Session 9: Adaptive Immunity
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
List the properties of the adaptive immune response
- Specificity
- Diversity
- Memory
- Clonal selection and expansion
- Specialisation
- Homeostasis
- Non-reactivity to self
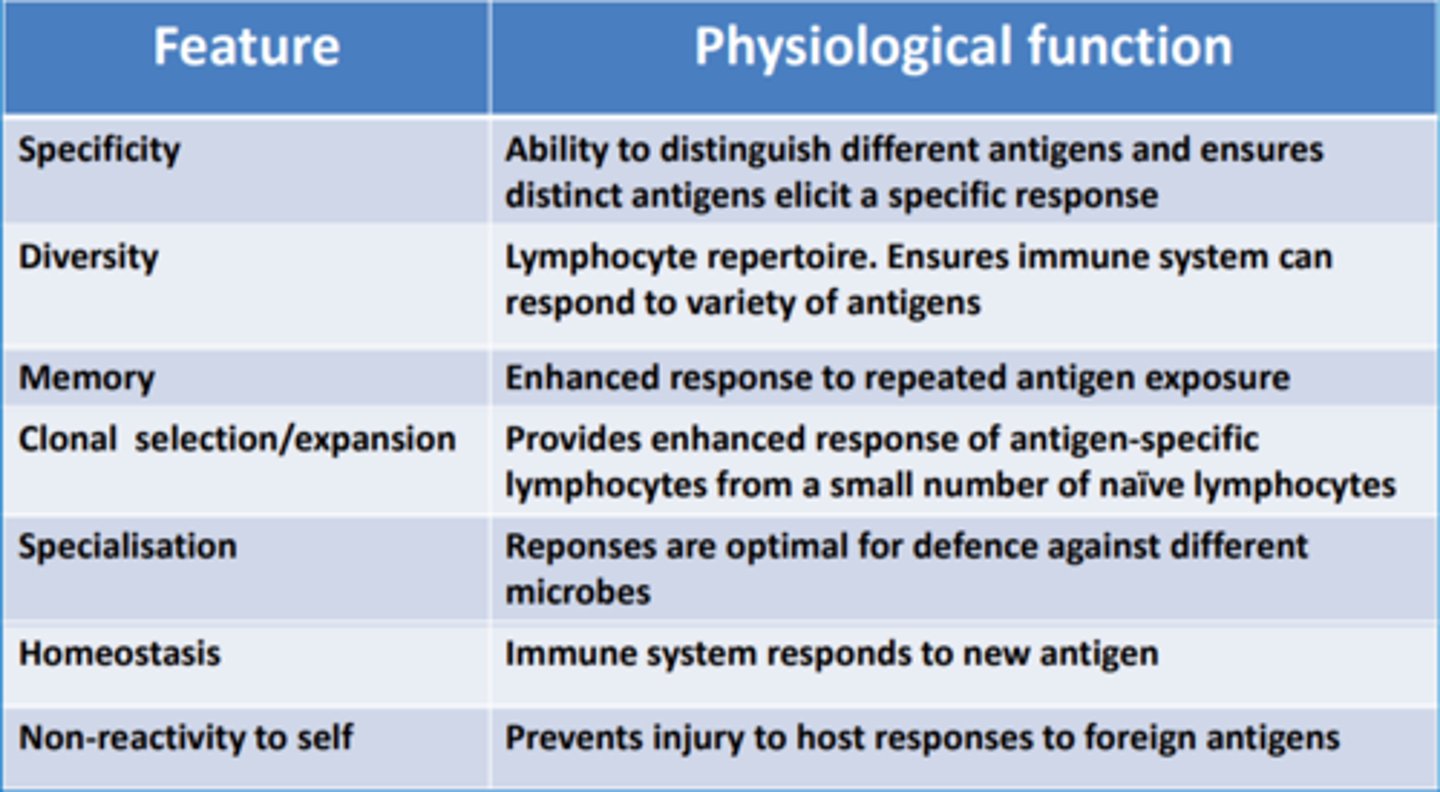
Difference between humoral adaptive and cell-mediated adaptive immune responses
HUMORAL
- Antibody-mediated
- B-cell (bone marrow)
- Recognizes proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acid
- Targets extracellular pathogens
- Antibodies in serum
- Primary defense against bacteria
CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY
- Cell-mediated
- T-lymphocytes (thymus)
- Recognizes proteins
- Targets intracellular pathogens
- Direct cell-to-cell contact
- Defense against viral, fungal, tumor antigens, graft rejection, intracellular organisms
Natural Killer T cells (NKT)
- Kill tumor cells
- Kill virally-infected cells
- NKT cells determine the type of adaptive response

What do NKT cells recognize
IgG
Lipids
MHC class I

What cytokines do NKT cells release?
IFN
TNF
IL12

How do NKT cells induce apoptosis?
Induce apoptosis by pumping proteases through target cell membrane

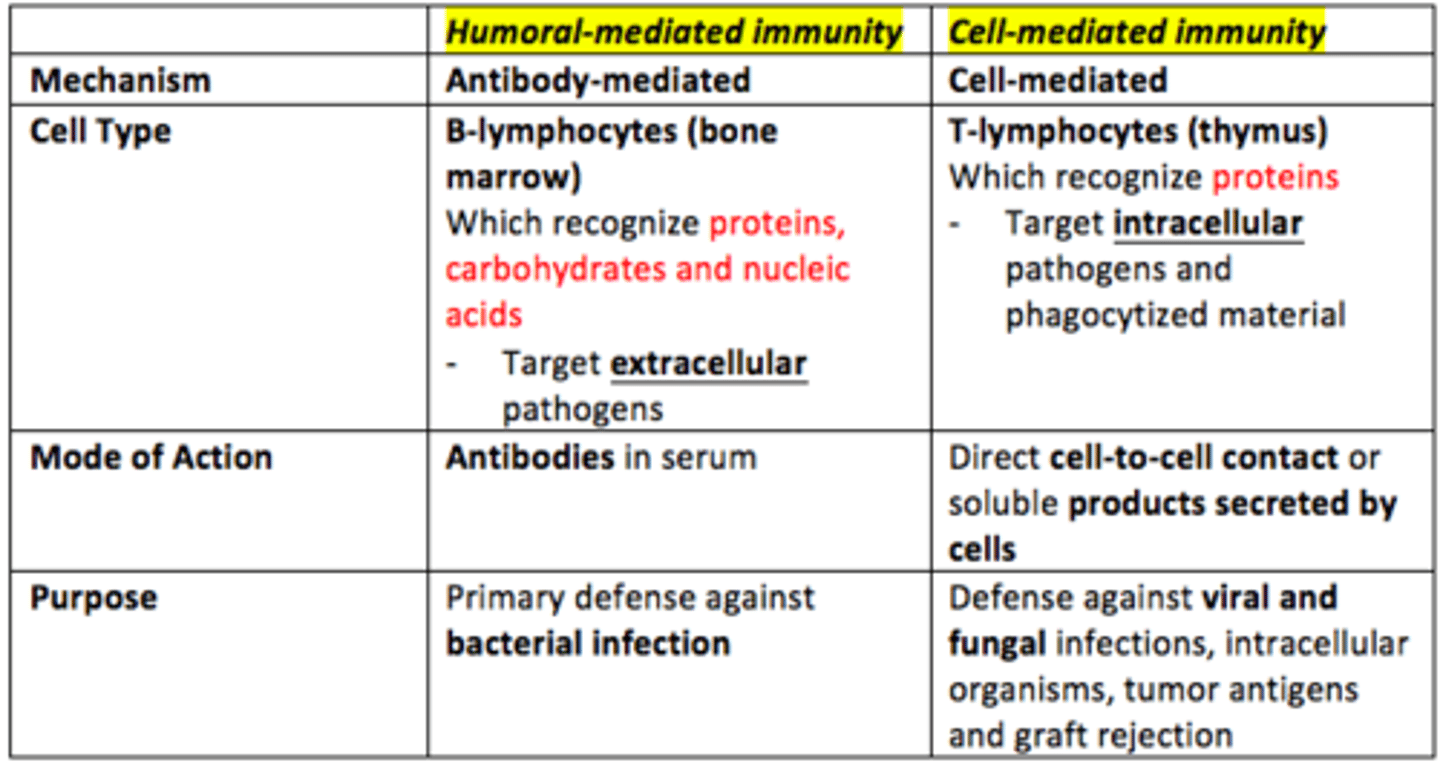
Where do B lymphocytes originate
Bone marrow
Where do T lymphocytes originate
Thymus
B-cells recognize ___ pathogens
extracellular
T-cells recognize ___ pathogens
intracellular
What percentage of lymphocytes are circulating?
2% of lymphocytes are circulating
The rest of the lymphocytes are in lymphoid tissues
Which division of the immune system...
