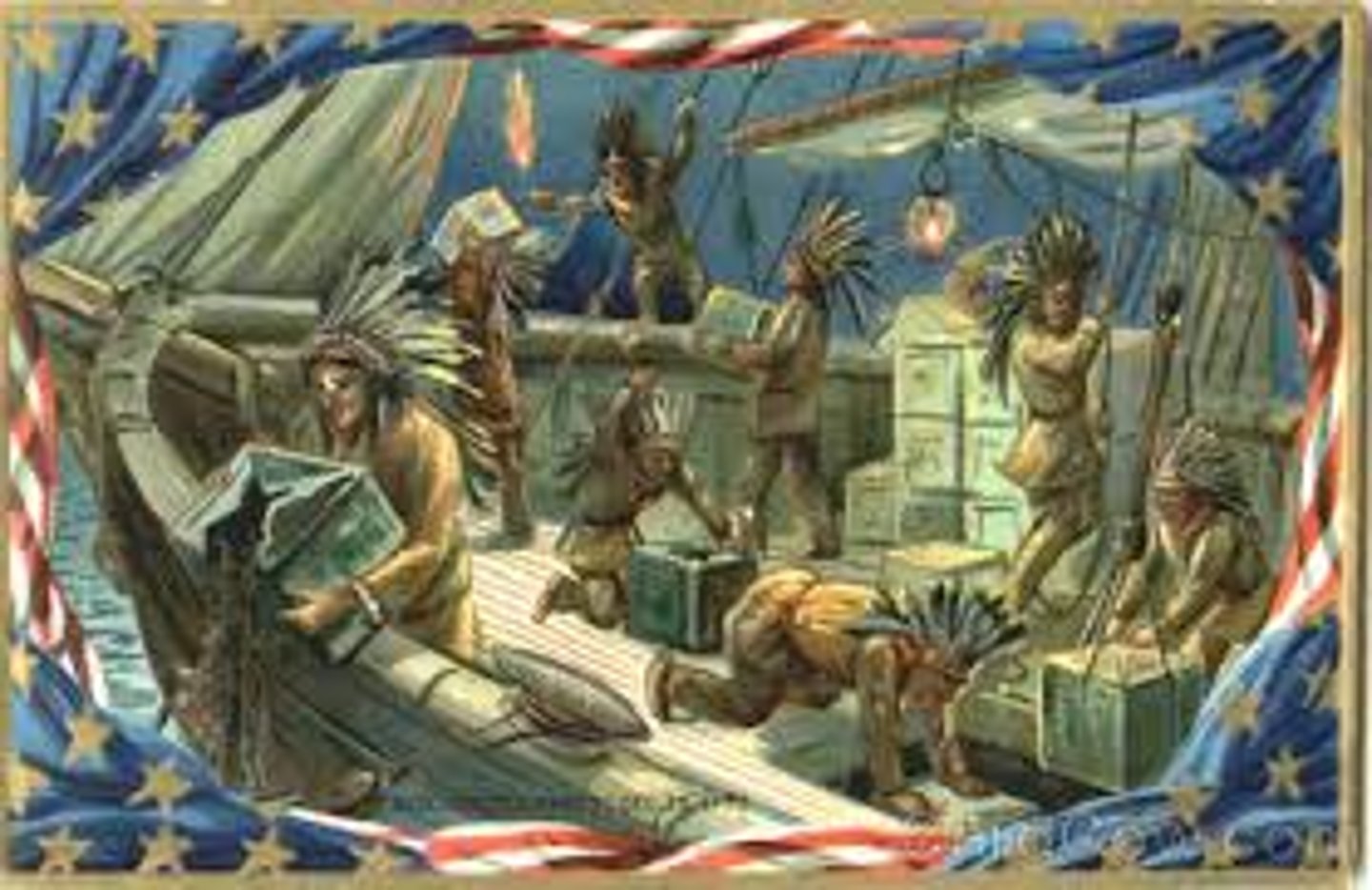
Boston Tea Party
Protest by Americans in 1773 whereby they threw tea from British ships into the sea.

