Ecology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Native (endemic) Species
Refers to a species that is naturally found in a specific geographical region, occurs without human intervention
Non-Native Species
An organism that is not indigenous, or native, to a particular area and can potentially cause harm to the ecosystem
Invasive Species
Non-native species that cause harm to the environment
Density-dependent limiting factors
Factors that influence population dynamics and vary in impact according to the population density. These factors, such as competition for resources, predation and disease, tend to have a stronger effect as population density increases.
Negative feedback
A mechanism by which a system responds to changes in its internal or external environment by reversing the direction of the change, thereby maintaining homeostasis.
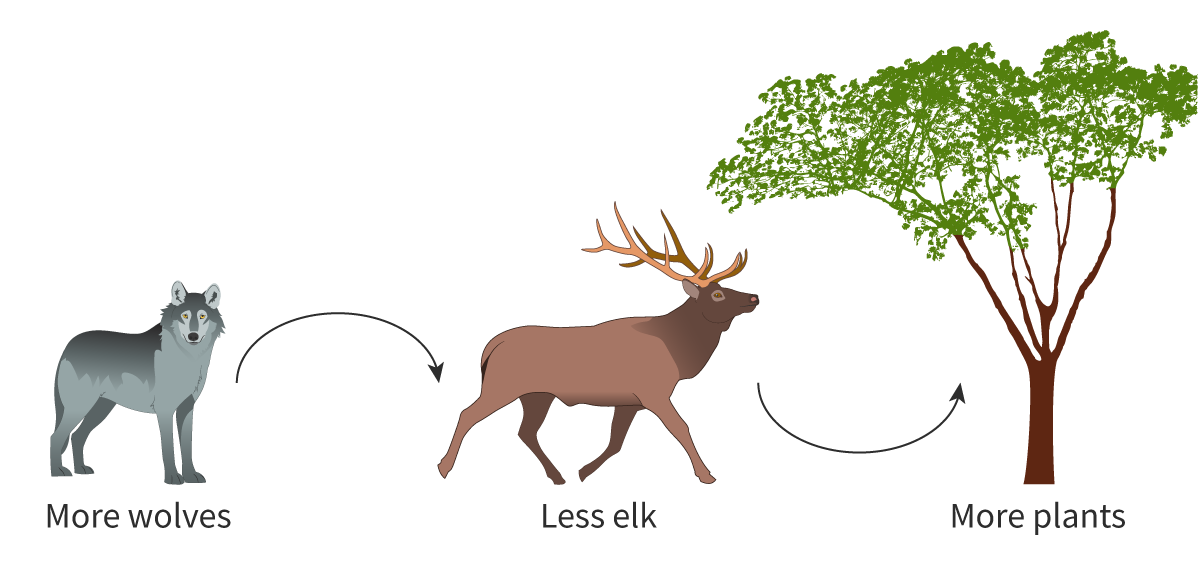
Top-down control
Occurs when the abundance or behaviour of lower trophic levels in a food chain is regulated by the presence and activities of organisms at higher trophic levels.
→Reintroduction of the Yellowstone Grey wolves limited elk population (a grazing animal) and allowed woody plants and saplings to flourish
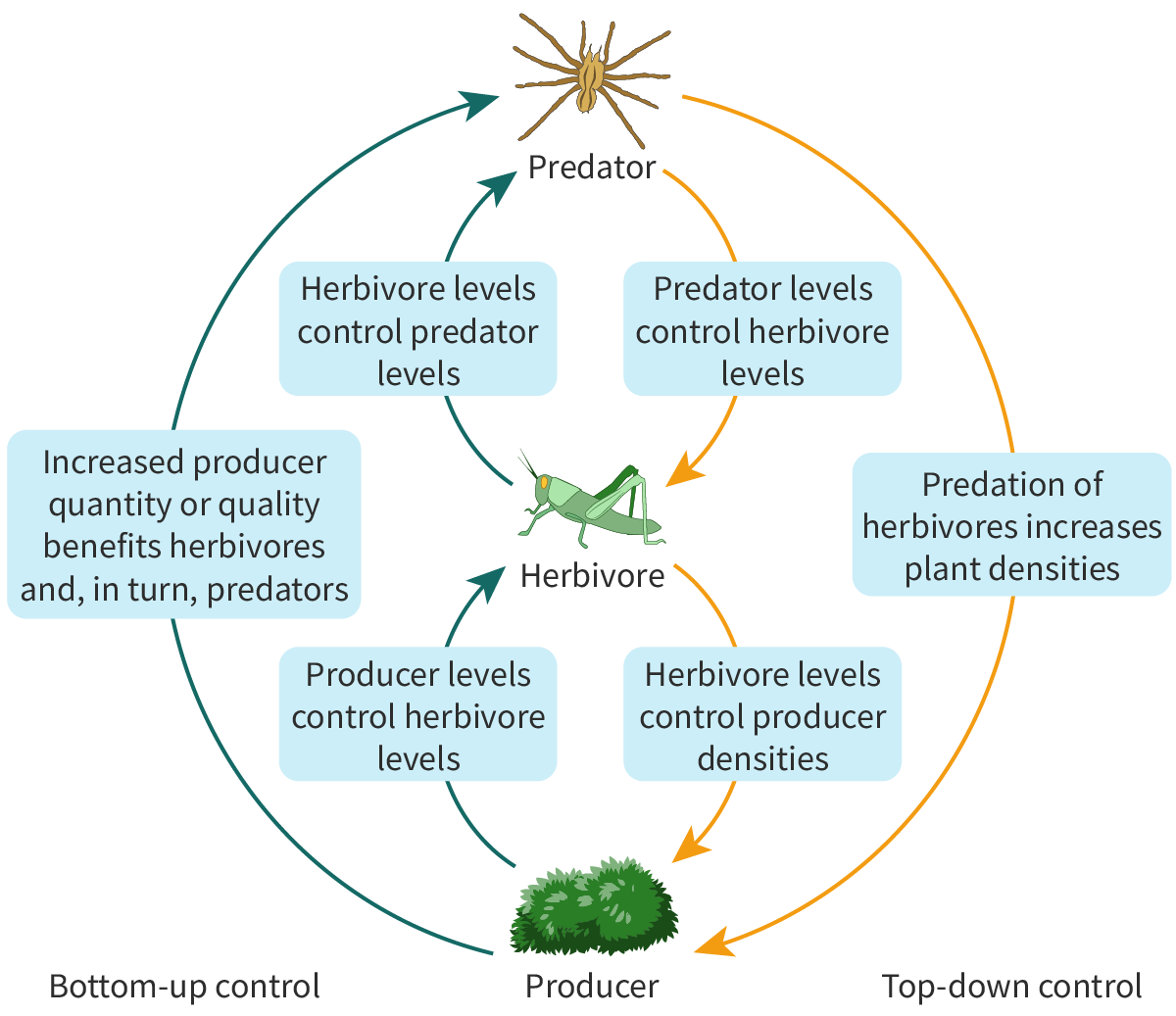
Bottom-up control
Occurs when the availability of resources at lower trophic levels influences the abundance and distribution of organisms at higher trophic levels.
Allelopathy (plant-to-plant interraction)
The process by which organisms release biochemical compounds into the environment, influencing the growth, survival or reproduction of other organisms.
→black walnut trees release toxic chemicals by their roots and suppress the growth of nearby plants
Antibiotic Secretion
Microorganisms secrete antibiotics to hinder the growth of other bacteria (microorganism-to-microorganism)
Ecological Niche
An organisms role in the ecosystem
Biome
Groups of ecosystems with similar communities due to similar abiotic conditions and convergent evolution.
Ecosystem
All organisms that live in a place, together with their physical enviornment
Community
All the different populations that live together in a defined area
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Species
A group of similar organisms capable of breeding and producing fertile offspring.
Detritivore
Organisms that feed on dead/decaying matter
Habitat
A geographical or physical location that provides the necessary resources for an organisms survival and reproduction
Halophyte
A plant species that has adapted to grow in high-salt environments, such as coastal areas, salt flats or salt marshes.
