L38 Summary and understanding vaccine
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from the lecture on the immune system, including innate and adaptive immunity, autoimmune disease, immunodeficiency, antigen presentation, and vaccination.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Autoimmune Disease
Caused by loss of immune tolerance and infection as a trigger. Eg rheumatic arthiritis.
Immunodeficiency
A condition caused by genetics (e.g., SCID), infection (e.g., measles, HIV), environmental factors (e.g., malnutrition), or treatment (e.g., chemotherapy). Many causes.
Phagocyte Mobilization
The process where inflammation makes capillaries leaky, allowing neutrophils to squeeze out and enter tissue to phagocytose bacteria.
Neutrophils
Attracted to the site of infection by chemicals released from damaged/infected cells or leucocytes (especially macrophages) and phagocytose bacteria.
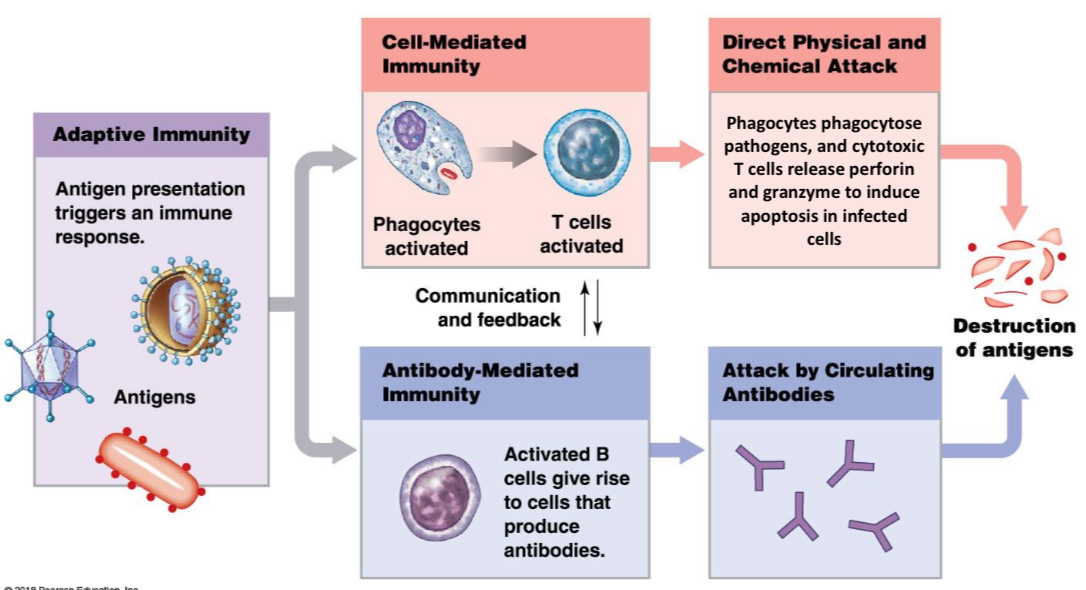
Adaptive Immunity summary
Usually a combination of cell mediated immunity and antibody mediated immunity. Eg. Optimal anti-viral immune responses require CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells and B cells (for antibody production – especially neutralising IgG)