Targeting of pathogens by secreted immunoglobulin molecules
Adaptive: humoral
Which division of the immune system...
Killing of infected cells in an MHC-dependent fashion
Adaptive: cell-mediated
Which division of the immune system...
A non-specific and rapid response to a challenge that does not create a memory of the pathogen
Innate immune system
Order the following circulating immune cells in order of abundance with 1 being the most abundant...
Basophils
Eosinophils
Monocytes
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
1) Neutrophils = most abundant
2) Lymphocytes
3) Monocytes
4) Eosinophils
5) Basophils = least abundant
Naive lymphocytes
Express antigen receptors but have not responded to antigen
Effector lymphocytes
Differentiated progeny of naive cells after antigen exposure - cells produce molecules which actively eliminate the antigen
Diagram remember labels for exam
T and B cells are morphologically indistinguishable. They are identified by cell surface markers known as ___ of ___
Cluster of Differentiation (CD)
Deletion of potentially self-reactive thymocytes, thereby generating a repertoire of peripheral T cells that is largely self-tolerant
Negative selection
Clonal selection
The process by which an antigen selectively binds to and activates only those lymphocytes bearing receptors specific for the antigen.
The selected lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate into a clone of effector cells and a clone of memory cells specific for the stimulating antigen.
Clonal expansion
The rapid multiplication of B or T cell clones after activation by an antigen
Where are lymphocytes activated?
Spleen and lymph nodes
After activation, memory lymphocytes are dispersed to ___ and ___ mucosa
GI and respiratory mucosa
These are close to sites of potential reinfection - allows for rapidity of response if exposed to the same antigen again
Strategic location of antigen presenting cells
- Skin (SALT)
- Mucous membranes (GALT, NALT, BALT)
- Lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen)
- Blood circulation (plasmacytoid and myeloid DC cels)
Pathogen capture occurs in two main ways - what are these?
1) Phagocytosis (whole microbe)
2) Macropinocytosis (soluble particles e.g., toxins released by bacterium)
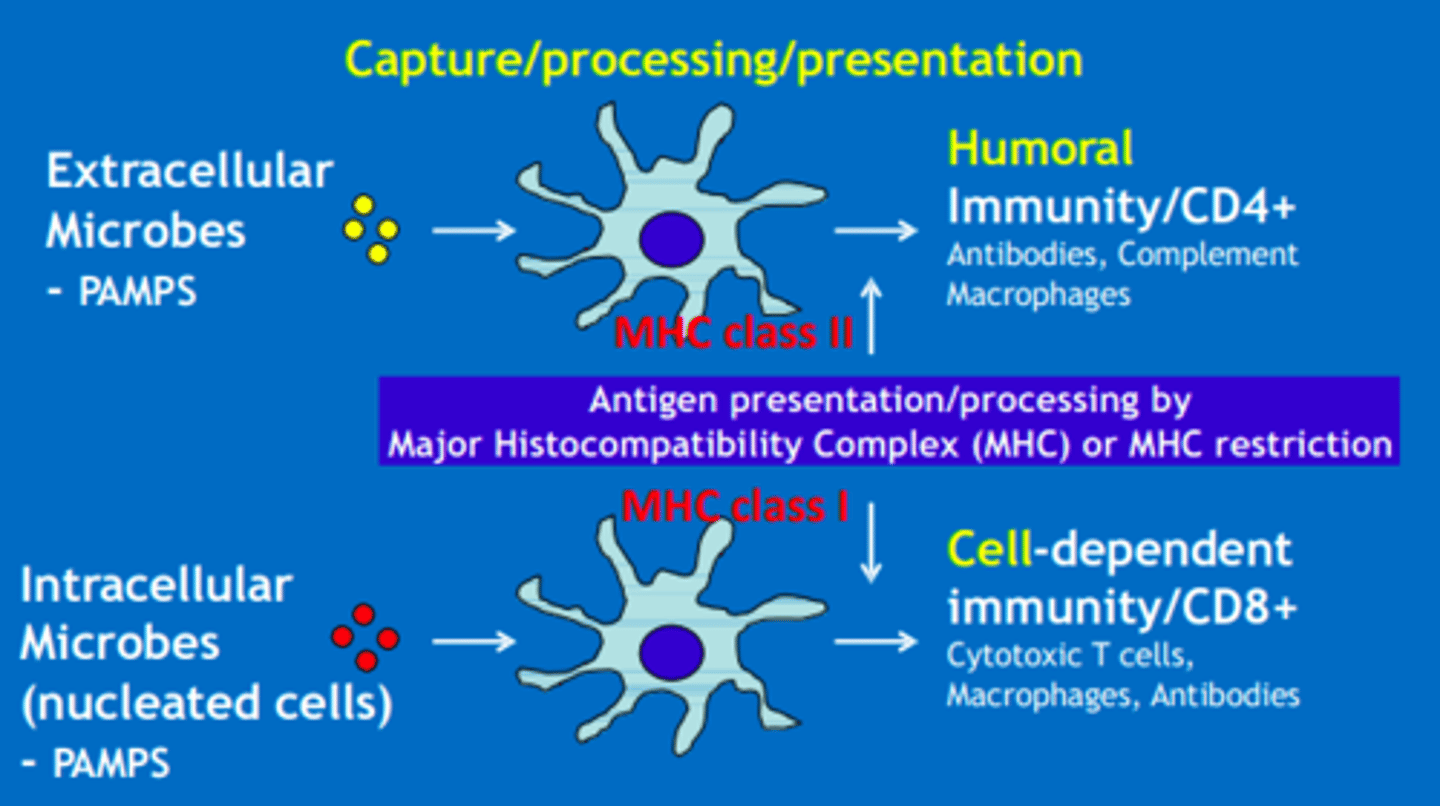
Humoral adaptive response MHC class
MHC class II
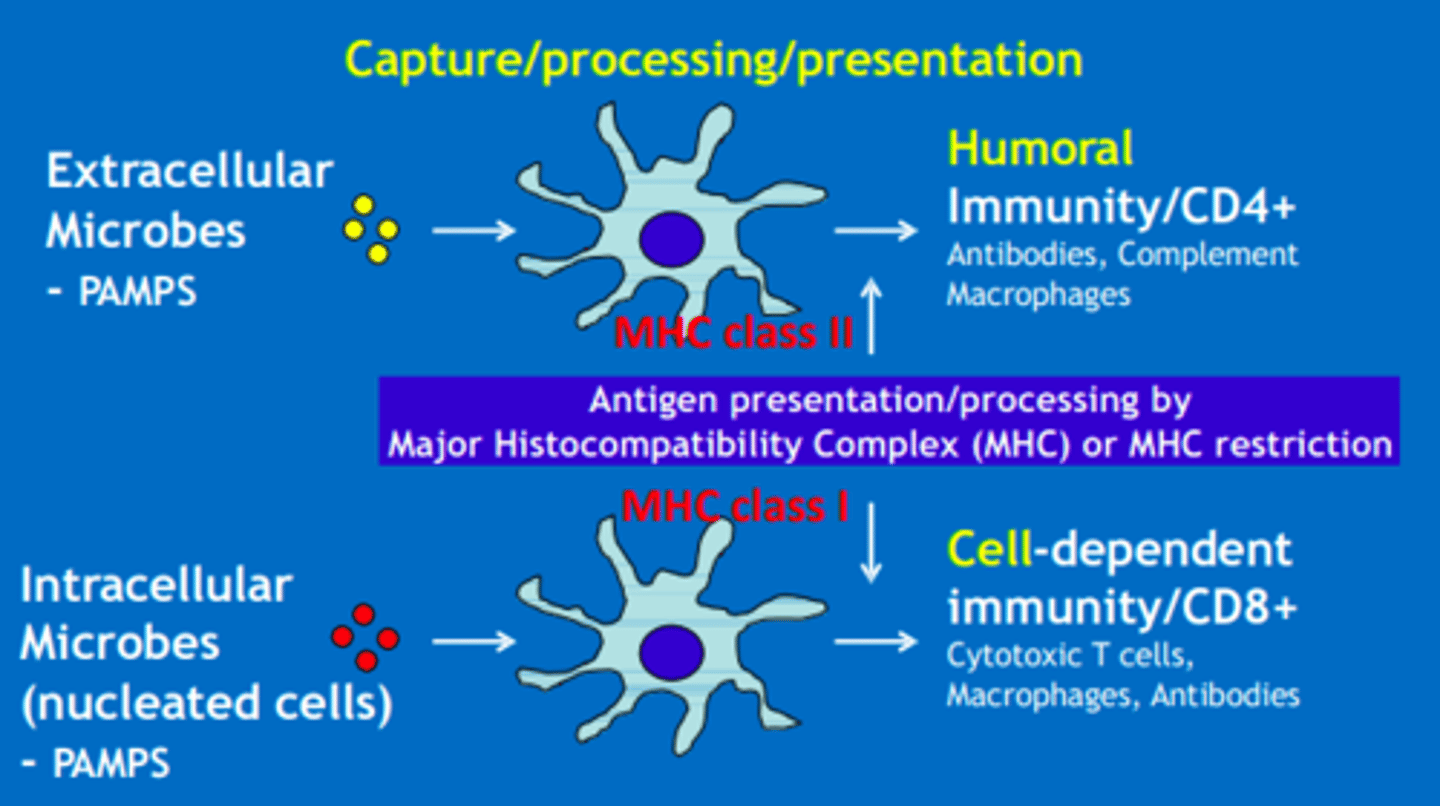
Cell-mediated adaptive response MHC class
MHC class I
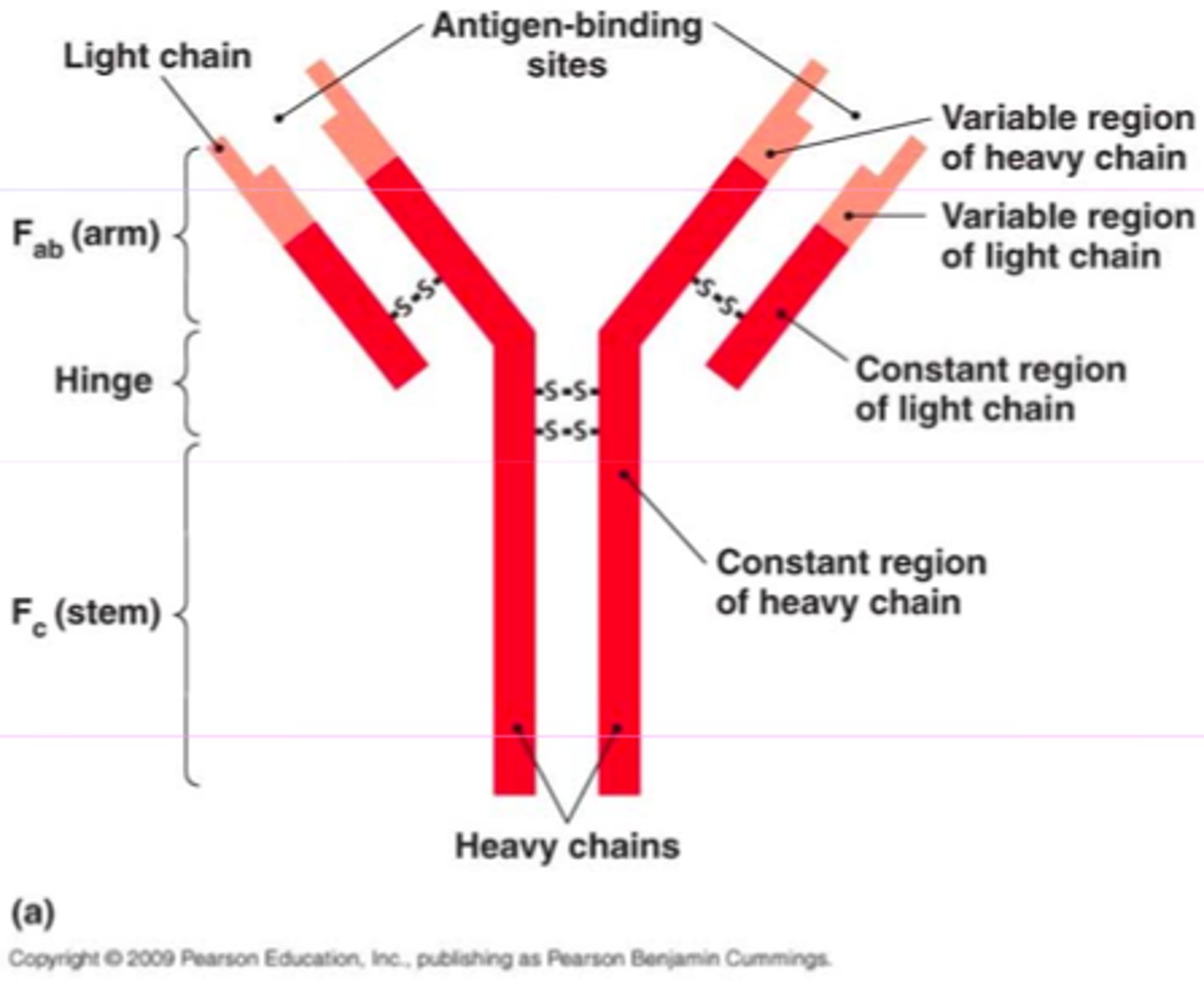
Antibody structure diagram labelled
Fab = arm
Fc = stem
MHC class I (cell-mediated adaptive)
Present in all nucleated cells and displays endogenous antigens to cytotoxic T-cells CD8+
MHC class II (humoral adaptive)
Found on macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells, it binds to CD4+ T-helper cells
How many signals are required for T cell activation?
Two signals required (co-stimulation)
1) TCR
2) Verification signal
Co-stimulation
Complete T cell activation requires T cell to also bind to one or more co-stimulatory signals on surface of APC
