Organic Chemistry in Pharmacy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
physicochemical properties
How functional groups present on a molecule affect acid base properties
functional groups
chemically distinct groups of connected atoms which are important determinants of drug properties
Hydrophilic
water loving
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
lipophilic
fat loving
lipophobic
fat hating
optical activity
the ability of a chiral molecule to rotate plane-polarized light
Enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
electronic effects
how groups affect electronic environment within/between molecules
Solubility Effects
to what extent does the drug dissolve in aqueous or organic media?
steric effects
how does the size and shape of the molecule impact its in vivo activity
intermolecular interactions
interactions between molecules
intermolecular forces, strongest to weakest
ion-ion, ion-dipole, dipole-dipole (Hydrogen bonding apart of), van der waals
ion-ion
(+,-) very strong
ion-dipole
is an ion bonded with a polar molecule
dipole-dipole
between polar molecules
hydrogen bonds
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
van der Waals forces
a slight attraction that develops between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules
ADRs
adverse drug reactions
DIs
Drug interacts
between two or more drugs or drugs with food, beverages, or supplements
In vivo
occurring within the body
disposition
the measure of the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a chemical or substance
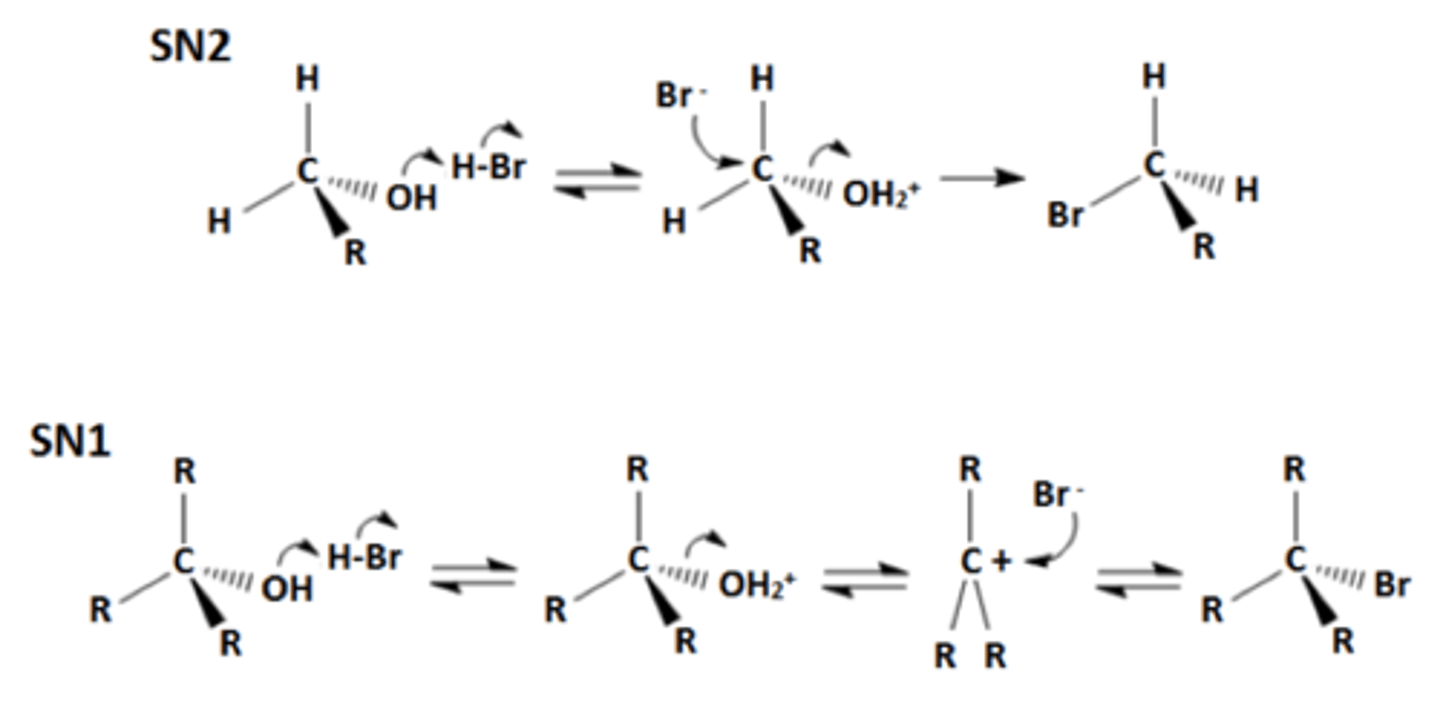
SN2
requires a strong nucleophile, adds antiperiplanar switching stereochemistry