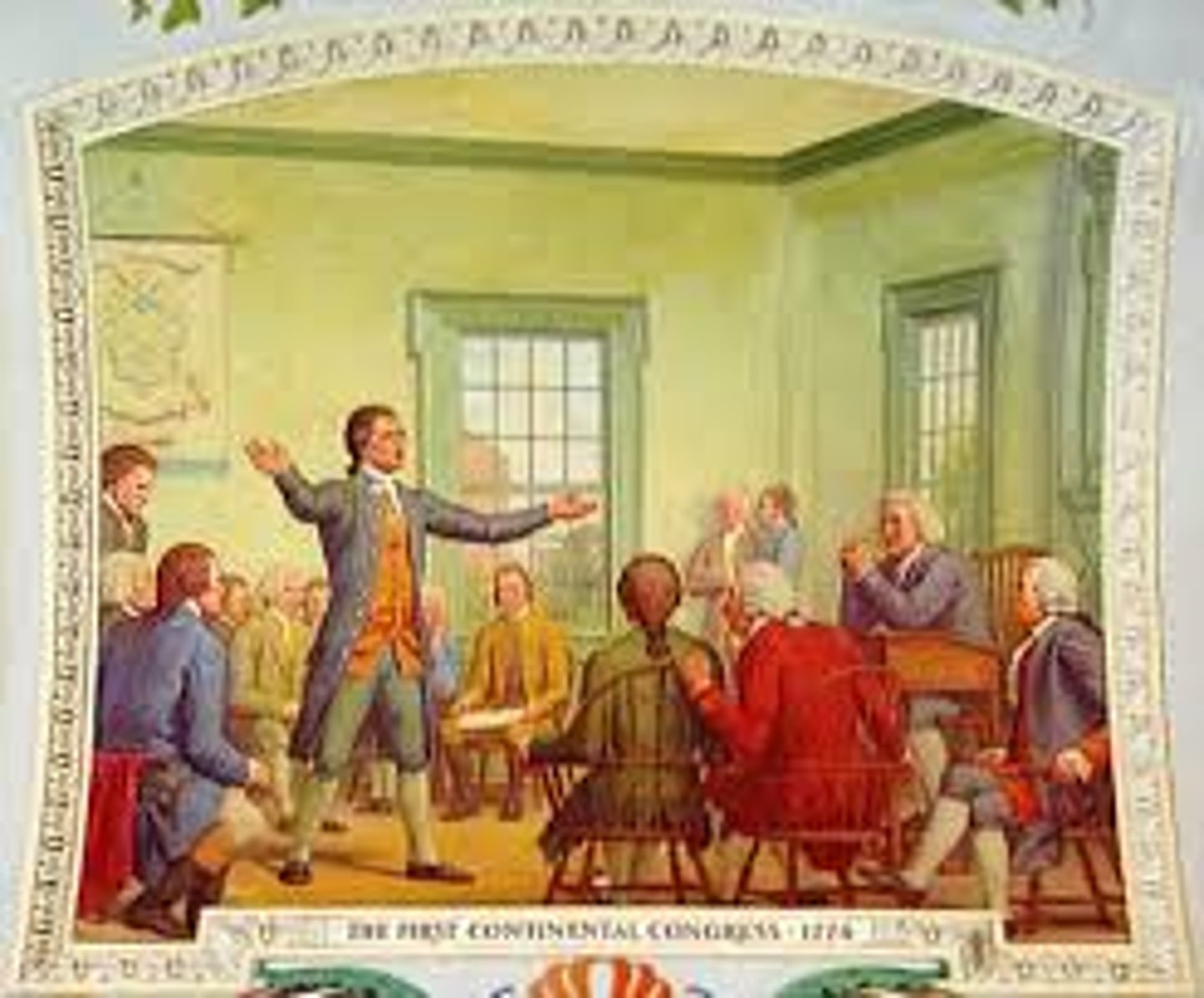
First Continental Congress (1774)
Meeting of the 13 American colonies to discuss how they would deal with the British.

Second Continental Congress (1775)
Second meeting of the 13 American colonies where their army was created.
