MCAT Official Prep Hub - Section Bank, Vol. 1 > Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
passage 7 52-57
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Passage 7 (Questions 52-57)
Two students performed an assay to determine the concentration of lactase in a commercial preparation used to make milk consumable by those who are lactose intolerant. Lactase catalyzes the cleavage of lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-1→4-D-glucose) into β-D-galactose and D-glucose. A glutamate residue (Glu-1) in the active site donates a proton to an oxygen atom. Another glutamate on the opposite axial side (Glu-2) acts as a nucleophile to liberate D-glucose and generate an α-D-galactopyranosyl-modified enzyme intermediate. Then, Glu-1 deprotonates water, and the resulting hydroxide ion acts as a nucleophile to liberate β-D-galactose and regenerate the enzyme.
Rather than use lactose as a substrate, which is difficult to quantify spectroscopically, the students chose Compound 1, which produces β-D-galactose and yellow Compound 2 under the action of lactase (Reaction 1)
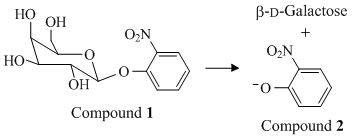
Reaction 1
The students prepared stock solutions of Compound 1 in four different concentrations in pH 7 buffer. A stock solution of the enzyme was prepared by diluting 0.100 mL of the commercial preparation to 25.0 mL in the buffer solution. Experiments were initiated by mixing 1.0 mL of each substrate solution with 1.0 mL of the enzyme solution. The initial rates Vo were measured for each trial. The students then plotted 1/Vo versus 1/[S] (Figure 1) to determine KM, Vmax, and [E]T for the four trials.
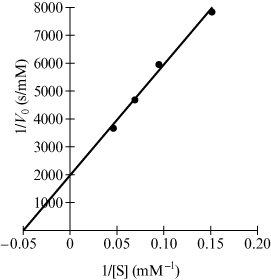
Figure 1 | Plot of 1/Vo versus 1/[S] |
null
Which experimental technique was most likely used by the students to determine the rate of reaction?
A
Monitor the increase in absorbance of the solutions at 200 nm.
B
Monitor the increase in absorbance of the solutions at 360 nm.
C
Monitor the decrease in absorbance of the solutions at 200 nm.
D
Monitor the decrease in absorbance of the solutions at 360 nm.
Solution: The correct answer is B.
This is a General Chemistry question that falls under the content category “How light and sound interact with matter.” The answer to this question is B since the experiment describes that the substrate was chosen based on the fact that it produced a yellow colored product, Compound 2. The complementary color to yellow is purple, which is 360 nm. It is a Reasoning about the Design and Execution of Research question because you are asked to reason about the appropriateness of particular research designs.
ic chose a as my intial answer think of roygbv belived the specturm started from at 400 nm to 600 and made a guess of where the wavellength would fall should have slected 360 as it is ckllsoer to the start of the spectrum
The question says the compound is yellow, meaning it reflects yellow light. When you draw the color wheel you'll see its complementary color is violet, meaning that the wavelength of light must be the highest energy, so the shortest wavelength of the visible color spectrum.
ROYGBIV is great because it gives you the order of the color wheel and the order of decreasing wavelength (red=700nm, violet=360nm). Knowing this general trend should suffice to answer the AAMC's questions, but they are full of surprises so who knows.
Just dropping this here for anyone who comes across it later:
The passage says Compound 1 produces β-D-galactose and yellow Compound 2. That’s key.
More product = more absorbance, so eliminate C & D (which mentions a decrease).
A is at 200 nm, which is deep UV - outside of Visible light. (Remember 700nm - ROYGBIV - 400nm)
So the correct answer is B.

Based on the description provided, if lactose was hydrolyzed under the action of lactase in O-18 labeled water, in which location(s) would the label appear?
A
Neither the galactose nor the glucose products
B
The glucose product only
C
The galactose product only
D
Both the galactose and the glucose products
Solution: The correct answer is C.
This is an Organic Chemistry question that falls under the content category “Structure, function, and reactivity of biologically-relevant molecules.” The answer to this question is C. The cleavage reaction described is a hydrolysis of the glycoside linkage in a disaccharide. In this case, the deprotonated water attacks the galactose and so this sugar will be labeled with O-18. The glucose is protonated and acts a leaving group without reacting with an oxygen atom provided by water. It is a Scientific Reasoning and Problem Solving question because you are asked to bring together theory, evidence, and observations to draw a conclusion.
o glucose product was already liberated before the reaction with O-18 labeled water. Galactose was only one to be substituted with O-18 labeled water because enzyme is always said to be unchanged/unconsumed or reverted back to same original enzyme structure!!!
Yeah I think that's right!! We're told that the D-glucose is released and the enzyme intermediate remains bound to almost-galactose. The almost-galactose is only released once the (labelled) OH attacks and turns it into completely liberated galactose, so the glucose is uninvolved in the use of water.
For what mechanistic reason does G1 of lactase first act as a Brønsted acid during catalysis?
A
G1 becomes a better nucleophile.
B
G2 becomes a better nucleophile.
C
Glucose becomes a better leaving group.
D
Galactose becomes a better leaving group.
Solution: The correct answer is C.
This is an Organic Chemistry question that falls under the content category “Structure, function, and reactivity of biologically-relevant molecules.” The answer to this question is C. Protonation of the oxygen atom in glucose makes this substance a better leaving group in much the same way that protonation of an alcohol facilitates substitution of an –OH group. It is a Scientific Reasoning and Problem Solving question because you are asked to bring together theory, evidence, and observations to draw a conclusion.
