BIO MASTER (3)
1/283
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
284 Terms
sticky wicky
cohesion, adhesion
cohesion/adhesion importance
surface tension, capillary action
capillary action
transport fluid through plants and body
not so hot
high specific heat
specific heat capacity importance
maintain homeostasis, climate temp is regulated
floats when frozen
ice floats
ice floating importance
bodies of water don’t freeze solid
dissolves a lot
universal polar solvent
solvent importance
solutes can dissolve and be transported easily
cohesion
water sticks to water thru polarity and h bonds
surface tension
how difficult it is to break the surface of a liquid
adhesion
water sticks to other charged molecules
capillary action
water moving up small tubes via adhesion
transpiration
evaporative water loss from a plant
hydrophobic
non-charged, nonpolar, substance repels water
hydrophillic
charged, polar, attracts water via adhesion
high specific heat
takes lot of energy to heat water, have to break h bonds
water has high boiling point
can absorb/release large amt of energy w/ little temp change
solid water less dense than liquid
h bonds cause frozen molecules to space out
water freezes at top
life exists under ice layer
solution
liquid homogenous mixture of substances
solvent
dissolving agent, liquid
solute
substance being dissolved, solid
hydration shell
sphere of water molecules around polar ions due to polarity
monomer
small building blocks
polymers
2+ monomers linked
carb monomer
monosaccharide, glucose
carb polymer
carbohydrate, disaccharide
fat polymer
lipids
protein monomer
amino acid, peptide
protein polymer
protein, polypeptide
nucleic acid monomer
nucleotide
nucleic acid polymer
DNA, RNA
dehydration synthesis
join monomers, water is released
hydrolysis
break monomers apart, water is added
carbs function
energy, storage, structure, genes
carbs energy
cellular respiration
carb storage
glycogen, starch
carb structure
chitin, cellulose
carb genes
deoxyribose, ribose
monosaccharides
1 carbon ring (fructose, glucose, galactose)
carbon ring
C6H12O6
disaccharides
2 carbon rings (lactose, sucrose, maltose)
oligosaccharides
3-9 carbon rings, found on cell membranes
polysaccharides
10+ carbon rings (glycogen, cellulose, amylose)
lipid properties
nonpolar, hydrophobic
lipid types
triglycerides, steroids, waxes, phospholipids
triglycerides structure
3 fatty acids bonded to glycerol
triglyceride function
long term energy, insulation, cushioning
saturated fat
no double bond, saturated w/ H, straight chain, solid at room temp, animal based
unsaturated fats
carbon double bond, kinks in chain, liquid at room temp, plant based
trans fats
hydrogenated unsat fats, solid at room temp, unhealthy
phospholipid stucture
phosphate, glycerol, 1 sat fat tail, 1 unsat fat tail
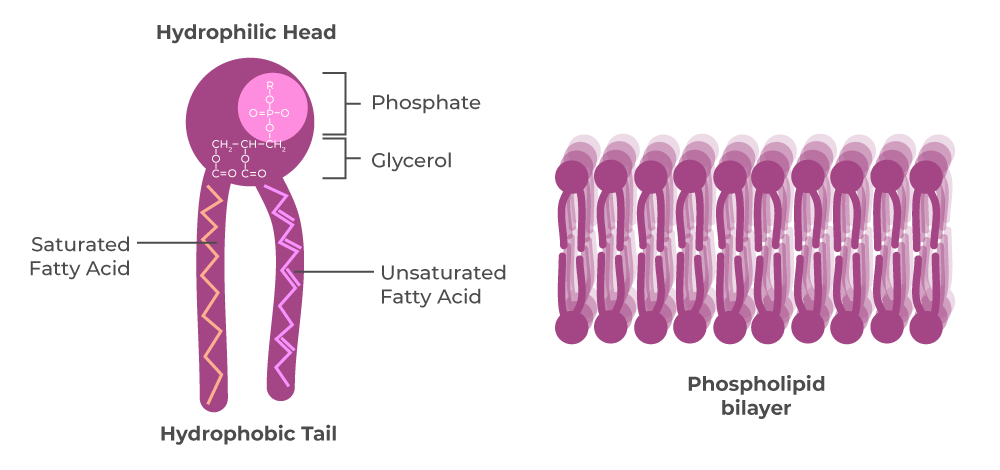
phospholipid function