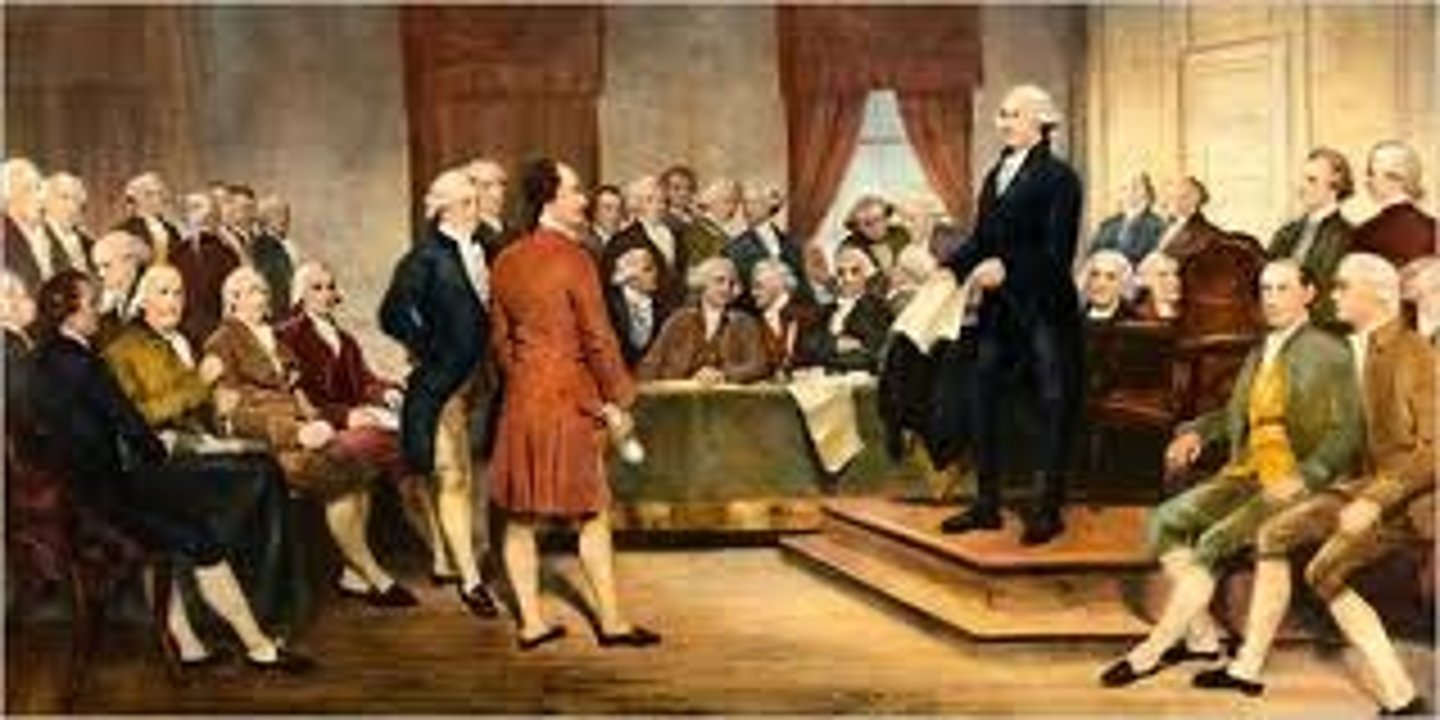

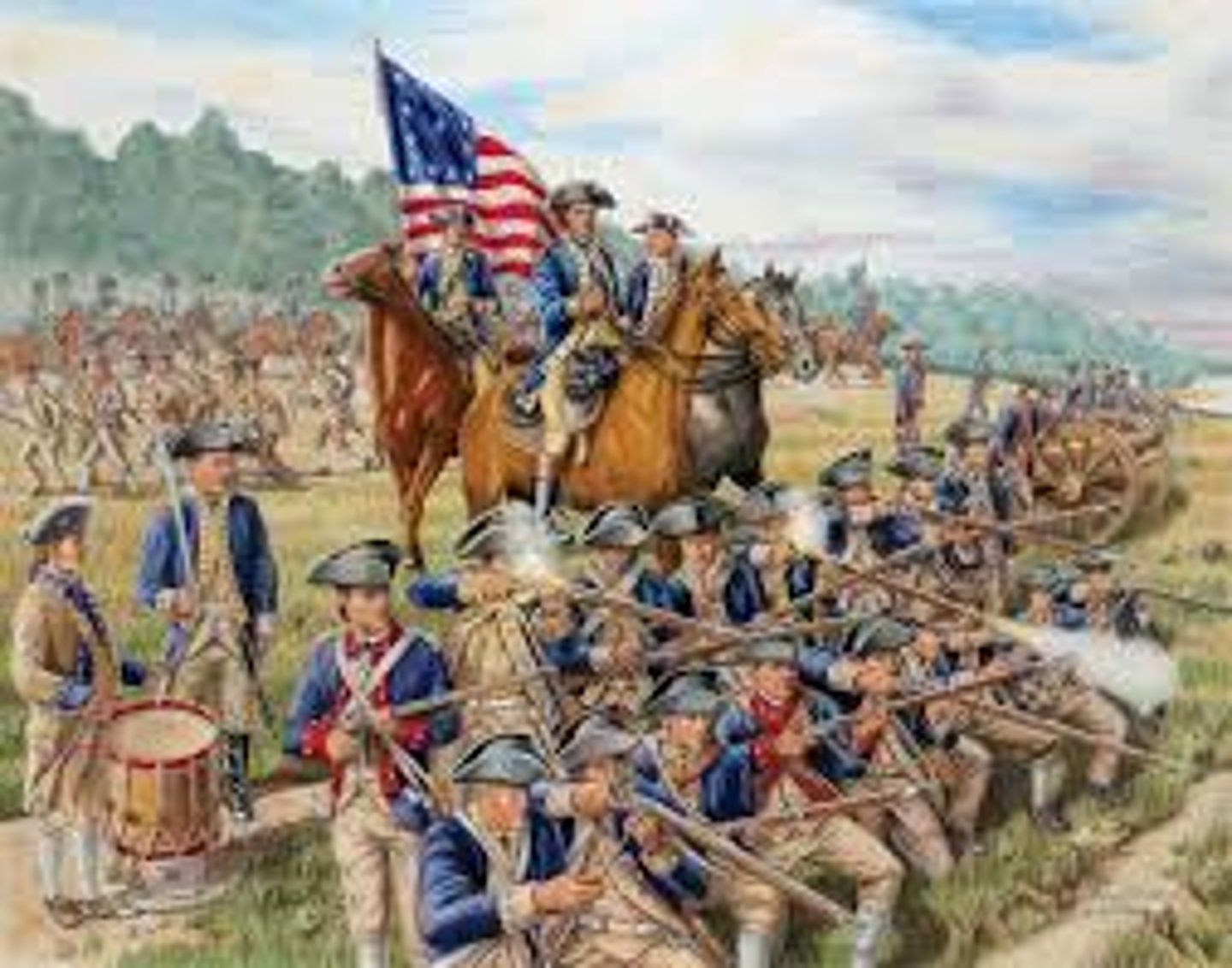
American Continental Army
Army of the American colonists led by George