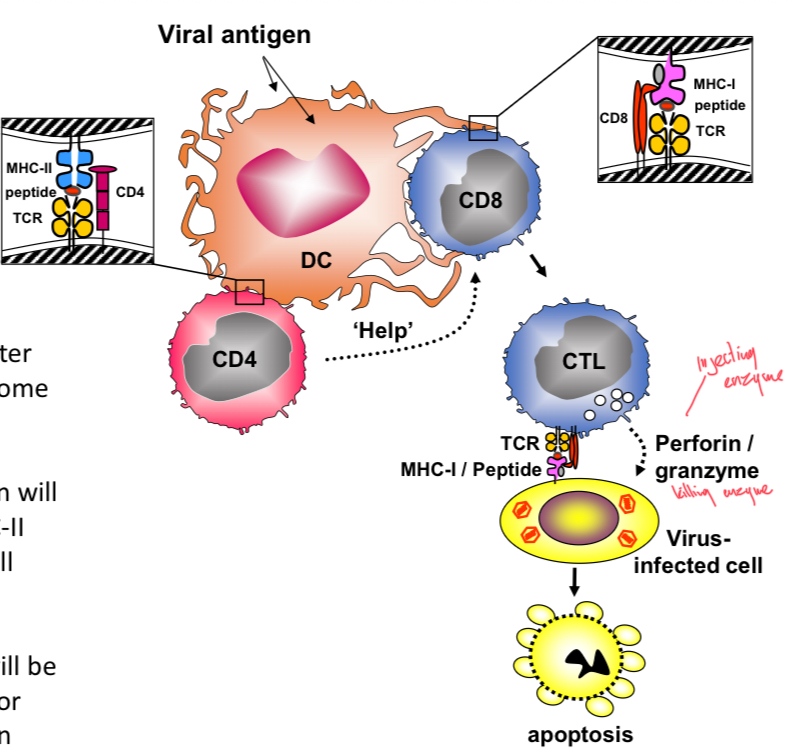
Viral antigen response
Viral proteins enter both the phagolysosome and cytosol of DC. Phagosomal antigen loaded onto MHC-II for CD4 (helper) T cell stimulation. Cytosolic antigen loaded onto MHC-I for CD8 T cell stimulation. CTL made, kills virus using perforin and granzyme causing apoptosis.
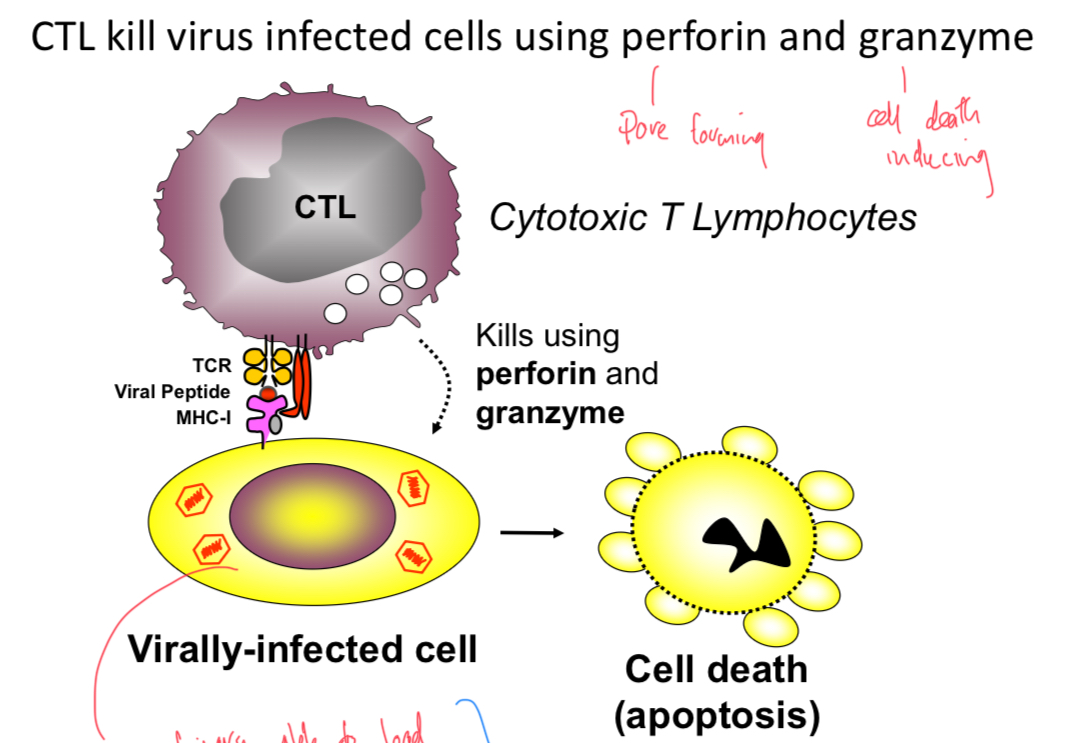
Cytotoxic T Cells
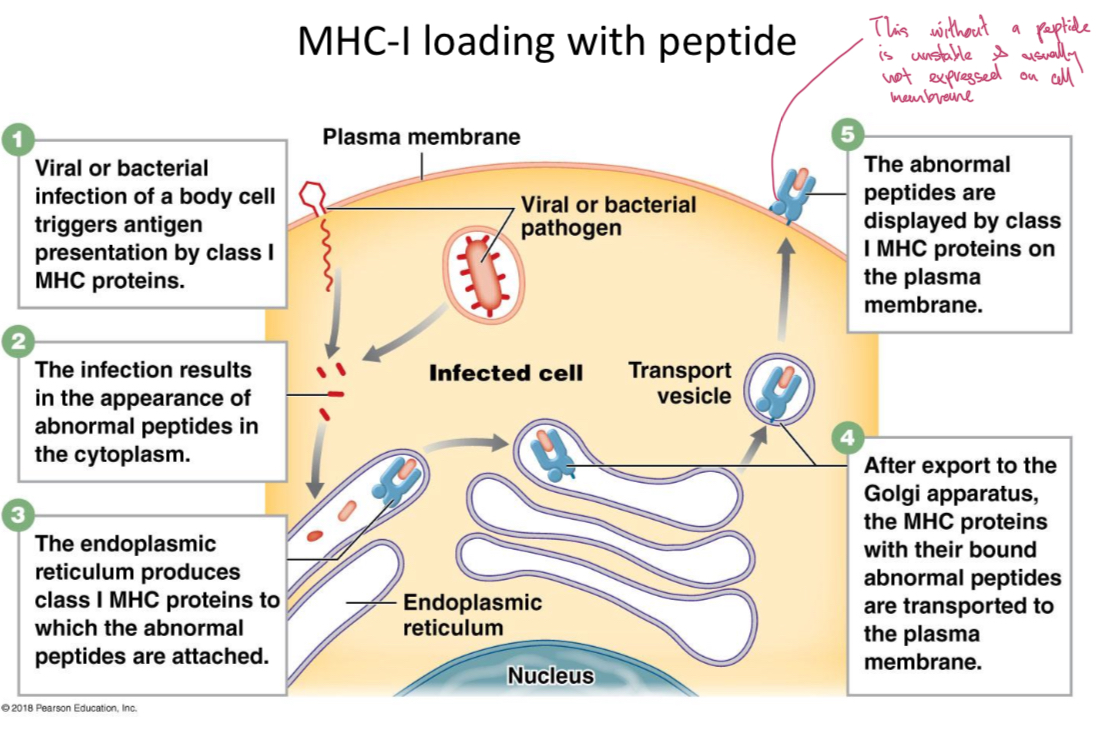
Release perforin (for forming) and granzyme (cell death) enzymes to induce apoptosis. Recognises machinary able to load MHC-1 with peptide of virus on virally infected cells.