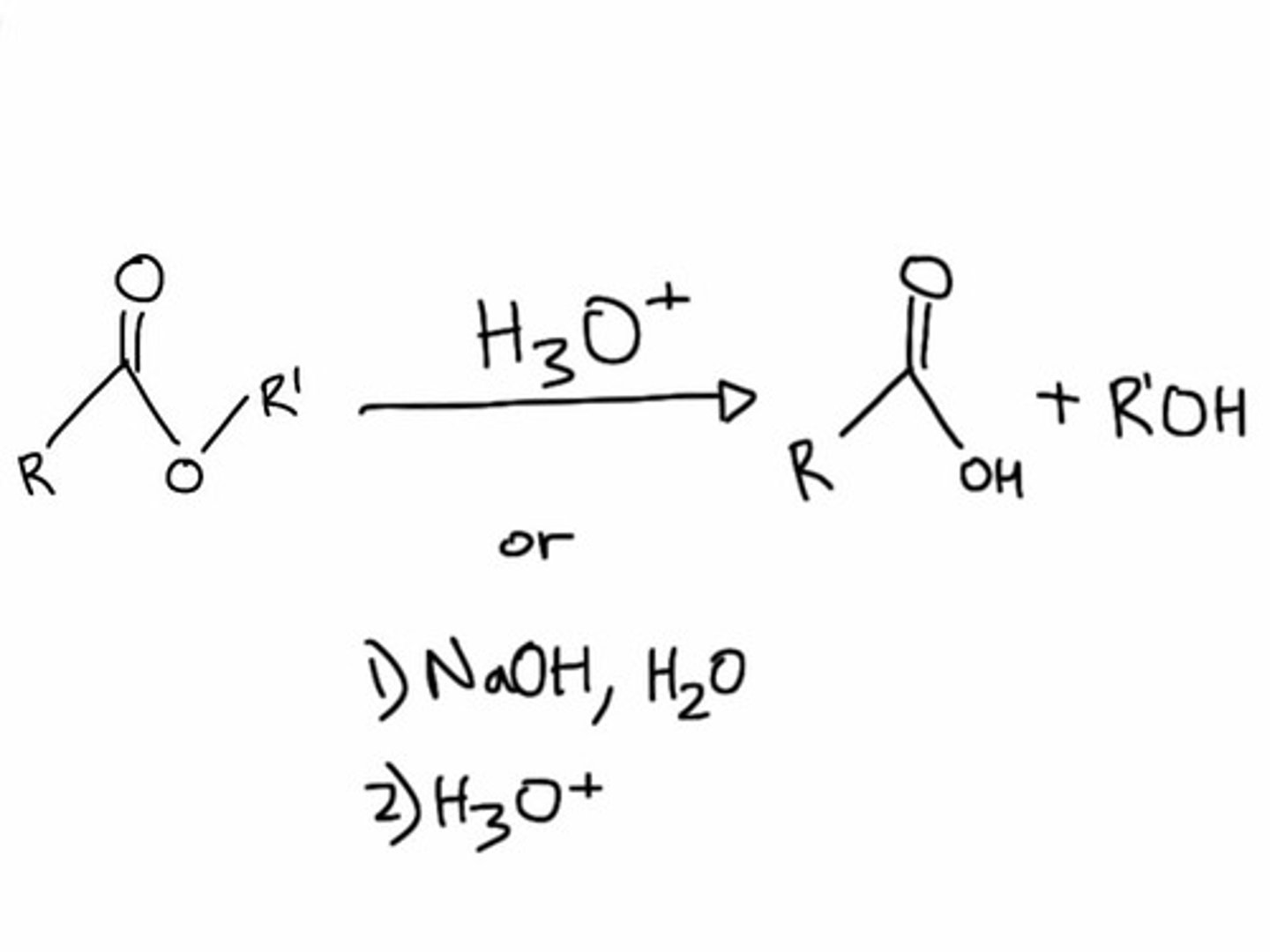
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
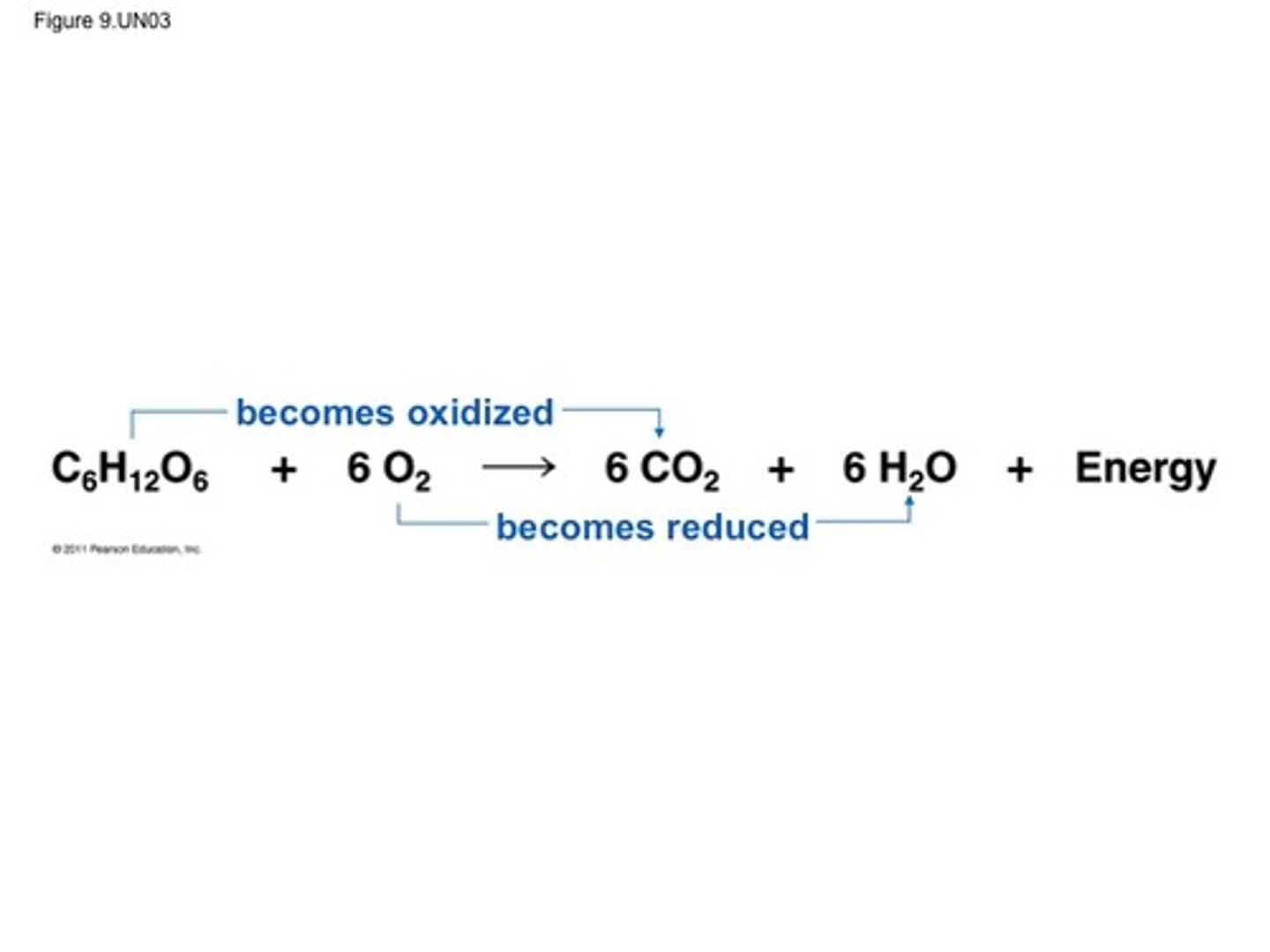
Oxidiation- reduction
is a reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one species to another
Conjugation
are overlapping P orbitals
Double bonds either cis or trans
Pharmacophore
essential functional groups of a drug
Which organic reactions occur in vivo and which cannot
nucleophilic addition can occur
Electrophilic aromatic substitution cannot occur
Organic oxidation/reduction reactions-- can occur
specifically when the agent is reduced
Pericyclic runs: cannot occur
What is the charged state for acidic groups based on pH?
Acidic groups become positive
What is the charge state for basic groups based on pH?
They become positive
What is the charge state for carboxylic groups based on pH?
