Exercise and the Immune System
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the two main components of the immune system?
The innate immune system
Physical, cellular system, complement system
acquired immune system.
Adaptive or specific immune system
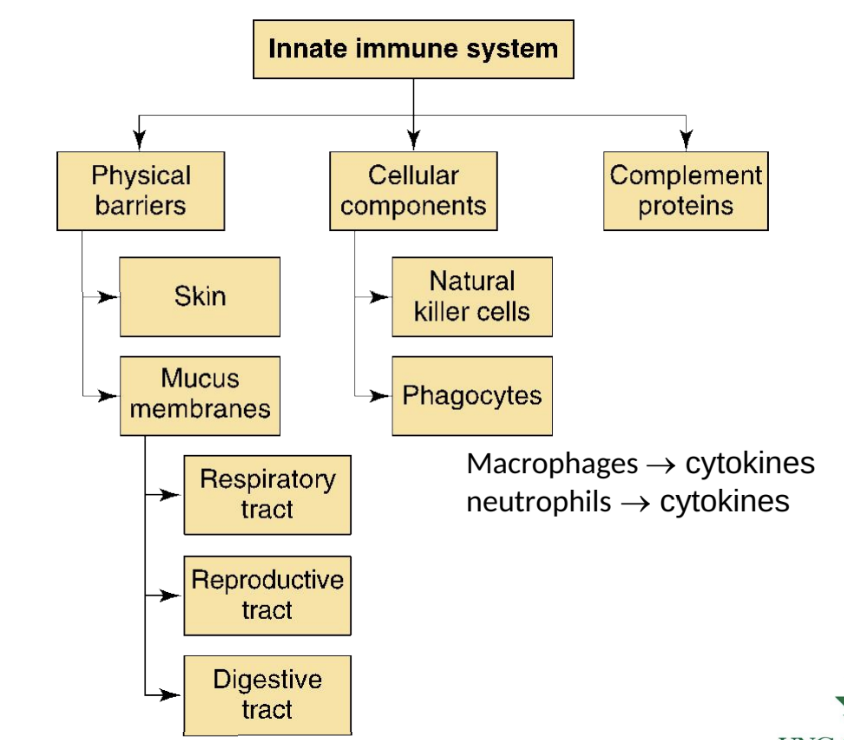
What physical barriers are part of the innate immune system?
Skin and mucus membranes.
Complement proteins
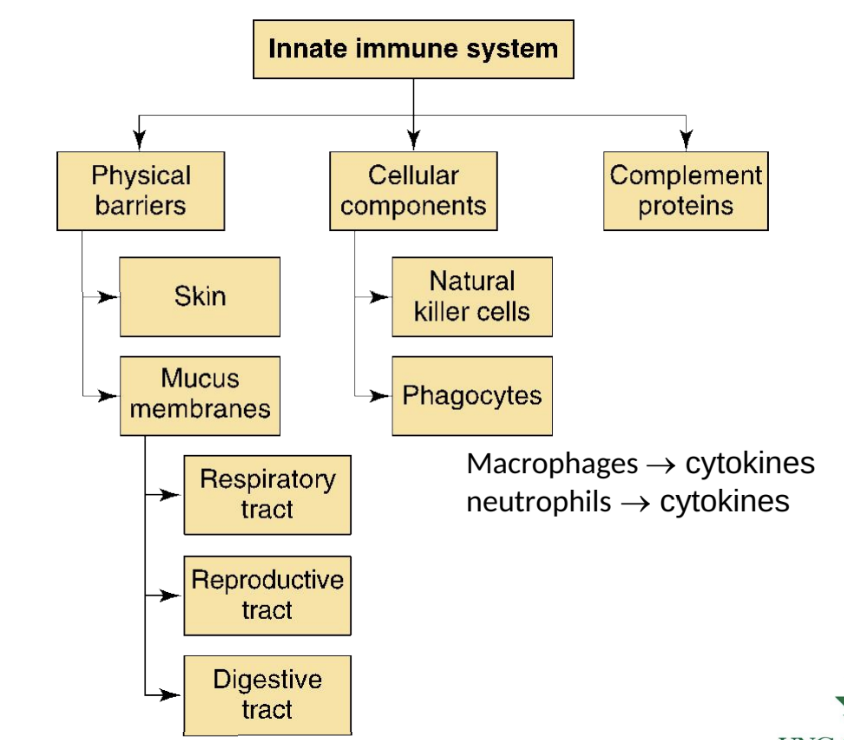
Which cells are key components of the innate immune system?
Neutrophils and macrophages
release cytokines
What are cytokines?
Cytokines are signaling proteins that mediate and regulate immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis.
What are B cells (B lymphocytes) responsible for in the acquired immune system?
They secrete antibodies to fight against foreign antigens.
Best Cells → B Cells
What are the different types of antibodies produced by B cells?
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE.
Antibodies called immunoglobulins
Fight against foreign antigens
What are the three types of T cells?
T cells are a subtype of white blood cells that are pivotal in the immune system. They originate in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus. There are several types of T cells, including:
Helper T cells (CD4+ T cells): They assist other immune cells by releasing cytokines, which help orchestrate the immune response.
Killer T cells (Cytotoxic T cells): They directly kill infected cells, cancer cells, and sometimes cells that are damaged in other ways.
Regulatory T cells (Tregs): They help maintain immune tolerance, preventing immune system from attacking normal body antigens
What is the impact of moderate aerobic exercise on the risk of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI)?
Moderate aerobic exercise protects against infections and may reduce the risk of URTI
Reduces risk of URTI 18-67%
20-40mins
@ 40-60% VO2 max
Resistance training may also help
What is the mechanism behind regular exercise reducing the risk of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI)?