Washington who fought the British.

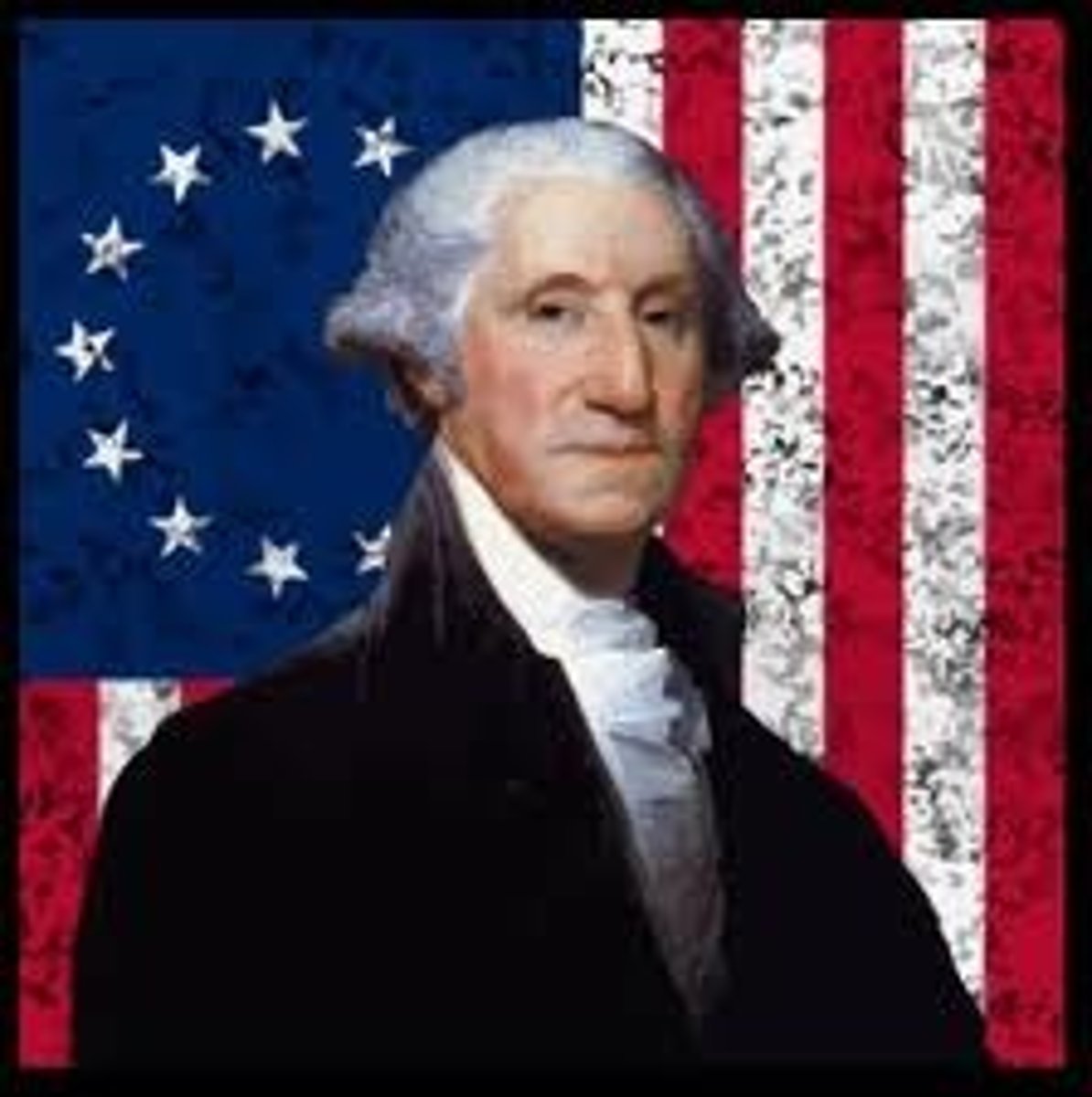
George Washington
Commander of the American Continental Army and first president of the USA.