Marram Grass in Sand Dunes
Marram grass has rhizomes which are horizontal underground stems that grow below the surface of sand. The rhizomes of marram grass are an important adaptation that allows the plant to spread, anchor itself in the sand, access water and nutrients, and help stabilise sand dunes. They can also tolerate high levels of salt in the soil.
Rhizophora apiculata in Mangroves
Mangroves develop where there is a mixture of saltwater and freshwater, and the water level fluctuates with the tides, leading to a high level of salinity.
→Rhizophora apiculata are halophyte plants that have pneumatophore roots that grow vertically from the soil, which help to provide the roots with oxygen even when the soil is waterlogged, and prevent soil erosion. They also have a unique method of propagation in which the seeds germinate and begin to grow while still attached to the parent tree. This allows the tree to establish itself in new areas without being dispersed by water.
Range of Tolerance
Range of environmental conditions, within which an organism can survive and function optimally.
Zooxanthallae in Coral tissue
Photosynthetic algae that live in the tissue of coral, provide coral with nutrients from photosynthesis, and acquire shelter from the coral.
Competitive Exclusion Principle
It is not possible for two species to occupy the same niche for a long period of time, and one will out compete the other
→results in niche partitioning
Niche Partitioning
The process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. This may be spatial or temporal.
Spacial Partitioning
Competitors occupy different areas within a location
Temporal Partitioning
Competitors are active at different times
Holozoic Nutrition
Organisms that consume food via the process of ingesting, digesting and assimilating the nutrients.
Saprotroph
Organisms that obtain nutrients by secreting digestive enzymes followed by absorbing and assimilating the nutrients (common in decomposers)
→break down dead leaves and logs, recycle carbon and nitrogen from dead organic matter
Obigate Anaerobes
Organisms that survive in the absence of Oxygen
Facultative Anaerobes
Organisms that can survive in the absence oxygen
Obligate Aerobes
Organisms that must have oxygen for survival
Fundamental Niche
Potential role of a species based on their adaptations and tolerance limits, excludes competition
Realized Niche
actual niche the organism plays when in competition with other species
Resistance
The ability of an ecosystem to remain stable in the face of disturbances
Resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to recover after a disturbance.