Regular exercise decreases the risk of upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) by:
enhancing circulation of immune cells throughout the body
reducing chronic inflammation
regulating stress hormones like cortisol
improving sleep quality
promoting lymphatic flow to transport immune cells.
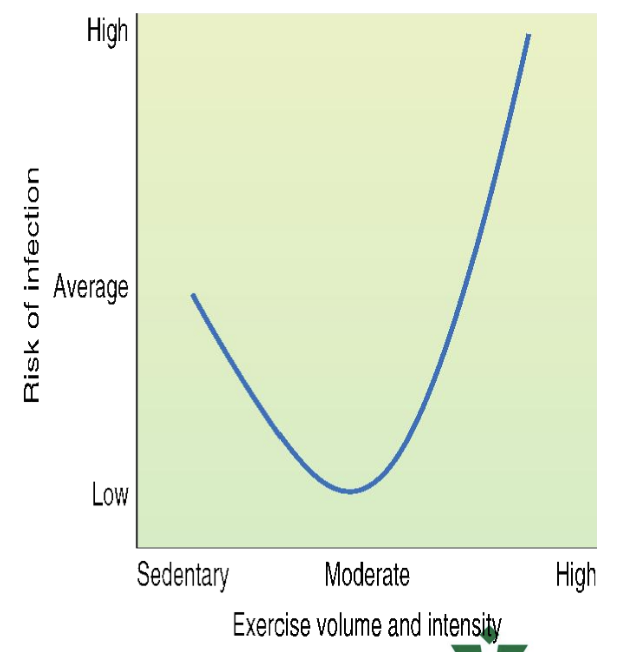
Exercise and resistance to infection?
Regular, moderate exercise decreases risk of URTI
Increased risk of URTI w/ intense and/or long duration exercise
Exhaustive exercise triggers illnesses
Causes IMMUNOSUPPRESSION and provide an opportunity for infections
What is immunosuppression?
Immunosuppression is the reduction of the immune system's ability to fight infections and diseases, often induced by medications.
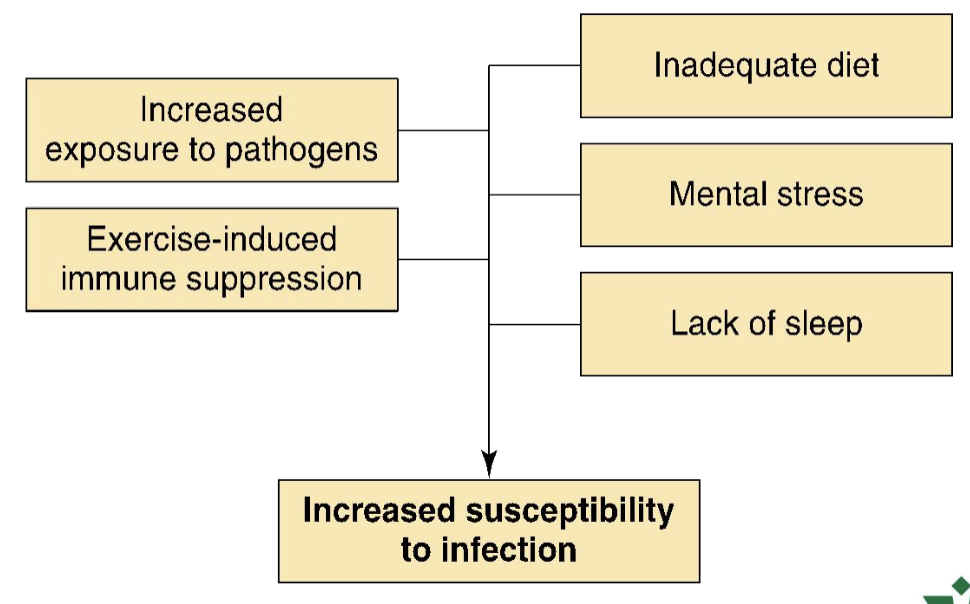
What are factors that affect susceptibility to infection in atheletes?
Increased exposure to pathogens
Exercise-induced immune suppression
Inadequate diet
mental stress
lack of sleep
What happens to the risk of URTI with high intensity or long duration aerobic exercise?
It increases the risk of URTI due to the 'open window' effect.
Decreases levels of:
B cells
T cells
natural killer cells
Decreases natural killer cell and t cell function
Decreased neutrophil phagocytosis
decreased nasal and salivary IgA
INCREASED cytokines
If Bad cytokines are released
exacerbates the infection itself
Induces immunsuppression
When is it safe to exercise if you have a cold?
It’s safe to exercise if symptoms are above the neck, such as a mild sore throat or runny nose.
What should you avoid if you have symptoms below the neck while having a cold?
You should not exercise if you have
chest congestion
cough
stomach pain.
What effect does regular exercise have on natural killer cells and lymphocytes?
Exercise boosts the levels of natural killer cells and lymphocytes.
What factors contribute to increased susceptibility to infection in athletes?
Increased exposure to pathogens
exercise-induced immune suppression
inadequate diet
mental stress
lack of sleep
What role do T cells play in the acquired immune system?
T cells, including killer T cells and helper T cells, combat virus-infected cells and enhance the immune response.
What was one finding about the effects of sedentary behavior on vaccine effectiveness?
Sedentary behavior decreases vaccination-induced immunogenicity.
According to WHO recommendations, how much exercise should healthy adults do per week?
At least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
What is the importance of exercise for individuals with pre-existing comorbidities during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Exercise may improve outcomes like reduced mortality from pneumonia and enhanced immune response.