Week 3: Economic Inequality and Labour
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Economic Inequality
The unequal distribution of income, wealth, or access to resources.
Labor
The work performed in exchange for wages; includes both paid and unpaid labor.
Evolution of Labour in Capitalism
The transition from feudalism to capitalism where peasants become wage workers and land becomes property.
Industrial capitalism
The rise of the factory system, urban migration, and deskilling of labor.
Colonial labor regimes
Systems involving forced labor, slavery, and indentured servitude.
Income vs. Wealth Inequality
A comparison of income distribution between the top 1% and the bottom 50%.
Labor precarity
Conditions characterized by gig economy, zero-hour contracts, and informal work.
Decline in union membership
A reduction in collective bargaining power among workers.
Gender and racialized labor
Issues related to pay gaps and occupational segregation based on gender and race.
Reproductive labor
Care work that is often undervalued and unpaid.
Historical labour movements
19th-century trade unions, WWI, socialist and anarchist movements.
Trade union
A continuous association of wage earners for the purpose of maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment.
Strikes and labor legislation
Actions and laws aimed at improving labor conditions, such as the 8-hour day and minimum wage laws.
Contemporary organizing
Current efforts to unionize, such as Amazon and Starbucks union drives.
Global South labour movements
Labor movements in developing countries, exemplified by garment workers in Bangladesh.
Labour as exploitation
The concept that labor is both a site of exploitation and potential for collective power.
Adam Smith's theory
The market is a self-regulated system capable of achieving equilibrium on its own without major deviations, known as the 'invisible hand'.
Malthusian Theory
The idea that population growth will outpace food production, leading to famine, disease, and war unless controlled.
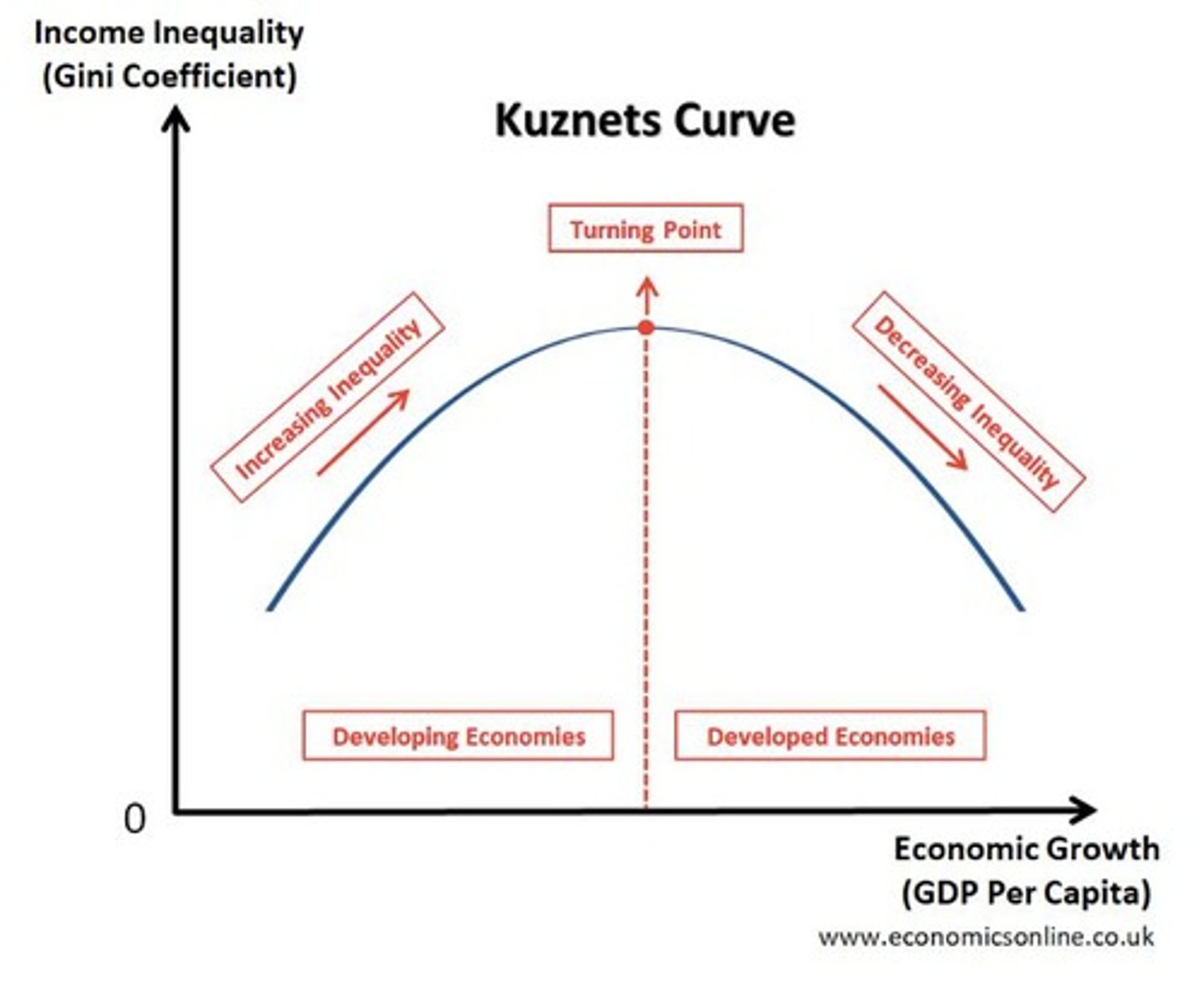
Kuznets Curve
A hypothesis suggesting that as an economy develops, income inequality first increases and then decreases, forming an inverted U-shape.
Marxism
The belief that capitalism is inherently exploitative, leading to an inevitable revolution by the proletariat against the bourgeoisie.
Ricardo's theory
The assertion that scarcity of resources like land increases their price, leading to greater inequality as landowners claim more national income.
Piketty's Key Formula: r > g
The formula where r is the rate of return on capital and g is the rate of economic growth, indicating that when r > g, wealth accumulates faster than economic growth.