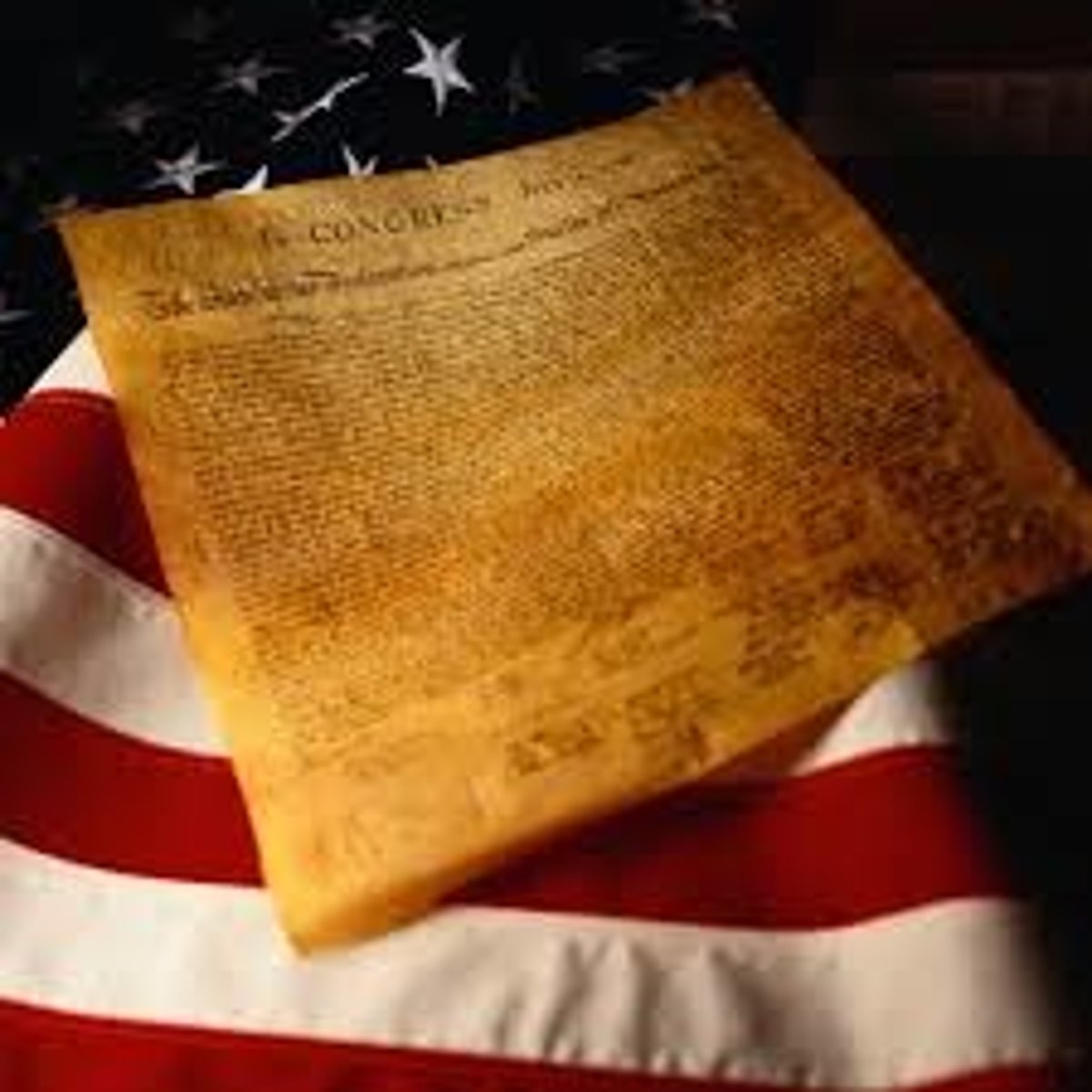
Declaration of Independence
Document in which the Americans set out their beliefs and aims for independence.