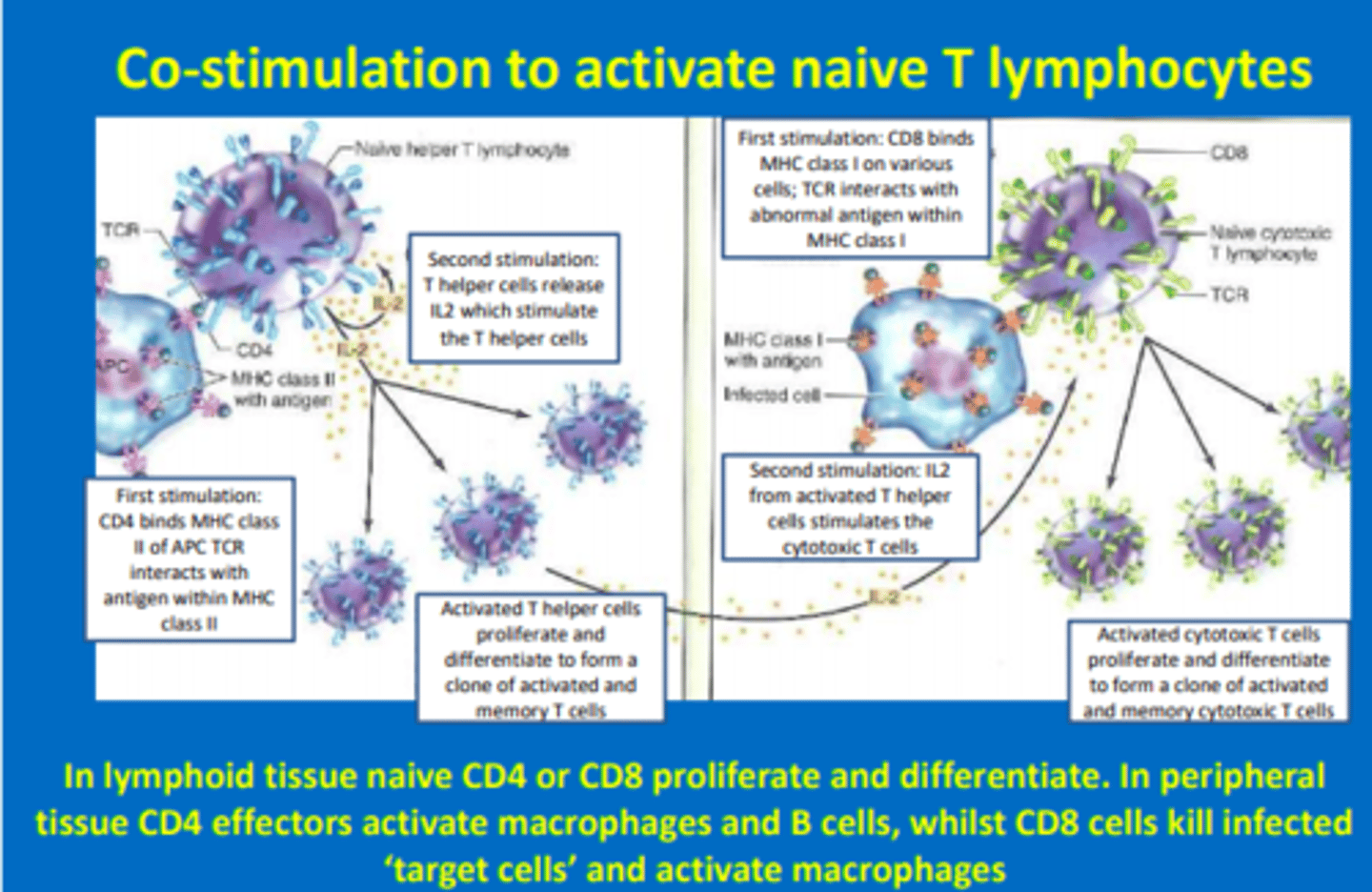
Describe the first and second stimulation (co-stimulation) of naive CD4 T-lymphocytes in the humoral adaptive response
First stimulation
- CD4+ T-helper cell binds MHC-II of APC
- TCR interacts with antigen within MHC-II
Second stimulation
- T-helper cells release IL-2 which stimulates T-helper cells to clonally expand
Activated T-helper cells proliferate and differentiate to form clone of activated and memory T-helper cells
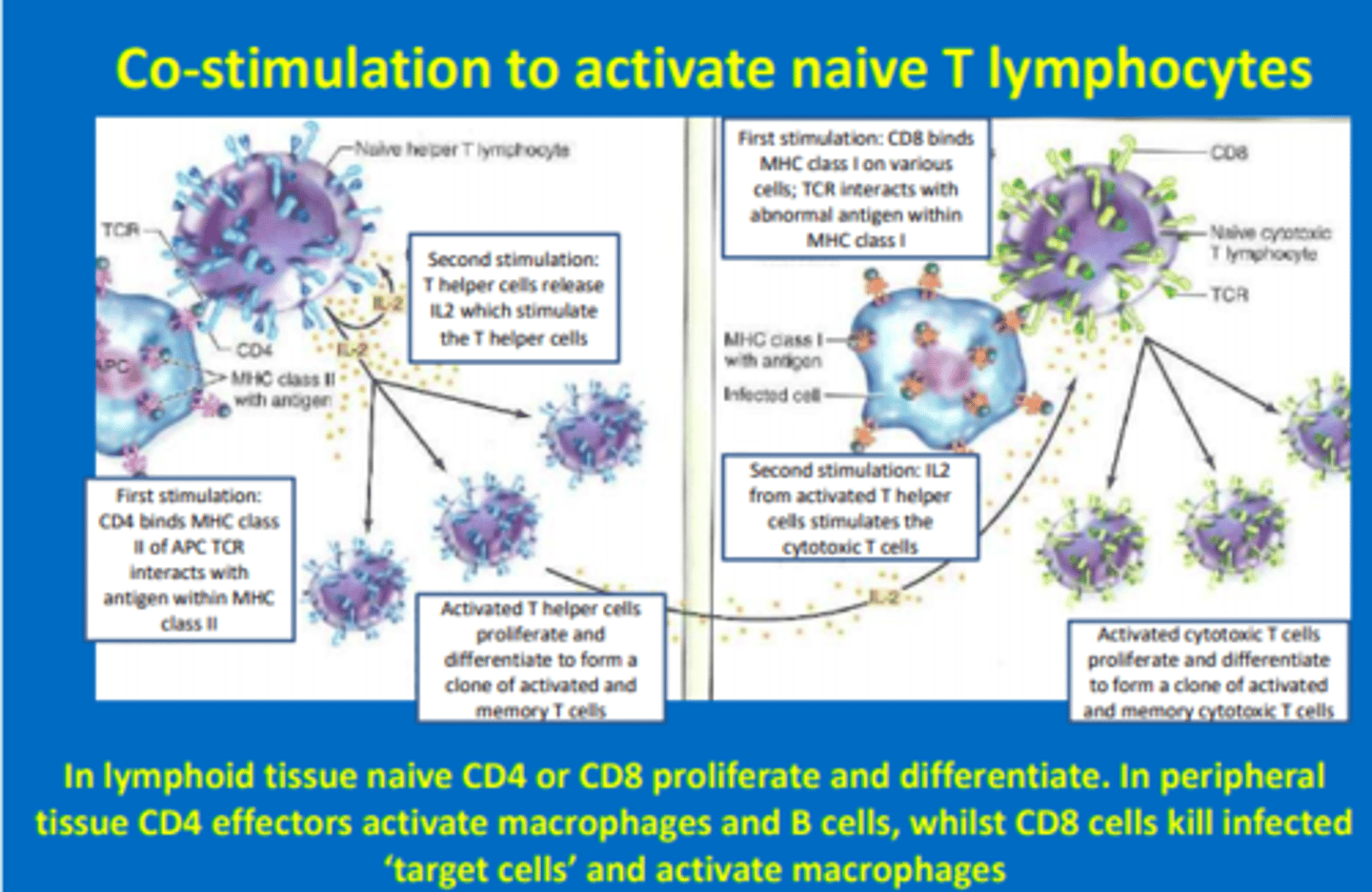
Describe the first and second stimulation (co-stimulation) of naive CD8 T-lymphocytes in the cell-mediated adaptive response
First stimulation
- CD8+ cytotoxic T cells bind MHC-I on various cells
- TCR interacts with antigen within MHC-I
Second stimulation
- IL-2 from T-helper cells stimulates cytotoxic CD8 cells to clonally expand
Activated cytotoxic T-cells proliferate and differentiate to form clone of activated and expanded memory cytotoxic T-cells
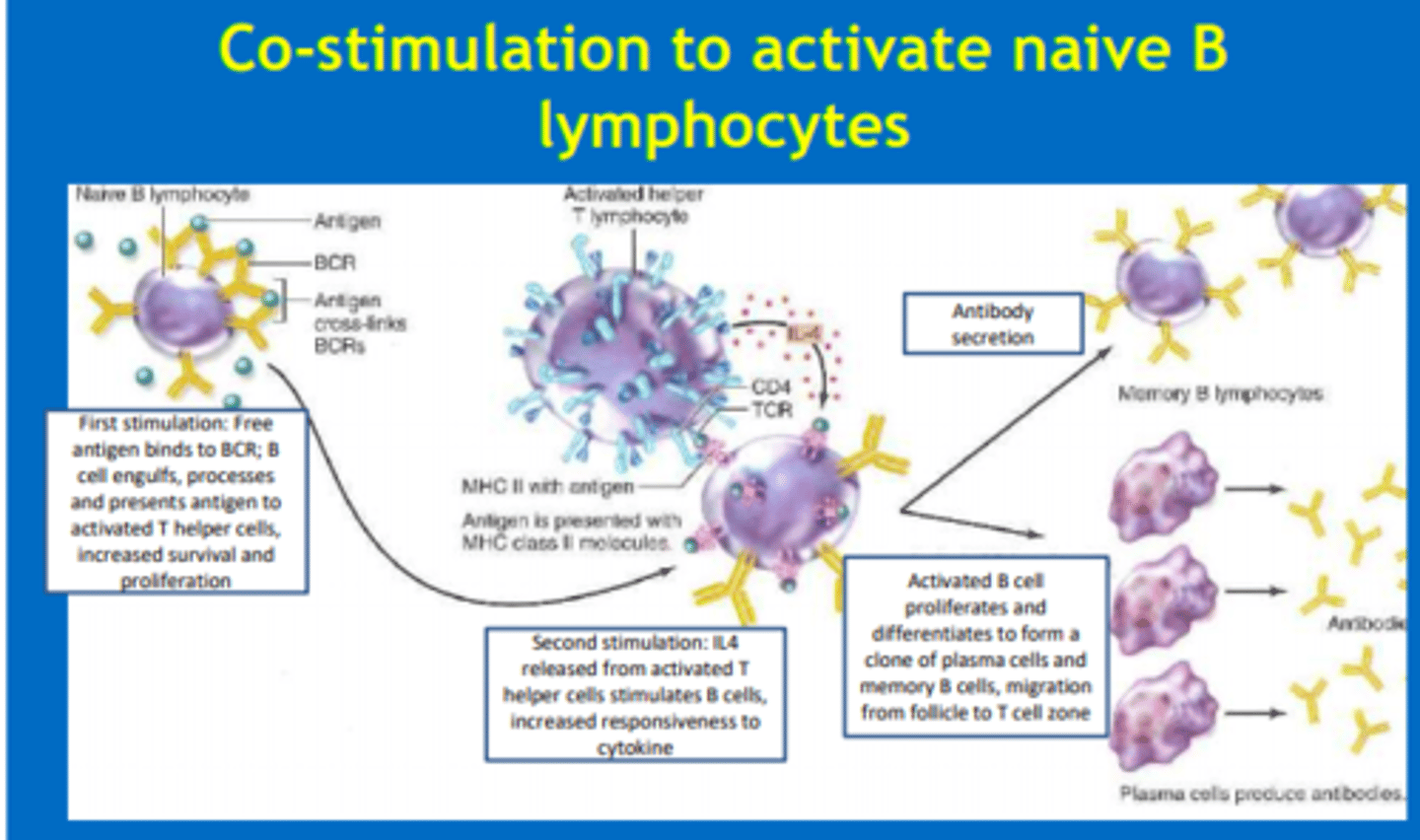
Describe the first and second stimulation (co-stimulation) of naive B-lymphocytes
First stimulation
- Free antigen binds to BCR
- B cell engulfs, processes and presents antigen to T-helper cells
Second stimulation
- IL-4 released from activated T-helper cells which stimulates B cells
Activated B cells then proliferate and differentiate to form clone of plasma cells and memory B cells via clonal expansion. Antibodies are secreted from plasma cells.