Negative
What is the charged state for nitrogen heterocycles/amines based upon pH?
Become positive
What is the charged state for phenyls and amides based upon pH?
Neutral
In vivo reactions of drug
nuc addition
oxid/red (Mostyly esters)
SN2
Conjugation
How do drugs react in the body?
They react two ways
forming new bonds (covalent or ionic | Using pairs or single electrons)
breaking covalent bonds (Results in a again, loss, or split of electrons)
what should be taken into consideration when comparing drug FGs?
water/lipid solubility
mech of interactions (IMFs!!)
pharmacokinetics (ADME)
ADRs, DIs
suitability for specific therapeutic situation
what FG can provide the initial ionic bond to active site
carbox acid (loses H = polar = very reactive)
what FG can incorporate binding affinity by interactions w hydrophobic site
phenyl/aryl
non C or non H atom?
hetero atom
what are & describe the parts that a FG is generally composed of
heteroatoms (could include C or H too)
pharmacophore - essential FG
auxophore - nonessential group but enhance activity/modify kinetics
cyclic molecule that contains atoms other than C
aromatic heterocycle
any ring that contains N + ex of where found in vivo
nitrogen heterocycle, ie nucleic acids
benzyl vs phenyl/aryl (carbocycles differntiation)
benzyl = ring + —CH2—
phenyl = ring w any side chains
what is optical activity in a molecule an indication of
molecular asymmetry/ atom in molecule is chiral
why is it important to differentiate between drug enantiomers
each configuration may have different chemical activity
ie 1 config can be toxic like S-thalidomide
why cant a pure drug enantiomer be adminstered
may react in body = change chirality = become toxic form
more active/potent enantiomer of a drug is called..?
+ root names that indicate this property?
enantiopure drug
-ar-, -es-, dextro-, levo-
3 major determinants for pharmacology/FGs (PK & PD)
electronic effects
solubility effects
steric effects
rxns that occur in vivo
nuc addition, organic oxid/red, hydrolysis (mostly esters), substitions (SN2, conjugation)
why cant most chem rxns work in vivo
body is mostly water
org chem involves P orbital rxns = too high E & heat = no safe
what are the only possible mechanisms of action a drug can have in body to cause its effects
organic chem (mostly covalent) rxns OR most often, IMF interactinos
how do drugs react in vivo
form or break bonds, IMFs
2 main considerations when testing drug effects in vivo
stability - whether drug breakdown/react quickly
if stable (for secs, min, days), then what happens to drug? if unstable, then biotransforms = inactive = excreted
disposition - what happens to drug based on chem property
where stable drug ends up based on solubility (water, fat)
how determine protein stability
it depends (on amino acid, sterics, how adminstered)
why cant carbocation, carbcanion, acyl chloride exist in vivo
too reactive
Determine stability/deposition of glycine
glycine = amino acid = hydrophilic + stable, ionized in most tissues
Determine stability/deposition of pyrimidine
pyrimidine = N heterocycle in DNA = stable + hydrophilic
Determine stability/deposition of 3-hexanone
3-hexanone = stable + lipophilc
determine stability/deposition of ethyl propionate
common FGs on drugs
alcohol, ketone, aldehyde, carbox acid, amine/N-containing, halide
what rxn is common in liver
oxidation/reduction (ie -COOH → -CO)
amides = acid or base?
neither/neutral always bc has acidic & basic properties that cancel eachother out
strongest base?
OH-
how determine which drug will be most soluble in vivo
compare # of polar/nonpolar FGs
SAR?
structure-activity relationships
what can increase drug-receptor affinity
electronic effect - drug has electron donating group = inc polarity/reactivity
steric effect - smaller FG = easier rxn
solubility effect - more soluble in body bc more polar = more reactive = stronger affinity
what FG can be hydrolyzed in vivo
ester
affinity
strength of drug-receptor binding interaction
potency
dose/amount needed to produce effect from binding (comparison of ED50s of drugs that bind to same receptor)
ED50
dose of drug producing half the maximum response
efficacy
change that occurs as a result of drug binding to receptors (drugs ability to cause physiological change, relationship bw size/strength of response & occupancy of receptor)
rank most basic to least basic: amide, carbox acid, amine
amine, amide, carbox acid
a drug that binds a receptor with higher affinity will have a ____________? Kd than a drug that binds w lower affinity
smaller
what func group is charged at physiological pH
phosphate (DNA)