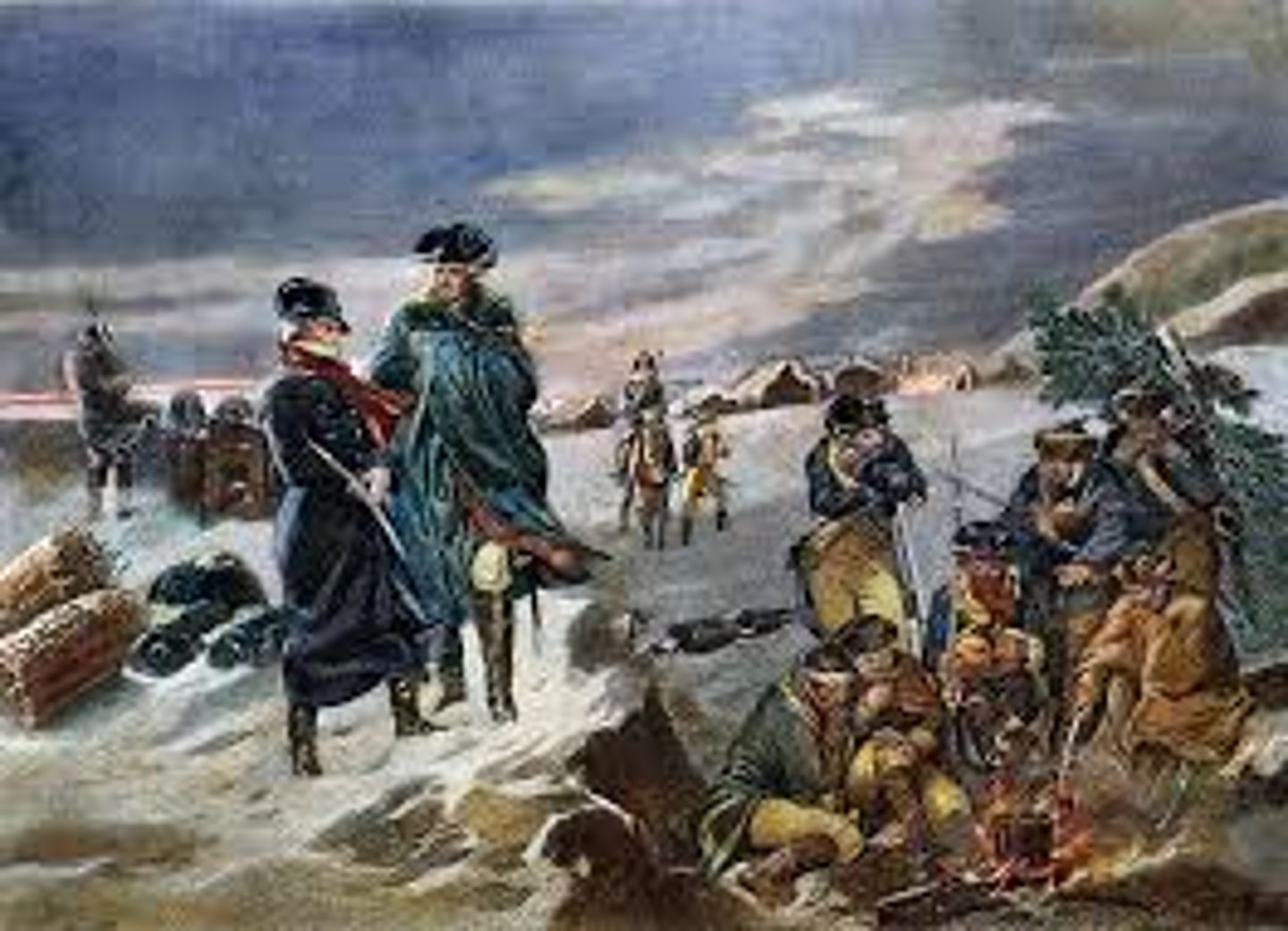
Valley Forge
American army camp where many soldiers died from the freezing weather and lack of supplies.

