ap micro
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
utility
what consumers want
profit
what producers want
goods
physical objects that satisfy wants and needs
services
actions and activities that satisfy needs and wants
needs
a basic requirement for survival without which you cannot live;its satisfaction brings utility
wants
something you desire that is unnecessary for survival; its satisfaction brings utility
inputs
resources used by firms to produce products
output
finished goods produced by firms for profit
wages
the price paid by firms to purchase inputs/factors of production
prices
income spent by consumers to purchase economic goods
costs
the combined wages paid by a firm to produce economic goods
revenue
price paid to the firm per unit of output sold(P*Q)
profit
revenue kept by firms after paying production costs
income
wages kept by consumers that are used to buy products
marginal cost
the cost for each additional unit of something; equal to supply
marginal benefit
the benefit from each additional unit of the good; equal to demand
explicit costs
costs in monetary form
implicit costs
opportunity cost and forgone benefits in non-monetary form
rational choice
made when MB is greater than or equal to marginal cost
excludable
a good that someone can be prevented from enjoying its benefits(Brink’s security, fish farm fish, concert)
nonexcludable
a good that someone cannot be prevented from enjoying its benefits(public police department, fish in ocean, TV concert)
rival
a good that, when it is used by one person, decreases the quantity available to another person
nonrival
a good that, when it is used by one person, does not decrease the quantity available to someone else
private good
a good that is rival and excludable; a can of soda
natural monopoly/ club goods
a good that is nonrival and excludable(produced at a lower cost than other firms)i.e., internet
common resource
a good that is rival and nonexcludable- it can only be used once, but no one can be prevented from using what is available
public good
nonrival and nonexludable goods- a good that can be consumed by everyone and no one can be prevented from experiencing its benefits
elasticity
the sensitivity of quantity to a change in price
percent change
(V2-V1)/V1
price elasticity of demand
how sensitive the quantity demanded is to a change in price; calculated by the (percent) change in quantity demanded divided by the (percent) change in price

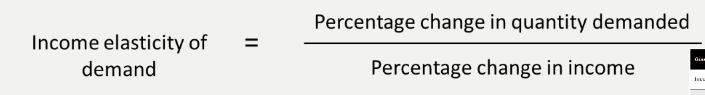
income elasticity of demand
the extent to which a goods demand changes when income changes

cross-price elasticity of demand
how demand for a good changes when the price of a substitute of a complement changes
Positive for substitutes, negative for complements
midpoint method
percentage change in price and qd
(new-initial/(new + initial)/2)*100

elastic
elasticity >1; QD change is greater than price change
perfectly elastic- QD changes immensely when price changes

inelastic
elasticity < 1: price change is greater than quantity demanded change
Perfectly inelastic- QD is not affected by price change and stays the same

unit elastic
elasticity = 1; Qd change = price change

total revenue test
if price and revenue move in the opposite direction, elastic demand
if they move in the same direction, inelastic demand
total revenue = PQ
substitutes and demand elasticity
a good with poor substitutes is a necessity and inelastic
a good with many subsitutes is a luxury and elastic
specificity of a good and demand elasticity
the more specific a good is the more elastic it is
the less specific a good is the more inelastic it is
time and elasticity
the longer since the time a price has changed for a good, the more elastic the goods demand is
income and elasticity
price rising means people cant afford the same q of a good; more income spent on a good = more elastic
price elasticity of supply
quantity supplied sensitivity to price change
QS/P