That is, whereas a nucleophile is the Lewis base that forms a new bond with a carbon, the leaving group is the Lewis base that results after breaking a bond with the carbon.
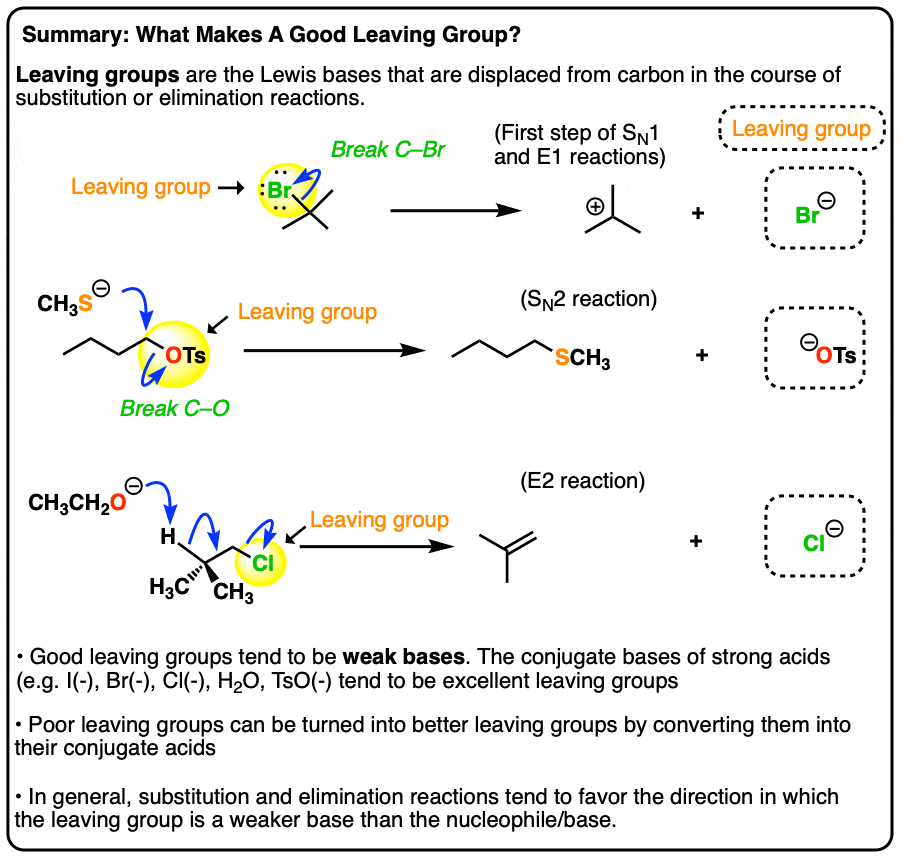
What is the KM of Compound 1 with respect to lactase?
A
0.05 mM
B
0.10 mM
C
5 mM
D
20 mM
Solution: The correct answer is D.
Solution: The correct answer is D.
This is a Biochemistry question that falls under the content category “Principles of chemical thermodynamics and kinetics.” The answer to this question is D because the value of 1/[S] when 1/Vo is zero (the x-intercept of the Lineweaver–Burk plot) is –1/KM and so KM = –(–1/0.05 mM–1) = 20 mM. It is a Data-based and Statistical Reasoning question because you are asked to analyze and interpret data presented within the context of an experiment to arrive at the conclusion.
What method did the students use to calculate Vmax?
A
Vmax was calculated as KM × kcat.
B
Vmax was determined as the fastest initial rate of Compound 2 formation obtained during the kinetics experiments from the passage.
C
Vmax was calculated as [S] × kcat for the trial with the highest substrate concentration.
D
Vmax was determined as the inverse of the y-intercept of the graph shown in Figure 1.
Solution: The correct answer is D.
This is a Biochemistry question that falls under the content category “Principles of chemical thermodynamics and kinetics.” The answer to this question is D since the plot shown in Figure 1 is derived from the inverse of the Michaelis–Menton equation Vo = (Vmax[S])/(KM + [S]). It is a Reasoning about the Design and Execution of Research question because you are asked to reason about the features of a research study that suggest relationships between the variables.
If [E]T was the concentration of lactase in the kinetics trials, what expression gives the concentration of lactase in the commercial preparation of this enzyme?
A
[E]T × 25
B
[E]T × 50
C
[E]T × 200
D
[E]T × 500
Solution: The correct answer is D.
This is a General Chemistry question that falls under the content category “Unique nature of water and its solutions.” The answer to this question is D because the commercial preparation was first diluted by 1 → 250 to prepare the stock solution, and it was further diluted by 1 → 2 by mixing with the substrate stock solution to perform the kinetics experiments. It is a Scientific Reasoning and Problem Solving question because you are asked to bring together theory, evidence, and observations to draw a conclusion.
.1 mL into 25 mL is a 1:250 dilution (25 / 0.1 = 250). This is the dilution of making the buffer solution. In addition, the 1 mL of diluted buffer solution is mixed with 1 mL of enzyme solution. This is going to half the concentration again. So basically, you did a 1/250 dilution, then halved that diluted solution which gives you a 1/500 dilution. Question states that [E]t is the concentration of lactase in the kinetics trial (i.e. the extremely diluted solution, which is 500 times weaker than the commercial preparation). I will let you figure out the end part!
hink of it this way: you have one cup of lemonade but its extremely sour. You mix that 1 cup of lemonade with 1 cup water, and now its half as sour because you have 2 cups of diluted lemonade instead of 1 cup of concentrated lemonade. It is just 1 cup lemonade / 2 cups total solution, which reduces the sourness by half. Same approach with concentration