What T-helper cells are the basis of the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction Mantoux test in response to tuberculin?
Th1
Th17
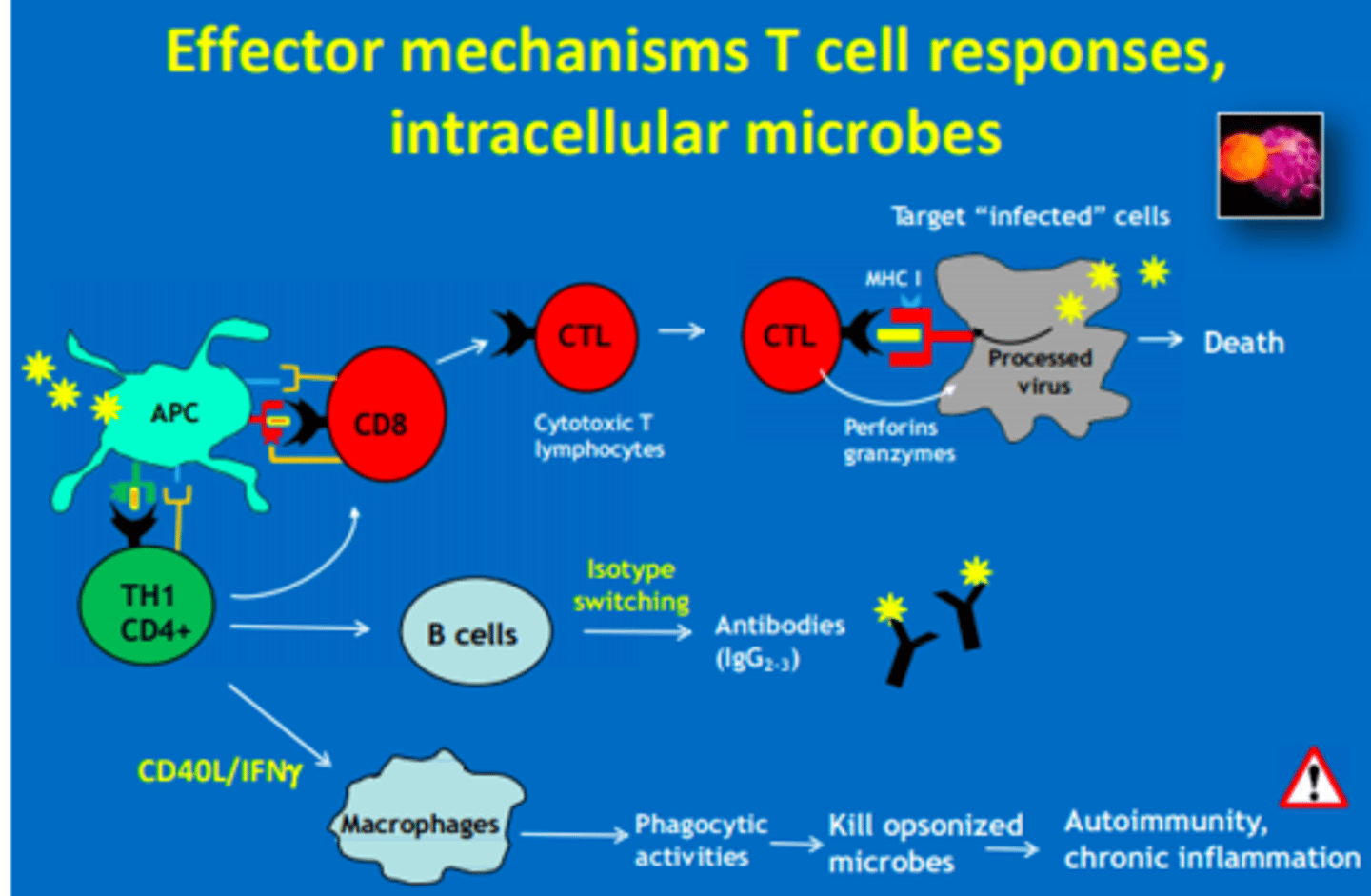
Cytotoxic T cells (CD8) kill cells expressing recognized antigens - these cells include...
1) Normal cells containing viruses
2) Mutated/cancerous cells
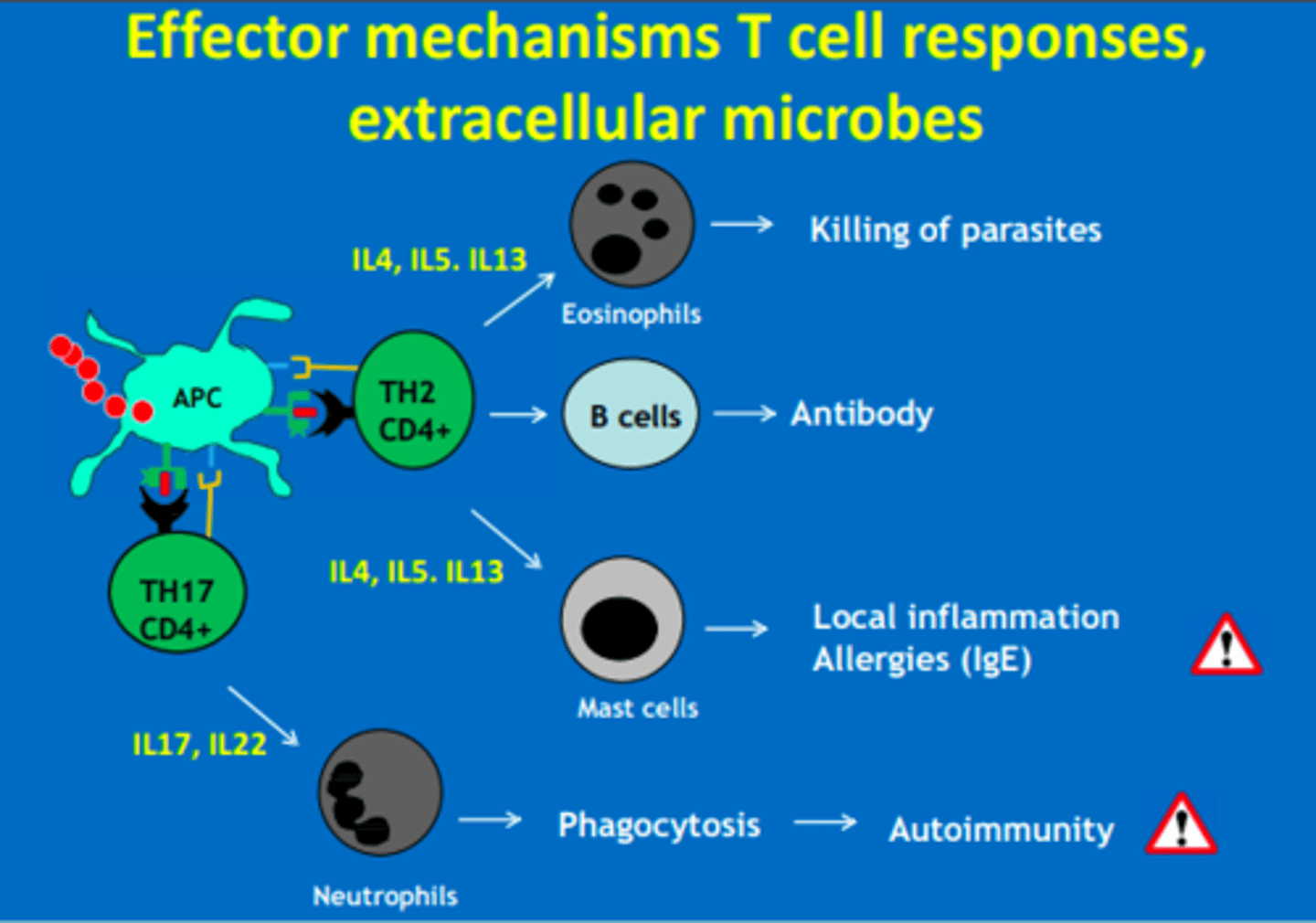
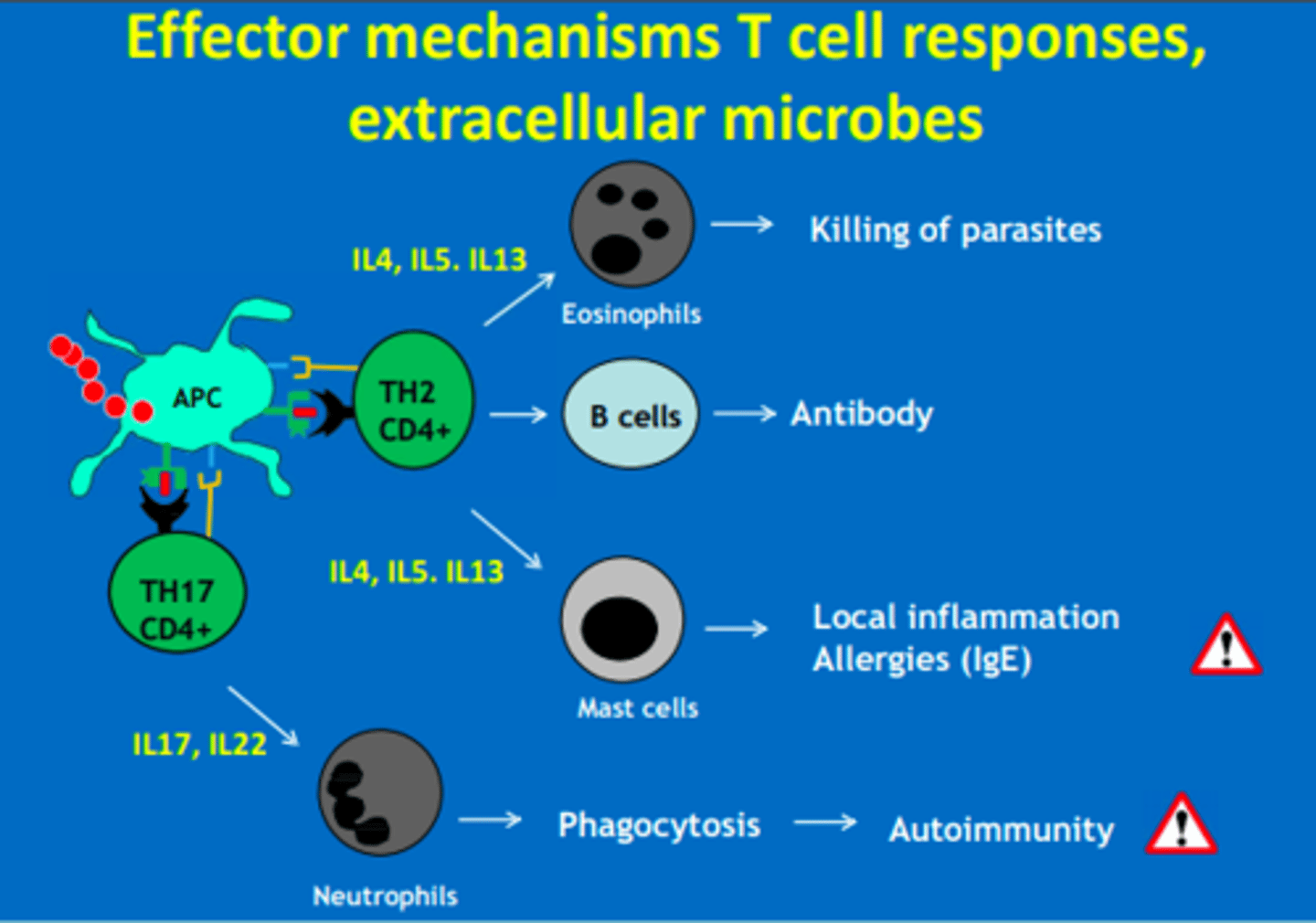