phospholipid bilayer semipermeable membrane, hydrophillic heads/hydrophobic tails
steroid structure
4-5 carbon rings, hydrophobic
steroid function
metabolism, immune response, sex hormones
wax structure
fatty acid w/ alcohol
wax function
prevent water loss
protein function
enzyme, structure, carriers, communication, defense, movement
enzyme
speed up chemical reaction (DNA polymerase)
structure
keratin, collagen
carriers/transporters
hemoglobin
cell communication
receptors, signals (insulin, hormones)
defense
antibodies
movement
actin, myosin
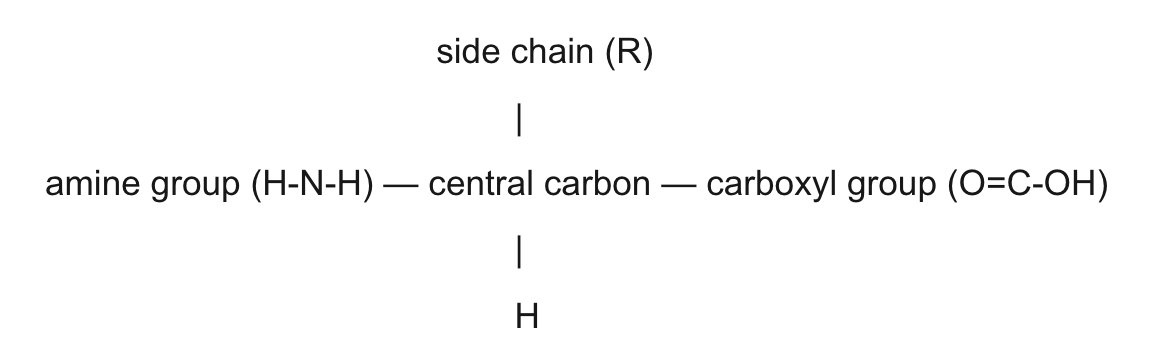
amino acid structure
central carbon, r side chain, carboxyl, amine, H
amino acid table
20 amino acids (64 possible combos)
polypeptides
aa bonds thru dehydration synthesis
peptide bond
covalent bond found in proteins
side chain types
nonpolar, polar, charged
nonpolar side chain
hydrophobic, lots of CH
polar side chain
hydrophilic, OH & N, bond with each other or water
charged side chain
hydrophilic, acidic: negatively charged H+ donors, basic: positively charged H+ acceptors
primary structure
order of amino acids in chain, single change has big effects
primary structure stabilizer
peptide bonds
secondary structure
local folding into alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
secondary structure stabilizer
H bonds with carboxyl and amine
tertiary structure
interactions btw distant AAs, 3D shapes, nonpolar cluster inwards
tertiary structure stabilizers
h binds, ionic bonds, disulphide bridges
quaternary structure
more than 1 polypeptide chain bonded together
protein denaturation
unfolding due to disruptions in H and ionic bonds (pH, temp, salinity), destroys functionality
nucleic acid function
code for amino acid sequence in proteins
nucleotide structure
pentose sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base
DNA structure
deoxyribose sugar, double helix, ATCG
RNA structure
ribose sugar, single strand, AUCG
pyramidine
single ring
purine
double rings
Adenine
purine, 2 bonds
thymine
pyramidine, 2 bonds
guanine
purine, 3 bonds
cytosine
pyrimidine, 3 bonds
antiparallel
strands run in opposite directions due to h bond structure
5’
top carbon in deoxyribose joined to P group
3’
bottom of sugar
evolution
change in genetic composition of a population from generation to generation
darwin’s observations
populations have varying traits
traits are heritable
not all offspring survive into adulthood due to limited resources
darwin’s conclusion
individuals with traits advantageous in survival and reproduction are able to have more offspring, leading to the accumulation of advantageous traits in future generations
adaptation
inherited characteristic that enhances survival/reproduction in specific environments
coevolution
reciprocal evolution between interacting species
macroevolution
big evolutionary changes over long periods of time; above species