Example of Piketty's formula
On every $100 of capital invested, receiving $10 in return results in a rate of return of 10%.
Increasing inequality
Occurs when the rate of return on capital (r) exceeds the rate of economic growth (g).
Patrimonial Capitalism
A system where inherited wealth dominates economic power.
Inequality of Capital Ownership
The disparity in ownership of capital assets, which is more extreme than income inequality.
Progressive Taxation
A tax system where the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases, often proposed as a solution to economic inequality.
Wealth Taxes
Taxes levied on the value of owned assets, aimed at reducing inequality.
Global Cooperation
Collaboration between countries to address global issues such as inequality.
Meritocracy
A social system where success is based on individual merit, which can be undermined by rising inequality.
Democracy
A system of government where the population exercises power, which can be threatened by economic inequality.
Social Dynamics of Wealth
The interactions and relationships influenced by wealth and inheritance, illustrated through literature.
Contemporary Examples of Inequality
Modern instances that demonstrate how economic inequality can undermine democratic institutions.
Upward Mobility
The ability of individuals or families to improve their economic status, often challenged within a capitalist system.
Parasite
A film that explores the relationship between wealth and space, and critiques class disparities.
Recurring Symbols in Parasite
Objects like the scholar's rock, stairs, and rain that deepen the film's critique of class.
Genre Blending in Parasite
The combination of comedy, thriller, and drama to comment on social issues.
Visual Composition in Parasite
The use of cinematography to reinforce the divide between the wealthy and the poor.
Ethical Questions Raised by Parasite
Moral dilemmas regarding labor, deception, and survival in a stratified society.
Cultural Resonance of Parasite
Themes in the film that reflect South Korean society while also having global significance.
Significance of the Film's Ending
The conclusion of Parasite, which can be interpreted as either hopeful or despairing.
Narrative Structure of Parasite
The arrangement of the film's plot, including twists and tonal shifts, that impacts its message.
Kim Family's Actions
The justifiability of the Kim family's behavior given their socio-economic circumstances.
Good and Bad People in Parasite
The film's complexity in portraying characters as neither purely good nor bad.
Real Parasite in the Film
The exploration of who or what truly represents parasitism within the narrative.