What interleukins do Th2 CD4 cells respond to?
IL4, IL5, IL13 = mast cells
IL4, IL5, IL13 = eosinophils
What interleukins do Th17 CD4 cells respond to?
IL17, IL22 = neutrophils
Th2 CD4 cells produce cytokines (IL4, IL5, IL13) that activate...
- B cells = antibodies
- Mast cells = allergy
- Eosinophils = helminth
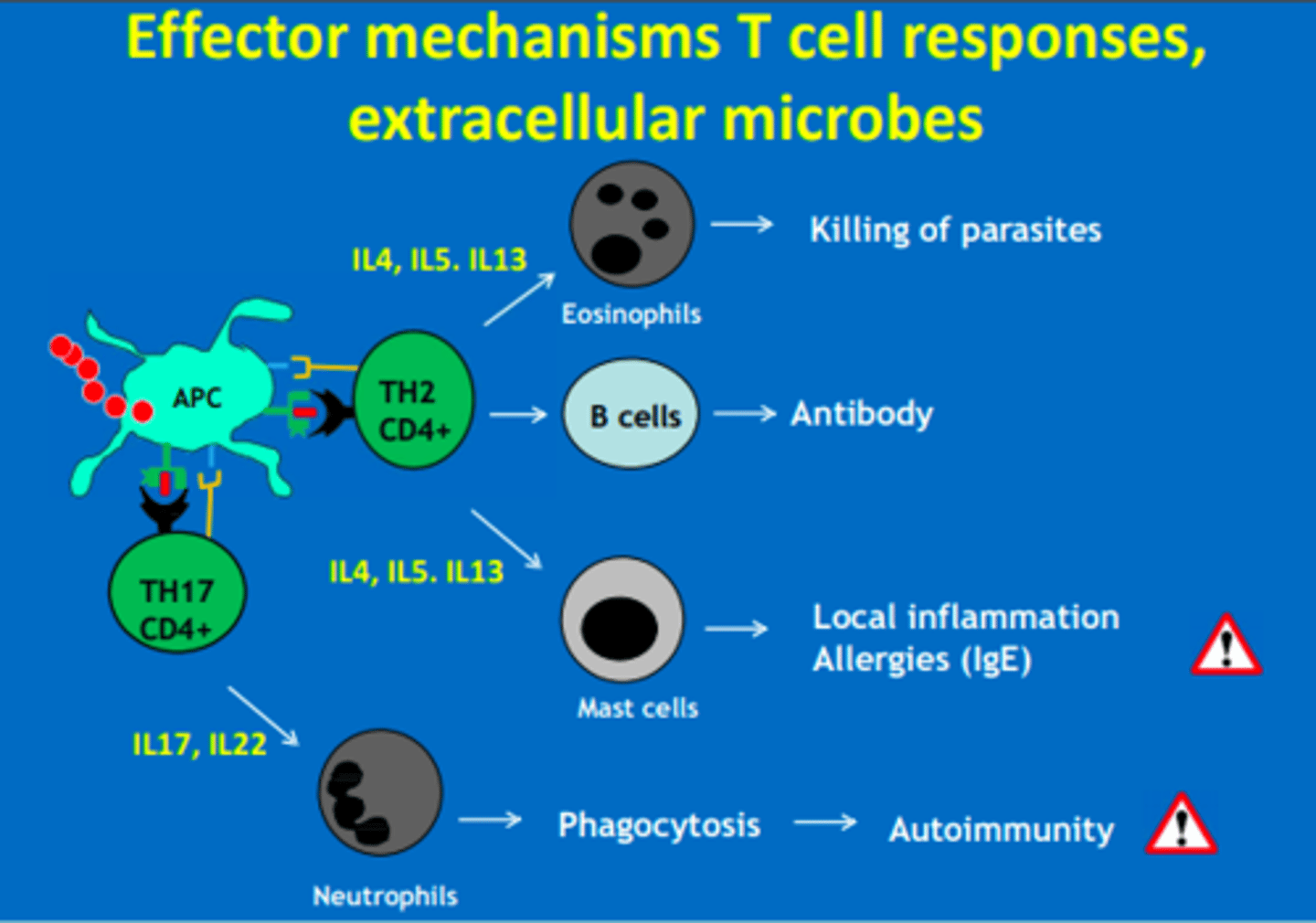
Th17 CD4 cells produce cytokines (IL17, IL22) that activate...