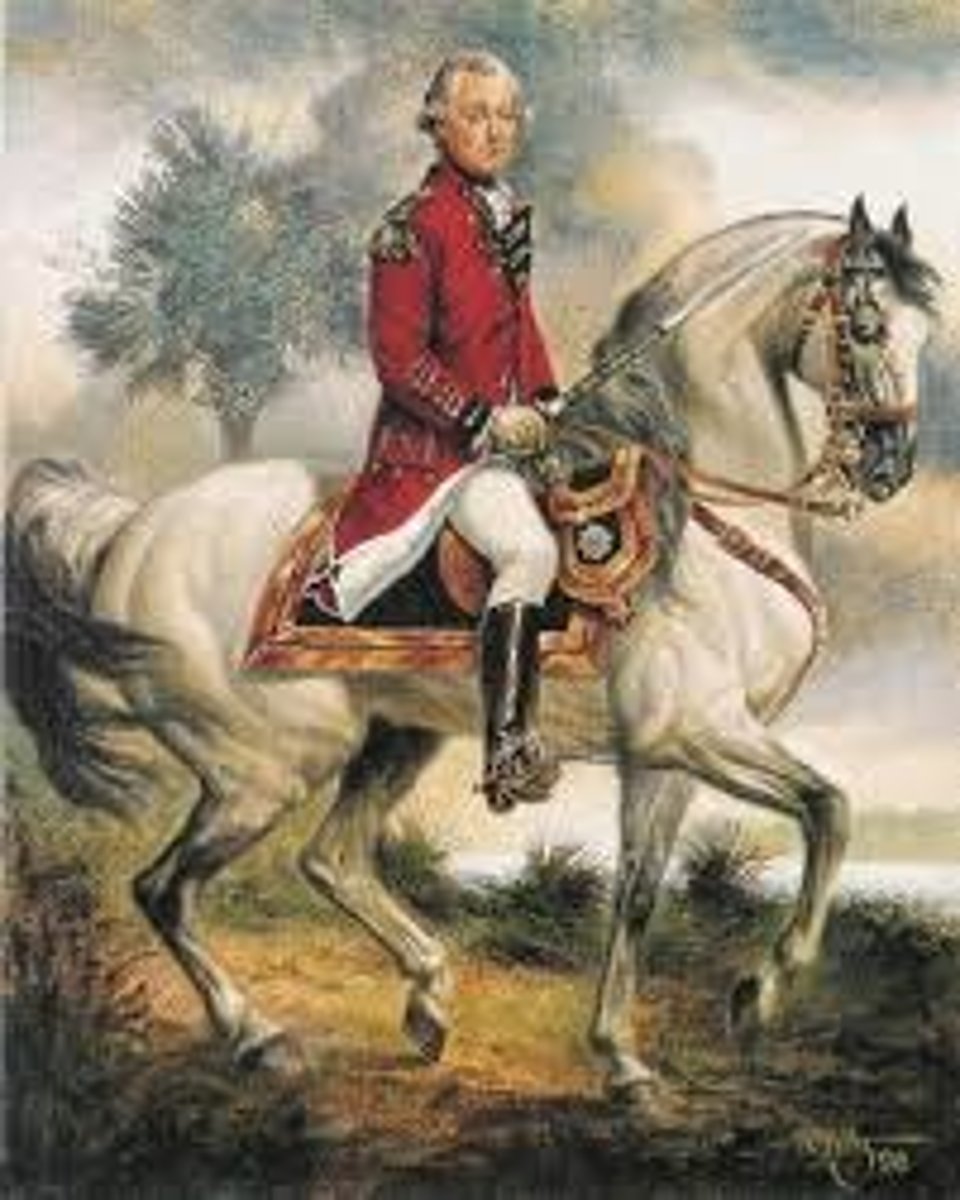
General Cornwallis
Commander of the British army.