PPC and elasticity
goods produced at a constant OC have elastic supply
storage and elasticity
goods that can be stored easily are elastic
normal good
elastic when >1, inelastic when between 0 and 1
inferior good
elasticity <1
allocation method
market price- those who can pay get it
command/authority- someone determines who gets what
majority rule- people vote for a decision
contest- whoever wins
first come first serve- first to get there
sharing equally- using resources
lottery- pure luck
personal characteristics- people who align with whatever the good is good for
force- war or theft
value
what the buyer gets
price
what the buyer pays
cost
what a seller gives up
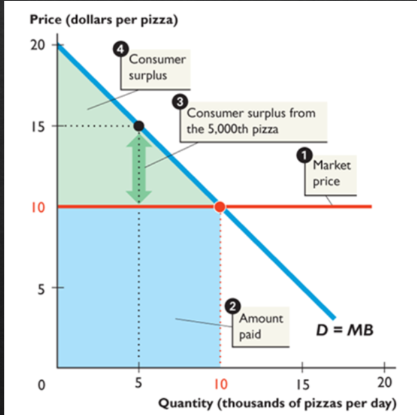
consumer surplus
the marginal benefit of a good or service subtracted by the price paid for it divided by the quantity consumed
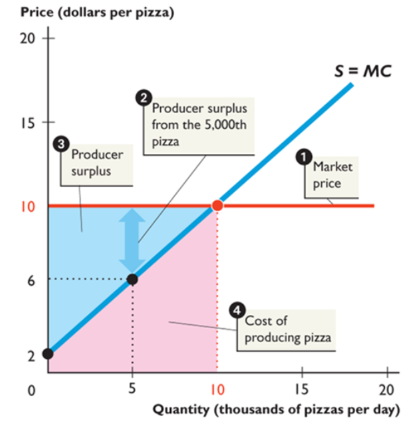
producer surplus
the price of a good minus the opportunity cost of producing it divided by the quantity produced
efficient
MB=MC
invisible hand
the total surplus is maximized, and consumers and producers pursuing their self interest serve the social interest
deadweight loss
decrease in total surplus from over/underproduction
Caused by p and q regulations, taxes and subsidies, externalities(cost or benefit to someone that isn’t the buyer), public goods and common resources
monopolies and high transaction costs
Market alternatives
fair rules
equality of opportunity
fair results
not fair if result isn’t fair
big tradeoff
tradeoff between efficiency and fairness
price ceiling
government regulation that places an upper limit on the price that a good can be traded; usually below equilibrium and causes a shortage
causes black markets and increased search activity
consumer surplus decreases and deadweight loss arises
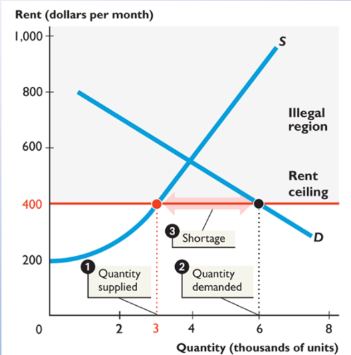
rent ceiling
makes it illegal to charge more than a specific price for house rent
price floor
places lower limit on price; above equilibrium and causes a surplus
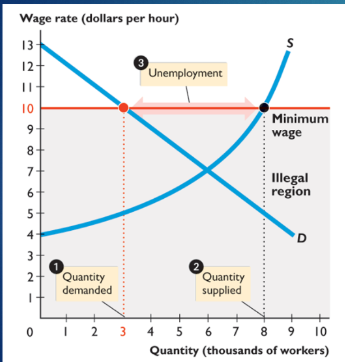
minimum wage
more people work at a higher wage but less people are hired
leads to illegal hiring and increased search activity
inefficient, decreasing firms and workers surplus
production quota
government regulation placing an upper regulation on the quantity supplied
inefficient and unfair
tax incidence
division of tax burden between buyer and seller
excess burden
deadweight loss; how tax cost exceeds revenue gov’t gets
elasticity and incidence
more inelastic demand means buyers pay
more elastic demand means sellers pay
budget line
limits to consumption and depends on consumer’s budgets and prices
Slope is OC
total utility
total benefit a person gets from the consumption of a good and service
marginal utility
the change in total utility that results from a one-unit increase in the quantity of a good consumed
diminshes
utility-maximizing rule
using entire budget and making marginal utility per dollar equal for all goods
marginal utility per dollar
marginal utility relative to the price paid; mu/p
firms goal
maximizing profit
accountant
cost and profit to ensure income tax is paid
economists
predict decisions a firm makes to maximize its profit
explicit cost
paid in money
implicit cost
an opportunity cost incurred by a firm when it uses a factor of production
economic depreciation
an opportunity cost of a firm using capital that it owns
normal profit
return to entrepreneurship; part of a firms OC
economic profit
total revenue - total cost(explicit + implicit)
short run
some resources are fixed
long run
all resources are variable
total product
total quantity of a good produced in a given period(units over time)
marginal product
change in total production over one unit increased in labor
average product
Total product/quantity
If marginal>average, average is increasing
If marginal<average, average is decreasing
If marginal= average, it is at max
total fixed cost
cost of a firm’s fixed factors of production; does not change
total variable cost
cost of a firms variable factor of production
total cost
TFC + TVC
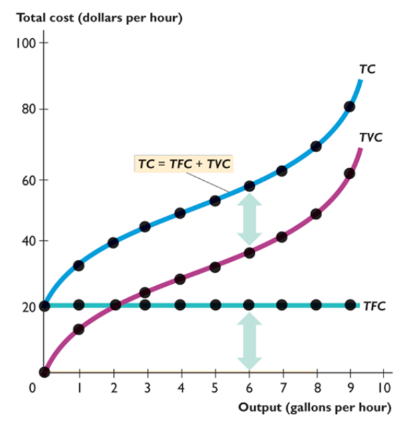
marginal cost
change in a firm’s total cost from a one-unit increase in total product
avg cost
total costs divided by quantity of output
curves
all U shaped
MC intersects curves at minimum
Decreasing marginal returns and spreading fixed cost over a larger output
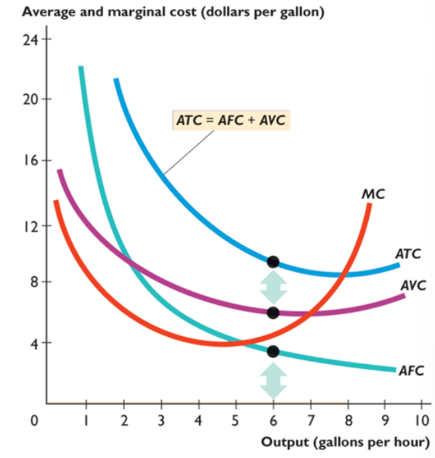
cost and product
when product rises, cost falls
small outputs
products rise, costs fall
intermediate outputs
MP and AVC falls, AP and MC rises
large outputs
product falls, cost rises
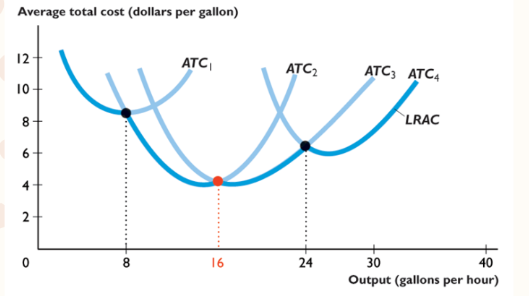
economies of scale
when labor increases and ATC decreases
caused by specialization
diseconomies of scale
when labor increases and ATC increases
Caused by difficulty of running a business
constant returns to scale
when labor increases ATC stays constant
due to firm replicating its production facility
Long Run Average Cost
shows lowest avg total cost at each output