- Neutrophils = phagocytosis
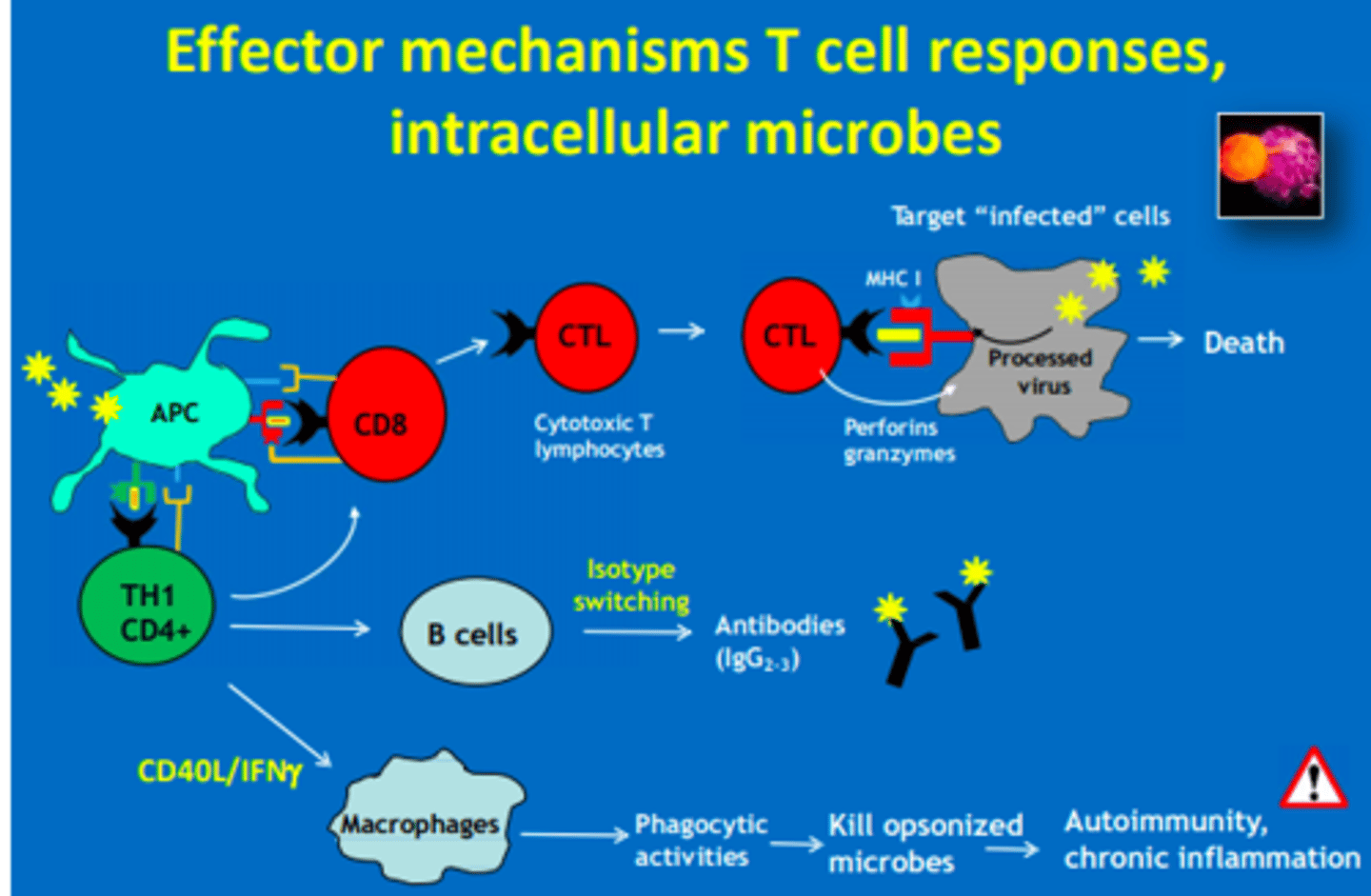
Th1 CD4 T cells produce cytokines (CD40, IFN-gamma) that activate...
- B cells = antibodies
- Macrophages = phagocytosis
- CD8 cells = cytotoxic T cells
Which CD4 T-helper cells are involved in attack of extracellular microbes (cell-mediated)
Th2 = B cells, Eosinophils, Mast cells
Th17 = Neutrophils
Which CD4 T-helper cells are involved in the attack of intracellular microbes (humoral)
Th1 = CD8, B cells & Macrophages
The Fc region of the antibody attacks ___ cells and ___
NK cells and phagocytes
Adaptive immune response deactivation is also known as ___
Contraction (homeostasis)
The elimination of microbes lead to a loss of activation signals. T-cell regulator signalling outweights the activation signals (homeostasis).
Reduction in response leads to apoptosis of phagocytes and the surviving lymphocytes are memory cells

T-cell memory
T-memory cells no longer express effector molecules - but their genes remain in low-methylation state.
Pool of memory cells determined by future exposure.
These memory cells are converted to effector cells on second encounter with antigen that binds receptor.
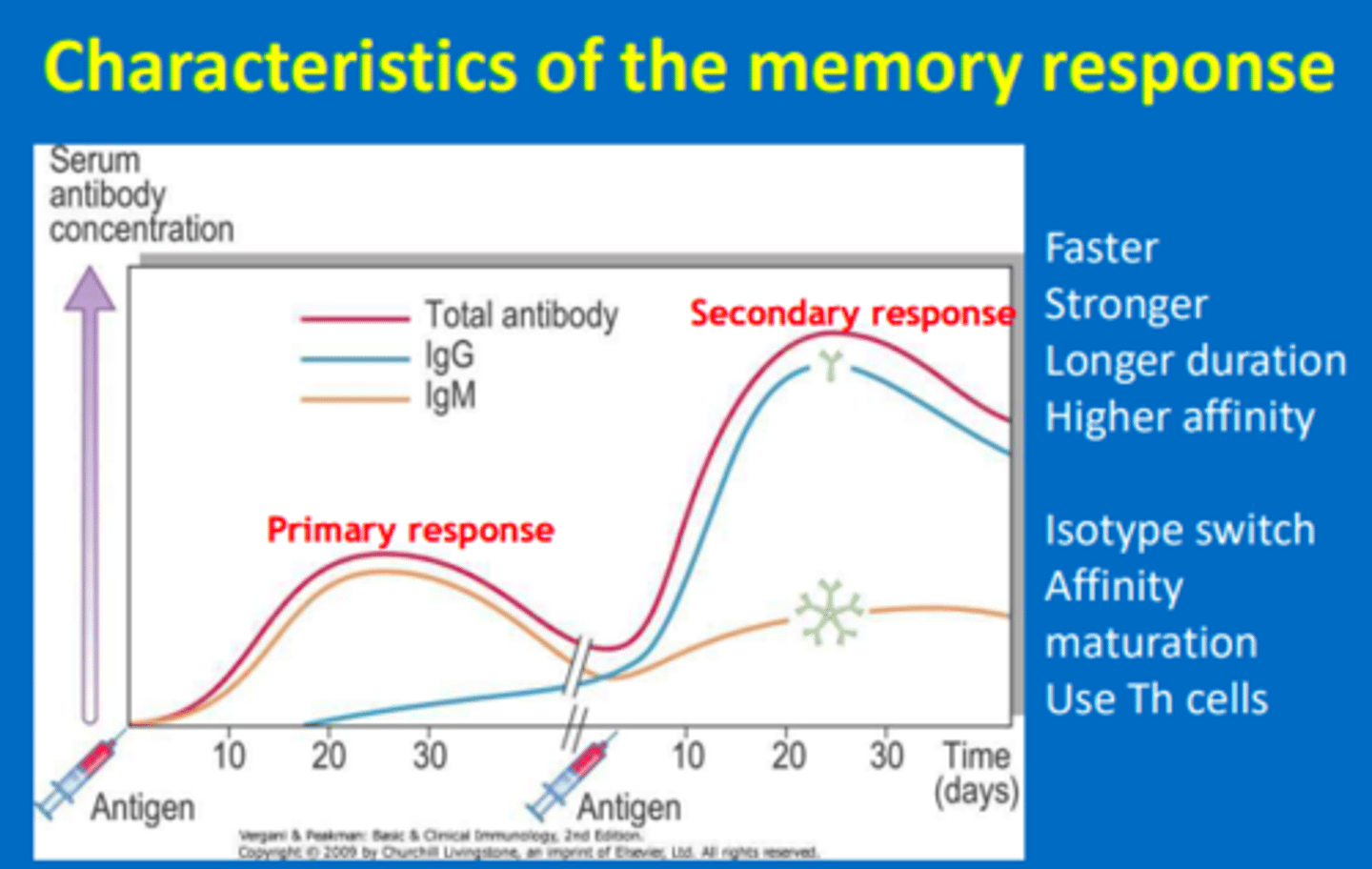
Characteristics of the memory response
- Primary response is lower
- Secondary response activates memory cells to convert to effector cells. This is a faster, stronger response with a longer duration.