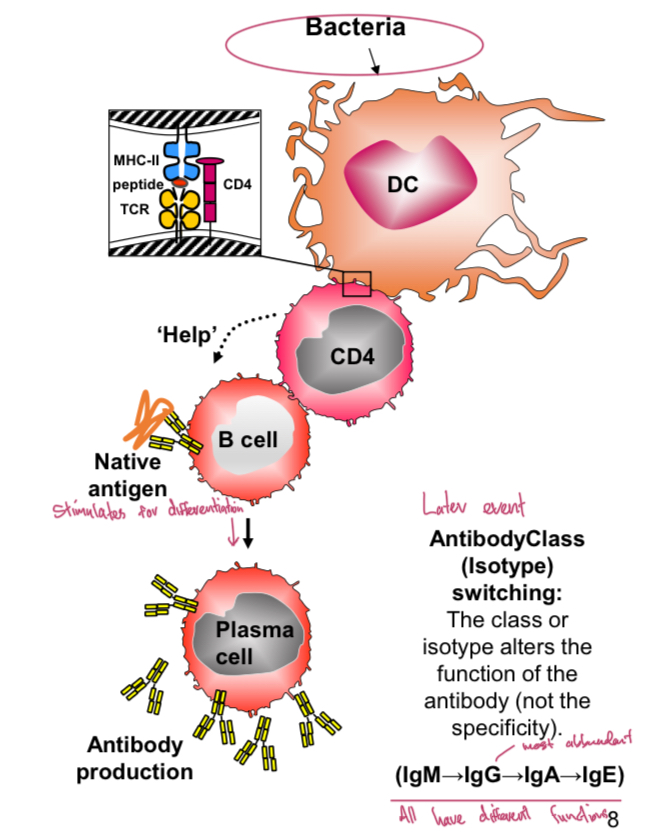
Bacterial antigen response
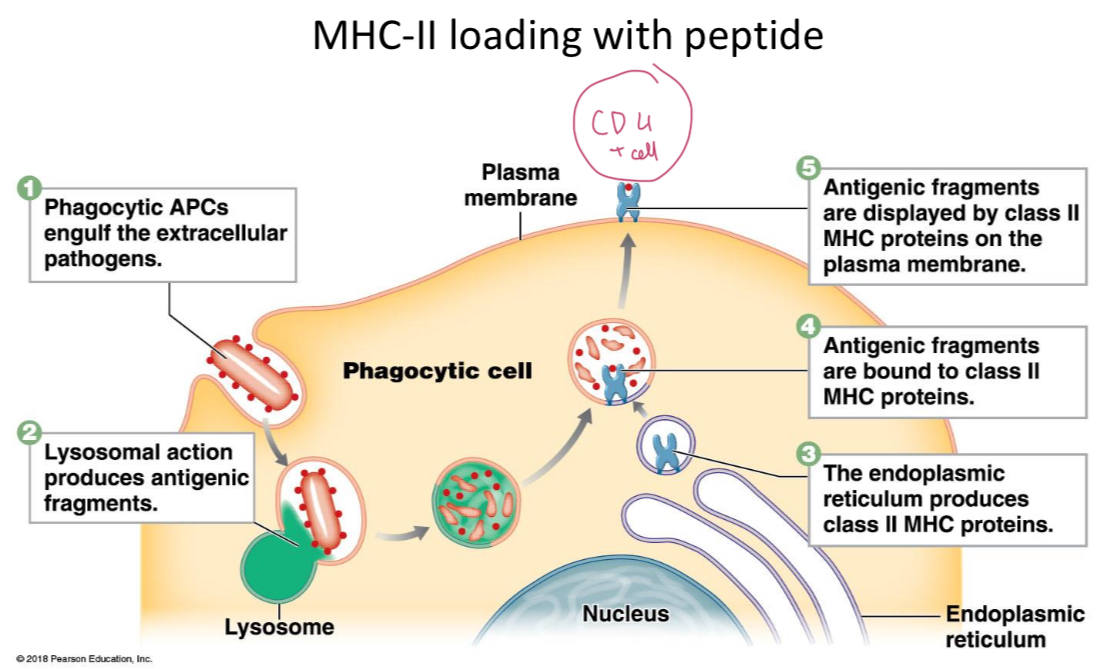
Bacterial proteins enter the phagolysosome of DC: Phagosomal antigen will be loaded onto MHC-II for CD4 (helper) T cell stimulation. Helper T cells stimulate B cells to make antibody. Only B cells that recognise antigen are activated.
MHC-I
Presents cytosolic antigen to CD8 T cells.
MHC-II
Presents phagosomal antigen to CD4 (helper) T cells.
Helper T Cells
Stimulate B cells to make antibodies.