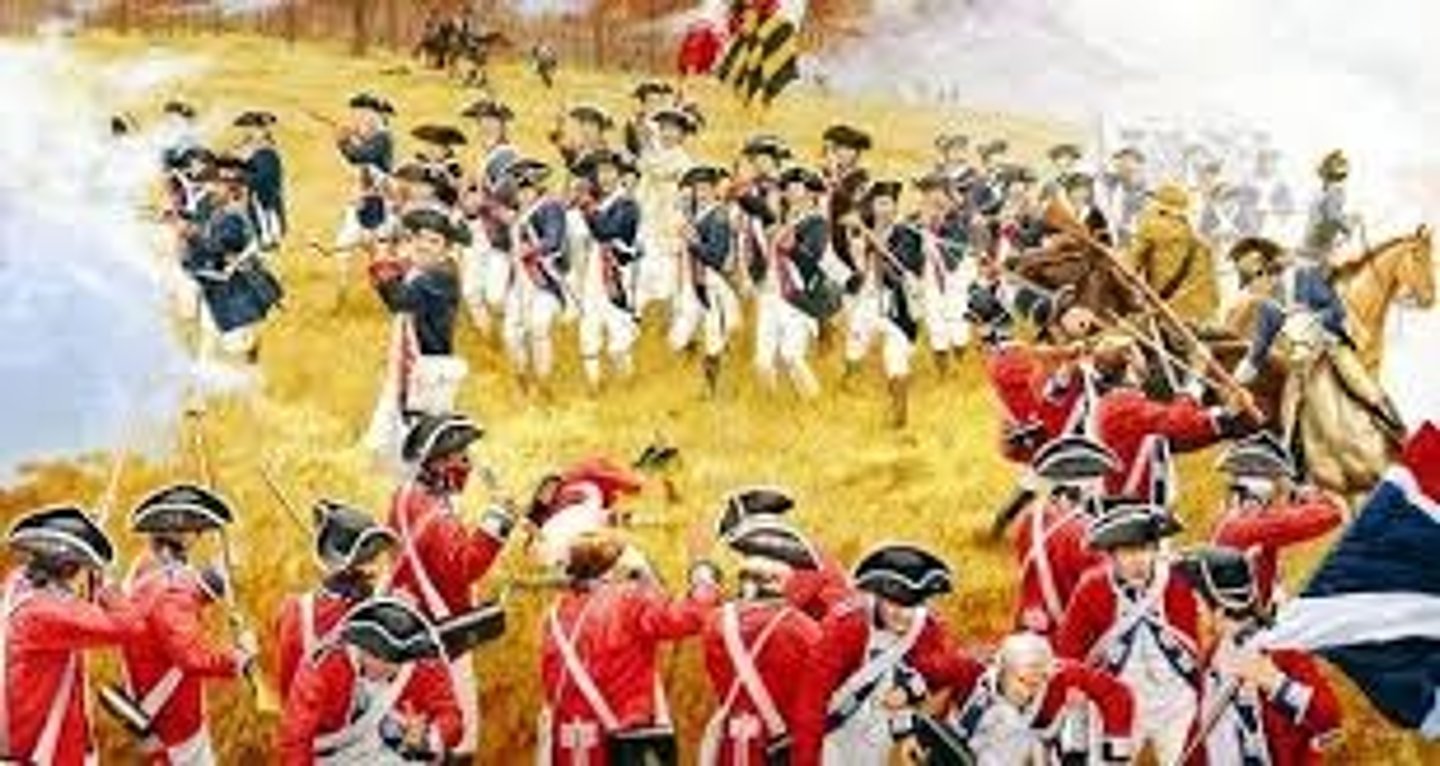
Yorktown
Last battle of the war of independence in 1789 where the British surrendered.

War of Independence (1775-1783)
War fought by American colonists for independence from Britain.

Was does repeal mean?
To take away, remove
Tax on various household items such as paper, glass, lead, silk, and tea.
Townshend Acts
Colonists had to provide food, housing, blankets, candles, etc. for the British soldiers.
Quartering Acts
Colonists did not feel they should be paying taxes to a government that was not hearing their voice. This is called?
No taxation without representation
A rioting mob confronted British soldiers at the Boston Customs House this becomes the?
Boston Massacre
Stamp Act of 1765
This tax was collected on every document or newspaper printed or used in the colonies.
Committee of correspondence
This committee was made to communicate with the other colonies.
Stamp Act Congress
This was created to draft formal petitions of protest to parliament.
Sons of Liberty
Was organized by Samuel Adams to protest the law.
Intolerable Acts
Were designed to make an example of Massachusetts and hopefully quell the growing resistance throughout to British authority.
Daughters of Liberty
Organized by the women of Boston and we're instrumental in maintaining the American boycott of British goods.
Common sense
Was published by Thomas Paine in January 1776. This short work helped to persuade many who were undecided to support the cause of independence.