Tipping Point
The critical threshold of a change that results in a significant and often irreversible change in an ecosystem’s structure, function or composition
→ where small changes can accumulate and trigger larger effects.
→ Deforestation of the Amazon Rain forest
Transpiration
Trees absorb water from the ground with their roots and release water from their leaves as water vapor.
Ecosystem Stability
The ability of a system to maintain its structure and function over time, despite changes or disturbances.
Bioaccumulation
The process by which certain substances, such as toxins or pollutants, accumulate and increase in concentration within the tissues of organisms over time because they are unable to be digested and excreted.
Rewilding
The process of restoring and reintroducing natural ecosystems and species to areas where they have been lost or significantly altered.
Biomagnification
As organisms consume other organisms, the accumulated toxins (typically mercury and microplastics) become more concentrated in the tissues of higher-level predators.
Ecological Succession
The natural progression of changes in species composition and community structure over time. Ecosystems undergo a series of transformations, shifting from bare and disturbed environments to thriving and diverse habitats.
→response to natural disturbances, human activities, and changes in the enviorment
Primary Succession
The process of ecological succession that occurs in a newly formed or exposed area with no pre-existing soil.
Pioneer species → Intermediate species → Climax community
Pioneer Species
They can survive in harsh conditions with limited nutrients and help break down rock or organic matter using decomposition to create a rudimentary soil layer.
(Pedogenisis = soil formation)
Secondary Sucession
The process of ecological change that occurs in an area that has been previously colonized by living organisms but has experienced a disturbance that disrupts the existing community and returns it to any previous stage of the development
→ begins with a preexisting soil base and remnant species
Cyclic Ecological Succession
A type of ecological succession where a community undergoes repeated cycles of change in response to periodic natural events.
→ wildfires in forests for replenishment
Arrested Succession
Refers to a disruption or interruption in the normal progression of ecological succession. It occurs when the development of a community is halted or slowed down due to repetitive/extreme disturbances.
→never reaches climax community
Carbon Sink
Any environment that absorbs more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases
→ Forests (continuously absorb CO2 from the atmosphere to use for photosynthesis), oceans, soil
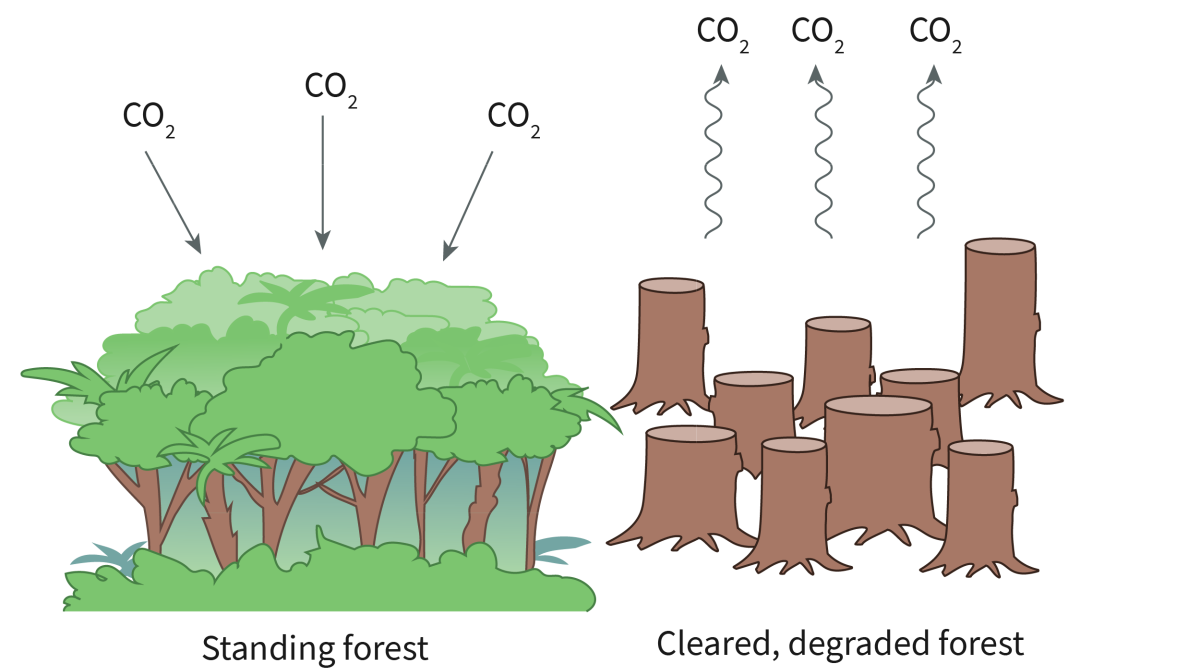
Carbon Sources
Locations or processes that release more carbon into the atmosphere than they absorb.
→factories (burning of Fossil Fuels), Forrest fires, cellular respiration (exhaling CO2)
Negative Feedback
A mechanism by which a system responds to changes in its internal or external environment by reversing the direction of the change, thereby maintaining homeostasis.