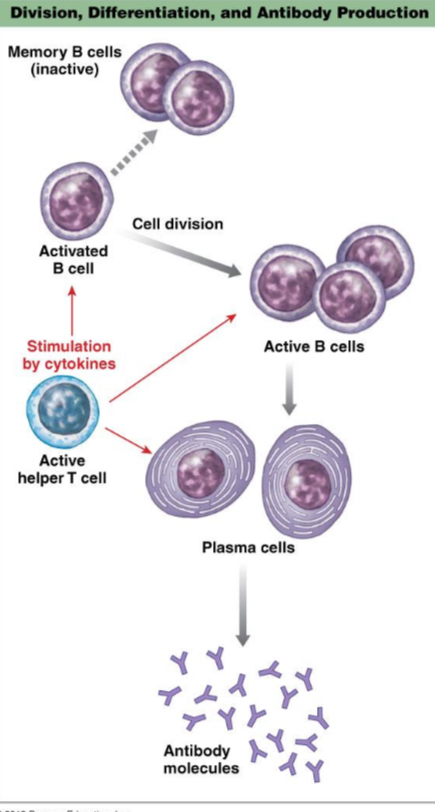
Division, differentiation of antibody production
Activated B cells divide and differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibody, as well forming a separate population of memory B cells.
At second encounter with antigen, Memory B cells are more numerous and are rapidly stimulated by antigen to become plasma cells.
Seccondary immune responses
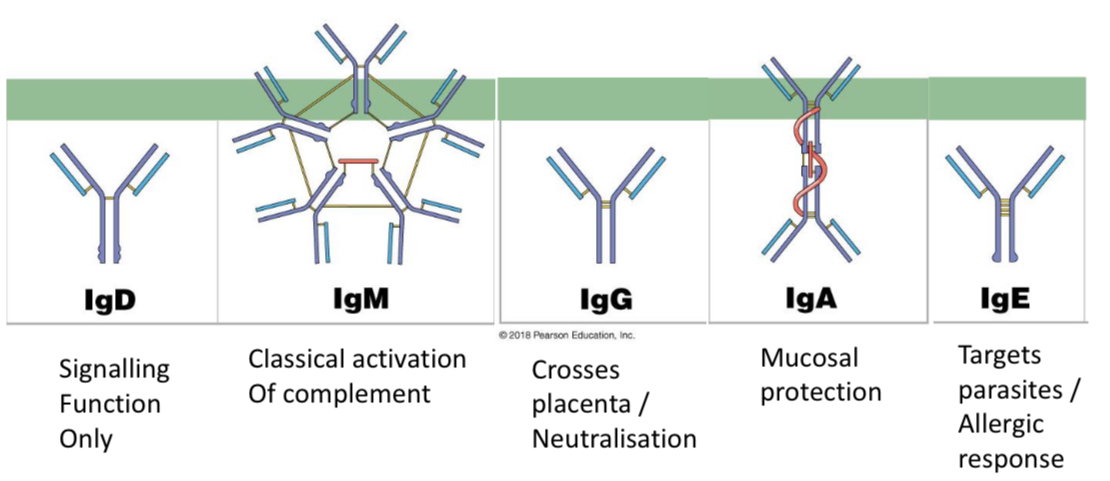
Characterised by the predominance of class-switched antibodies, IgG, IgA and IgE
Clonal Selection B cells
Selective expansion of lymphocytes that interact with antigen. B cell specific for native antigen is activated and undergoes extensive cell division (requires CD4 help).
Clonal selection t cells
T cell specific to peptide selected by APC are activated and undergo extensive cell division. Usually many t cells selected cause bugs have lots of peptides.
MHC-1 loading with peptide
MHC-11 loading with peptide
Isotype Switching
B cells genetically switch the heavy chain to change antibody class, altering function without changing specificity.
Live Attenuated Vaccine
Vaccine that uses a weakened form of the pathogen.
Killed Vaccine
Vaccine uses ‘dead’ pathogens so they cannot replicate. Eg some influenza and SARS-CoV2
Sub-unit protein/mRNA Vaccine
Vaccine that uses only a part of the pathogen to stimulate an immune response.
Adjuvants (usually requires sub unit vaccines)
Immune stimulants added to vaccines that enhance the activation of APCs. Eg. mRNA SARS-2 vaccine is adjuvanted, lipid-encapsulated mRNA is immunostimulatory.