Removal of self-reactive immune cells
Negative selection
Process by which T- and B- cells create a vast repertoire of distinct cell surface molecules
Somatic gene rearrangement
Enrichment and proliferation of cells producing cell surface receptors with a high affinity for foreign antigens
Clonal selection
Ingestion of foreign organisms and appearance of their components on the cell surface
Antigen presentation
All healthy nucleated cells express ___
MHC-I and self-antigens
Infected nucleated cells express ___
MHC-I and non-self antigens
Macrophages (professional APCs) present ___ following ingestion of microbes and are activated by the action of ___ cells
Macrophages (professional APCs) present MHC-II and non-self antigens following ingestion of microbes and are activated by the action of T-helper cells
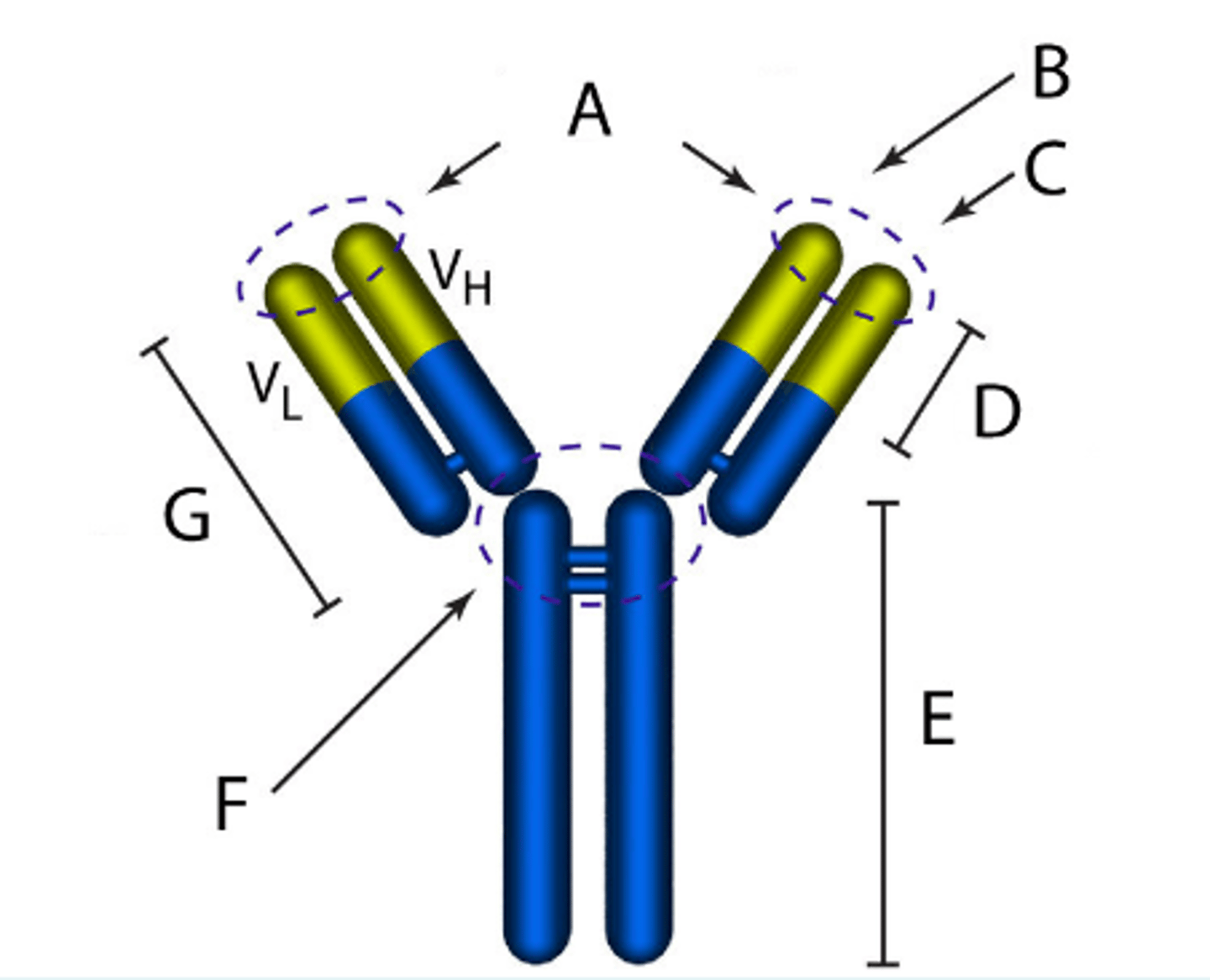
Label this antibody
A = Antigen binding site
B = Immunoglobulin heavy chain
C = Immunoglobulin light chain
D = Variable region Fv
E = Constant region Fc
F = Hinge region
G = Fab region
Which cytokine?
Promotes maturation of myeloid lineages
IL3
Which cytokine?
Secreted by NK cells in response to infection (or stressed cells) promoting the innate immune response
Interferon-γ
Which cytokine?
Stimulates neutrophil maturation
G-CSF
Which cytokine?
Stimulates maturation of Th2 T-helper cells
IL4
Which cytokine?
Stimulates lymphocyte proliferation
IL2
Which lymphocyte population is particularly impacted following HIV infection?
T-helper cells (CD4+)
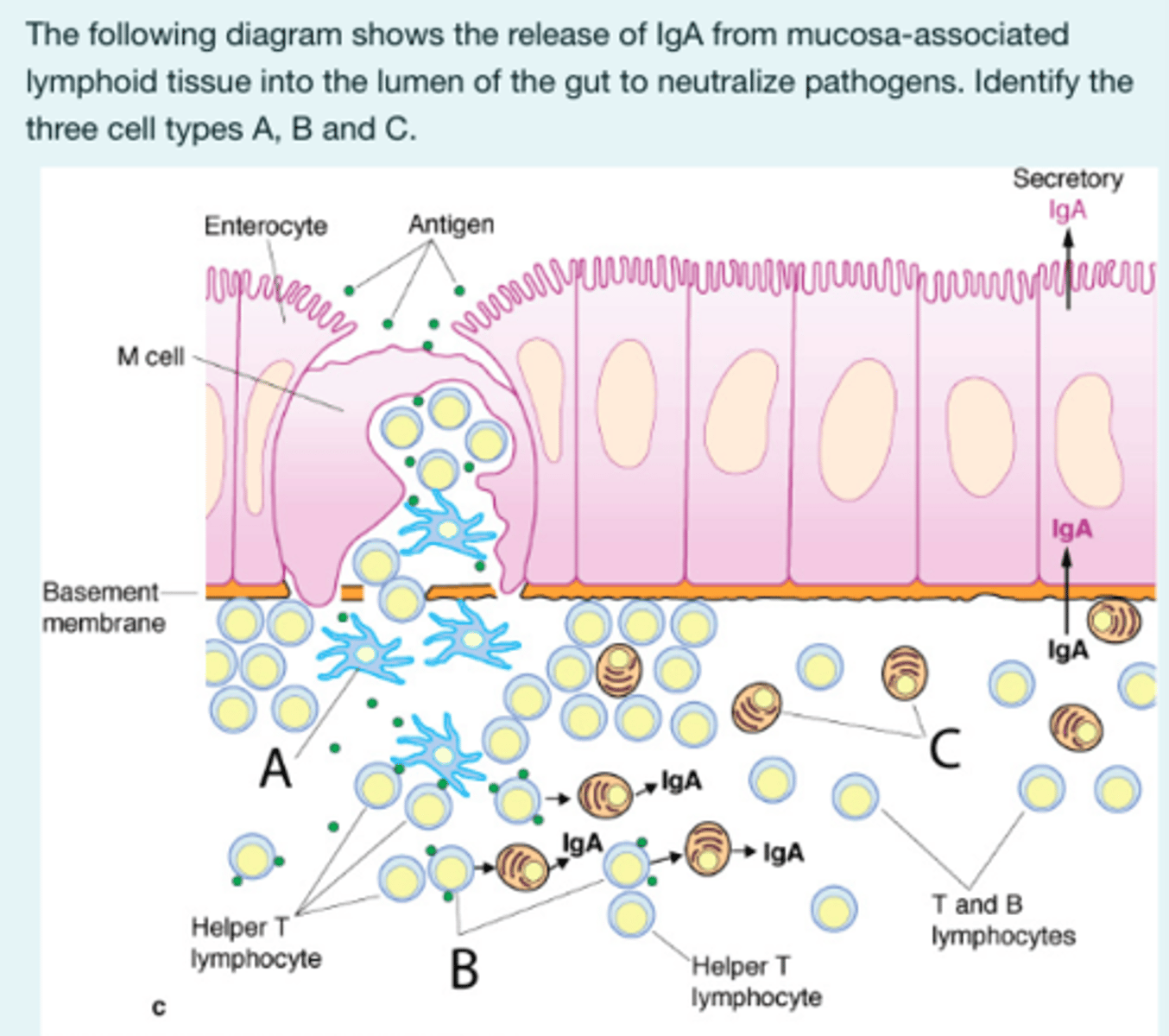
The following diagram shows the release of IgA from mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue into the lumen of the gut to neutralize pathogens.
Identify the three cell types A, B and C
A = Dendritic cells
B = B-lymphocytes
C = Plasma cells
When an extracellular microbe is presented to an APC, which effector cell is stimulated?
CD4+
Th2/Th17